Actin Filaments and Myosin
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
actin filament
thin type of protein filament composed of actin proteins
what does actin require to be assembled?
ATP
F-actin
fibrous protein made of a long chain of G-actin molecules twisted into a helix
G-actin
a globular subunit of F-actin with an active site for binding a myosin head
subunits of actin can be incorporated/released at either end, but which end tends to be added to?
plus end
actin binding protein
protein that interacts with actin monomers/filaments to control the assembly, structure, and behavior of actin filaments and networks
cortex of cell
network of microfilaments that form a semisolid support for the cell's shape
where are actin binding proteins commonly found?
in the cell cortex
monomer sequestering protein
protein that binds to free actin monomers and alters the G- to F-actin equilibrium
capping protein
protein that attaches to and stabilizes microtubules and prevents disassembly
monomer polymerizing protein
protein that promotes growth of actin filaments
membrane binding protein
protein that connects the cytoskeleton to the cell surface
what do cross-linking and bundling proteins do?
link actin filaments together to create strong structures
steps of cell migration
1. polarization
2. protrusion
3. adhesion
4. translocation
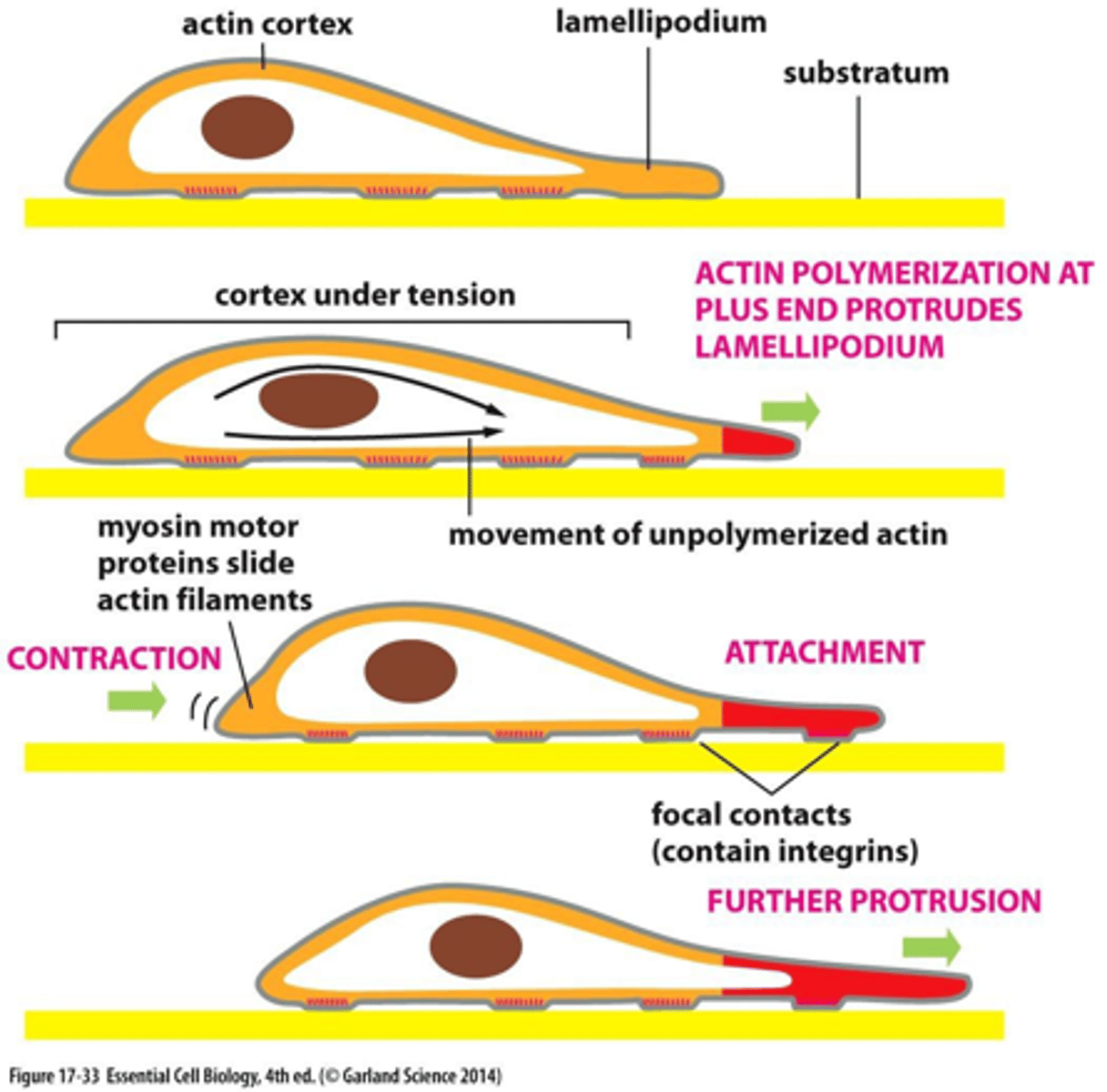
lamellipodium
sheetlike extension, rich in actin filaments, on the leading edge of a motile cell
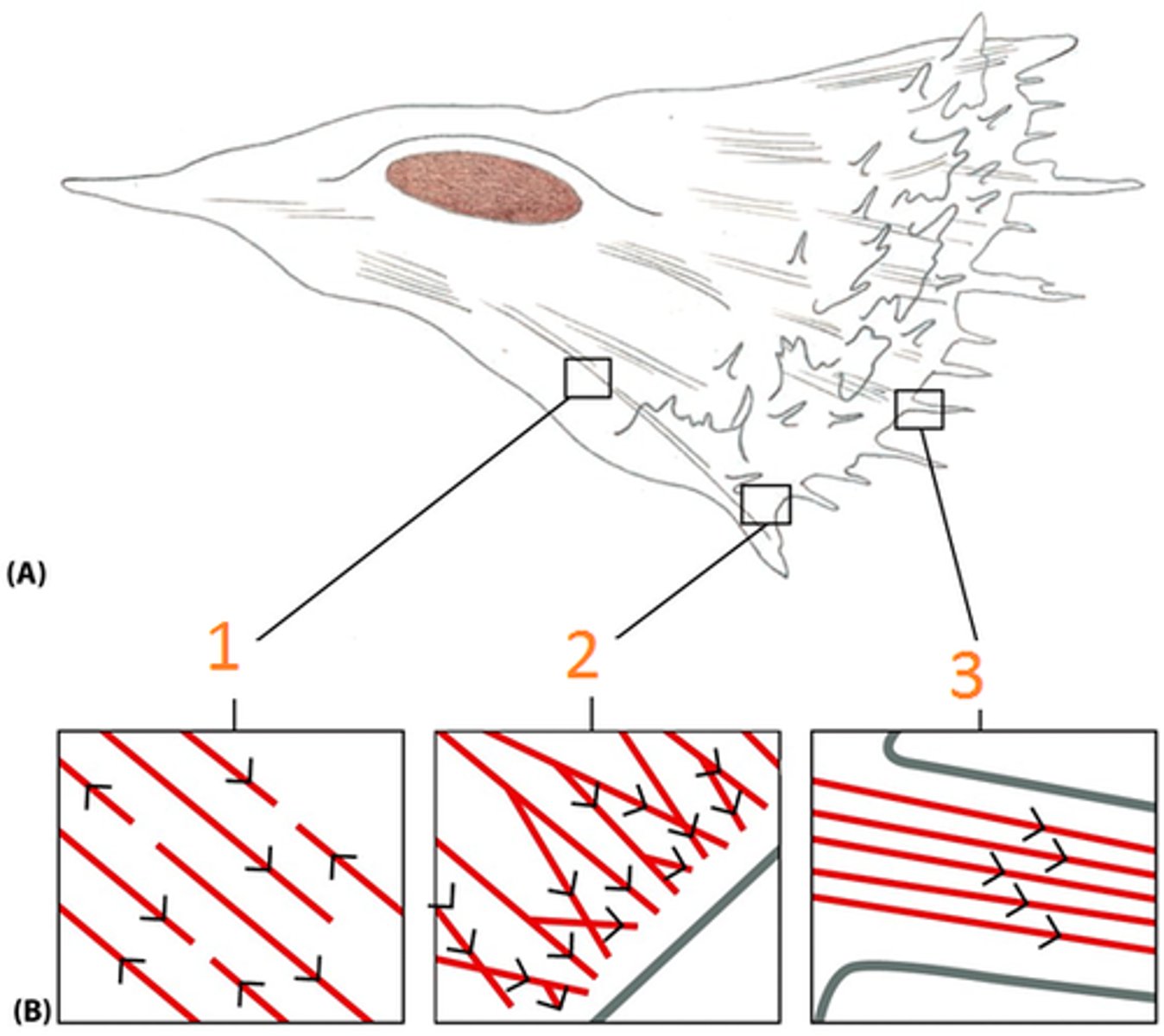
where does actin polymerization occur in a migrating cell?
occurs at the plus end
where does unpolymerized actin go during cell migration?
moves towards the lamellipodium
an epithelial cell has __________ polarity
(constant/changing)
constant polarity
what determines the leading and lagging edge of a motile cell?
cell signaling reacts to the environment, which polarizes the cell
a motile cell has __________ polarity
(constant/changing)
changing polarity
how is the lamellipodium pushed forward?
a pool of actin monomers in the cytoplasm react to cell signaling, then the actin outgrowth pushes the membrane forward/out along the cell's leading edge
myosin
motor protein present in muscle fibers that aids in contraction
conventional myosin (type II)
motor protein; head domain binds to actin and it hydrolyzes ATP to move in its power stroke
unconventional myosin
motor protein that walks along an actin filament carrying cargo
actinmyosin
contracted form of actin and myosin
where do the myosin heads bind during contraction?
bind to actin
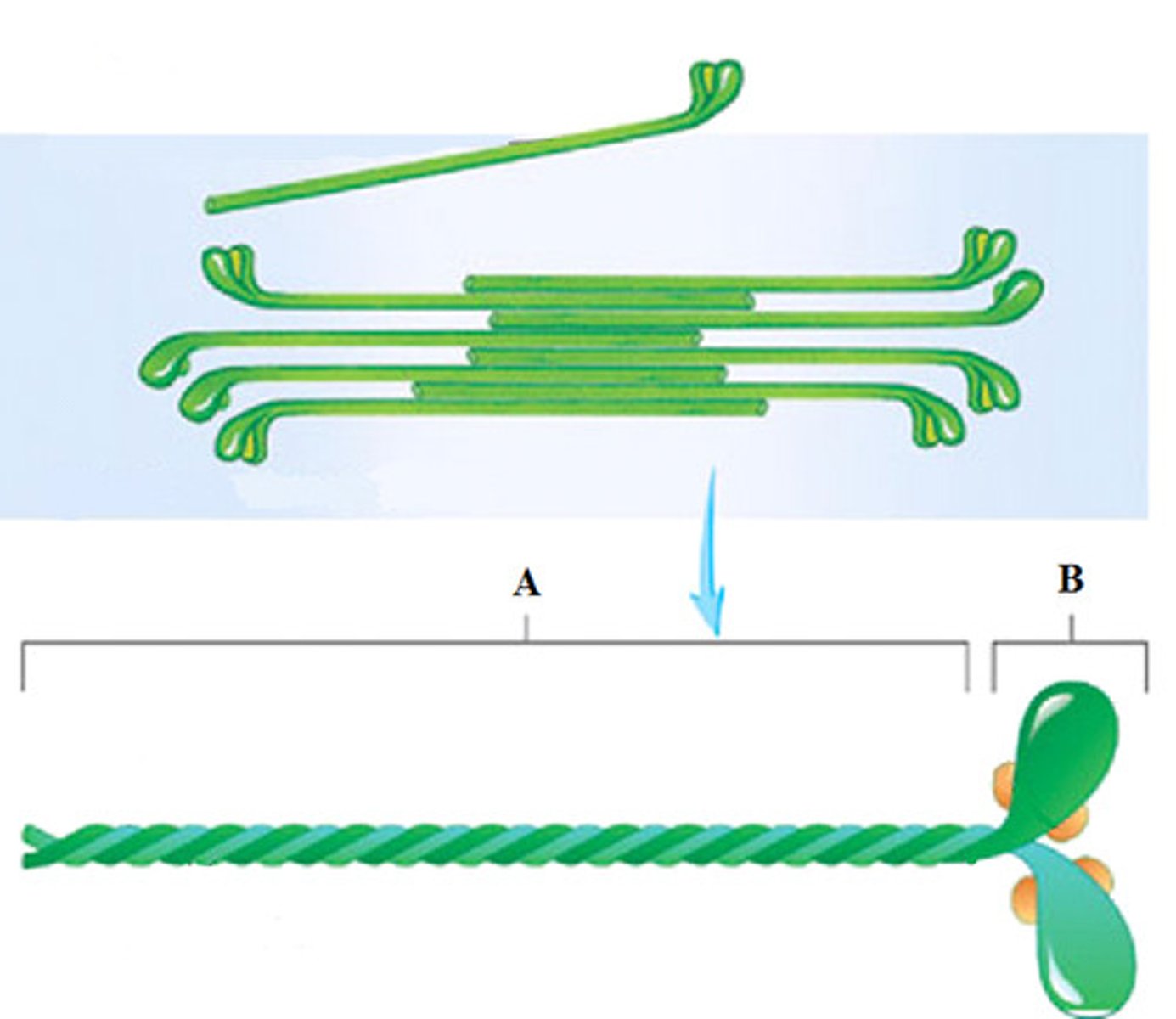
draw and label the following:
• a bundle of myosins
label A: myosin globular head and alpha-helical neck
label B: myosin tail domain
name the parts of myosin