CH 23 Systematics, Phylogenies & Comparative Biology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Systematics
Study of evolutionary relationships among organisms.
All organisms have
Composed of one or more cells
Carry out metabolism
Transfer energy with ATP
Encode hereditary info. In DNA & RNA
Respond to stimuli
(not virus)
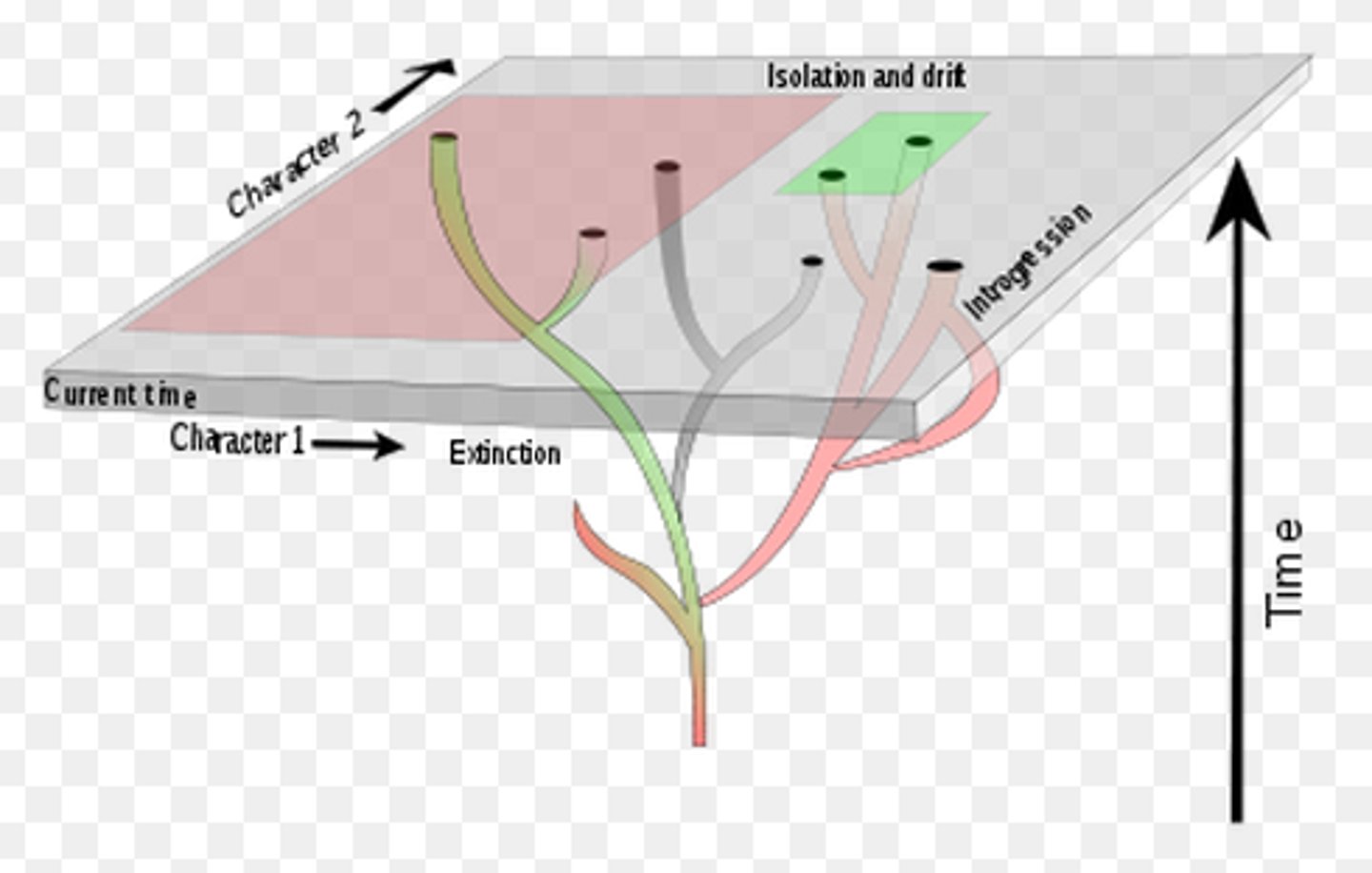
Phylogeny
hypothesis about patterns of relationship among species
Ancestral Characteristic
similarity that is inherited from the most recent common ancestor of an entire group
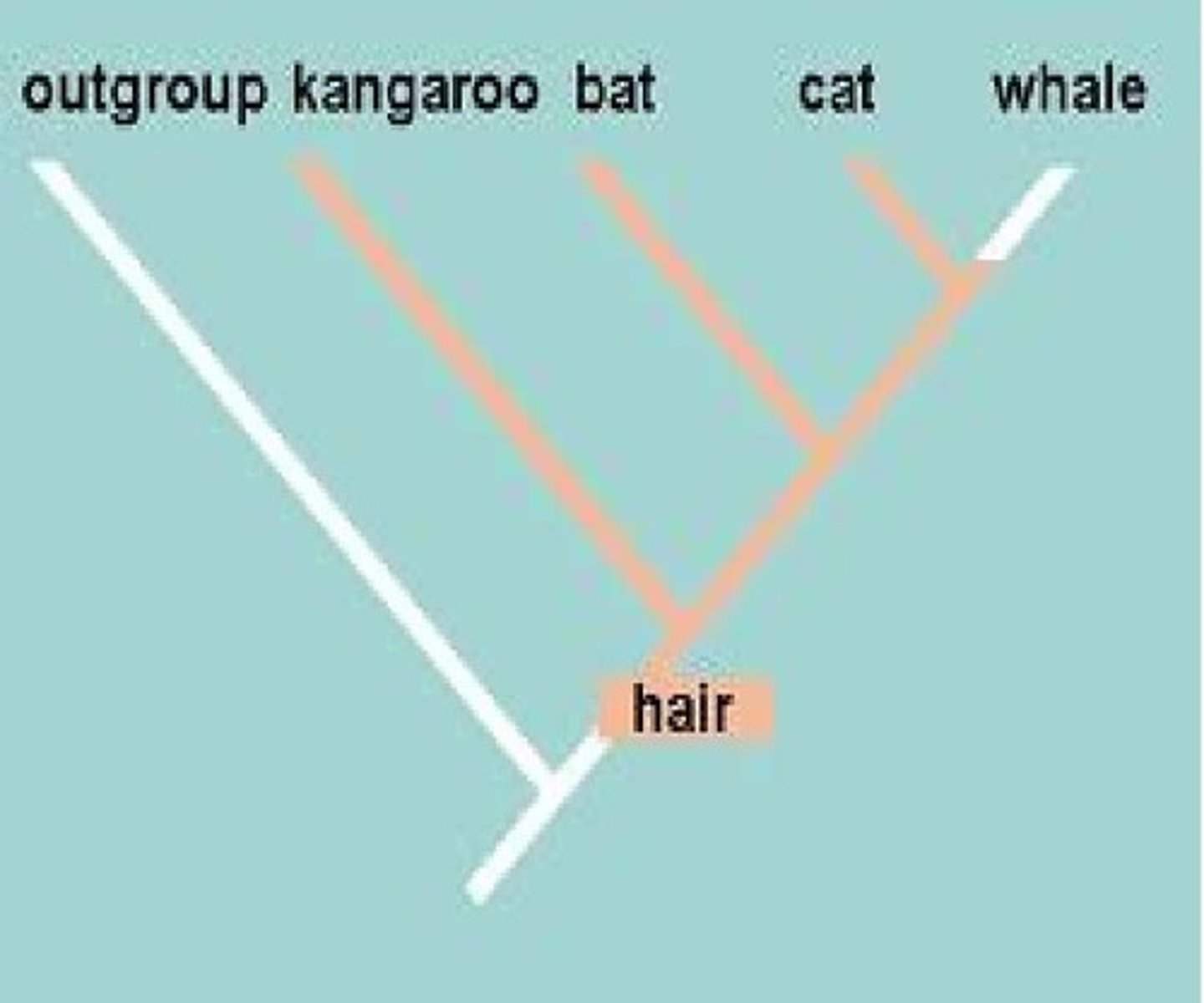
Derived Characteristic
similarity that arose more recently & is shared only by a subset of the species
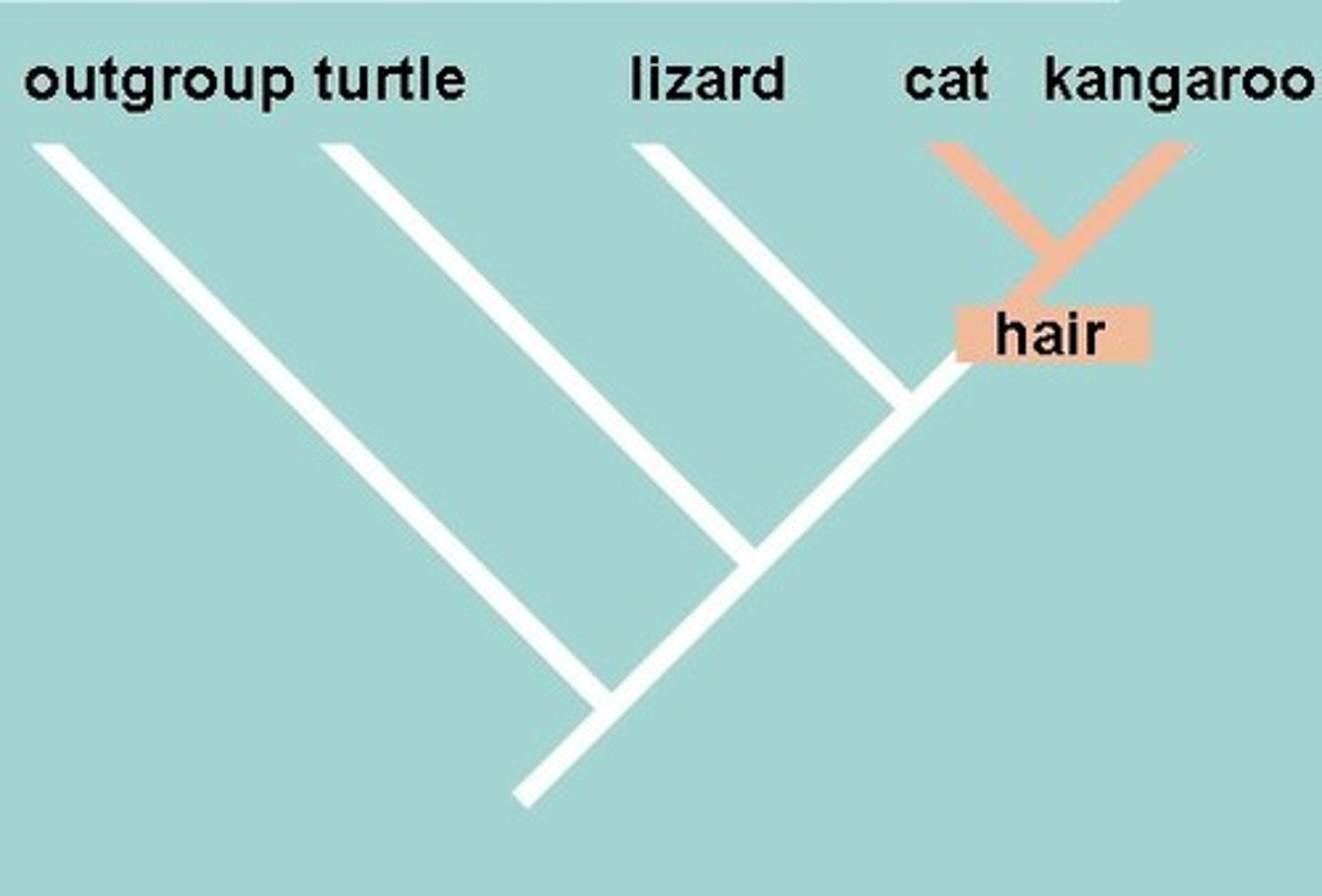
Cladistic Method
only derived characters are considered informative about evolutionary relationships
used for cladistic analysis
Character States
Recognizable forms of traits in organisms. ("tail" in vertebrates has two states, present in most & absent in humans, apes & some other groups such as frogs)
Morphology, Physiology, Behavior, or DNA
(very binary, does it have it or not)
Cladistic Analysis
Polarize characters (are they ancestral or derived)
Outgroup comparison (related but not member of group studies, may exhibit ancestral character)
When group states & one other traits is exhibited by outgroup, then state is ancestral & others are derived
Morphology
Study of organism structure and form.

Physiology
Study of organism functions and processes.
Outgroup
Species closely related but not part of study group. (is outed when b/c it does not share the derived characteristics of the rest)
Clade
species that share common ancestor as indicted by possession of shared derived characters
Clade is evolutionary unit & refers to common ancestor & all descendants
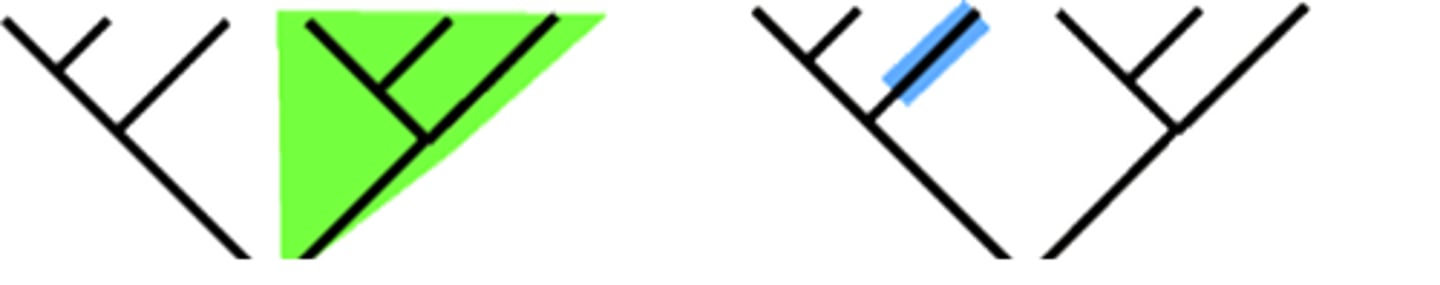
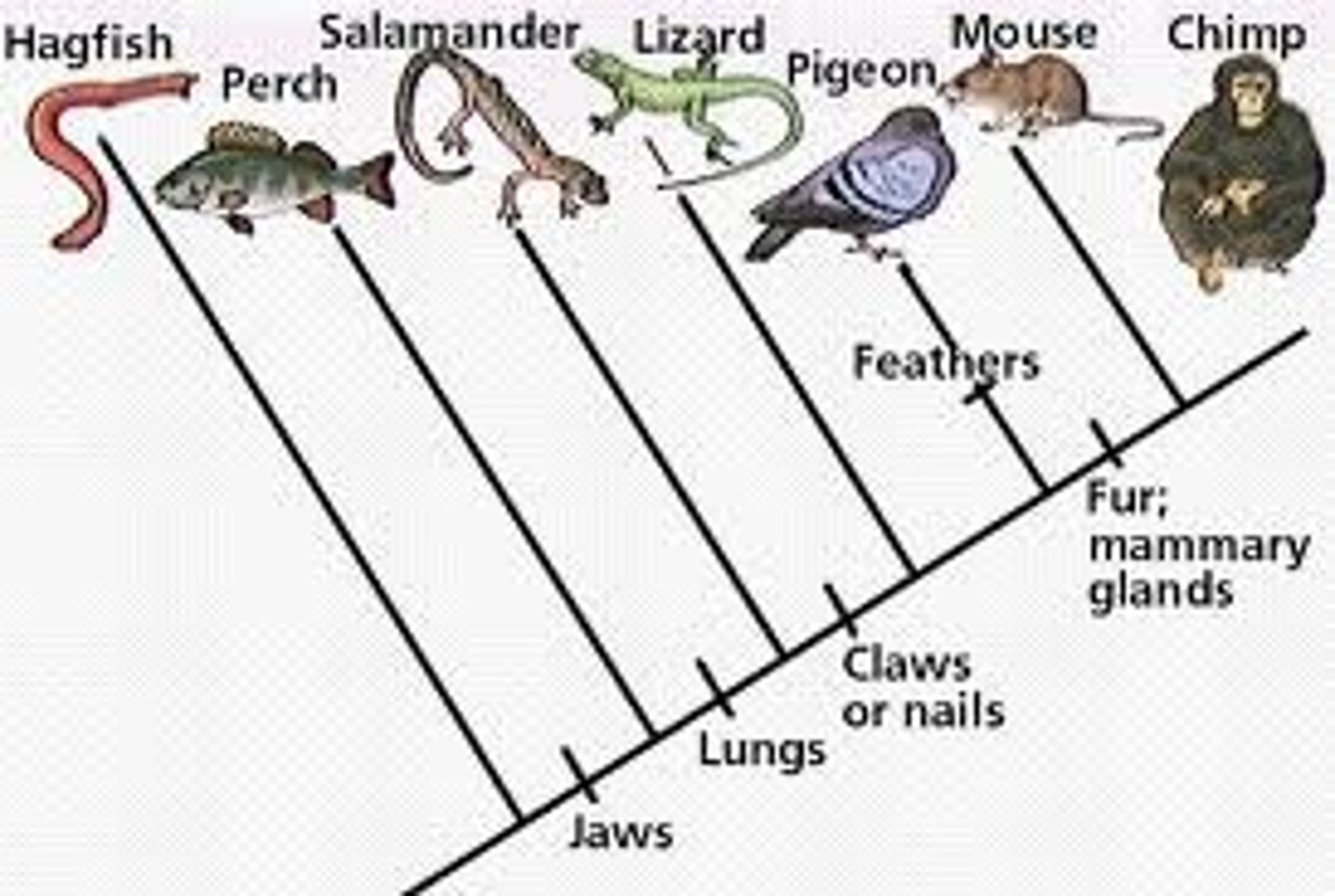
Cladogram
Diagram showing hypothesized evolutionary relationships based on characters.
Synapomorphy
Derived character shared by members of a clade. (similar morphy)
Pleiomorphism
Ancestral states of characters in evolution. (more/previous morphism)
Symplesiomorphy
Shared ancestral traits among different species. (shared morphy)
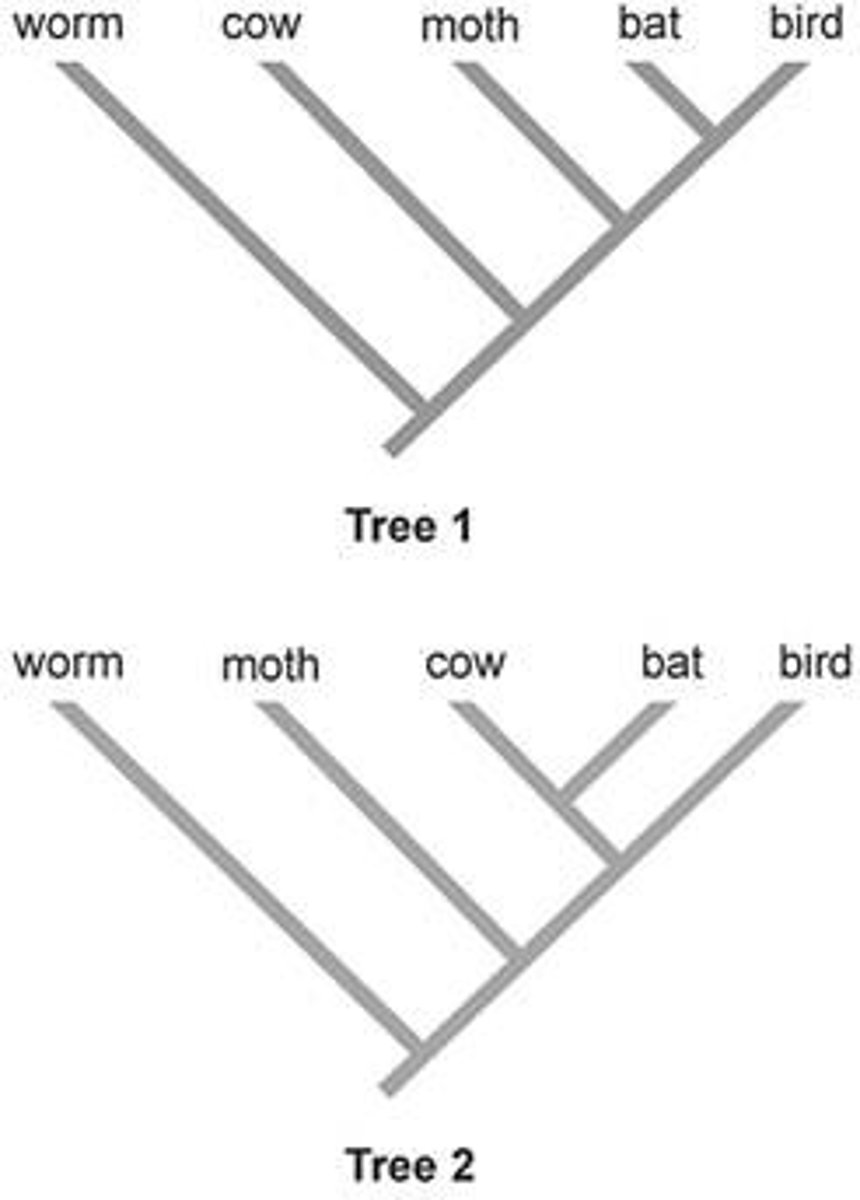
Parsimony Principle (KISS)
Favoring cladograms with fewest evolutionary changes.
Molecular Clock Approach
Rate of evolution of a molecule is constant through time
Divergence in DNA can be used to calculate the times at which branching events have occurred
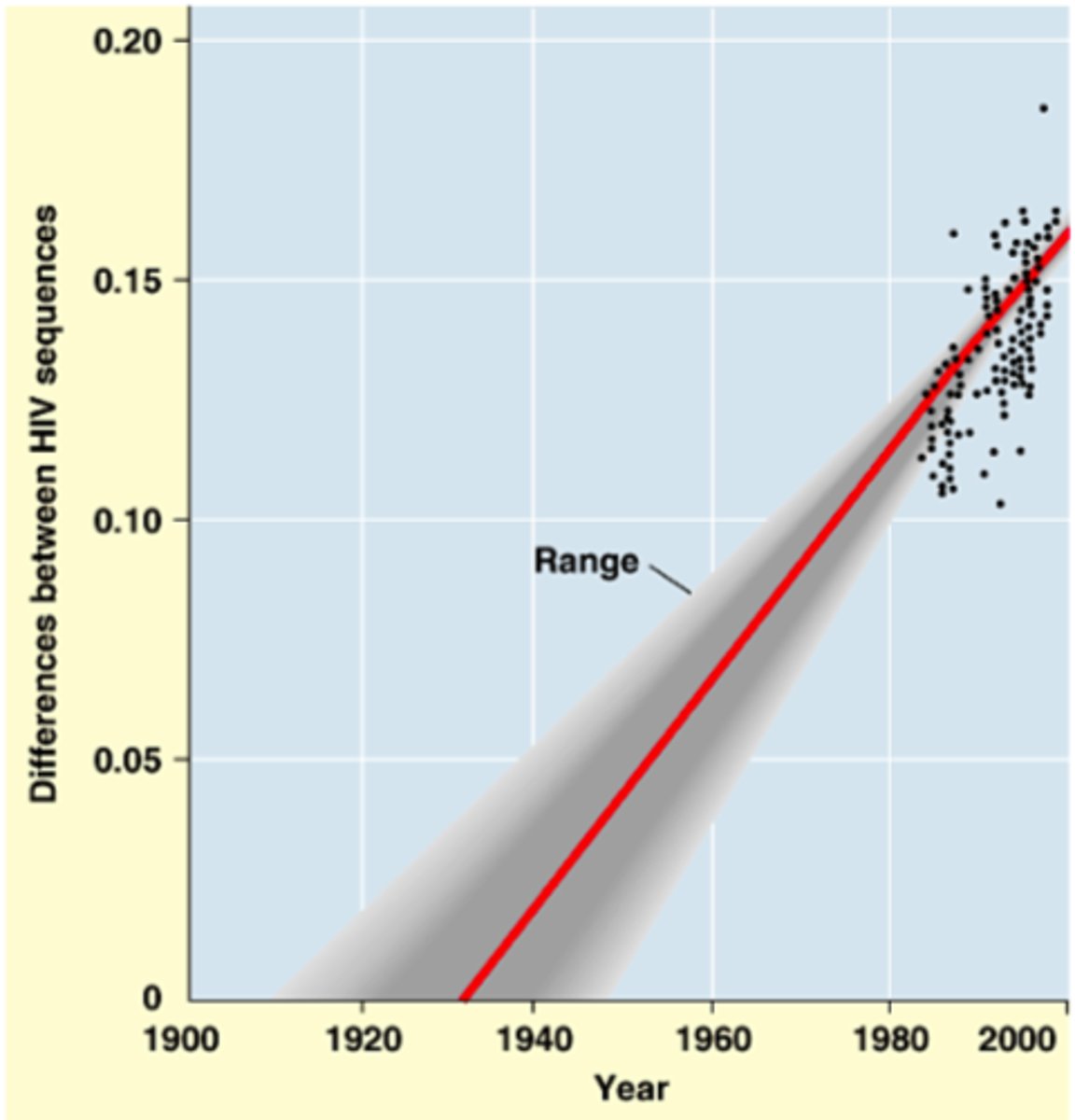
DNA Sequencing in Cladograms
Systematists increasingly use DNA sequence data to construct phylogenies b/c of the large number of characters that can be obtained through sequencing
Character states are polarized by reference to sequence of an outgroup
Cladogram is constructed that minimizes amount of character evolution required
Cons/Controversy of Phylogenetic Methods
rapid evolution + parsimony principle may be misleading (doesn’t show time)
Stretches of non-functional DNA have higher rates of evolution b/c of zero selection
Only ATCG so probability two species will independently evolve same derived character state is high
b/c of convergent evolution cladistic method can be misleading (make them seem more related than they are)
could recognize even slightly diff. populations as distinct species
Statistical Approach
Start with an assumption about rate at which characters evolve
Fit the data to these models to derive the phylogeny that best accords (that is max. Likely) w/ these assumptions
Evolutionary Unit
Clade representing a common ancestor and descendants.
Phylogenetic Methods
Cladistic Method (relations ships based on characters)
DNA sequence on Cladograms
Statistical Approach
Molecular Clock
Taxonomy
Science of classifying organisms into groups.
Classification
How we place species & higher groups into the taxonomic hierarchy
Scientific Name
is the same anywhere in the world; no two organisms have the same one
First word is the genus organism belongs to (capitalized)
Second is the species (not capitalized)
Genus & species italicized
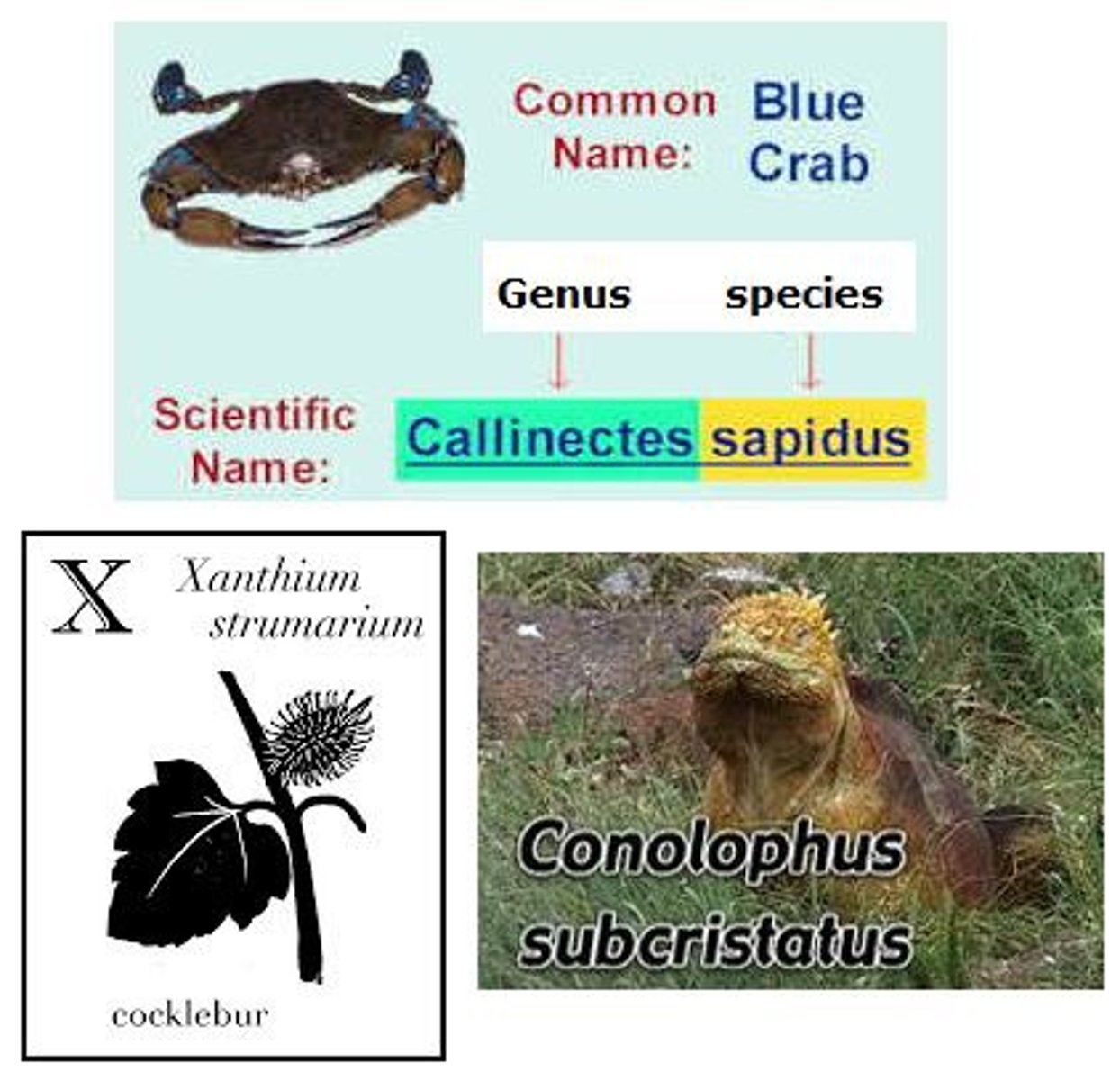
Genus
First part of a scientific name, capitalized.
Species
Second part of a scientific name, lowercase.
Classification Order
Dear King Philip Came Over For Great Spaghetti
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
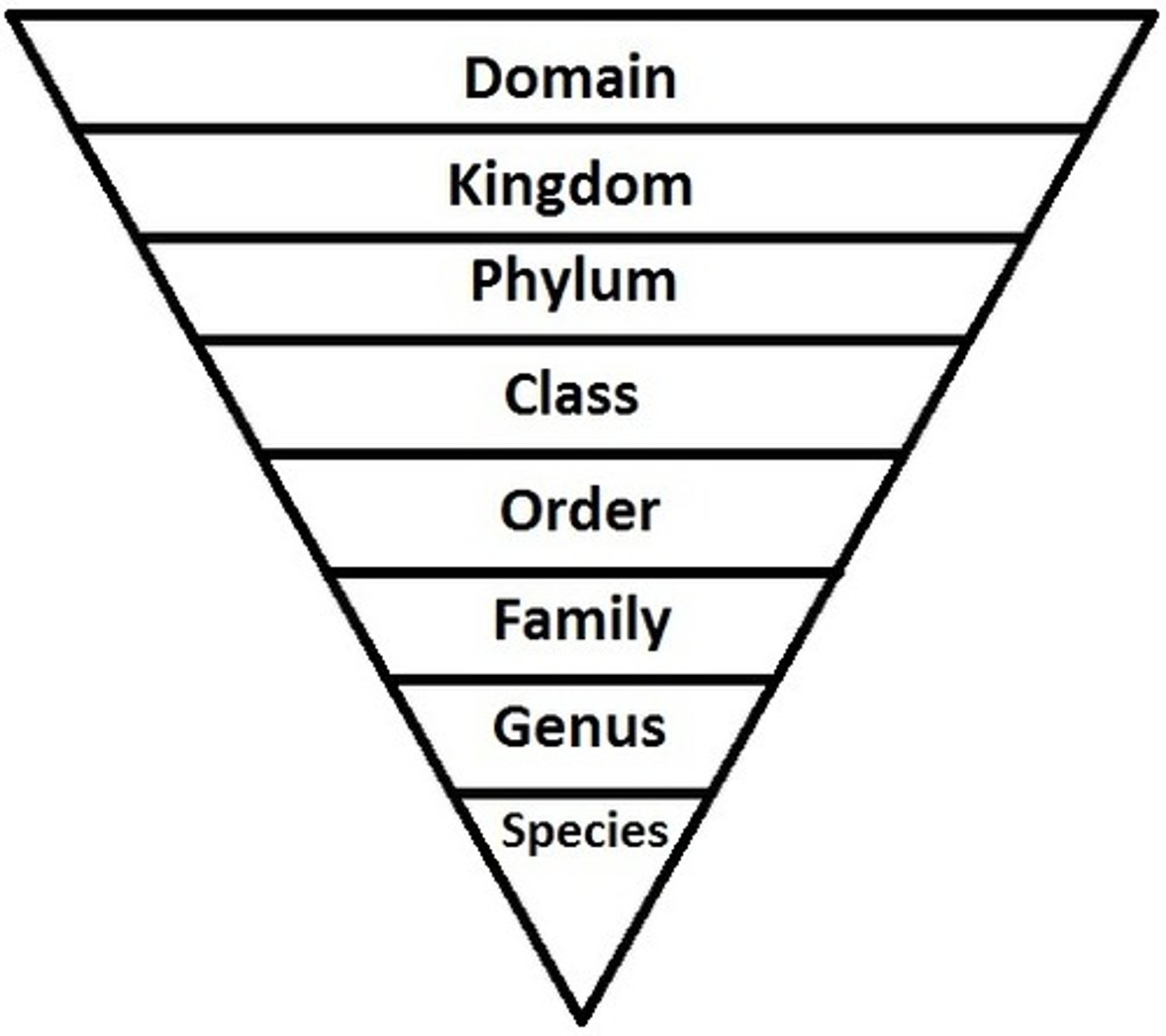
Domain
Divides cellular life into three domains
(Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya)
Kingdom
Groups similar organisms into 6
(Plantae, Animalia, fungi, Protista, eubacteria, archbacteria)
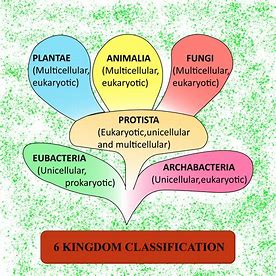
Phylum
Groups organisms based on major body plans.
Class
Further division within a phylum.
Order
Groups families sharing common characteristics.
Family
Groups related genera sharing traits.
Monophyletic Group
Includes most common ancestor and all its descendants. (clade)
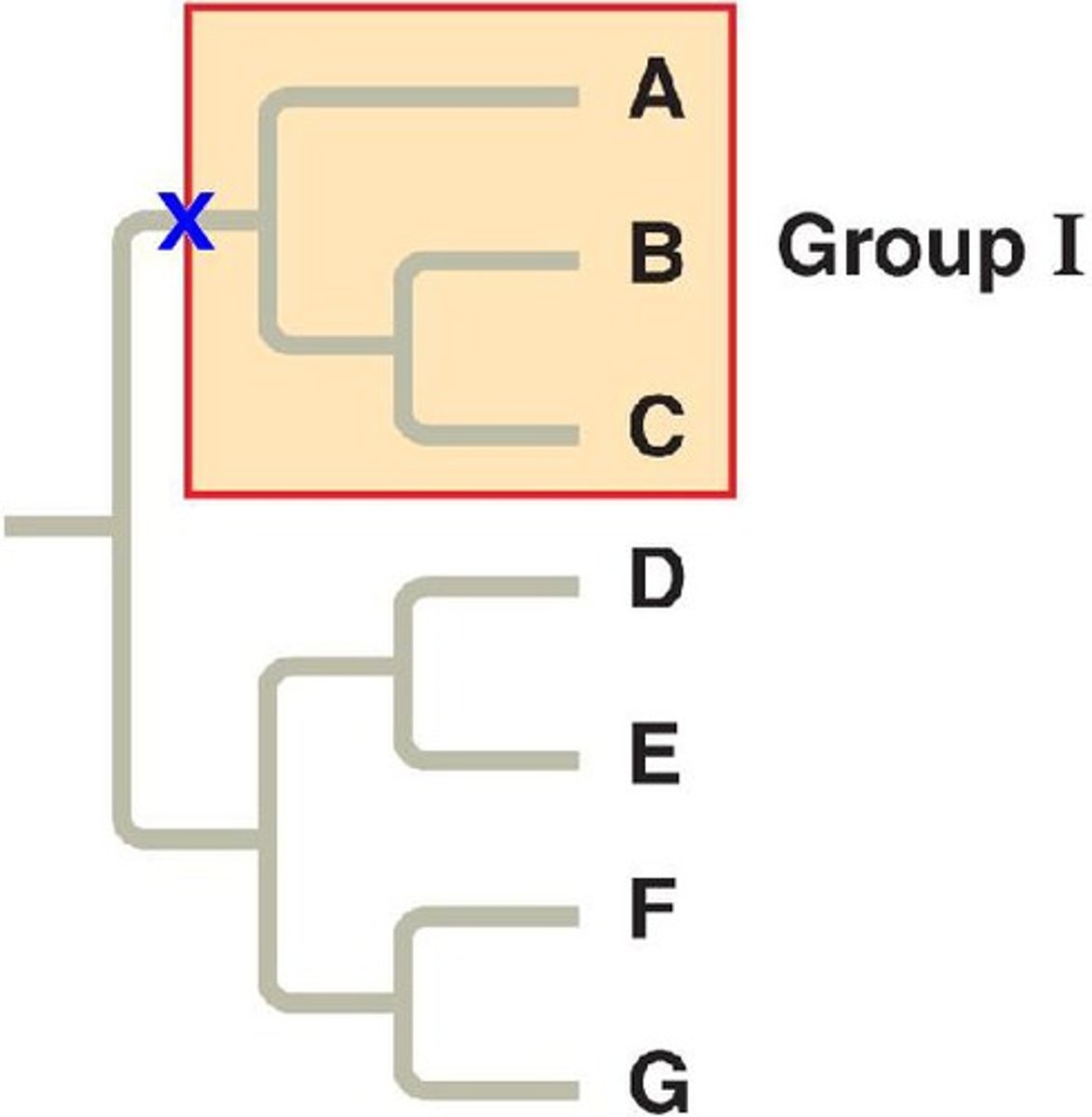
Paraphyletic Group
Includes most common ancestor but not all descendants.
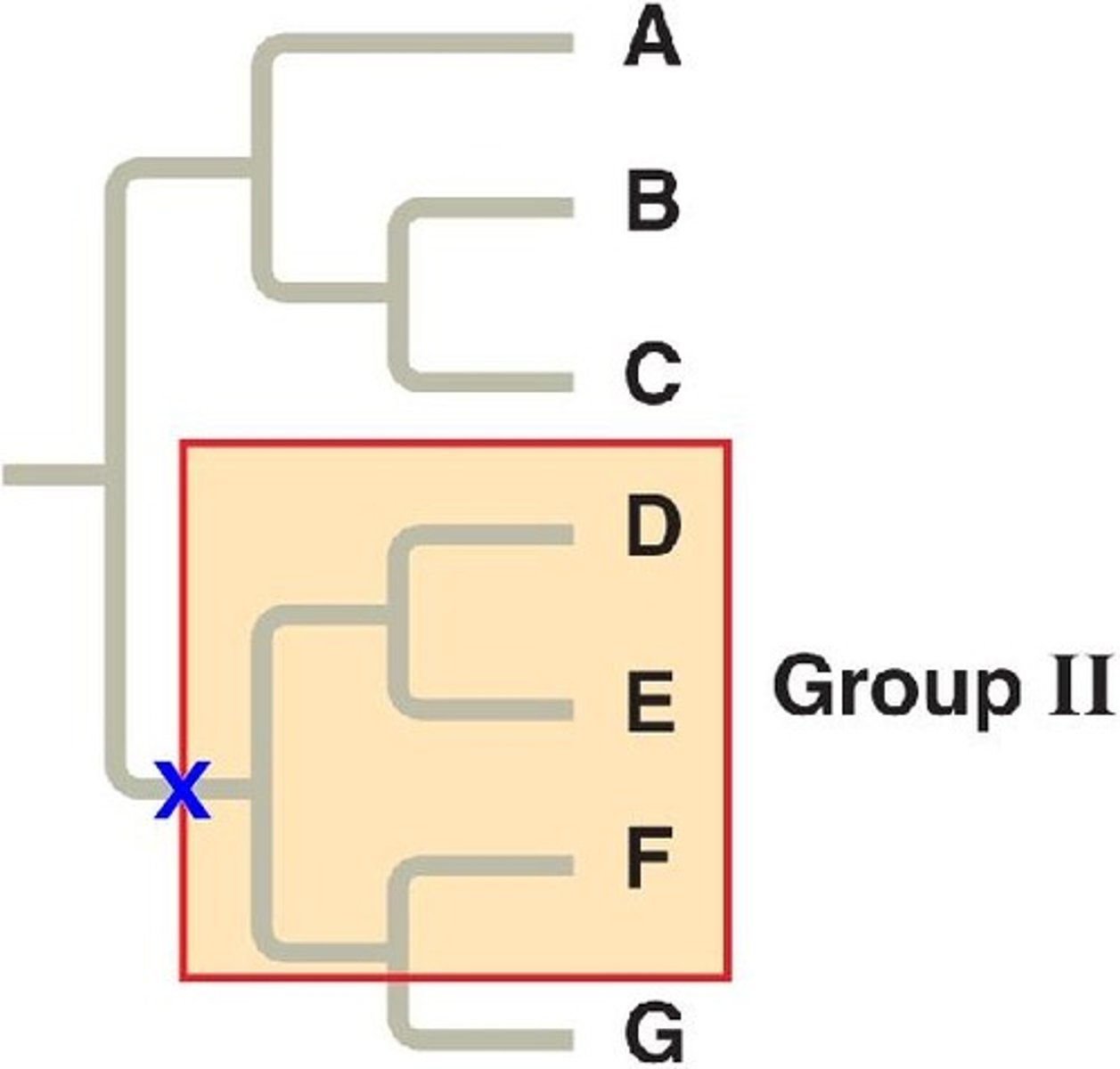
Polyphyletic Group
Does not include the most recent common ancestor.
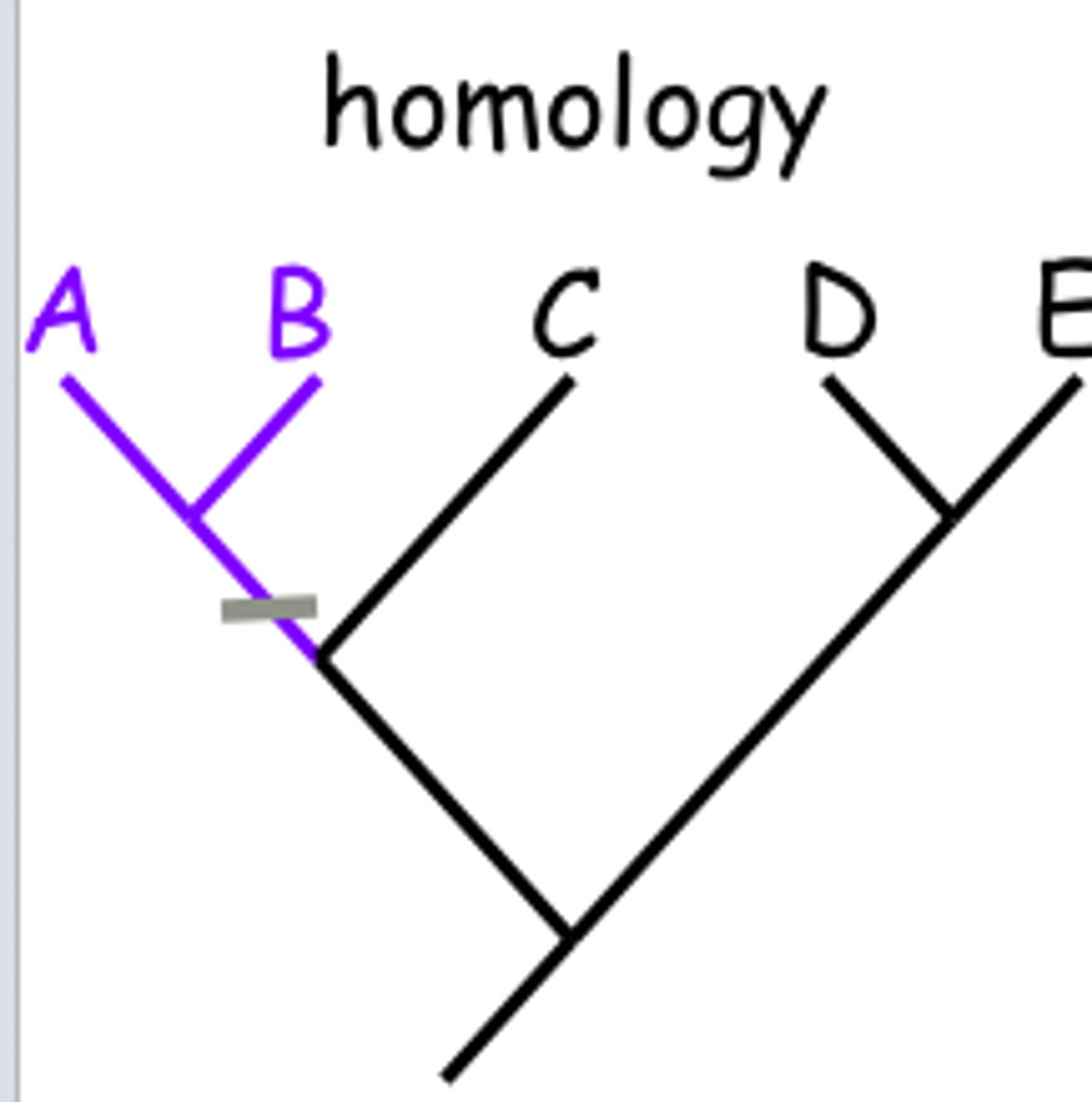
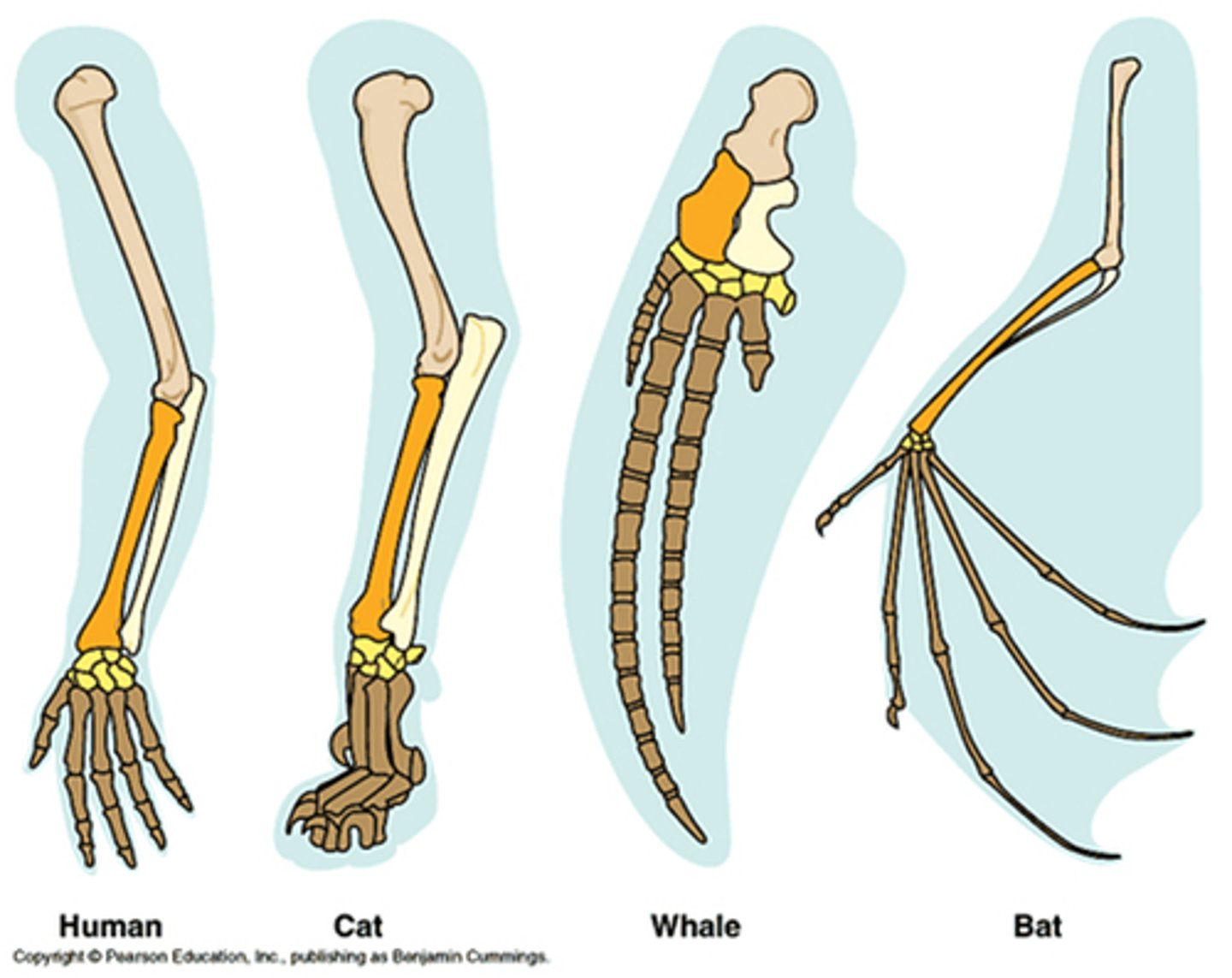
Homologous Structures? AKA what?
Similar structures derived from a common ancestor. (Non- homoplastic)
includes similiar behaivor (parental care)
Analogous Structures? AKA what?
Similar functions but different evolutionary origins. (homoplastic = similar, repair/function)
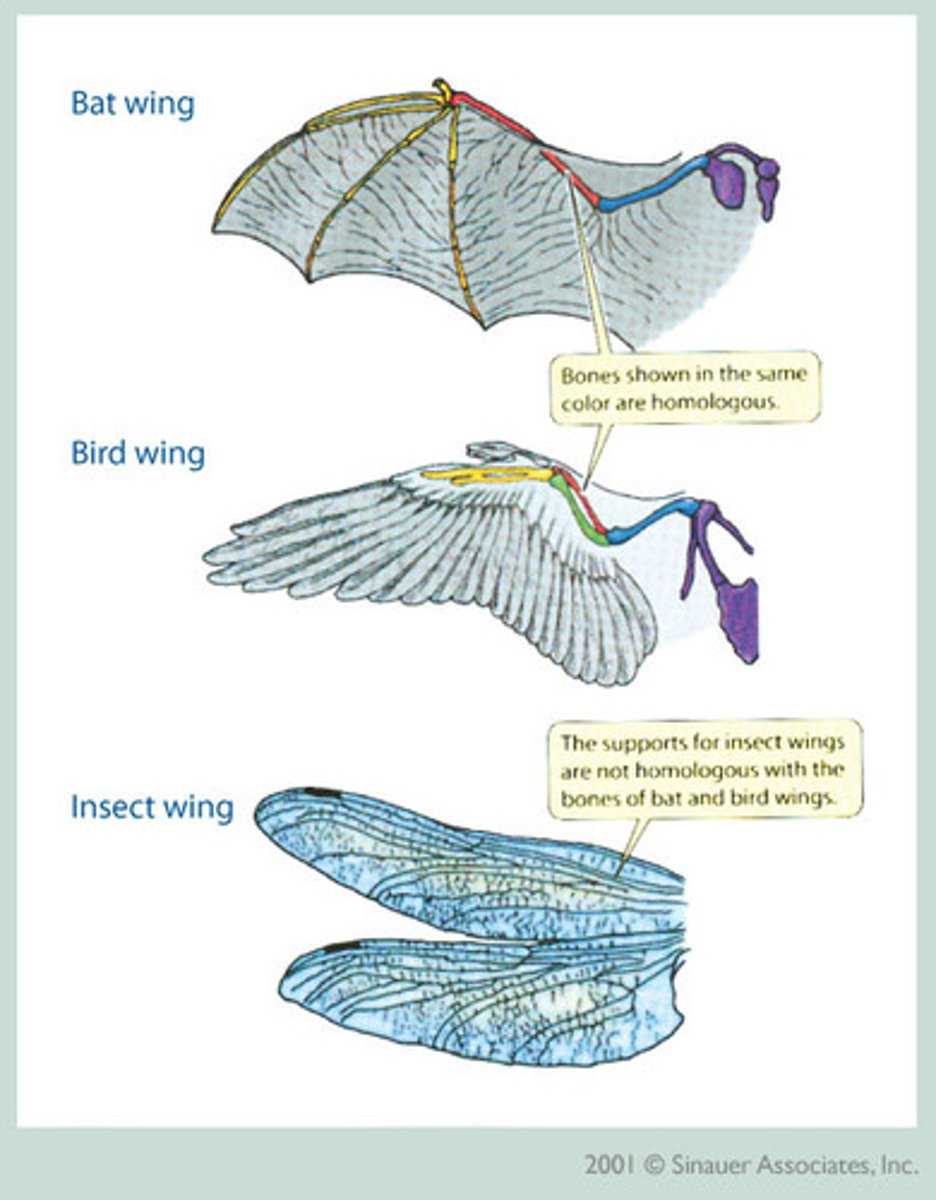
Homoplastic Convergence
Similar traits evolved independently in different lineages. (clades)
Comparative Biology
Most complex characters do not evolve in one step
Evolve through a sequence of evolutionary changes
Ex. Modern-day birds are exquisite flying machines (wings, feathers, light bones, breastbone
Competing Hypothesis
Phylogenetic methods distinguish between different evolutionary theories.
Phylogenetic Species Concept
species is a population or set of populations characterized by one or more shared derived characteristics (useful for situations that don’t fit other species concept)
What conclusions were drop after testing larval dispersal of snails?
Evolutionary increase in no dispersing larvae through time may be a result of both bias in evolutionary direction & increase in rate of diversification
Selection increased a trait, lack of evolutionary reversal is not surprising (one-way street)

How does phylogenetics help explain species diversification?
can give insight on correspondence b/w phylogenetic position & timing of origins
Gives time and how species started diverging and where they went
Beetle diversification
different beetles have a specific diet
highest diverse species

Disease evolution
Study of evolutionary changes in pathogens over time.
Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV
Descended from SIV
Diff. strains exist and evolve so rapidly they are closer to SIV than each other
infected often contain a mix of strains so you can track were they got it from
Humans have acquired HIV from different host species
Phylogenetic Analysis of SIV
found in multiple primates
humans are immune, suggests adaptation
Community v. Independent Transmission
community indirect spread of infection in a population, or from traveling to a place affected by a pandemic (greater event of an event occurring)
separate occurrences of a pathogen being passed from infected to individual (does not affect probability of reassurance)
Phylogenetic Analysis of Covid
showed closely related virus lineages from bats
fist emerged in a market in Wuhan China, were bats weren’t present, possible intermediate species host
Virus
Aren’t alive (lack cells, metabolism, ATP, hereditary) but respond to some stimuli and have DNA or RNA (not both)
are able to mutate and evolve