Geography CFE Study Guide
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
developing country
A country that has low industrial production and little modern technology

industrialization
The development of industries for the machine production of goods.

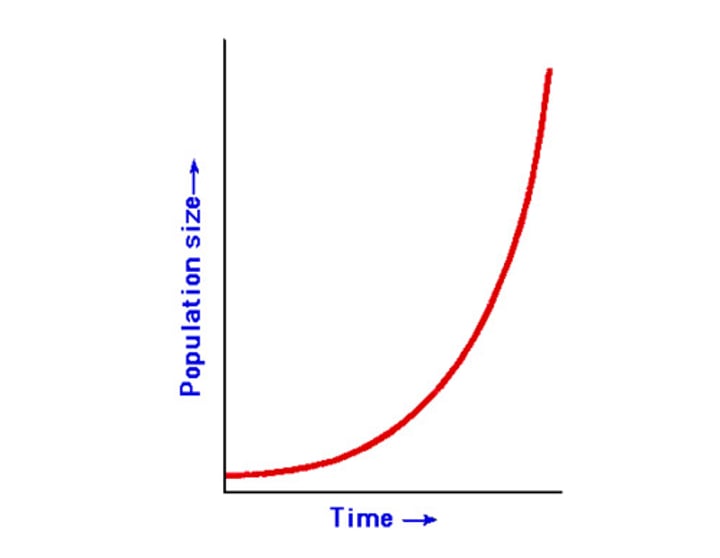
population growth
increase in the number of people who inhabit a territory or state
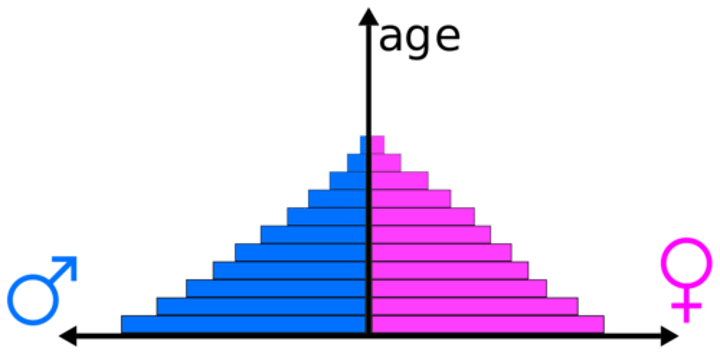
population pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
health
The combination of physical, mental/emotional, and social well-being

literacy rate
The percentage of a country's people who can read and write.

education
A formal process of learning in which some people consciously teach while others adopt the social role of learner.

Women's Rights
rights that promote a position of legal and social equality of women with men.

Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Old Testament.

Torah
A Hebrew word meaning "law," referring to the first five books of the Old Testament.

Abraham
Founder of Judaism who, according to the Bible, led his family from Ur to Canaan in obedience to God's command.

Moses
(Old Testament) the Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites from Egypt across the Red sea on a journey known as the Exodus

Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.

Holy Bible
Christian holy book, which consists of both the New and Old Testament.

Jesus Christ
A teacher and prophet whose life and teachings form the basis of Christianity. Christians believe Jesus to be Son of God.

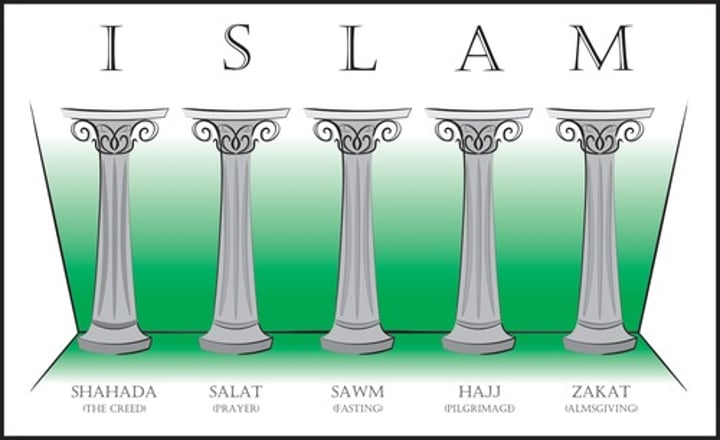
Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), Paradise and Hell, and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.

Koran (Qur'an)
The holy book of Islam

Prophet Muhammad
the founder of Islam, believed to be the last true prophet sent by God, wrote the Koran which were his revelations

5 Pillars of Islam
belief, prayer, charity, fasting, pilgrimage
Monotheism
Belief in one God

Polytheism
Belief in many gods

Localization
the transformation of global culture by local cultures into something new

Regionalism
loyalty to the interests of a particular region
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.

Polarization
A deep and wide conflict over some government policy

Silk Trade
(Imperial China) - Han Dynasty - The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes, formally established during the Han Dynasty of China, which linked the regions of the ancient world in commerce between 130 BCE-1453 CE.
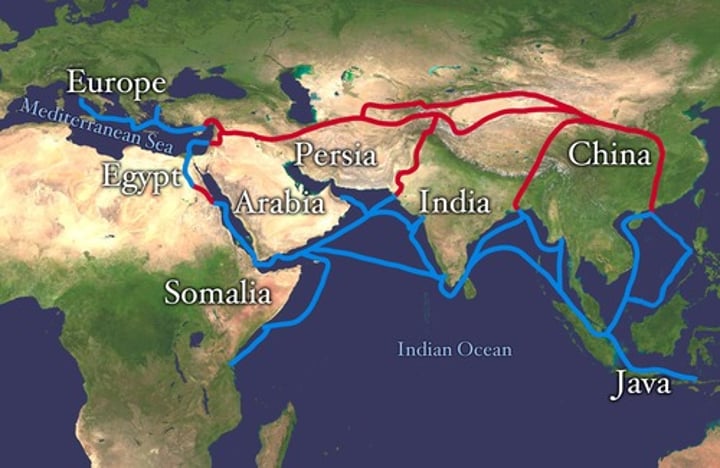
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
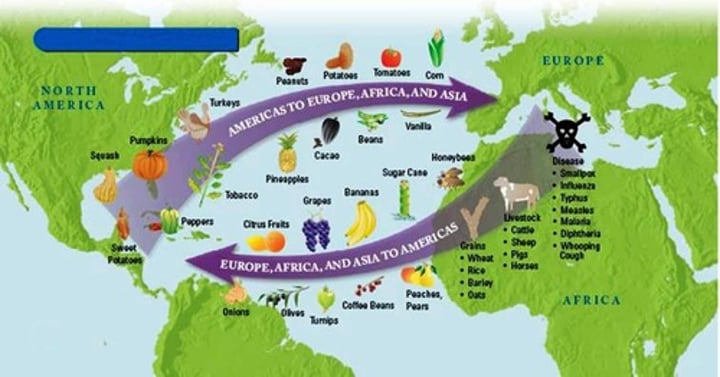
cultural diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another

Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

Immigration
Migration to a new location

Emigration
movement of individuals out of an area

Push Factors of Immigration
economic troubles, overcrowding, and poverty
Pull Factors of Immigration
Economic Opportunity ($)
Jobs/ workers were needed
Land
Peace and stability
Freedom to make a better life
Nativism
A policy of favoring native-born individuals over foreign-born ones

desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.

global warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes)

natural disaster
great destruction or loss of life caused by natural forces rather than by human actions

NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement; allows open trade with US, Mexico, and Canada.
NATO
North Atlantic Treaty Organization; an alliance made to defend one another if they were attacked by any other country; US, England, France, Canada, Western European countries

European Union
An international organization of European countries formed after World War II to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation among its members.

United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

Diplomacy
Negotiation between nations

trade embargo
a government order that forbids trade with a specified nation

sanctions
a threatened penalty for disobeying a law or rule

treaty
A formal agreement between two or more sovereign states

ambassador
an official representative of a country's government

Democracy
A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them

Absolute Monarchy
A system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power

Constitutional Monarchy
A King or Queen is the official head of state but power is limited by a constitution.

Autocracy
a system of government by one person with absolute power.

Oligarchy
A government ruled by a few powerful people

Anarchy
nobody is in control

Dictatorship
A form of government in which the leader has absolute power and authority.

Communism
A theory or system of social organization based on the holding of all property in common, actual ownership being ascribed to the community as a whole or to the state.

Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.

Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.

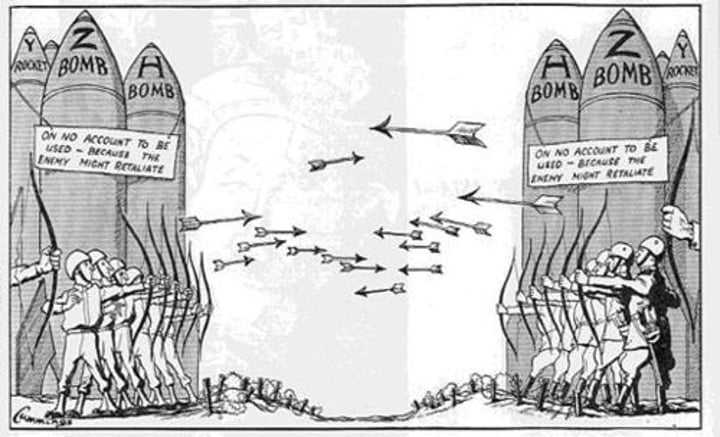
Cold War
the power struggle between the Soviet Union and the United States after World War II

Nuclear Weapons
Weapons in which the explosive potential is controlled by nuclear fission or fusion.

Containment Policy
US policy to stop expansion of Soviet Union and Communism
Domino Theory (Cold War)
the idea that if a nation falls under communist control, nearby nations will also fall under communist control

Brinkmanship
A policy of threatening to go to war in response to any enemy aggression.
Mutually Assured Destruction
(MAD) if either US or the USSR was hit with a nuclear weapons they would respond with the same
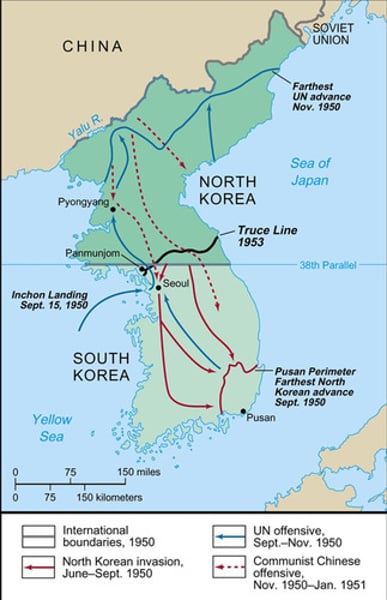
Korean War
The conflict between Communist North Korea and Non-Communist South Korea. The United Nations (led by the United States) helped South Korea.
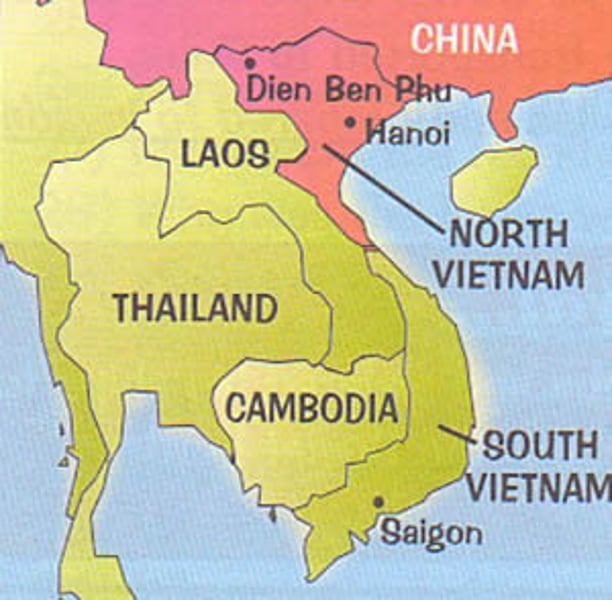
Vietnam War
A prolonged war (1954-1975) between the communist armies of North Vietnam who were supported by the Chinese and the non-communist armies of South Vietnam who were supported by the United States.
Global War on Terrorism
An international action, initiated by President George W. Bush after the 9/11 attacks, to weed out terrorist operatives throughout the world.

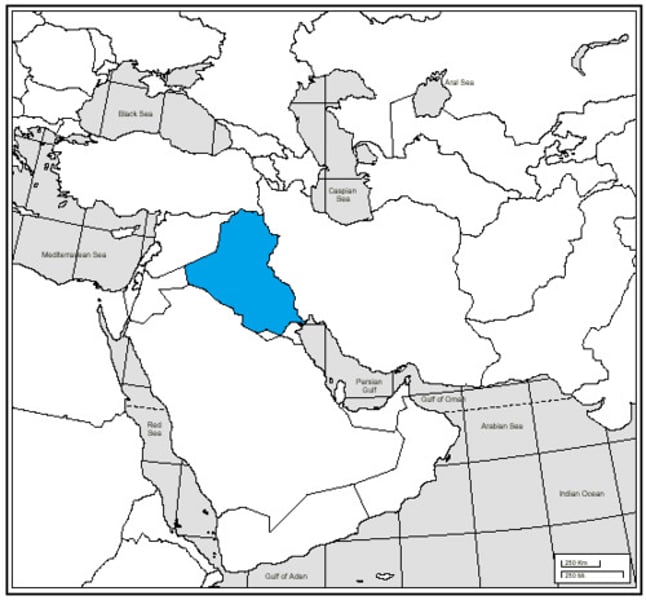
Iraq War
A war fought to end Sadaam Hussein's influence in Iraq and disarm them of WMD's
War in Afghanistan
began on October 7, 2001,[28] as the armed forces of the United States and the United Kingdom, and the Afghan United Front (Northern Alliance), launched Operation Enduring Freedom in response to the September 11 attacks on the United States, with the stated goal of dismantling the Al-Qaeda terrorist organization and ending its use of Afghanistan as a base.
![<p>began on October 7, 2001,[28] as the armed forces of the United States and the United Kingdom, and the Afghan United Front (Northern Alliance), launched Operation Enduring Freedom in response to the September 11 attacks on the United States, with the stated goal of dismantling the Al-Qaeda terrorist organization and ending its use of Afghanistan as a base.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cbf6b2d8-aafa-46e7-9e0b-e266b7beafb6.png)
Five Themes of Geography
Location, Place, Human-Environment Interaction, Movement, Region
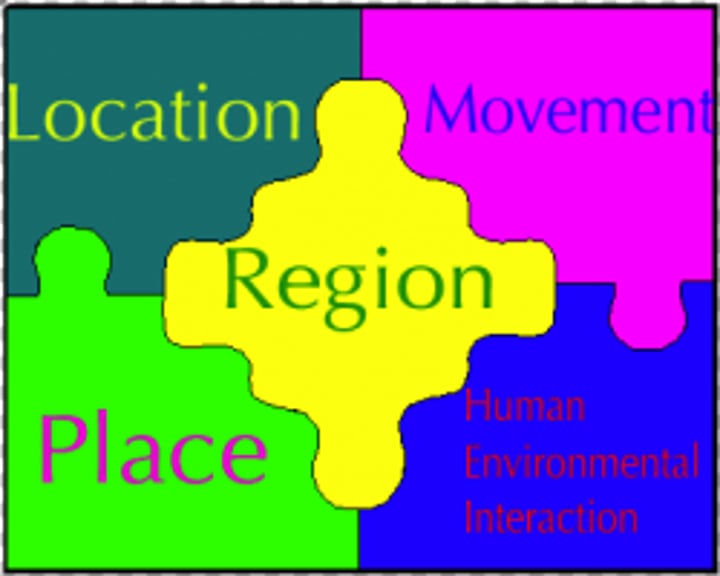
Six Essential Elements of Geography
The world in spatial terms, places and regions, physical systems, human systems, environment and society, uses of geography

GIS (geographic information system)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
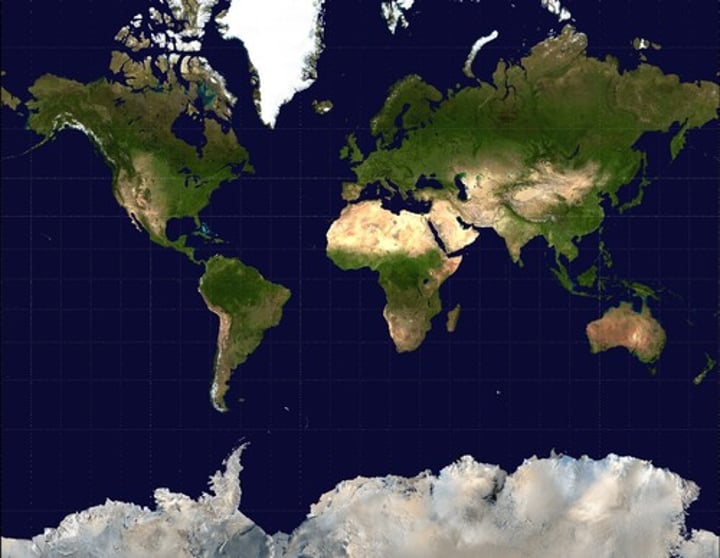
Mercator Projection
a map projection of the earth onto a cylinder
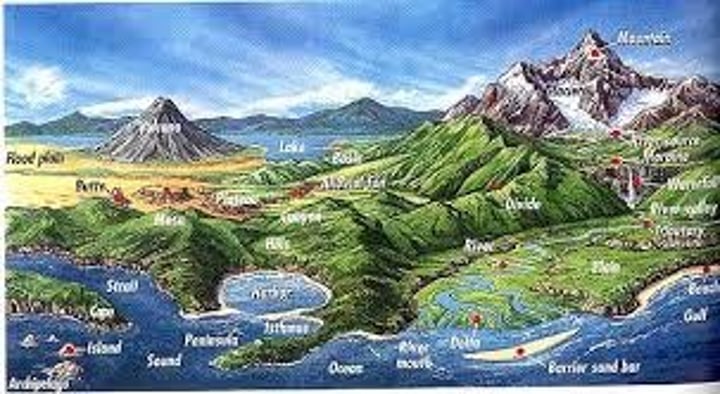
physical geography
the study of physical features of the earth's surface
human geography
The study of where and why human activities are located where they are
demographics
statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.

climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time

terrain
the landscape, especially considered with regard to its physical features or fitness for some use

culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.

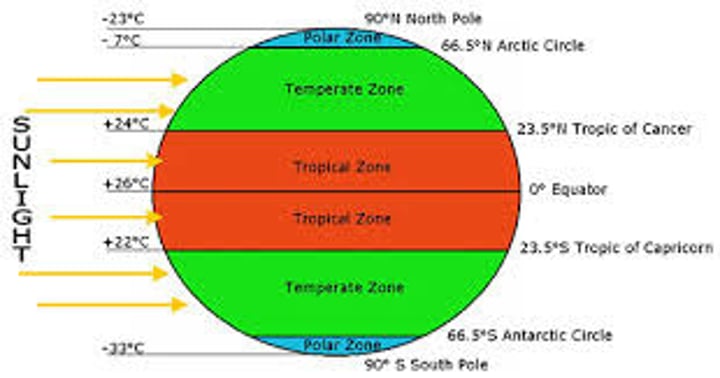
climate zones
a large area of Earth with a particular pattern of weather
birthrate
the number of live births each year per 1,000 people
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.

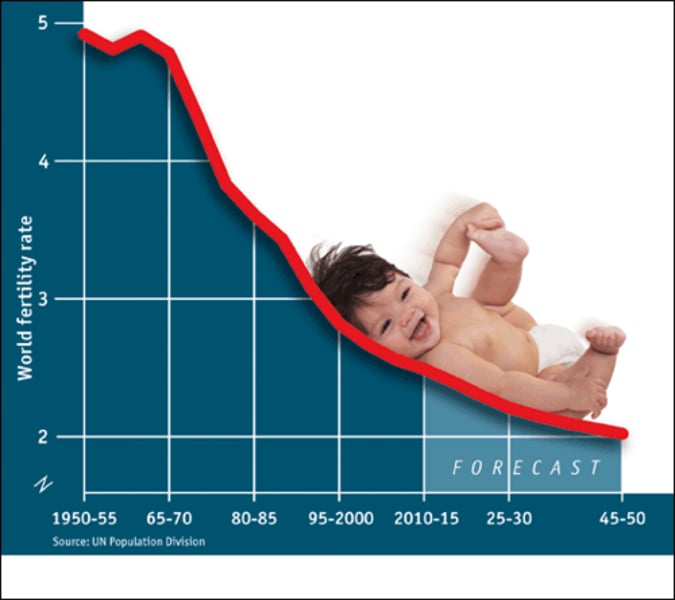
fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her lifetime in a population
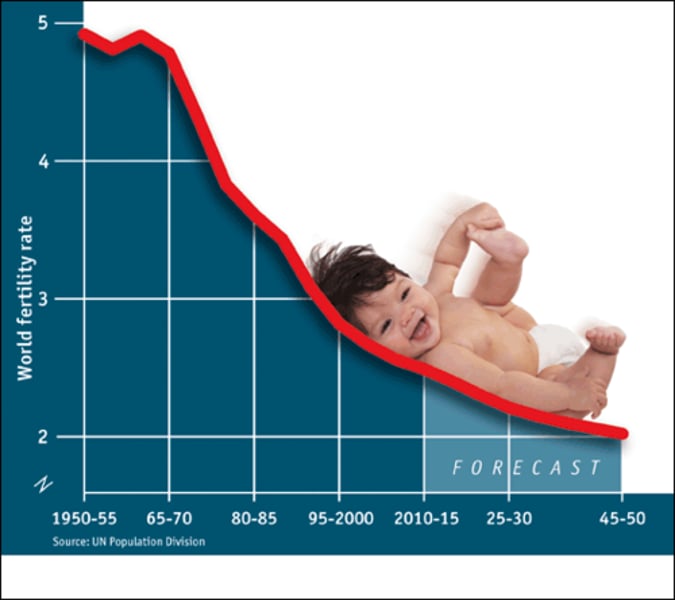
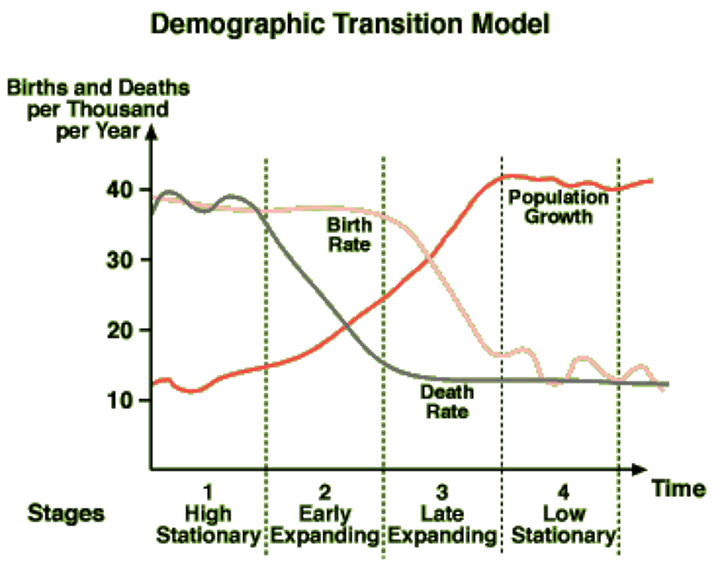
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.