Escherichia coli
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Common name:
Colon bacillus
Habitat and transmission
• Normal flora in the large intestine; may colonize the vagina and urethra
• Acquired during birth and by fecal-oral route
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Commonly caused by E. coli, in approximately ___________________.
Urinary tract infection
90% of cases
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Results from endogenous spread of the bacteria from the large intestine as resident flora, and mechanically introduced into the urethra (e.g., careless personal hygiene, sexual intercourse, or catheterization)
Urinary tract infection
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
The colonization facilitates the ascent of bacteria from the urethra into the bladder causing ______________.
Urinary tract infection
cystitis
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
If the invading bacteria pass up the ureters to the kidney, ________________ results
Urinary tract infection
pyelonephritis
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Occurs primarily in women, a finding attributed to 3 features:
a. short urethra
b. proximity of the urethra to the anus
c. colonization of the vagina by members of the fecal flora
Urinary tract infection
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract infection
Occurs primarily in women, a finding attributed to 3 features:
a. short urethra
b. proximity of the urethra to the anus
c. colonization of the vagina by members of the fecal flora
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract infection
Signs and Symptoms:
a. Urinary frequency
b. Dysuria
c. Hematuria
d. Pyuria
e. Flank pain
None of these symptoms or signs is specific for E coli infection.
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract infection
Signs and Symptoms
The urge to pass urine more often than usual
Urinary frequency
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Signs and Symptoms
Painful urination
Dysuria
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Signs and Symptoms
The presence of blood in urine
Hematuria
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Signs and Symptoms
The presence of leukocytes, commonly referred to as pus, in the urine
Pyuria
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Signs and Symptoms
Pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back; associated with upper tract infection, a sign of kidney involvement
Flank pain
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
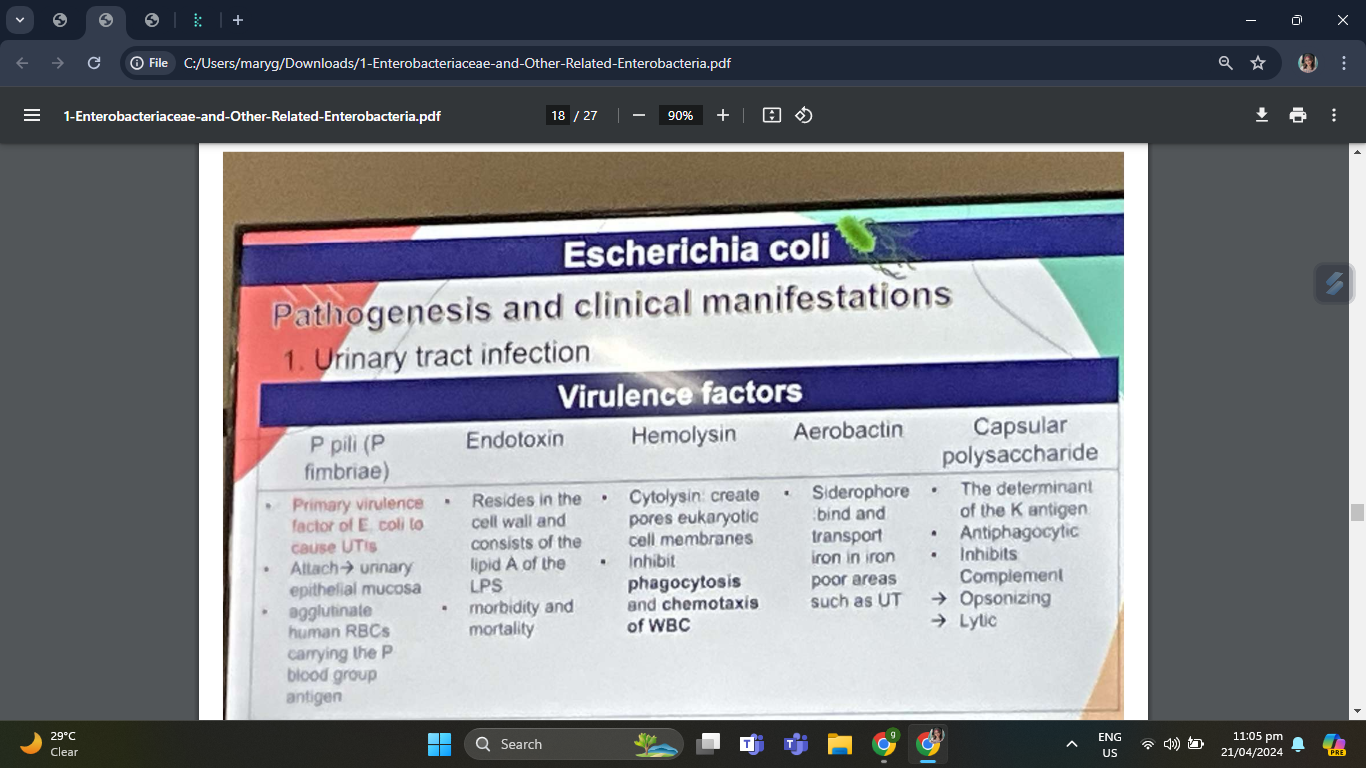
Virulence Factors
Primary virulence factor of E. coli to cause UTIs
P pili (P fimbriae)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Allow the bacteria to attach to the urinary epithelial mucosa and not be washed out with urine flow
P pili (P fimbriae)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Named for their ability to bind to and agglutinate human RBCs carrying the P blood group antigen
P pili (P fimbriae)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Resides in the cell wall and consists of the lipid A of the LPS
Endotoxin
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Responsible for much of the morbidity and mortality resulting from infections associated with these bacteria
Endotoxin
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Cytolysin that creates pores in eukaryotic cell membranes
Hemolysin
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Inhibits phagocytosis and chemotaxis of certain white blood cells
Hemolysin
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
A siderophore, .i.e., iron chelating agent, enabling E. coli to bind and transport iron for use by bacteria in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract
Aerobactin
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
The determinant of the K antigen
Capsular polysaccharide
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Is antiphagocytic and inhibits the opsonizing and lytic activities of complement because of the identity of the capsular polysaccharides and the host carbohydrates
Capsular polysaccharide
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Urinary Tract Infection
Virulence Factors
Table PPT
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
A major cause of meningitis and septicemia and meningitis among newborns, along with Group B streptococci
Escherichia coli
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Acquired by newborns by vertical transmission from the birth canal just before or during delivery, when the mother’s vagina is heavily colonized or infection may also result if contamination of the amniotic fluid occurs
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
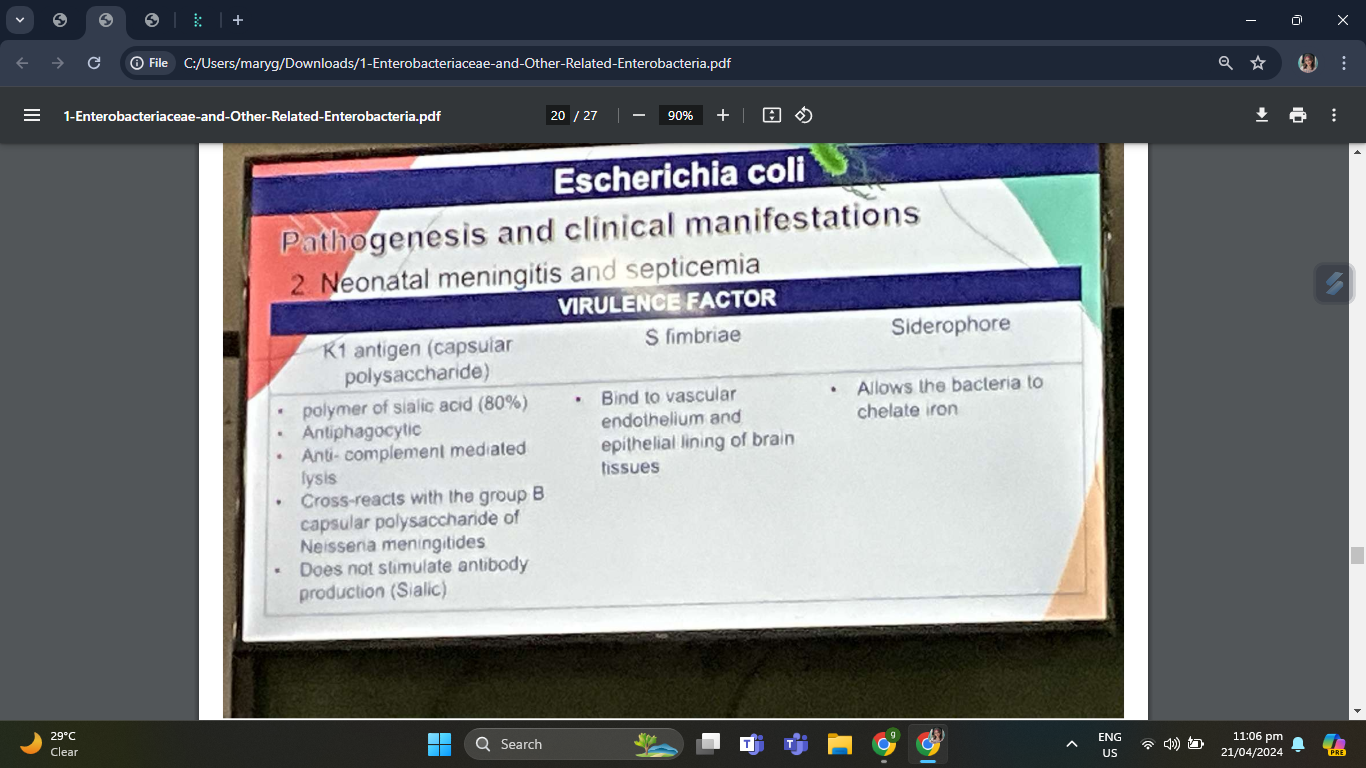
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
A polymer of sialic acid possessed by approximately 80% of E. coli from meningitis cases
K1 antigen (capsular polysaccharide)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Antiphagocytic and provides some resistance against the usual sensitivity of E. coli to complement-mediated lysis
K1 antigen (capsular polysaccharide)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Cross-reacts with the group B capsular polysaccharide - of Neisseria meningitidis
K1 antigen (capsular polysaccharide)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Does not stimulate antibody production antibodies because of its similarity to host sialic acid polymers
K1 antigen (capsular polysaccharide)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Bind to vascular endothelium and epithelial lining of brain tissues
S fimbriae
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Allows the bacteria to chelate iron
Siderophore
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Neonatal Meningitis and Septicemia
Virulence Factors
Table PPT
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Diarrheal diseases associated with certain strains of E.coli
Gastroenteritis
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
________________ — the ultimate source of contamination; transmission by fecal-oral spread through contaminated water and food
Gastroenteritis
Human or animal feces
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
5 pathotypes of diarrheagenic E. coli, each causing diarrheal diseases with different distinct features in their epidemiology, clinical syndrome, and pathogenic mechanism:
Gastroenteritis
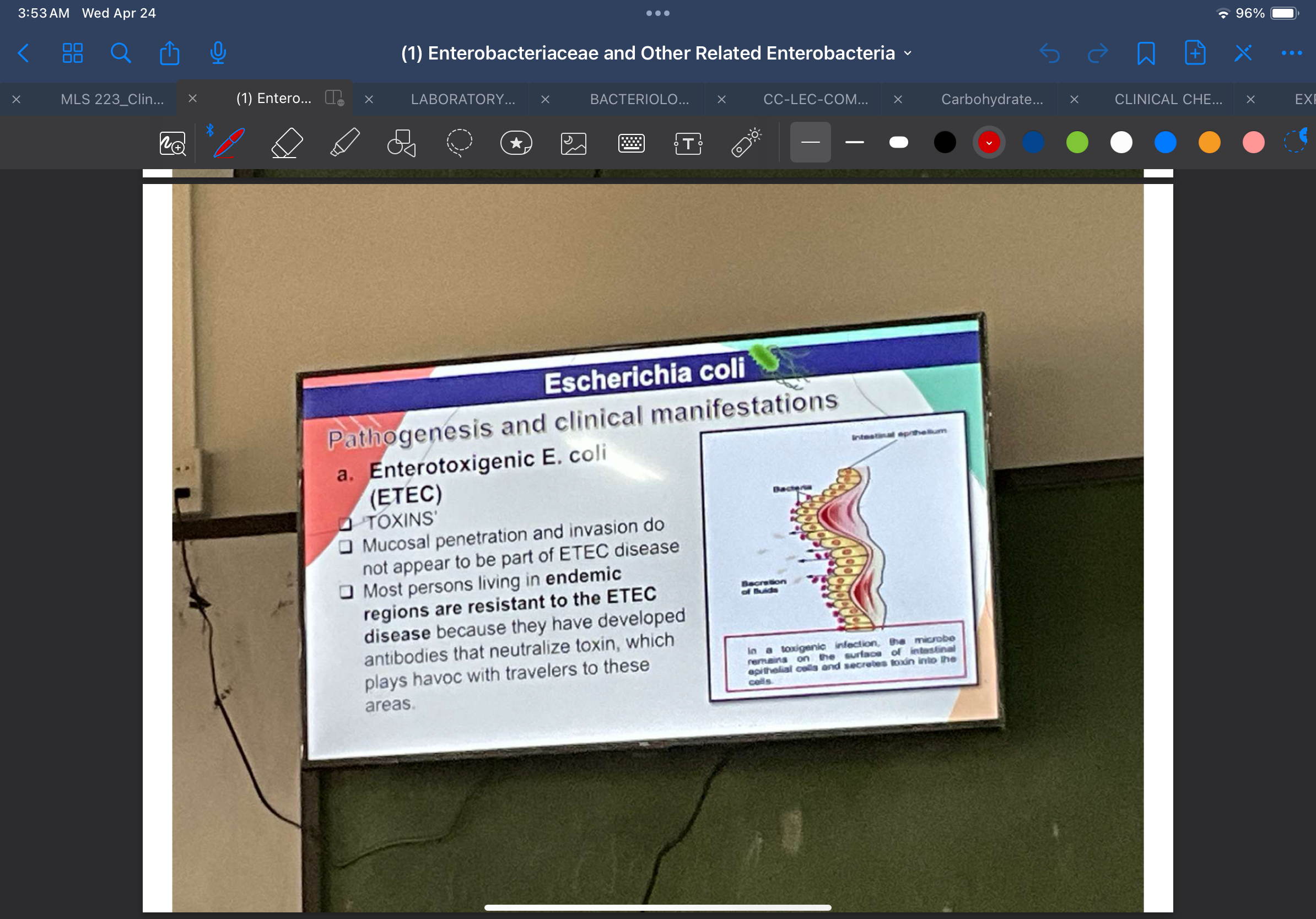
a. Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
b. Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
c. Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
d. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
e. Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Two Clinical Syndromes
Table (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
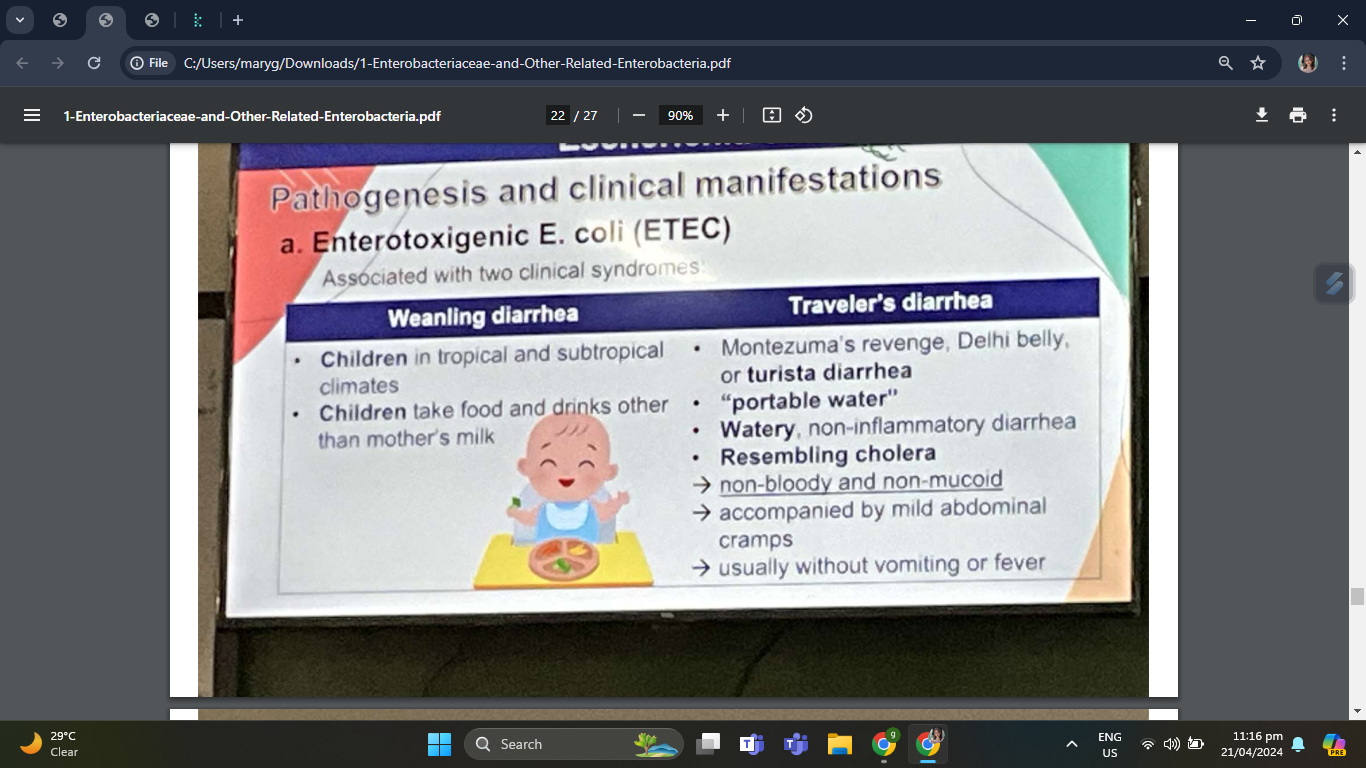
Among children in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in developing countries, when they are being weaned off nursing and start to take food and drinks other than mother’s milk
Weanling diarrhea
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
When a person eats food, or drinks water contaminated with ETEC, esp. during travel to developing countries, to an area with poor public hygiene, inadequate sanitation, or reduced availability of sources of potable water
Traveler’s diarrhea (also referred to as Montezuma’s revenge, Delhi belly, or turista)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Causes watery, non-inflammatory diarrhea , resembling cholera, i.e, non-bloody and non-mucoid, accompanied by mild abdominal cramps; usually without vomiting or fever
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Facilitate attachment to the intestinal epithelium by binding to specific carbohydrate receptors on the intestinal microvilli
Pili (fimbriae)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
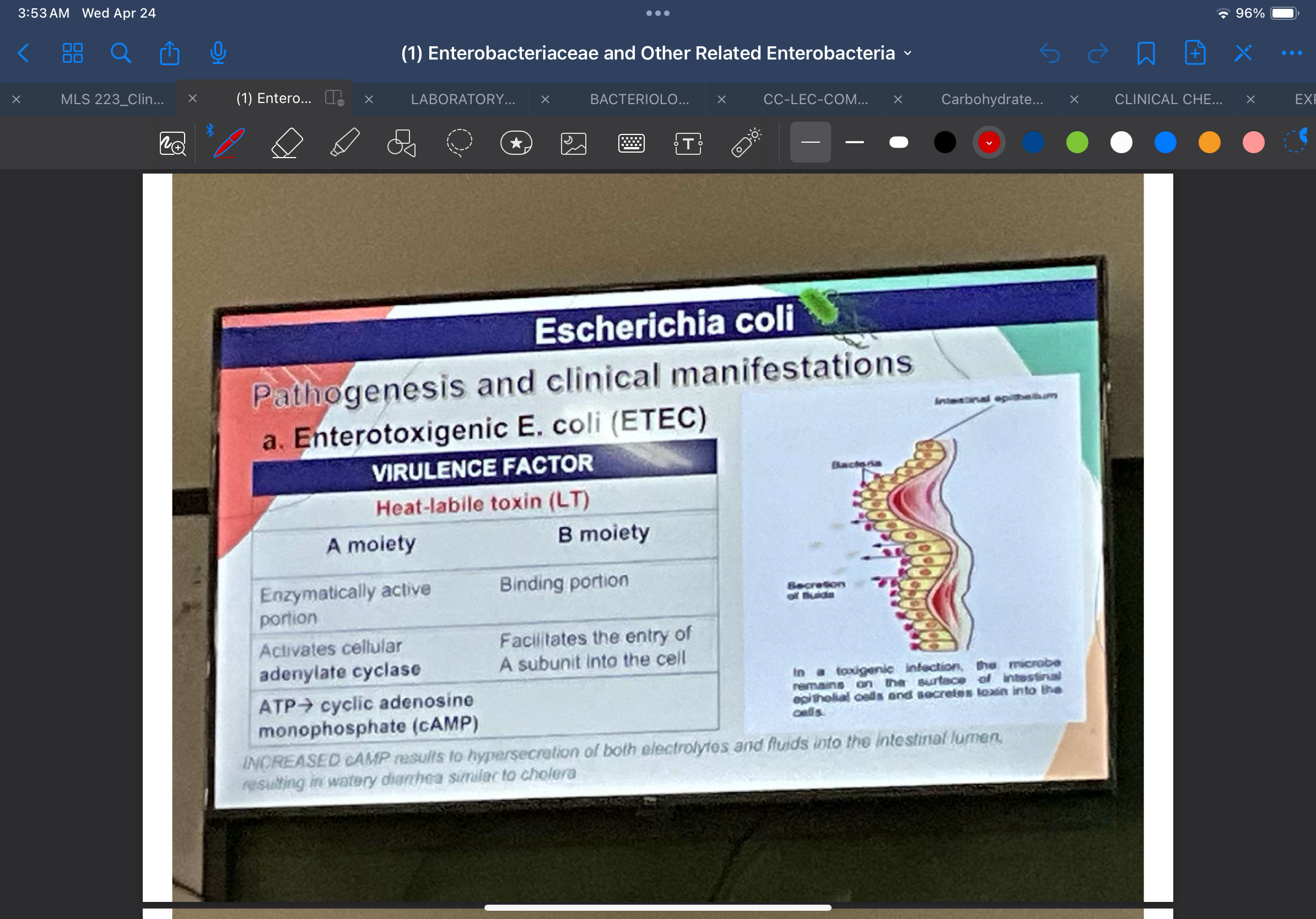
Enterotoxins
(a) Heat-labile toxin (LT)
(b) Heat-stable toxin (ST)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
________________ is similar in structure and action to cholera toxin (choleragen) from Vibrio cholerae.
Heat-labile toxin (LT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
An A/B toxin composed of A subunit and 5 identical B subunits arranged in a ring.
Heat-labile toxin (LT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
Heat-labile Toxins
Enzymatically active portion
A moiety
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
Heat-labile Toxins
Activates cellular adenylate cyclase, causing an increase in the conversion of adenosine triphosphate to cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); accumulation of cAMP results to hypersecretion of both electrolytes and fluids into the intestinal lumen, resulting in watery diarrhea similar to cholera.
A moiety
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
Heat-Labile Toxins
Binding portion — binds strongly to the epithelial cells of the small intestine and facilitates the entry of A subunit into the cell
B moiety
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
Stimulates guanylate cyclase, causing increased production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
Heat-stable toxin (ST)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Enterotoxins
Intracellular accumulation inhibits intestinal fluid uptake, resulting in hypersecretion
Heat-stable toxin (ST)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Table (PPT)

PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Virulence Factors
Heat-Labile Toxin
Table (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Additional Notes (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Associated with ______________, usually less than 2 years of age; diarrheal outbreaks occurring in hospital nurseries and daycare centers, but cases in adults are rarely seen
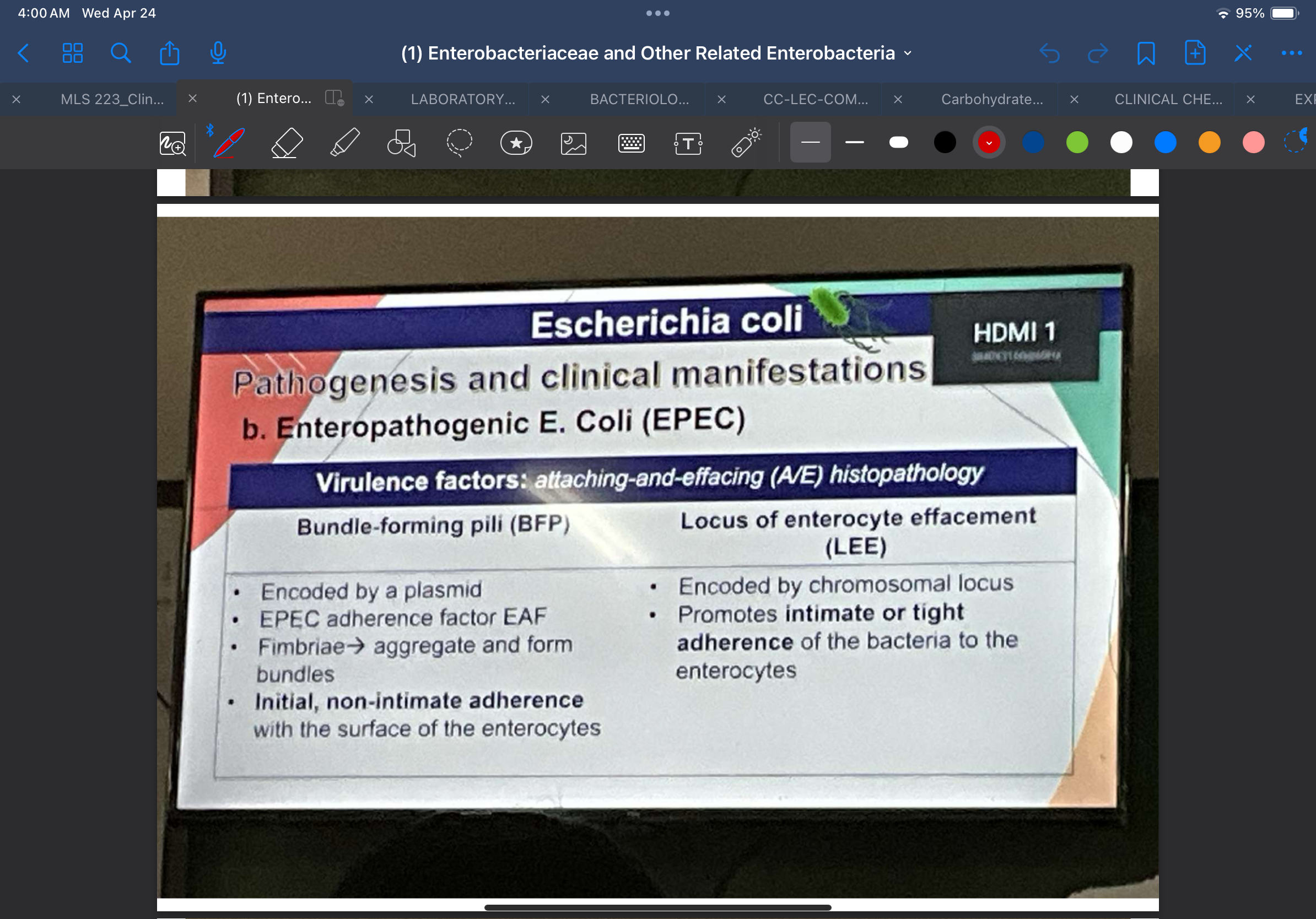
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
infantile diarrhea
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Causes watery diarrhea with mucus, but without gross blood; also characterized by low-grade fever, malaise, and vomiting
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Adheres to intestinal epithelial cells in localized microcolonies producing characteristic known as _____________________
attaching-and-effacing (A/E) histopathology
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Encoded by a plasmid, EPEC adherence factor EAF
Bundle-forming pili (BFP)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Fimbriae produced by EPEC strains which tend to aggregate and form bundles
Bundle-forming pili (BFP)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Mediate initial, non-intimate adherence of the bacteria with the surface of the enterocytes
Bundle-forming pili (BFP)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Encoded by chromosomal locus
Locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Promotes intimate or tight adherence of the bacteria to the enterocytes
Locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Virulence Factors
Table (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteropathogenic E. Coli (EPEC)
Additional Notes
Table (PPT)

PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Causes disease in people of all ages, however, it occurs most commonly in children in developing countries and in travelers to these countries
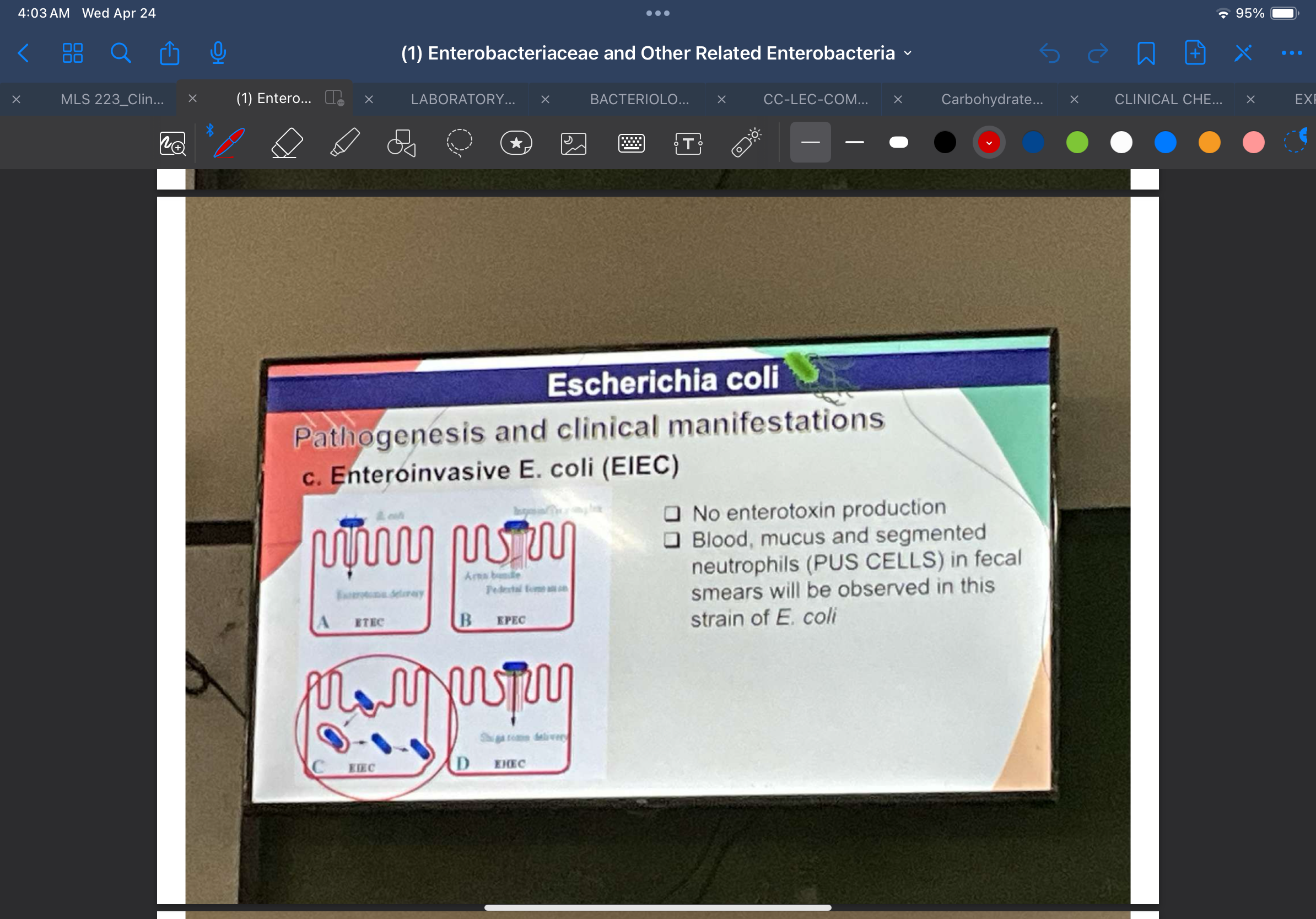
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Produces watery diarrhea with fever and abdominal pain
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Some patients present with dysentery, with very little stool, but much blood and mucus, closely resembling _____________
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
shigellosis
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
Virulence Factors
i. Invasion of intestinal epithelial cells
ii. Lysis of the phagosomal vacuole
iii. Movement through the cytoplasm, ultimately spreading to adjacent epithelial cells.
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
Additional Notes
PPT
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Alternative nomenclature:
Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC)
Verotoxin-producing E. coli(VTEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
The most common involved serotype
E. coli O157:H7
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Associated with epidemic and sporadic diarrhea, mostly in developed countries
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Has high prevalence of colonization in cattle or cows; transmission is by contamination of meat with cattle’s feces during slaughter, thus.
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
The source of most cases is considered to be ground beef, hamburgers in particular; unpasteurized dairy products and apple cider, bean sprouts, and spinach have been implicated in the spread of infection
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Prevalence
PPT

PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Clinical Manifestations
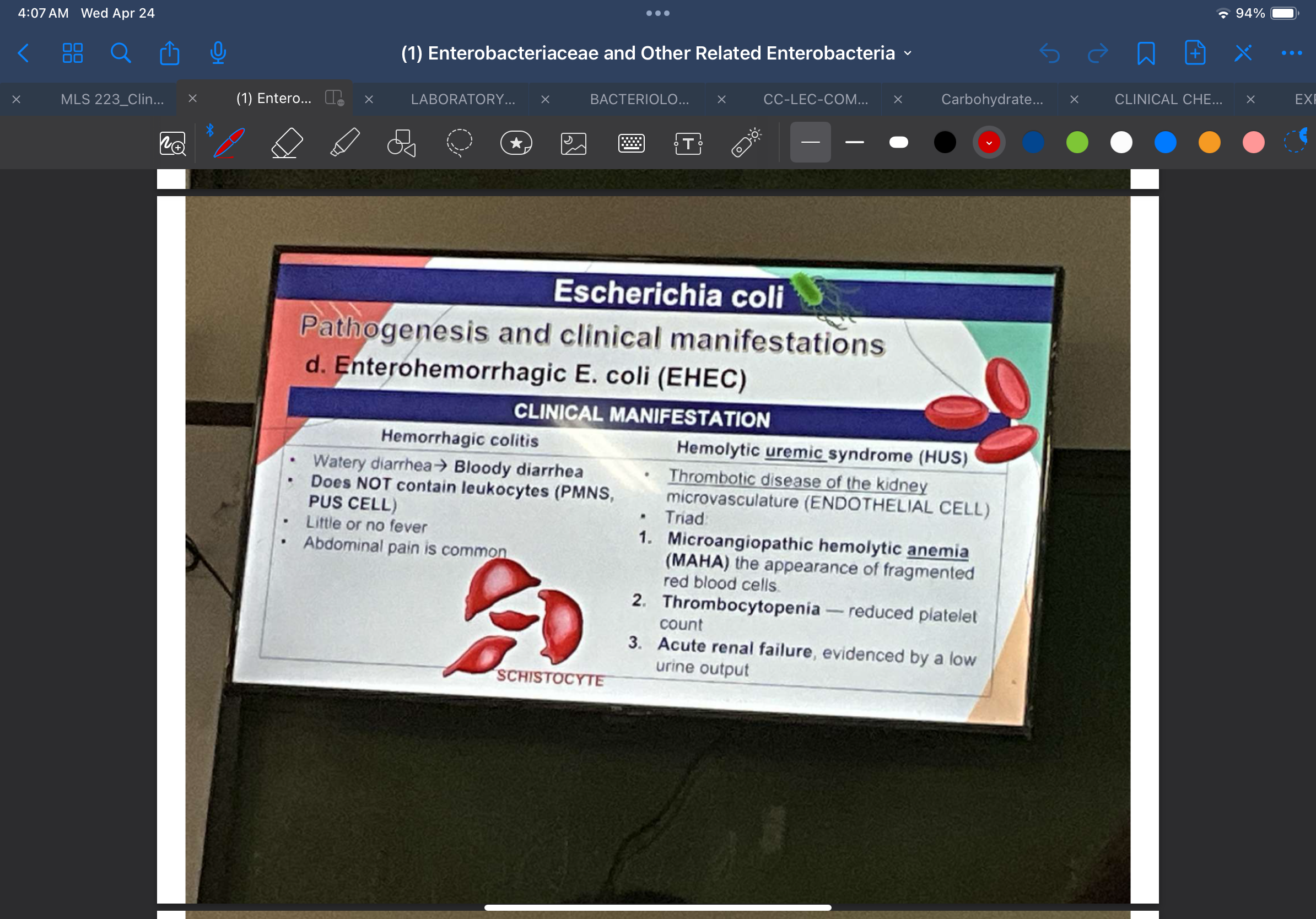
Characterized by a watery diarrhea that progresses to bloody diarrhea, but the stool does not contain leukocytes; patients typically have little or no fever, and abdominal pain is common
Hemorrhagic colitis
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Clinical Manifestations
A thrombotic disease of the kidney microvasculature in which the endothelial cell is the primary site of damage
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Clinical Manifestations
Defined by a triad of features:
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
‣ Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia — the appearance of fragmented red blood cells
‣ Thrombocytopenia — reduced platelet count
‣ Acute renal failure, evidenced by a low urine output
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Clinical Manifestations
Table (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
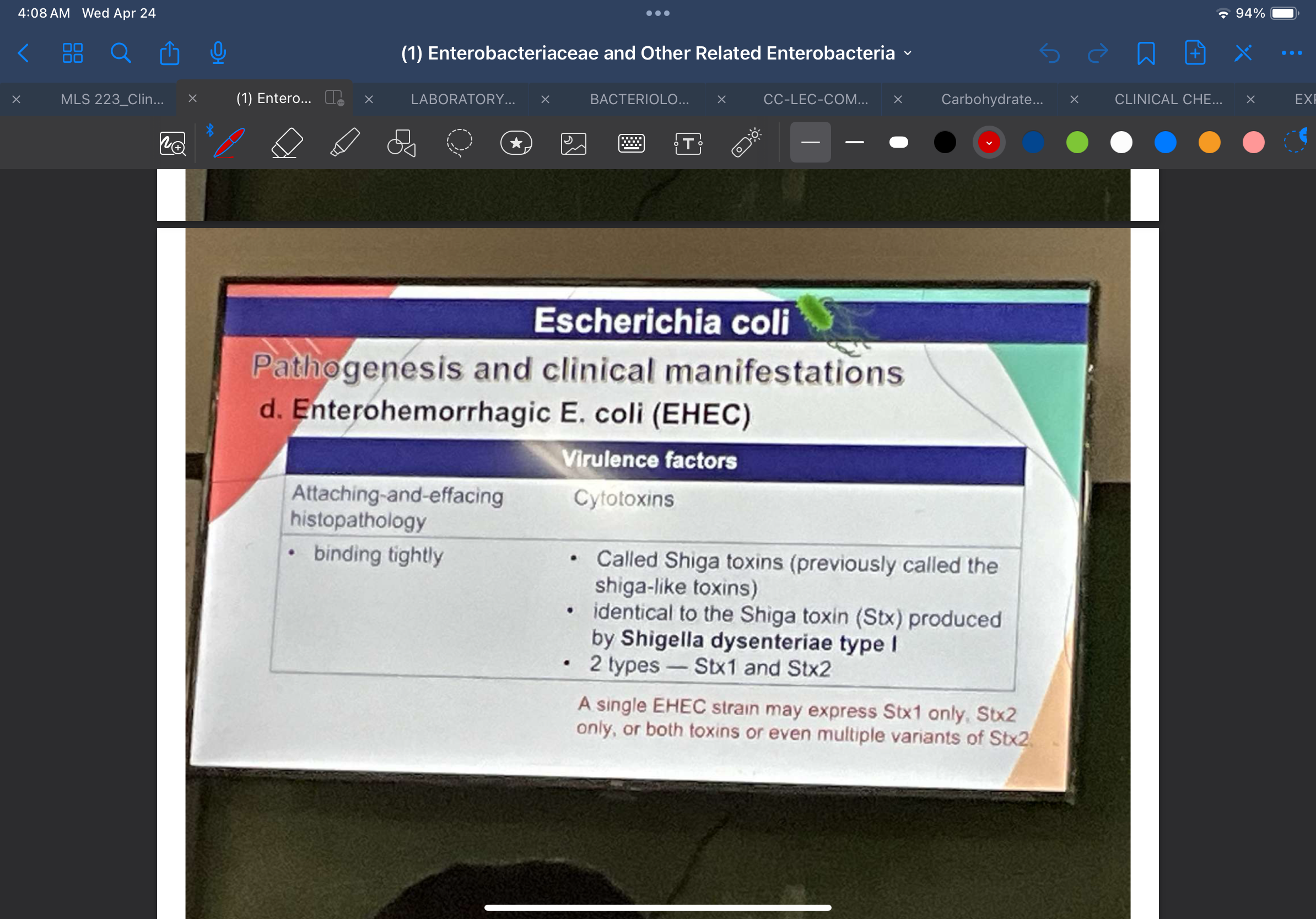
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Virulence Factors
By binding tightly to cells and produce the same A/E phenomenon seen with EPEC strains
Attaching-and-effacing histopathology
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Virulence Factors
Called Shiga toxins (previously called the shiga-like toxins) which are identical to the Shiga toxin (Stx) produced by Shigella dysenteriae type I
Cytotoxins
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Virulence Factors
2 types — Stx1 and Stx2
Cytotoxins
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Virulence Factors
Table (PPT)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Newest strain
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Associated with diarrhea in persons of all ages in developing countries, but occurs predominantly in infants
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Is increasingly recognized as a cause of traveler's diarrhea, possibly second only to ETEC
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Characterized by watery, persistent diarrhea occurring more than 14 days in duration
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
With grade fever and little or no vomiting
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
White blood cells and red blood cells are absent.
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
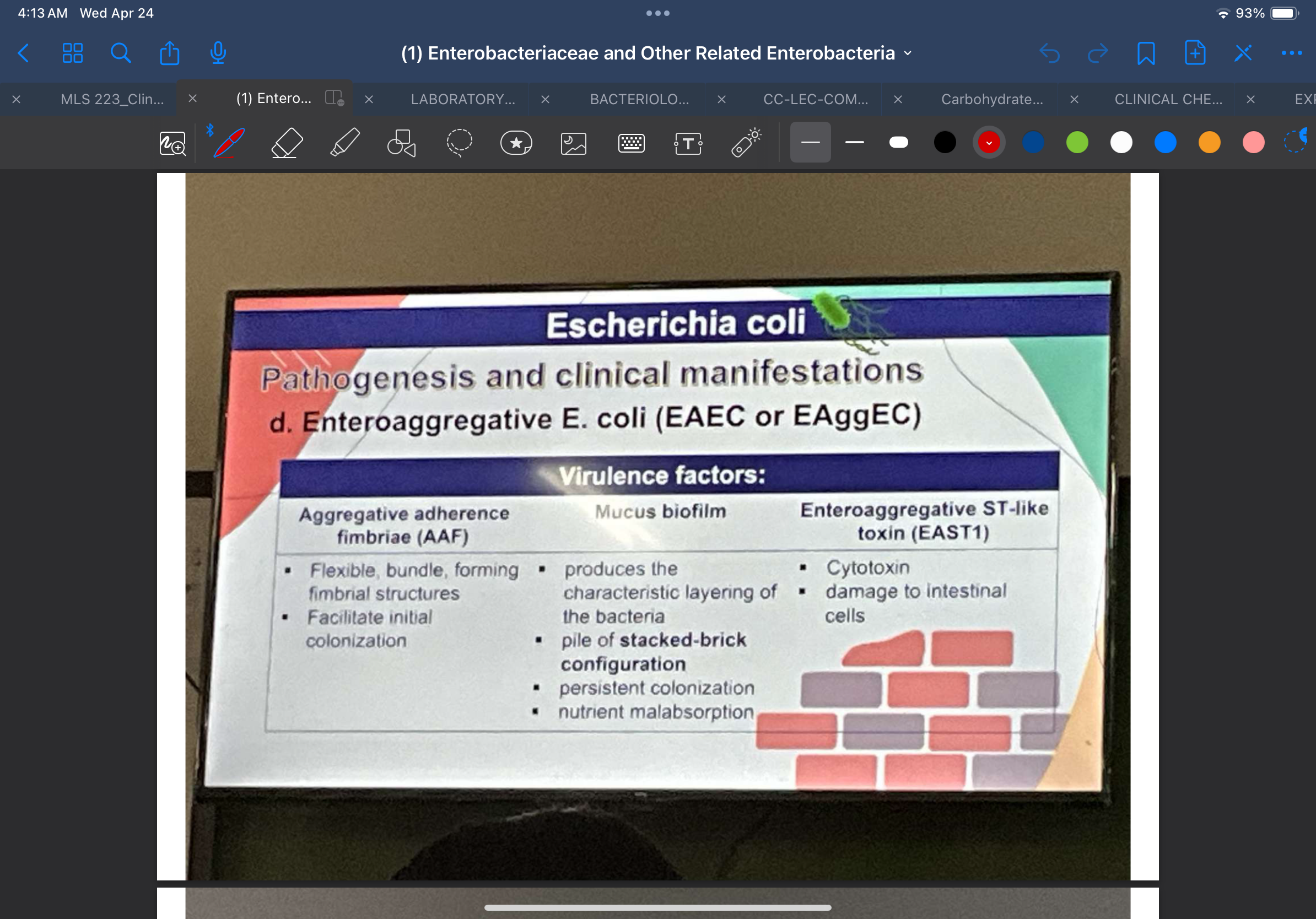
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Flexible, bundle-for ming fimbrial structures
Aggregative adherence fimbriae (AAF)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Facilitate initial colonization
Aggregative adherence fimbriae (AAF)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Enhanced mucus production traps bacteria in biofilm producing the characteristic layering of the bacteria described as a pile of stacked-brick configuration
Mucus biofilm
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Promotes persistent colonization
Mucus biofilm
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Promotes nutrient malabsorption
Mucus biofilm
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
It is a cytotoxin
Enteroaggregative ST-like toxin (EAST1)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Results in damage to intestinal cells
Enteroaggregative ST-like toxin (EAST1)
PATHOGENESIS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Gastroenteritis
Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC)
Virulence Factors
Table (PPT)
PREVENTION AND CONTROL
• Control measures are not feasible as far as the normal endogenous microbiota is concerned.
• Sanitation and hygiene are important, however.
- Sanitation
Sewage treatment and disposal
Treatment of drinking water
- Hygiene
Handwashing
Proper food preparation