Saving & Investing Test
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Soltau - Saving & Investing, 5 Steps to Investing, The development of money
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Investing
redirecting resources from being consumed today so that they may create benefits in the future
Financial System
system that allows the transfer of money between savers and investors

Financial Asset
claim on the property or income of a borrower (ex: contract)
Financial Intermediary
institution that helps channel funds from savers to borrowers
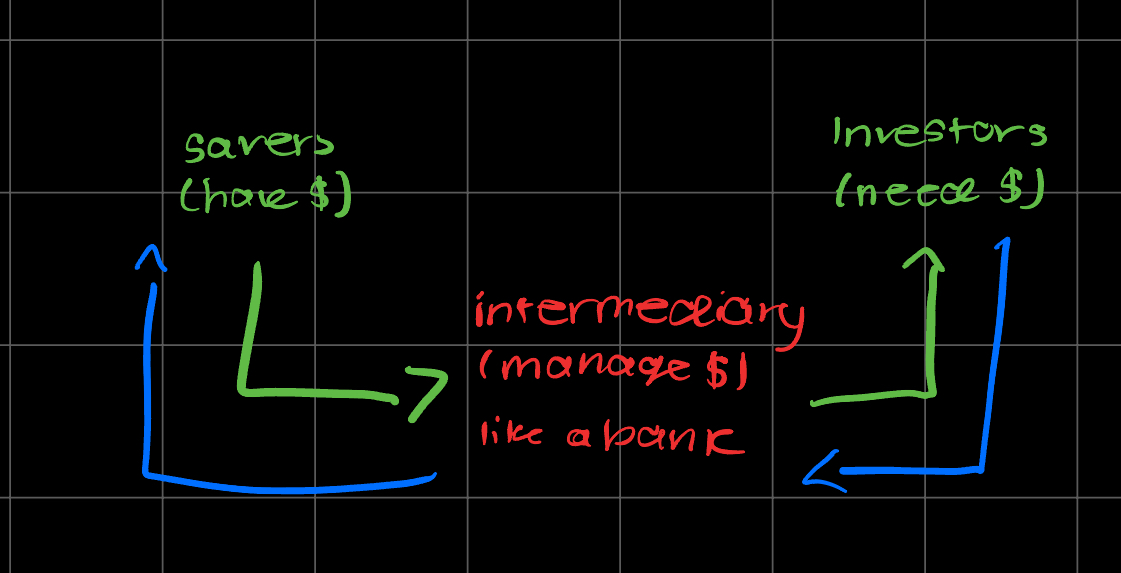
Types of Intermediaries
Banks, savings and loan associations, credit unions
Finance companies & mutual funds (lend $ to people who do not repay their loans)
Life Insurance policy
pension funds
Risks involved with investing
Credit risk
liquidity risk
inflation rate risk
time risk
Credit risk
borrowers do not pay back loan or are late
Liquidity Risk
cannot convert investment back into cash quickly enough for your needs (selling an ipad)
Inflation rate risk
inflation erodes value of your assets
time risk
have to pass up on opportunities now for investments in the future
Step one of investing
Put and take account (checking, keep 3-6 months of pay in here for bills and emergencies)
Step two of investing
Beginning to invest
low risk investments (savings bonds and mutual funds)
Step three of investing
systemic investing
companies that have been around for a long time
Step four of investing
strategic investing
diversification of stocks to reduce risk
step five of investing
speculative investing
high risk, high reward (owning company)
national bank
issued currency backed by federal bonds
gold standard
1900- money worth a particular amount of gold
Pros of gold standard
-ppl feel secure about currency
-gov’t doesn’t create too much money
-money keeps its value
Cons of gold standard
-dependent on gold being valuable and available
-if people convert their $ into gold, gold could go away