Motor Units
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What do motor units consist of?
a single motor unit and all the muscle fibers it stimulates
What are motor neurons?
nerve cells
What do these nerve cells send?
electrical signals from the brain or spinal chord to muscle fibers
What these electrical signals initiate the process of?
muscle contraction
All or nothing principle
.
What must a signal sent by a motor neuron reach?
a certain level (threshold) to activate the muscle fibers
What will happen if the signal manages to reach this threshold?
all the muscle fibers in the motor unit contract fully
What will happen if the signal doesn't reach the threshold?
none of the fibers contract
How is more force produced?
by recruiting more motor units
How is more force not produced?
by making fibers contract harder
What do muscle contractions require?
energy provided by ATP
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
Usage of ATP when the motor unit contracts
.
What is released from actin?
mysoin
What does ATP allow myosin heads to do?
let go of actin after the muscle has contracted
What does ATP pump calcium back into?
storage to help the muscle relax
What does ATP prepare myosin for?
the next contraction
What does ATP do to the myosin heads?
resets them for the next contraction
What does the principle of orderly recruitment refer to?
how motor units are activated in a predictable sequence when muscles contract
What happens when a motor unit is activated?
all the muscle fibers in the unit contract
What happens when all the muscle fibers in the unit contract?
developes force
What needs to be activated to produce more force?
more motor units
What is recruited first?
smaller motor units
What do smaller motor units have?
smaller muscle fibers
What are smaller motor units responsible for?
fine, precise movements (writing)
When are larger motor units recruited?
when the demand for forces increases
What do larger movements help with?
more powerful movements (lifting heavy weights)
What does it ensure the body uses the appropriate amounts of?
force for each task
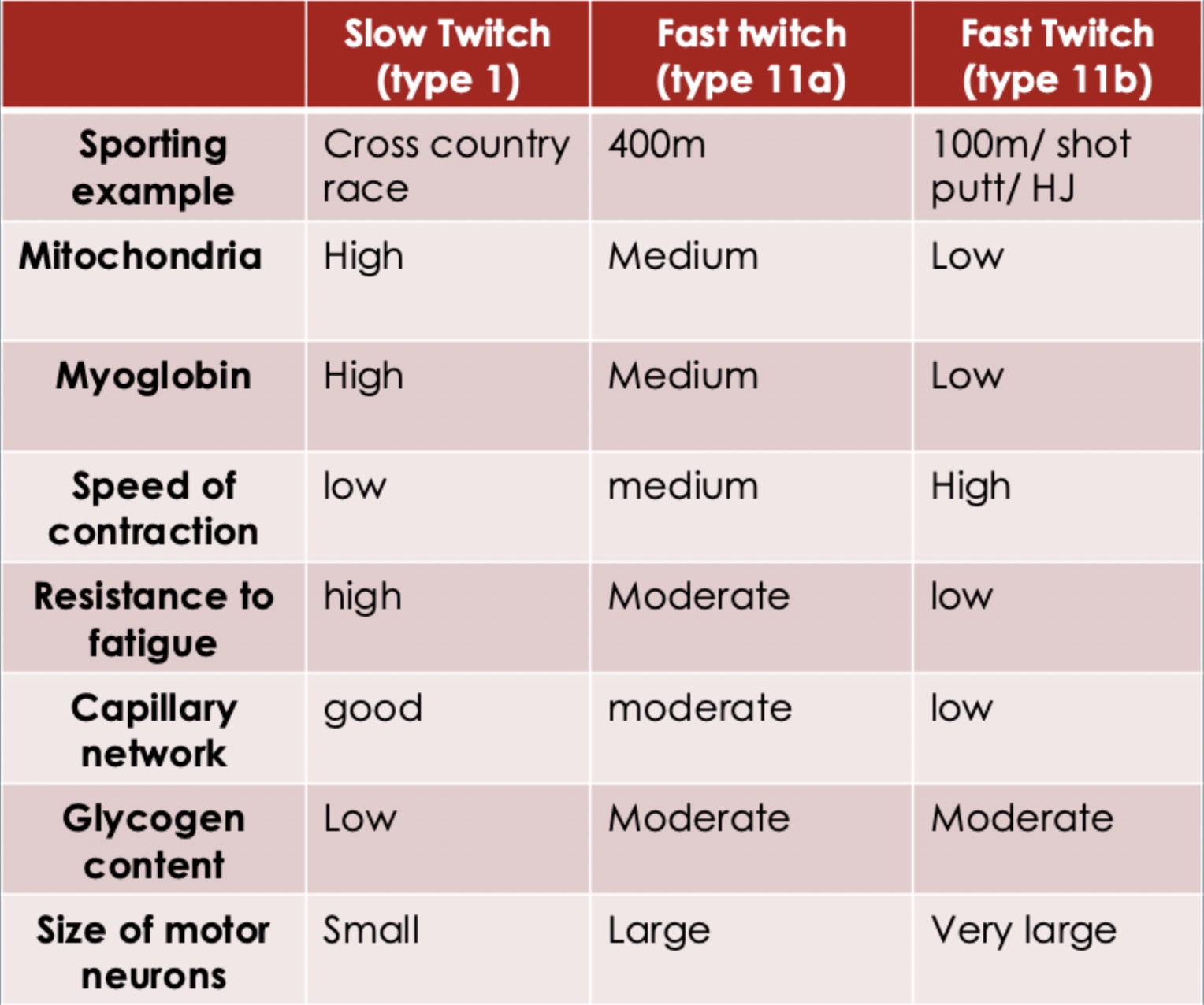
Types of motor units
type 1, type IIa, type IIx
Type 1
slow nerve transmission speeds (cross country race)
Type IIa
fast transmission times and stronger contraction force (400m)
Type IIx
fastest transmission times and strongest contraction forces (100m)
What do IIx motor units do the quickest?
fatigue
Motor Units