Coastal systems and landscapes
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Dorset coast landforms and geology
Major landforms: Arch, cove, wave-cut platform, headland, beach, bays, stacks, sand dunes, spit, offshore bars
Geology: chalk, weaden clays and greensand, purbeck limestone, Portland limestone
Holderness coast - benefits and costs of management strategies
East coast of Yorkshire, hard engineering strategies including sea wall, groynes, revetments and rip rap to protect the quickly eroding clay cliffs
Benefits- protects high value land
Costs- upset locals on intrusive defences, seen as unsustainable, expensive
Formby point management strategies
Sefton coast north of Liverpool, soft engineering strategies including planting used Christmas trees, fencing off dunes, banning off road vehicles and educating local children about protection and conservation
The Sundabans location, opportunities, challenges and responses
Located in the south of India and Bangladesh, mangrove forests that are vunrable to flooding with rising sea levels.
Opportunities: provides goods such as fuel, foods, materials and medicines, protects land, cultural value, ecologically diverse
Challenges: human eating tigers, lack of fresh water, poor accessibility, one fifth of homes have electricity, few income opportunities, high risk of natural hazards, over exploited recourses damaging habitats
Responses: NGOs training fishers and farmers on sustainable methods, extending electricity, improving roads and increasing access to clean water, promoting eco tourism to provide income, embalmers build to prevent flooding
coastal zone
a dynamic environment with distinctive landforms formed by interaction of marine, terrestrial and wind processes
examples of mass movement
rockfall
slump
landslides
creep
examples of coastal landforms
erosional:
stack, stump, arch, headland, cave
depositional:
spit, bar, tombolo
examples of coastal erosion
attrition, abrasion, saltation, hydraulic action, corrosion
examples of coastal transportation
traction, solution, suspension, saltation, longshore drift
landform
a distinctive geomorphological feature created by processes of erosion, weathering, mass movement and transportation
landscape
part of the earths surface that can be viewed at one time from one place. distinctive landforms are made up of a series of landforms
backshore
land only effected under storm conditions. cliffs, sand dunes and beaches may be present
foreshore
area lying between the HWM and the LWM. It is the most important zone for marine processes in times that are not influenced by storm activities
inshore
area between LWM and the point where waves cease to have any influence on the land beneath them
offshore
water depths are over half the wave length of the incoming waves. limited sediment movement by waves
swash zone
varies with the tide, water moves up as swash and down as backwash
surf zone
broken waves that travel towards the shore. Sediment movement may be onshore/offshore or along the shore
breaker zone
varies in width depending on the type of wave approaching the shore
wave length
the distance between the two crests of a wave
wave height
distance between the crest and trough of a wave
wave frequency
number of waves per minute
crest
the peak/highest point the wave reaches
trough
the lowest point a wave reaches between 2 waves
fetch
the distance a wave moves due to wind
swash
movement of water upwards a beach
backwash
movement of water down a beach back out to sea
ridges and runnels
Small semi-circular hollows in a beach, formed by a collection of waves reaching the same point. The sides of the U shape channel incoming swash into the center of the depression and this produces stronger backwash; dragging material down the beach from the centre.
cusp
The spreading out of wave energy across a wide area of the beach tends to produce a series of raised areas above the adjacent shore which dips it to depressions.
berm
ridges that develop at the position of the mean HWM resulting from deposition at the top of the swash.
storm beach
at the back of the beach, very strong swash during storm conditions may deposit larger material
coastal plain
a lowland area adjacent to the sea, which may have formed from marine sediments which may have been revealed by a fall in sea level
beach
an accumulation of sediment deposited by waves and longshore drift along the coast
longshore bar
a ridge of sand, gravel or mud built by the seashore by waves and currents, generally parallel to the shore and submerged by high tides
concordant coastline
a coastline with alternating bands of more and less resistant rock PARALLEL to the sea
discordant coastline
a coastline with bands of more and less resistant rock PERPENDICULAR to the sea (at a right angle)
differential erosion
erosion that occurs at different rates due to the type of rock on a coastline
coastal current
permanent or seasonal movement of surface water in the sea
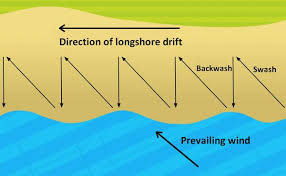
longshore current / littoral drifts
Occurs as most waves do not hit the coastline ‘head on’. The angle generates a flow of water running parallel to the shore, which moves water along the surf zone and transports sediment parallel to the shore.
rip currents
Strong currents moving away from the shore. They develop when sea water piles up along the coast. Initially, current runs parallel to coast before flowing out of breaker zone at a headline where it changes direction - can be hazardous for swimmers or small boats.
upwelling
Movement of cold water from deep in the ocean towards the surface, replacing the warmer surface water creating nutrient rich cold ocean currents - forming patterns of global ocean circluation.
tides
changes in water levels of seas and oceans caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun
spring tide
when sun and moon align, enhancing moons pull, creating larger tides than usual
neep tide
when sun and moon are at right angles, meaning the pull from the sun takes away some from the moon, causing lower than usual high tides
tidal range
difference in height between low and high tide
sediment
natural material that has been broken down through erosion/weathering, can be transported and deposited.
sediment cell
distinct area of coastline and its nearshore area, movement of sediment is usually contained within the cells boundaries (closed system)
sediment budget
balance of sediment entering and exiting a coastal system POSITIVE= surplus sediment NEGATIVE= deficit of sediment
accretion
build up of sediment
geomorphology
study of the shape of the land
longshore drift
process of material being moved along coastline as swash carries sediment on the angle of the prevailing winds and backwash returns at a right angle to the beach
aeolian (wind) deposition
saltation= sediment repeatedly lifted by wind and dropped, causing a bouncing of particles
surface creep= similar to traction - rolling of larger particles along a surface
When does marine deposition occur
water carrying sediment percolates (sand sinks in to surface)
water pauses at the shore during longshore drift
waves slow after breaking
sand and shingle accumulate faster than removed
low energy waves are present
5 types of transportation
solution - dissolved sediment in sea
suspension - very small sediment carried along
saltation - bouncing of particles along seabed
traction - heaviest sediment rolling along
longshore drift - sediment deposited as swash hits coast at an angle and waves retract parallel
5 types of erosion
hydraulic action - sheer force of water against cliff
wave quarrying - air trapped in a crack of cliff causing pressure
abrasion - sediment thrown against cliff in a wave
attrition - sediment hitting each other in a wave
solution/corrosion - calcium rocks being dissolved by slightly alkaline water
how rate of erosion is increased
steeper waves= more energy
breaking point of wave close to cliff
longer fetch
deeper sea level
flat + wide beaches absorb less energy
humans removing sediment - alternatively building coastal defences lowers erosion
biological weathering
animals burrowing in cliffs, plant roots in cliff, piddock (shellfish) drilling into cliff, seaweed in cliff dragging waves
chemical weathering
oxidation - oxygen in water reacts with minerals in rock
hydration - porous rock expands creating stress, weakening it
hydrolysis - acid rain dissolves rock
carbonation - calcium carbonate (in limestone) + carbonic acid=calcium bicarbonate
mechanical/physical weathering
depends on climate, freeze thaw = water enters crack, freezes overnight, melts back to water when temp rises releasing pressure exerted from the ice
mass movement
downhill movement of weathered sediment under the force of gravity, rate depends on angle of slope, saturation, cohesion and size of sediment, 5 types
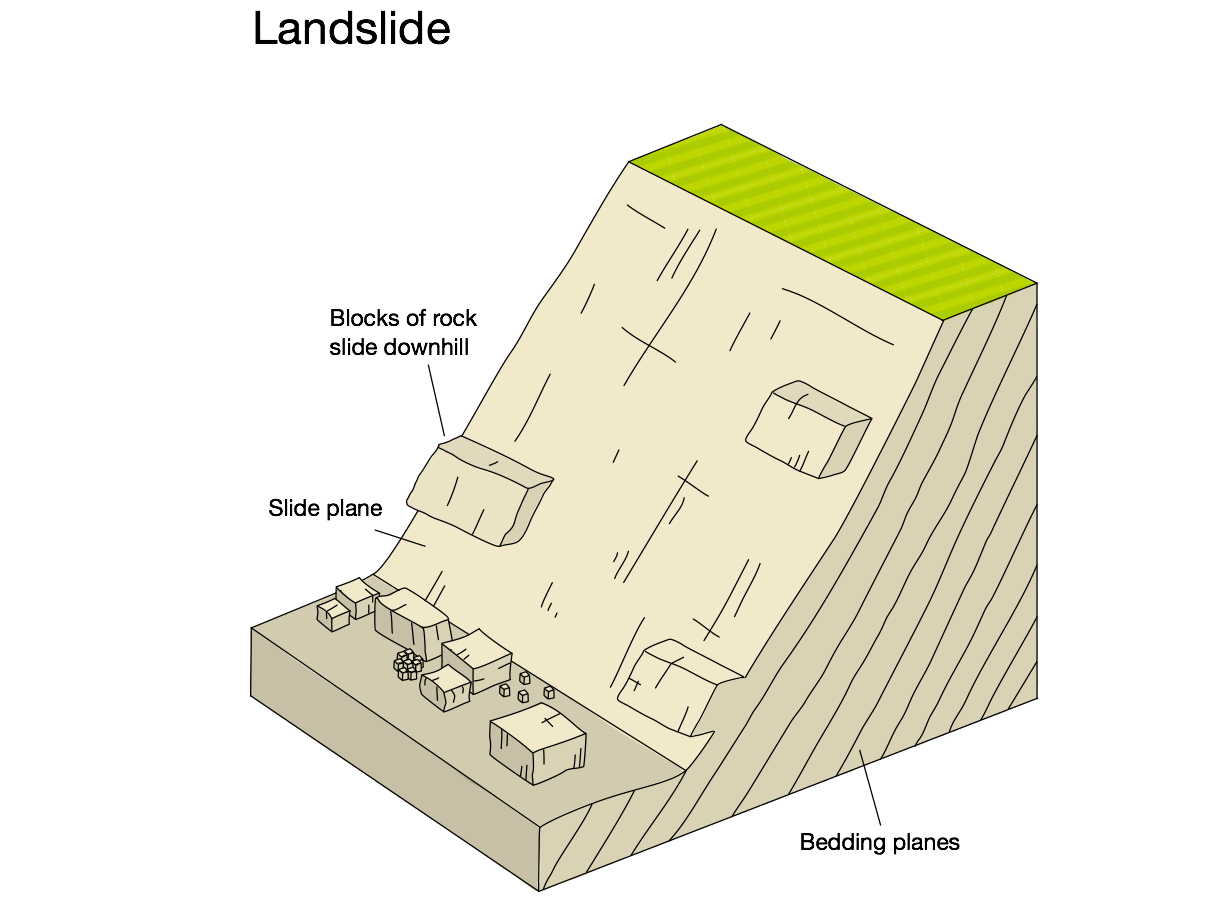
landslides
rapid movement of weathered material down a straight slip plane
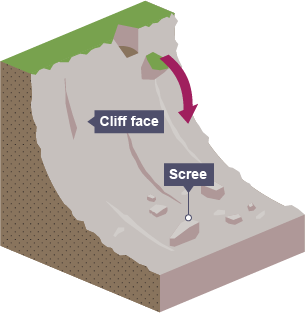
rockfalls
when exposed to mechanical weathering, cracks in the cliff looses support for sediment higher up causing rapid falls
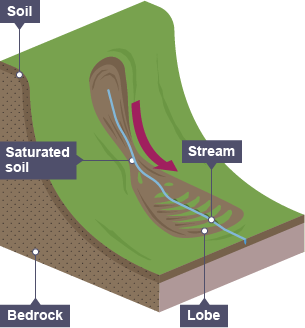
mudflows
movement of earth and mud flowing downhill over impermeable rock due to saturation reducing friction, very fast-flowing
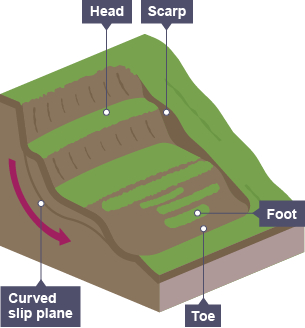
rotational slip / slumping
whole sections of rock move along a curved slip plane as sediment collapses under its own weight, rotational movement
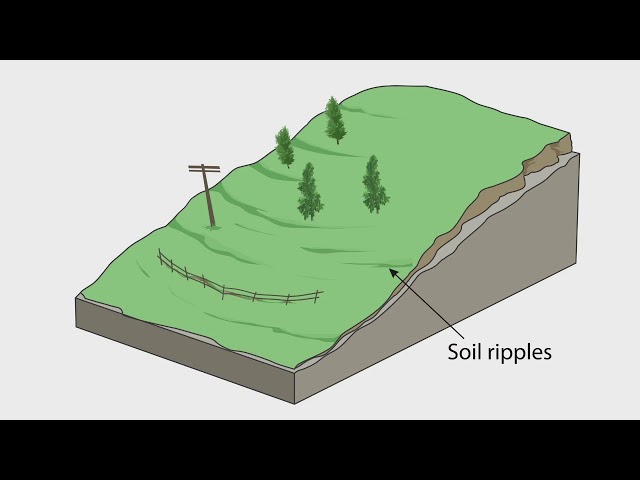
soil creep
very slow movement of individual soil particles moving downslope due to wetting and freezing
geology
a branch of natural science concerned with the earth, the rocks of which its composed and the processes by which they change over time (earths structure and processes)
sedimentary rock
layers of small chipped off sediment compacts to form a larger rock, weakest type, e.g. mudstone, limestone and coal
metamorphic
heat and pressure from magma changes the chemical state of the rock, binding it together stronger, takes a very long time e.g. marble
igneous
rocks become so hot, they melt into a liquid (molten rock) then cools down and hardens, e.g. granite and pumice
rock cycle
the newly formed igneous rocks eventually get weathered and small sediment gets chipped off, starting the sedimentary rock process - a continuous cycle over millions of years
differential erosion
when rates of erosion occurs at different speeds due to varying rock resistance
factors that affect rate of erosion
resistance to erosion - well-jointed rocks are more venerable to erosion
permeability and porosity - ability to hold fluids and allow them to flow through
orientation - discordant / concordant coastline
dip - angle of the rock strata
rock strata
layers of rock that have formed over time
swash aligned beach
parallel to incoming waves, minimal longshore drift, irregular coastlines
drift aligned beach
parallel to direction pf longshore drift, considerable amounts f sediment, regular coastline
tombolo
a spit that joins an island to mainland
estuary
the zone were the freshwater of rivers meets the salt water of the sea and begin to interact
bar
a spit that forms two headlands, can form a lagoon
sand dune formation
sand gets transported up the beach by wind, larger sediment rests against an obstacle creating a ridge which builds up to a crest of an embryo dune. the dune becomes a new obstacle and larger and mores stable sand dunes are formed further inland
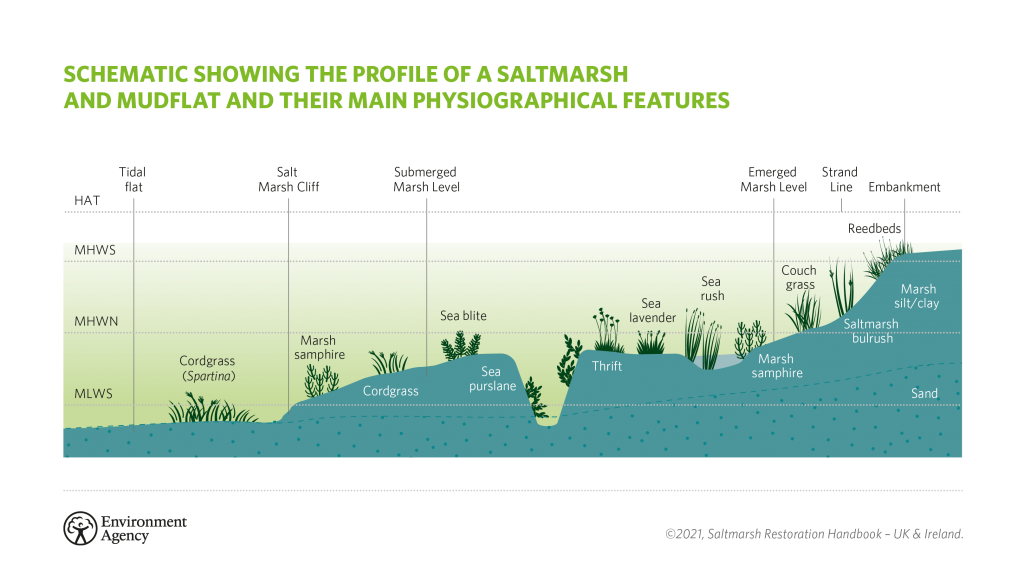
mudflats
Mudflats are created by the deposition of fine silts and clays in sheltered low energy coastal environments such as estuaries. saltmarshes
flocculation
particles in sediment like clay and silts clump together, sinking to the bed as they are heavier
halosere
tolerant of salty conditions
salt marsh structure
climate
average weather over a 30 year period
weather
the atmospheric conditions (temperature and rainfall) of each day
climate change
a long term change in the climate, could be global warming or cooling
Eustatic change
Change in the sea, global effect, caused by tectonic movements and change in climate
Isostatic change
Changes in land movements, local effects, caused by tectonic uplift or depressions, compression/decompression of the crust and subsidence of land
Sequence of sea level change
Colder climate, more water in glaciers, sea level falls, weight of glaciers compress land, sea levels rise, climate warms, ice melts, sea levels rise
Emergent landforms
Raised beaches with relic cliffs and wave-cut platforms where the sea level has dropped so a new beach has been formed
Rias
A submergent landform, a flooded river valley with a dentritic pattern
Fjords
A submergent landform, flooded glacial valley, shallower at the mouth where the ice would have lost energy as it melted, very steep sided and narrow
Dalmatian coast
Where a landscape of valleys and ridges are parallel to the coastline, the low lying parts of the valleys will be flooded when sea level rises. The exposed tops of the ridges become small offshore islands parallel to the coast. The best known example of this is the Dalmatian Coast in Croatia
Groynes
Timer or rock structures perpendicular to coast that trap sediment moved by longhairs drift
+work with natural processes, protects land, not too expensive
-starve other beaches leading to erosion, unattractive
Sea walls
Stone or concrete walls at foot of cliff or top of beach with curved face to reflect waves back to sea
+effectively prevents erosion, provided a promenade
-dosnt absorb waves energy, intrusive and unnatural looking, very expensive
Rip rap
Large rocks at foot of cliff or top of beach forming a permeable barrier to break waves
+relatively cheap and easy
-intrusive, dangerous to people climbing
Revetments
Sloping wooden/concrete/rock structures at foot of cliff or top of beach breaking waves energy
+relatively inexpensive
-intrusive, needs high maintained
Offshore breakwater
Partly submerged concrete/rock structures designed to break waves before they reach the coast
+effective permeable barrier
-visually unappealing, navigation hazard
Beach nourishment
Adding sand or pebbles to an existing beach
+cheap and easy, looks natural, makes a bigger beach
-needs constant maintained because of erosion and transportation
Cliff regrading and draining
Regrading reduces angle of cliff to stabilise it
Draining removes water to prevent landslides and slumping
+effecting on clay or loose rock, cost-effective
-causes cliff to retreat, drained cliffs and dry out and lead to collapse (rockfalls)
SMP (shoreline management plan)
Strategy for managing flood and erosion for a particular coast of coastline in the UK, aiming to provide strategic and sustainable improvements