Gr 9 Science Exam review
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
niggas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What is matter
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space
What is an atom
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of elements
What is atomic mass?
Atomic mass is the weighted average of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom measured in atomic mass unit (AMU)
What is an atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom which defines its identity
What are the subatomic particles
Electron, Proton, Neutron
Where is the Electron, what is its charge and what is it’s relative mass?
The electron is located outside the shell and has a negative charge. The relative mass of an electron is about 1/1836 of a proton’s mass which is about 0.0005 amu.
Where is the proton, what is its charge and what is its relative mass?
the proton is located in the nucleus and has a positive charge. The relative mass of a proton is about 1 amu.
Where is the neutron located, what is its charge and what is its relative mass
The neutron is located in the nucleus and has a neutral charge (no charge). The relative mass of a neutron is approximately 1 amu.
What are families
Groups or families are columns on the periodic table where elements have similar chemical properties and the same number of valence electrons.
What are periods?
Periods are the horizontal rows on the periodic table, and they show the number of energy levels (shells) an atom's electrons occupy.
What are groups?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table, and elements in the same group have similar properties and the same number of valence electrons.
What are the properties and location of non metals?
Nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table (except hydrogen, which is on the top left). Their properties include:
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Brittle when solid
Low melting and boiling points (compared to metals)
Often dull in appearance
Tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions
Can exist as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature (e.g., oxygen is a gas, bromine is a liquid, sulfur is a solid)
What are the properties and location of Halogens?
Halogens are located in Group 17 (second column from the right) of the periodic table. Their properties include:
Very reactive nonmetals, especially with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals
Have 7 valence electrons, so they tend to gain 1 electron in reactions
Exist in all three states at room temperature: fluorine and chlorine (gases), bromine (liquid), iodine and astatine (solids)
Often have a strong smell and are toxic in pure form
Form salts when combined with metals (e.g., NaCl – table salt)
What are the properties and location of noble gases?
Noble gases are located in Group 18 (the far right column) of the periodic table. Their properties include:
Very unreactive (inert) due to having a full outer electron shell
Exist as colorless, odorless gases at room temperature
Do not easily form compounds
Have low boiling and melting points
Used in lighting (e.g., neon signs) and coolants (e.g., helium) due to their stability
What are the properties and location of metals?
Metals are located mostly on the left and center of the periodic table. Their properties include:
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and ductile (can be drawn into wires)
Have a shiny, metallic luster
Usually solid at room temperature (except mercury)
Tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions, forming positive ions
Have high melting and boiling points
Are strong and dense compared to nonmetals
What are the properties and location of metalloids?
Metalloids are located along the stair-step line between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table (between Groups 13 and 17). Their properties include:
Have mixed properties of both metals and nonmetals
Semiconductors—can conduct electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals
Can be shiny or dull in appearance
Are brittle, not malleable or ductile
Reactivity varies depending on the element and the reaction conditions
What are the properties and location of alkali metals
Alkali metals are located in Group 1 of the periodic table (the far left column, excluding hydrogen). Their properties include:
Highly reactive, especially with water, forming alkaline solutions
Have 1 valence electron, which they lose easily to form +1 ions
Are soft metals that can be cut with a knife
Have low melting points compared to most metals
Are shiny and silvery when freshly cut but tarnish quickly in air
Reactivity increases down the group (from lithium to cesium)
What are the properties and location of alkaline earth metals?
What are physical properties?
Physical properties are characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its identity, such as states of matter, hardness, malleability, ductility, melting and boiling points, colour, lustre, conductivity, viscosity, magnetic
What are chemical properties?
Chemical properties describe a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances, combustion, reaction with acid, corrosion
What are physical changes?
What are chemical changes?
Chemical changes are changes where a substance transforms into one or more new substances with different properties, such as burning, rusting, or baking.
What are the 5 principles of the particle theory of matter
All matter is made up of tiny particles.
Particles are always moving.
Particles have spaces between them.
Particles are attracted to each other.
Adding heat makes particles move faster; removing heat makes them move slower.
What are pure substances
Made of only one type of atom (e.g., oxygen, gold).
What are the 2 types of pure substances?
Elements: Made of only one type of atom (e.g., oxygen, gold).
Compounds: Made of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed ratios (e.g., water H₂O, carbon dioxide CO₂).
What are mixtures
Mixtures are when 2 or more pure substances are mixed physically
What are the different types of mixtures?
Homogeneous Mixtures (Solutions):
Uniform composition throughout.
You can’t see the different parts.
Examples: saltwater, air, sugar dissolved in water.
Heterogeneous Mixtures:
Non-uniform composition; you can see different parts.
Examples: salad, sand and water, trail mix.
What are suspensions?
A type of heterogeneous mixture where particles are large enough to settle out over time.
Examples: muddy water, flour in water.
What is a solution
A homogeneous mixture where one substance (solute) is completely dissolved in another (solvent).
Examples: sugar water, saltwater, pop.
What are 2 different types of atomic bonds?
Ionic and Covalent
What is an Ionic bond?
One atom transfers electrons to another, creating charged ions.
Occurs between metals and nonmetals.
Forms ionic compounds (e.g., NaCl, MgO).
What is a covalent bond?
Atoms share electrons to fill their outer shells.
Occurs between nonmetals.
Forms molecular compounds (e.g., H₂O, CO₂).
What are the types of atomic compounds?
Ionic and Molecular (Covalent)
What is an Ionic compound
Made of positive and negative ions held together by ionic bonds.
Usually high melting and boiling points.
Conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water.
What is a molecular compound?
Made up of molecules with atoms held together by covalent bonds.
Tend to have lower melting and boiling points.
Usually do not conduct electricity in solid or liquid form.
What is bonding capacity?
The number of covalent bonds an atom can form depends on how many electrons it needs to complete its outer shell (usually 8 electrons for most elements).
Examples:
Hydrogen forms 1 bond (needs 1 electron)
Oxygen forms 2 bonds
Nitrogen forms 3 bonds
Carbon forms 4 bonds
How to Determine if a Substance is Ionic or Molecular
Ionic compounds: usually metal + nonmetal, high melting/boiling points, conduct electricity in liquid/solution, solid crystals.
Molecular compounds: nonmetal + nonmetal, lower melting/boiling points, poor conductors, exist as gases, liquids, or low-melting solids.
Why do ions form
Atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a full outer shell (octet rule).
What is a positive ion
Form when atoms lose electrons (usually metals).
What is a negative ion
Form when atoms gain electrons (usually nonmetals).
What are valence electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom.
What is an ecosystem?
A community of living organisms interacting with their physical environment.
What is an herbivore?
An animal that eats only plants.
What is a carnivore?
An animal that eats other animals.
What is an omnivore?
An animal that eats both plants and animals.
What do decomposers do?
Break down dead material and return nutrients to the soil.
What are producers?
Organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis.
Name the trophic levels in order.
Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers → Decomposers.
What’s the difference between a food chain and a food web?
What is a heterotroph?
An organism that obtains energy by consuming others.
What does the pyramid of biomass show?
The total mass of living matter at each trophic level.
What is the 10% rule?
Only 10% of energy transfers to the next trophic level; the rest is lost as heat.
What is bioaccumulation?
Build-up of toxins in an organism over time.
What is biomagnification?
Increase in toxin concentration as it moves up the food chain.
What is the main process in the carbon cycle that removes CO₂?
Photosynthesis.
Write the photosynthesis equation.
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Write the cellular respiration equation.
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
What human activity increases atmospheric CO₂?
Fossil fuel combustion.
What role do nitrogen-fixing bacteria play?
Convert nitrogen gas into usable forms like ammonia.
What is denitrification?
Conversion of nitrates back to nitrogen gas by bacteria.
How does fertilizer affect the nitrogen cycle?
Overuse causes nutrient runoff, polluting water bodies.
Define commensalism.
One benefits, the other is unaffected.
What’s the difference between native and invasive species?
Native species naturally occur; invasive species disrupt ecosystems.
Why is biodiversity important?
It supports ecosystem stability and resilience.
Name some threats to biodiversity.
Pollution, habitat loss, climate change, invasive species.
What causes static electricity?
Friction causes electrons to move and charge objects.
What are conductors?
Materials that allow electrons to flow easily (e.g., metals).
What are insulators?
Materials that resist electron flow (e.g., rubber).
What does an electroscope do?
Detects electric charge.
What happens to electroscope leaves when charged?
They spread apart due to repulsion.
What is charging by contact?
Transfer of charge through touching.
What is charging by induction?
Charge rearrangement without direct contact.
What is voltage?
Electric potential difference; measured in volts (V).
What is current?
State Ohm’s Law.
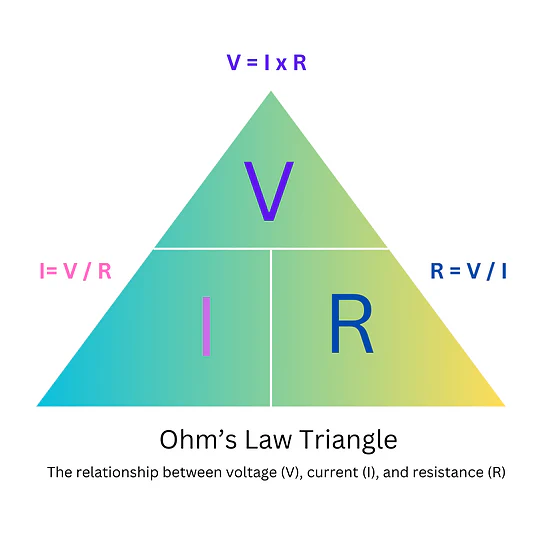
How do you calculate total resistance in a series circuit?
Rtotal=R1+R2+...
How do you calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit?
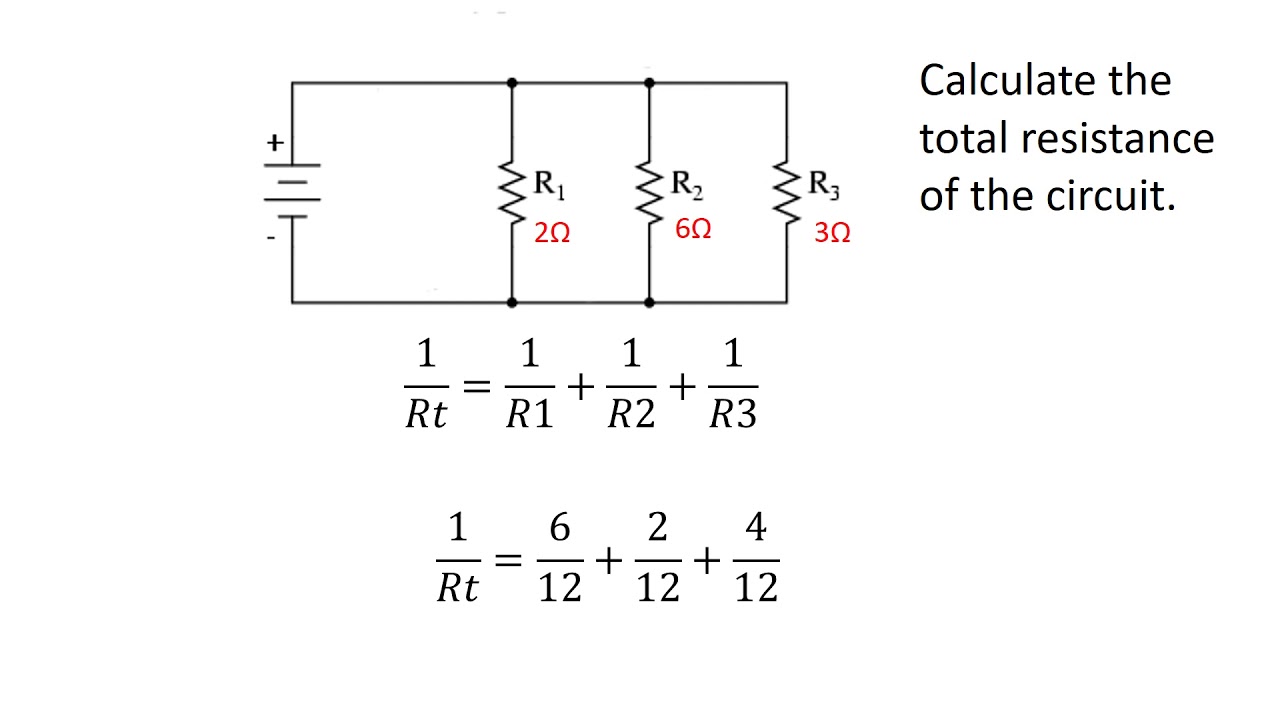
Write the formula for current I based on charge and time.
I=Q/t
Write the formula for voltage V based on energy and charge.
V=E/Q
What is an astronomical unit (AU)?
The average distance between Earth and the Sun (~150 million km); used for distances within our solar system.
What is the life cycle of a small to medium-sized star (like the Sun)?
Nebula → Protostar → Main Sequence → Red Giant → Planetary Nebula → White Dwarf
What is the life cycle of a large star?
Nebula → Protostar → Main Sequence → Red Supergiant → Supernova → Neutron Star or Black Hole
What does the H-R diagram show?
The relationship between stars' brightness (luminosity) and temperature (color/spectral type).
Where are main sequence stars on the H-R diagram?
They form a diagonal band from hot, bright stars to cool, dim stars.
What is the Big Bang Theory?