4.1. APPENDICULAR SKELETON
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
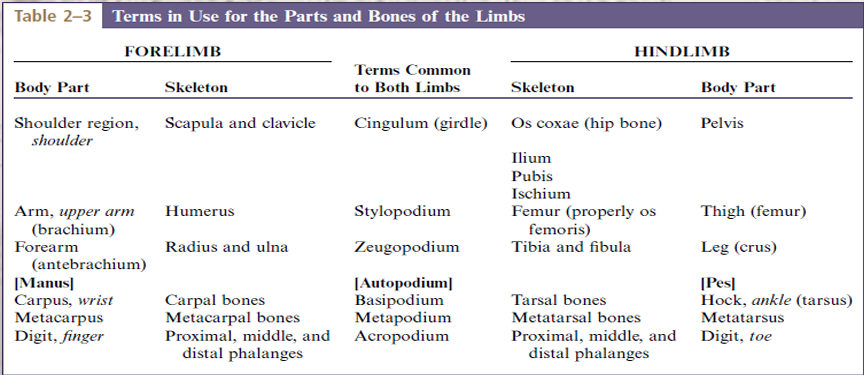
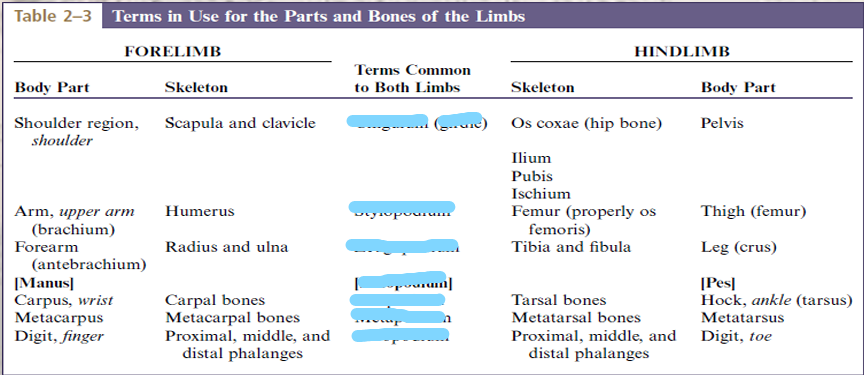
Thoracic Limb and Pelvic Limb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Thoracic girdle (clavicle and scapula)
Arm/brachium (humerus)
Forearm/antebrachium (radius and ulna)
Forepaw/manus ( carpal bones, metacarpal bones, phalanges)
bones of the thoracic limb is composed of?
Pelvic girdle (Ilium, Ischium, Pubis)
Thigh (Femur, Patella)
Leg or Crus (Tibia and Fibula)
Hindpaw or Pes ( Tarsal bones, Metatarsal bones, Phalanges)
bones of the pelvic limb is composed of?
clavicle
Small, oval-plate located cranial to the shoulder within the clavicular tendon in the brachiocephalicus muscle
This is frequently absent in canines
This is described as a “vestigial bone”
It is present in felines, but it does not articulate with other bones
Scapula
Large, flat, triangular bone seen at the lateral surface of the trunk at the junction between the neck and ribs
It possess two surfaces, three border, and three angles
Also known as “shoulder blade”
Paired bone which makes up the shoulder girdle
Spine
Supraspinous fossa
Infraspinous fossa
Acromion
Subscapular fossa
Serrated face
Glenoid cavity
Supraglenoid tubercle
Infraglenoid tubercle
Coracoid process
Scapular notch
Enumerate the parts of the scapula (11)
Spine
is a prominent ridge running down the middle of its lateral surface.
area cranial to the spine for the attachment of the supraspinatus muscle
Supraspinous fossa
area caudal to the spine for the attachment of infraspinatus muscle
Infraspinous fossa
expanded distal end of the scapular spine.
Acromion
located on the medial side of the scapula for the attachment of the subscapularis muscle
Subscapular fossa
a small proximal and rectangular area in which serratus ventralis muscle is attached.
Serrated face
a shallow articular socket which forms the shoulder joint with the head of the humerus.
Glenoid cavity
is a process near the cranial aspect of the glenoid cavity for the attachment of the biceps brachii muscle.
Supraglenoid tubercle
caudal border in which the teres minor and long head of the triceps arises
Infraglenoid tubercle
is a small process on the medial side of the supraglenoid tubercle for the attachment of the coracobrachialis muscle
Coracoid process
forms the distinct neck of the scapula; this is where suprascapular nerve lies.
Scapular notch
Humerus
Largest bone of the thoracic limb.
It articulates proximally with scapula forming the shoulder joint
It articulates distally with the radius and ulna forming the elbow joint
Humeral head
Greater tubercle
Lesser tubercle
Bicipital groove/intertubercular groove
Body/shaft
Deltoid tuberosity
Lateral epicondyle
Medial epicondyle
Enumerate the parts of the humerus (8)
Humeral head
round process at the medial side of the bone articulating with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Greater tubercle
lateral/major tubercle
is a large process craniolateral to the head of humerus.
Lesser tubercle
medial/minor tubercle
process at the medial side of humeral head.
Bicipital groove/intertubercular groove
is a sulcus between the greater and lesser tubercle through which the tendons of the biceps brachii runs
Body/shaft
connects the two extremities or epiphysis of the humerus.
Deltoid tuberosity
large tuberosity at the lateral side of the humerus
Lateral epicondyle
lateral side of the condyle giving rise to the extensors muscle of the forearm
Medial epicondyle
medial side of condyle giving rise to the flexors muscle of the forearm.
Radial Nerve Paralysis
this occurs because the animal is unable to use the extensor muscles to bring the limb into its normal position.
the damaged nerve may recover but if it has been severed the only treatment may be to amputate the forelimb
Radial Nerve Paralysis
a condition where an animals forelimb will knuckle over on its forepaw, leading to excessive wear of the skin on the dorsal surface of the paw; the ventral surface is protected from normal wear by the pads.
Musculo-spiral groove
it refers to when the shaft of the humerus has a slight twist on it
If the humerus is broken, the resulting fracture is often in the form of a spiral and may affect the radial nerve that runs within the spiral, causing temporary or permanent radial nerve paralysis.
this is indicated by the animal knuckling over on its lower forelimb
Radius
shorter and more massive and it is located medially.
Ulna
longer and slender compared to radius and is located laterally.
is located on the caudal part of the forearm
Head
Body
Medial styloid process
Fovea capitis
Radial tuberosity
Trochlea
Ulnar notch
Styloid process
Groove for abductor digiti I longus
Groove for extensor carpi radialis
Groove for common digital extensor
Enumerate the parts of the radius (11)
Head
proximal end of the radius
Body
also called shaft of the radius
Medial styloid process
pointed projection on the distal end of radius.
Fovea capitis
oval, depressed articular surface, which articulates with humerus
Radial tuberosity
lies distal to the neck on the medial border of the bone of the radius.
Trochlea
distal extremity of the radius.
Ulnar notch
slight concave area with facet for the articulation with ulna
Styloid process
rounded projection in the distal end of ulna on the medial border.
Groove for abductor digitiI longus
small, short, and oblique; the most medial groove of the radius
Groove for extensor carpi radialis
middle and longest groove of the radius
Groove for common digital extensor
the most lateral groove of the radius, wide, and with variable distinctness
Olecranon process
Trochlear notch/semilunar notch
Anconeal process
Ulnar tuberosity
Medial and lateral coronoid process
Lateral styloid process
Medial styloid process
Interosseous space
Enumerate the parts of the ulna (8)
Olecranon process
proximal end of the ulna; acts as a lever for the attachment of the extensor muscles of the forearm.
This is the point of the elbow
Trochlear notch/semilunar notch
depression for the articulation with the humerus and ending in the anconeal process
Anconeal process
proximal end of the trochlear notch which fits in the olecranon fossa of the humerus when the elbow is extended.
Ulnar tuberosity
elongated eminence of the ulna on the medial surface of the bone at its proximal end.
Medial and Lateral coronoid process
are the larger distal end of the trochlear notch
Medial is larger than the lateral
In Medial and Lateral coronoid process, which is larger?
Lateral styloid process
where ulna narrows to a point distally.
Medial styloid process
pointed projection at the distal end of radius
Interosseous space
border between the radius and ulna
Elbow Dysplasia
is a common condition of the heavier breeds of dog (e.g., Newfoundland, St Bernard, Rottweiler, Basset Hound).
It encompasses a number of developmental conditions, such as an ununited anconeal process and detached olecranon process, which result in instability of the elbow joint, leading to osteoarthritis.
Elbow dysplasia
abnormal development of the elbow
Fragmented or Ununited Medial Coronoid Process (FMCP/ UMCP)
Osteochondrosis Dissecans (OD)
Ununited Anconeal Process (UAP)
what are the primary lesions of elbow dysplasia in canine
CARPALS/CARPUS
Composed of seven short bones and are arranged into two rows( proximal row and distal row)
proximal row
distal row
two rows of the carpus
radial carpal bone
intermediate carpal bone
ulnar carpal bone
accessory carpal bone
bones of the proximal row of the carpus
radial carpal bone and intermediate carpal bone
Intermedioradial carpal bone
which bones of the proximal row of the canine and feline carpus are fused? What is it called?
Radial carpal bone
most medial, articulates proximally with the radius
Intermediate carpal bone
also known as lunate bone
Intermedioradial carpal bone
located on the medial side and articulates proximally with the radius;
1st carpal bone
2nd carpal bone
3rd carpal bone
4th carpal bone
bones of the distal row of the carpus