Abstract data types
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
If questions repeat, i am so sorry x. Cambrdige AS level computer science 2025. Textbook references: Cambridge International AS and A level computer science coursebook Sylvia Langfield, David Duddell 2019 press ||| Cambrdige International AS and A Levels Computer science by David Wastson, Helen Williams press 2019
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
what does ADT stand for
Abstract data type
what is ADT
collectiion of data and a set of operations on that data
name the types of ADTs
stack, queue, linked listt
how can ADTs be implemented
from arrays
how can ADTs be stored
in a record
what is a node
an element of a list
what is a pointer
what is a pointer a variable that stored the address of the not it points to
what is a null pointer
a pointer that does not point at anything
what is a start pointer
a variable that stored the address of the first element of a linked list
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: isFull()
checks if the stack is full
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: initialize()
initialising it to be empty
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: push()
intsert an element into the stack
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: pop()
delete an element from the stack
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: isEmpty()
checks if stack is empty
what does a stack consist of
elements of stame type arranged in a sequential order
what does LIFO stand for
last in; first out
what is a stack
a structure in which elements are added or removed from only one end
what does push mean in stacks
add
what does popped mean in a stack
remove
what variable type is push and pop usually in
boolean
how can you implement a stack ADT
arryas or linked lists
what is the advantage of ADTs
you don’t need to worry about how implementations are peformed to use stacks in your program
what is a client program
a program that uses data structures
what is implementation
program which utilises data structures
what does ADT provide
abstraction
what is a stack
linear data structure with insertions and deletions allowed only at the end called the top
what is a lineear data structure
data organization method where elements are arranged sequentially, one after another
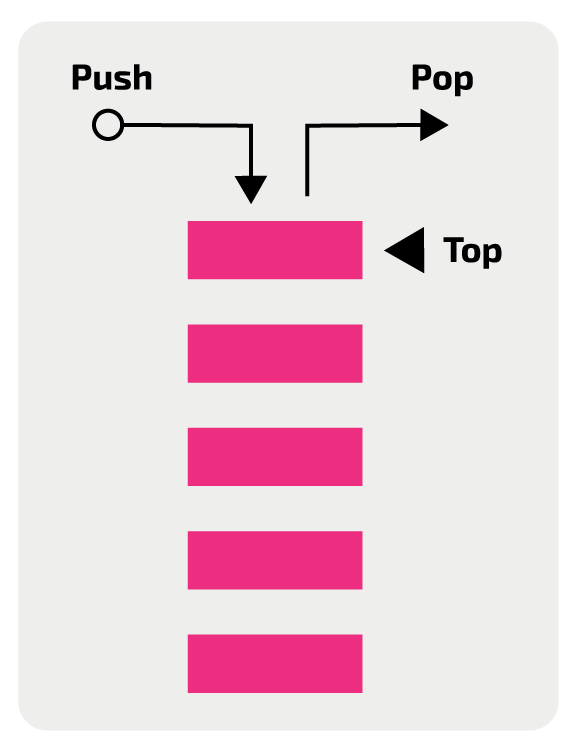
what ADT is this?
stack
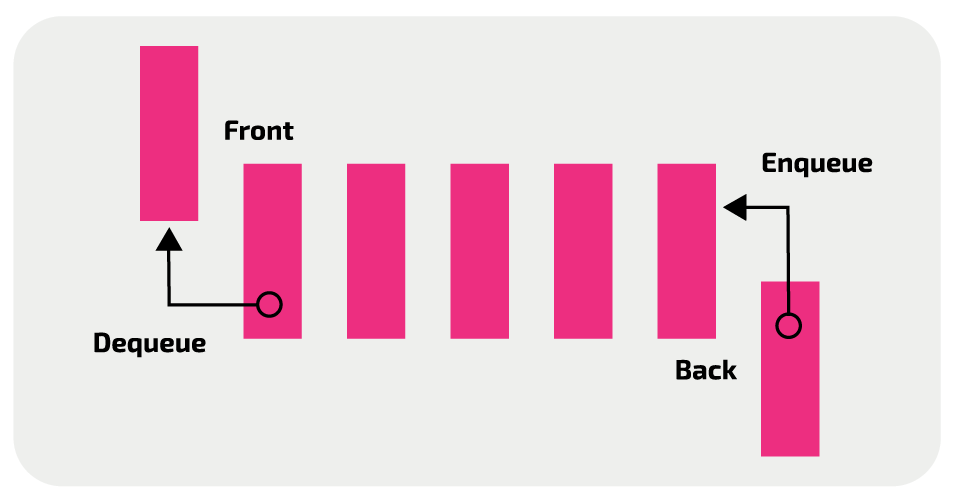
what ADT is this
queue
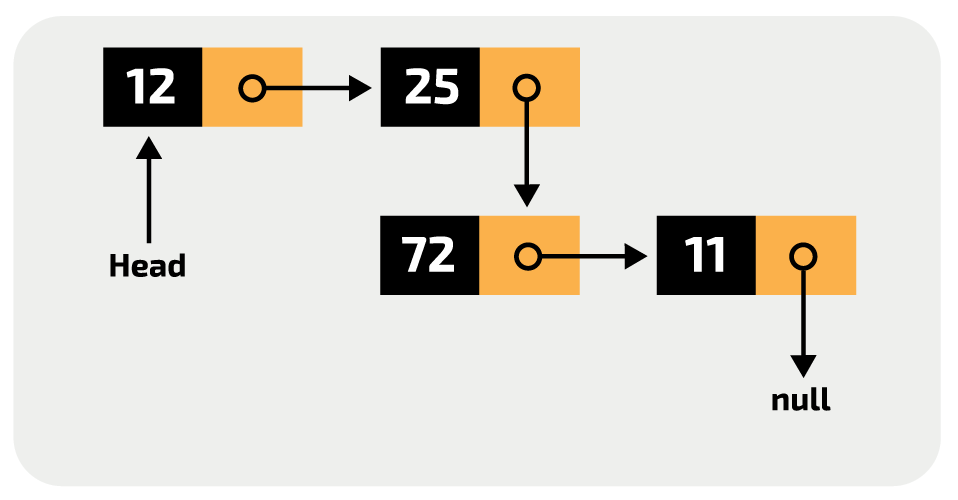
what ADT is this
linked list
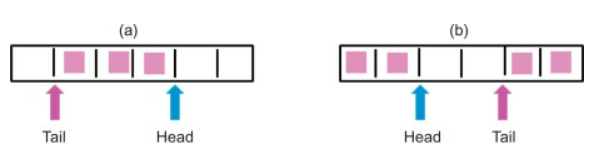
what ADT is this?
circular queue
how do you understand data in a stack
from the users point of view
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: top()
returns the last inserted elements without removing it
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: size()
returns the size or the number of elements in the stack
how do you declare a stack
DECLARE Stack ARRAY[0:7] OF CHAR
what makes a stack array different from a normal array
it behaves like a stack by using a variable usually called top
what makes a normal array different from a stack array
you can insert or remove data from any point of the array
what does the variable stack do
keep track of the last inserted element
how would you indicate the stack is empty
make the variable top -1
what does the BaseOfStackPointer() do
point to first slot in a stack
what does TopOfStackPointer() do
points to the last slot added to the stack
What does this operation in a stack ADT do?: peek()
return the lement at the top of the stack without removing it
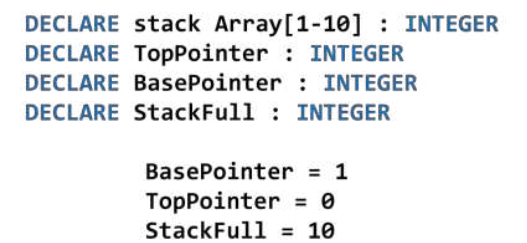
what does this pseudocode do?
set up a stack

what does this pseudocode do?
add an item to a stack

what does this pseudocode do?
remove an item from a stack
how does the push() operation work
increment value of top by 1, new element is pushed to the position top
what happens when a stack is now in an overflow state
new element cannot be pushed because stack is full
how does the pop() operation work
element at top position is deleted, pop is decremented by 1
how would you declare a stack array. global or local?
global
how would you declare a top variable. global or local?
global
why would you need a max variable for a stack
to show the total amount of element spaces in a stack
how to delete an element at the top index in a stack
give an illusion just by decrementing the top variable
if the top variable is pointing to the middle of a stack, what happens to the other elements after that index
they are still stored there but cannot be accessed
what does underflow state mean
new element cannot be pushed because too many elements were popped
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: enqueue()
insert an element at the end of the queue
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: dequeue()
remove and return the first element of queue, if the queue is not empty
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: peek()
return the element of the queue without removing it, if the queue is not empty
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: size()
retunr the number of elements in the queue
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: isEmpty()
return true if the queue is empty, otherwise return false
What does this operation in a queue ADT do?: isFull()
return true if the queue is full, otherwise retunr false
how can a queue ADT be represented
array, linked list
what is a queue ADT
linear data structure which insertion and deletion operations are performed at two different ends
what does rear mean in queue ADT
insertion point
what does front mean in queue ADT
deletion point
what does FIFO stand for
first in; first out
which ADT uses FIFO
queue
which ADT uses LIFO
stack

what does this pseudocode do?
to set up a queue

what does this pseudocode do?
to add an item onto a queue

what does this pseudocode do?
to remove an item from the queue and store it
How do you show an empty queue
EndOfQueuePointer = -1
what is a more efficient queue
circular queue
how does a circular queue work
wraps around to the beginning and you will see an empty space
what happens when something is moved out the queue
everything is pushed forward and adjusts EndOfQueue pointer
how is a queue implemented
using an array and a set of pointers

what does this pseudocode do
set up a linked list
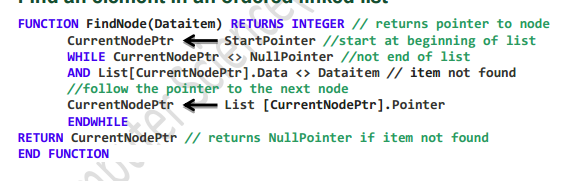
what does this pseudocode do
find an element in an ordered linked list
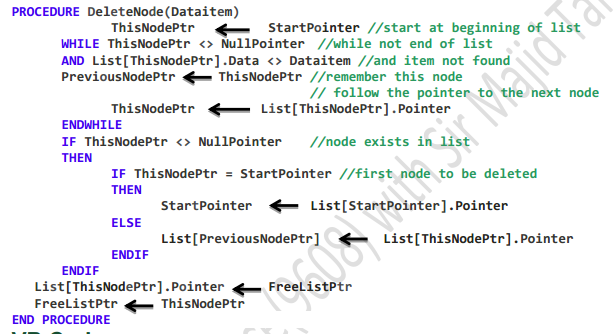
what does this pseudocode do
delete a node from an ordered linked list
how do you add a node at the front
startPointer is copied into the new node's pointer field and startpointer is set to point to the new node
how do you add a node after a given node
we copy the pointer field a node into the pointer field of a new node. Change the pointer field of first node to point to the new node
how do you add a node at the end
pointer field of last node points to new node. new node contains null pointer
how do you delete the first node in the list
copy pointer field of the node to be deleted into startpointer
how do you delete the last node in the list
set the pointer field for the preveious node to the null pointer
how do you delete a new node within the list
copy the pointer field of the node to be deleted into the pointer field of the node before that
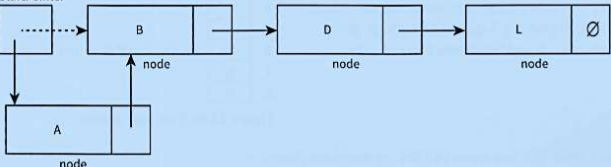
what does this diagram do?
add a node at the front of the list
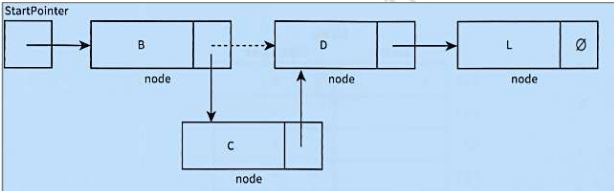
what does this diagram do?
add a node after a given node
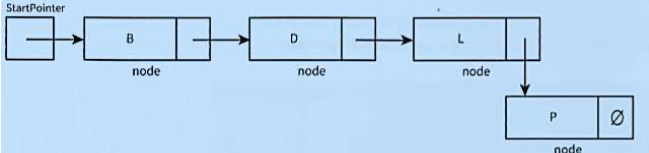
what does this diagram do?
add a node at the end
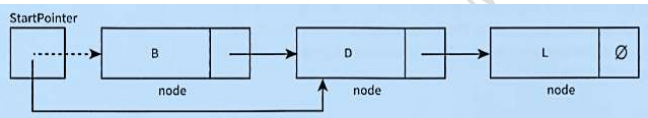
what does this diagram do?
delete the first node in the list
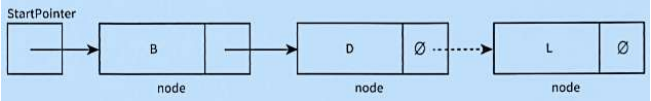
what does this diagram do?
delete the last node in the list
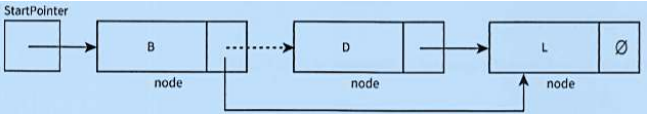
what does this diagram do?
delete a node within the list
what is a pro of using linked lists
saves time, only the pointer needs to change in a linked list
what is a con of using linked lists
need more storage space
what do you do with unused nodes
form another linked list
what do you call a linked list with all emptu nodes
free list
how will a linked list appear when first inistialised
empty and null pointer will be the start pointer
what does the data value in the node box represent
key field of that node
what is an ordered linked list
list linked together in order of key field value
how can you implement a linked list
using arrays
what is a use for stacks?
memory management, expression evaluation, backtracking in recursion
what is a use for queues?
management of files sent to a printer, buffers used with keyboards, scheduling