A level AQA Psychology Paper 2
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Human Nervous System Branches
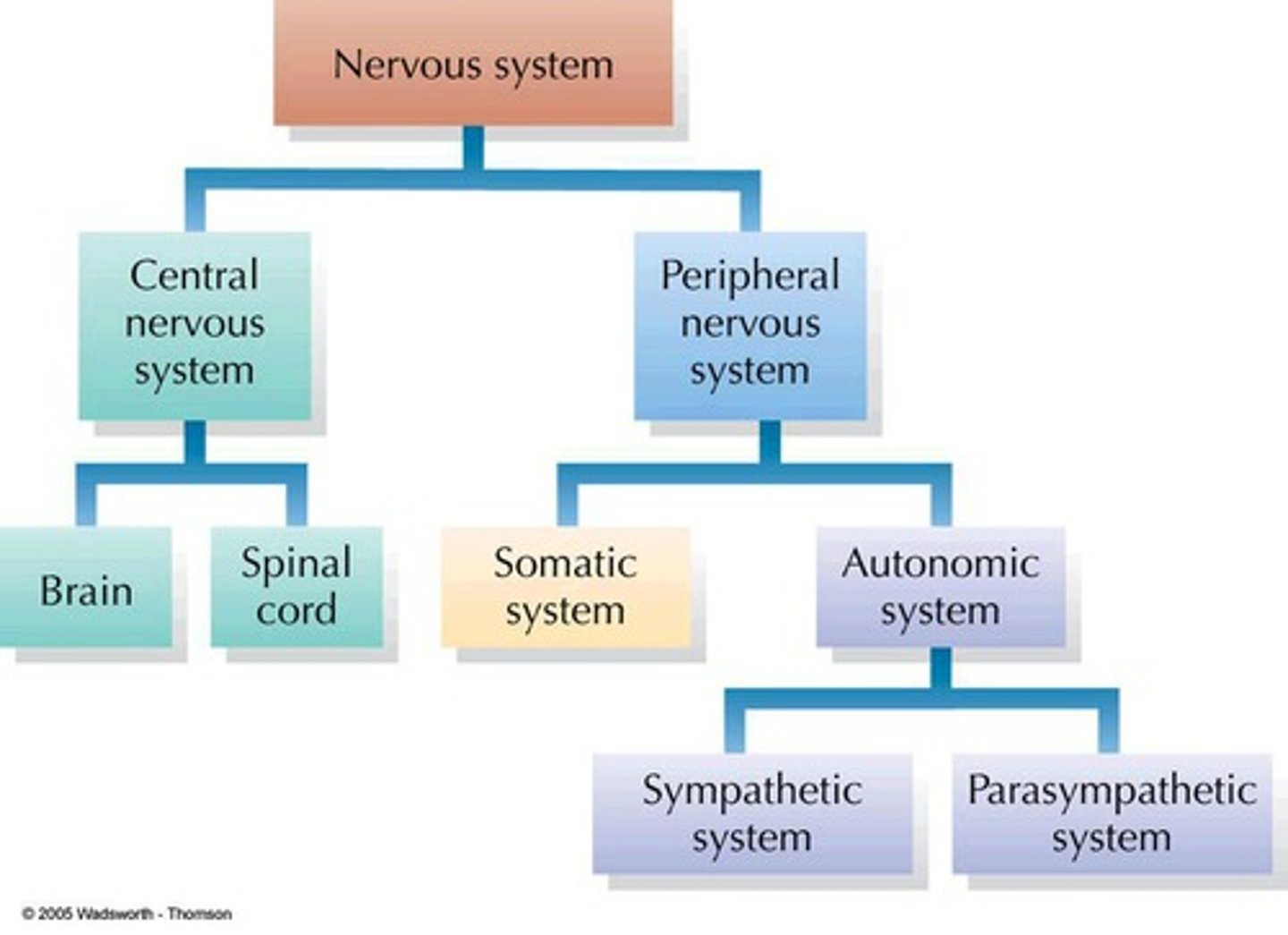
Central Nervous System
-Brain: consciousness, hemispheres
-Spinal Cord: passes messages from the brain, reflex actions, connects to PNS
Peripheral Nervous System
Transmits Messages via neurons
-Autonomic: breathing heart rate stress
-Somatic: muscle and sensory neurons
Endocrine System
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Examples
-Thyroid, Thyroxine, heart rate
-Pituitary gland, regulates other glands
-adrenal, adrenaline, arousal
Adrenaline Steps
-Hypothalamus in brain activates pituitary gland
-ANS Sympathetic state
-Adrenaline Released for fight or flight
Immediate and Automatic
-Once threat has passed, parasympathetic nervous system returns body to original state
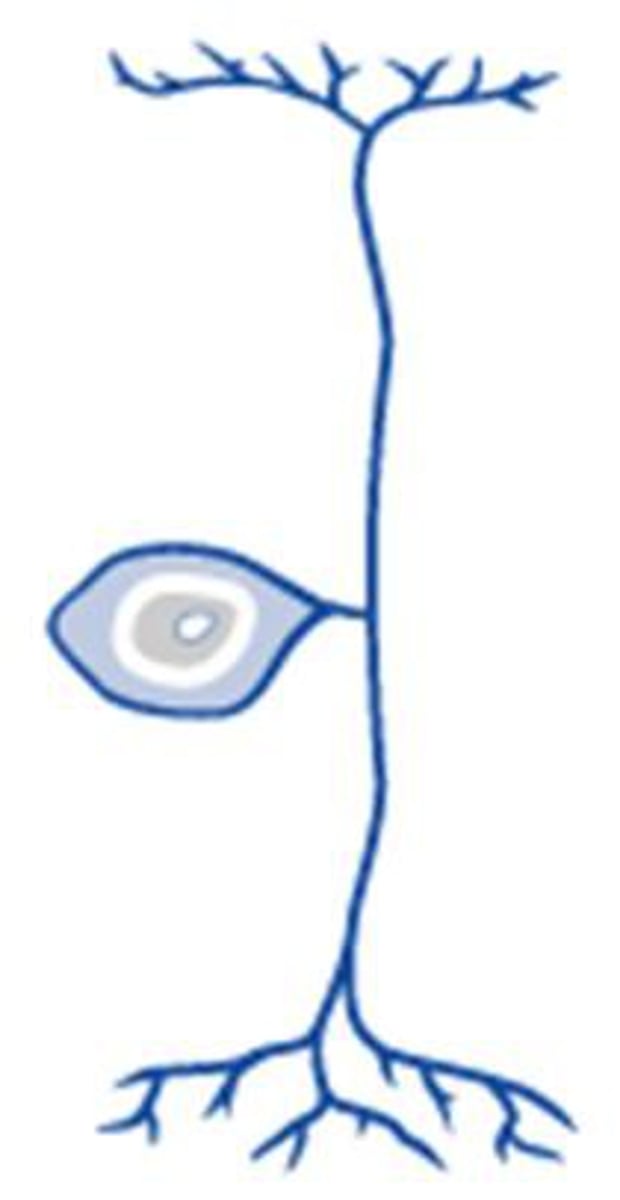
Structure of a neuron
cell body
dendrites
axon (myelin sheath nodes of ranvier)
synapse
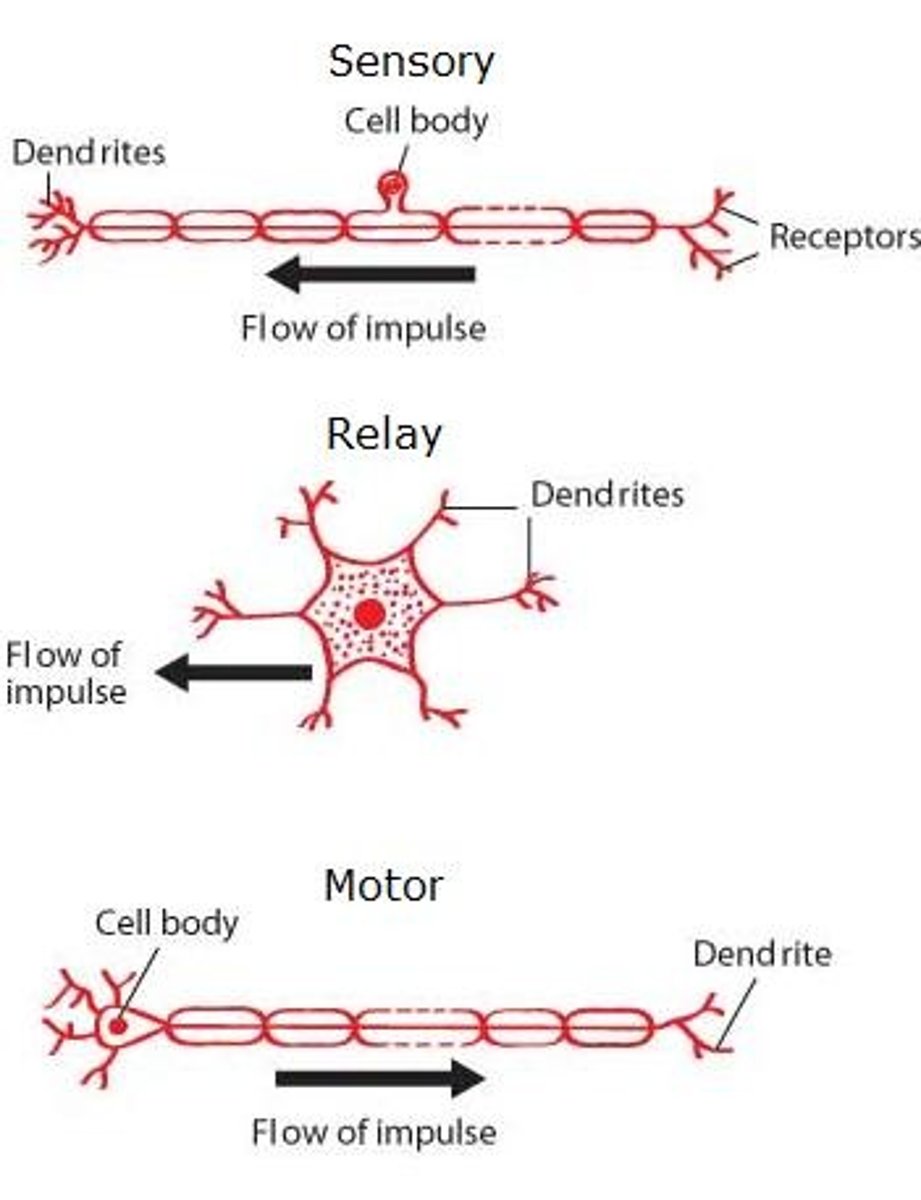
Neuron Types
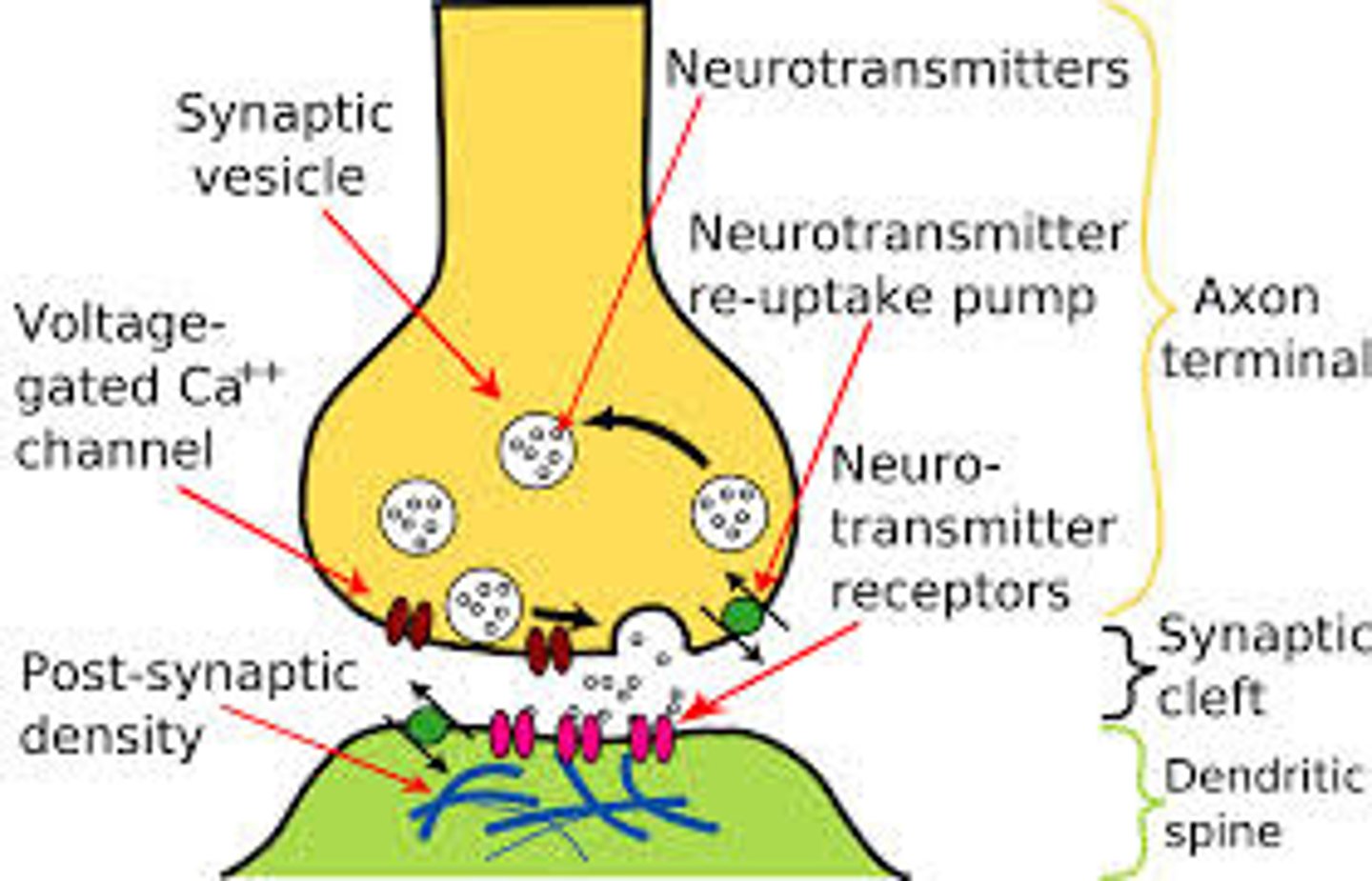
Electrical Tranmission
Action Potential, sum of the excitory and inhibitory hormones
Synapse
Localisation vs holistic theory
before Broca and Wernicke, scientists supported the holistic theory of the brain that all parts were involved in the processing of though and action. however, later scientists argued that different parts of the brain perform different tasks and are involved with different parts of the body. if the brain area is damaged, the associated function will also become affected
Hemispheres of the brain
Right side is more Creative (deals with art, music, holistic thought, and intuition). Left side is more Analytical (deals with logic, language, science, and math).
Brain Localisation
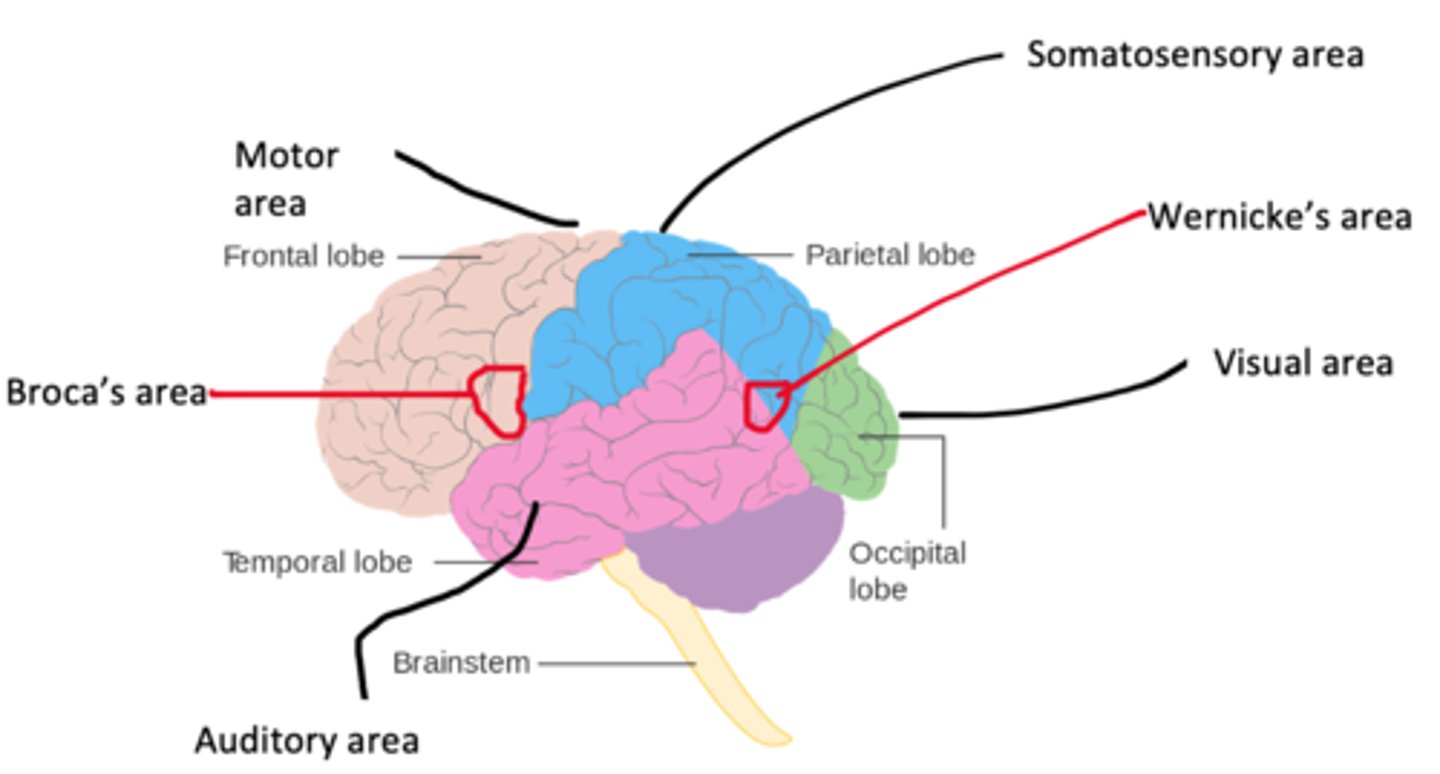
Brain Part Functions
Motor- movement
Visual- sight
Somatosensory- sensory
Auditory- analysis of sound based info
Broca's- Speech production
Wernicke's- language understanding
Localisation of brain function Evaluation
+EVIDENCE FROM NEUROSURGERY
>OCD area of brain can be treated, showing specific area
+BRAIN SCAN EVIDENCE
>activity during tasks
COUNTER
>rats having cortexes severed could still do maze (holistic)
-LANGUAGE QUESTIONED
>not just broca and wernicke, fmri showed greater spread
Left and Right Hemispheres
Together, the two hemispheres control much of your behaviour. The left is relatively more specialized for speech and language; the right, for appreciation of 3D space and spatial relationships. Right hem controls RVF and vice versa
Split brain research - Sperry
Sperry studied individuals who had undergone a commissurotomy (corpus callosum cut to separate the two hemispheres)
Images in both visual fields
When image shown to RVF (LH) they could descibe it but not on the opposite side, as the RH could not relay to language centres in the LH
They could however select the object from sight
LVF (RH) had emotional response to pinups but couldnt describe
Supports Lateralisation
Lateralisation Evaluation
+RESEARCH SUPPORT
>PET scans in tasks
-ONE BRAIN
>No dominant side for personality
Split Brain evaluation
+RESEARCH SUPPORT
> Split B Better performance in some tasks shows lateralisation
-GENERALISATION ISSUES
>causal relationships hard to establish
>epilepsy caused not split brain
plasticicty
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
Maguire et.al London Taxi drivers had larger posterior hippocampus, longer done more grey matter
Draganski et al medical students brains changed after exams
Plasticity Evaluation
-NEGATIVE PLASTICITY
>drugs lead to poor function, dementia
>phantom limb syndrome
+AGE
> could be a life long ability
>40 hrs training 40-60yo golfer fmri increased activity
Functional Recovery
Axonal Sprouting- new nerve endings
Denervation Supersensitivity- axons doing a similar job are aroused
Recruitment of homologous areas- opposite side does more
Functional Recovery Evaluation
+RW APPLICATION
>our understanding aids our ability to help
>constraint induced movement therapy
-COGNITIVE RESERVE
>level of education may influence recovery rate
>implications on less educated
Ways of studying the brain
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Event Related Potential (ERP) FILTERS OUT EEG unuseful stuff
- Post Mortem
fMRI evaluation
+no radiation
+spatial resolution
+straightforward
-expensive
-poor temporal resolution
EEG evaluation
+stages of sleep
+temp res
+cheap (ish)
-general info, hard to pinpoint
-different but adjacent locations
ERP Evaluation
+more specific than EEGs
+temporal resolution
-lack of standardisation of methodology
-hard to remove noise
Post Mortem Evaluation
+foundation for early understanding
+establish links
-causation
-ethical issues consent
Circadian Rhythms
The 24-hour biological cycles found in humans and many other species.
Biological Rhythms
periodic fluctuations in physiological functioning
Sleep-Wake Cycle
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus endogenous pacemaker
Reset by exogenous zeitgeber daylight
Siffre Cave Study
- Caver spent long periods in dark caves to examine the effects of free-running biological rhythm
o Two months in cave
o Six months in cave
- In both studies, his free running circadian rhythm settled down to about 25 hours
- He did have a regular sleep/wake cycle
Other Circadian Rhythm Research
1)Wever et al
WW2 bunker 4 weeks
no natural light
24 to 25 hr cycle bar one (29)
naturally be a bit longer but trained by ex zeit
2) Folkard et al
12 ppl in cave
sped up clock
only 1 could adjust
Circadian Rhythm Evaluation
+SHIFT WORK
>understanding of consequences
>poor health and shift economic impact
COUNTER
>correlationary, other factors eg loneliness
+MEDICAL TREATMENT
>aspirin better taken at night as heart attack likely in morning
-INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES
>small samples
>only make averages not generalisations
Infradian Rhythms
Less than one cycle in 24 hours
Menstrual Cycle 28 days
Synchronisation study showed 68% of women pheromones synced closer
Seasonal Affective Disorder
melatonin production has a knock on effect to seretonin
Infradian Rhythms Evaluation
+EVOLUTIONARY BASIS
>natural selection sync babies to look after them
-METHODOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS
>many other factors acting as confounding variables
Ultradian Rhythms
More than 1 cycle in 24 hours
SLEEP STAGES:
S1&2) high frequency, short amplitude easily woken, 2: alpha still but occasional changes in pattern
S3&4) Deep slow wave sleep, lower frequ high amp
S5) REM paralysed but brain activity resembles active brain, theta waves, eye movement
Ultradian Rhythms Evaluation
+IMPROVED UNDERSTANDING
>age related changes, growth hormone and sleep
-INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES
> biological, hard to define normal
Endogenous pacemakers and the sleep/wake cycle
EPs are the internal body clocks that are thought to regulate circadian rhythms.
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is thought to be the primary pacemaker
SCN - a bundle of nerves located in the hypothalamus. primary EP. it is located just above the optic chiasm, which receives info from eyes about light (happens even when eyes are closed)
Animal Study- 30 chipmunks with destroyed SCN, no cycle, most killed by predators
-Bred hamsters with 20hr scn cycle, implanted tissue into normal ones, defaulted to 20 hrs
Pineal Gland and melatonin- SCN psses info to pin g released melatonin induces sleep
Endogenous pacemakers and the sleep/wake cycle Evaluation
-BEYOND THE MASTER CLOCK
>research on scn obscures other body clocks eg peripheral oscillators in organs
-INTERACTIONIST SYSTEM
>cant be studied alone
>pacemakers and zeitgebers interact hard to separate,
Exogenous Zeitgebers and the sleep/wake cycle
External factors in environment that reset biological clocks through entrainment
Light - plays a role in maintenance of sleep/wake cycle, indirect influence on key processes which control functions like hormones secretion and blood circulation
Social Cues - infants sleep/wake cycle pretty random, 6 weeks the circadian rhythm begins and at 16 weeks most babies are entrained, adult determined mealtimes and bed times, adapting to local eat and sleep times is effective at entraining CR and beating jet lag
Exogenous Zeitgebers and the sleep/wake cycle Evaluation
-ENVIRONMENTAL OBSERVATIONS
>dont have the same effect in all environments
>arctic circle, barely any daylight, similar patterns
-CASE STUDY EVIDENCE
>blind man, abnormal cycle, social cues alome not enough
Origins of Psychology
Wundt founded first ever psychological lab in Germany in 1879.
Aimed to document and describe the nature of human consciousness.
Developed introspection
Wundt and Introspection
- Fist ever lab in 1879 in Leipzig, aimed to analyse the nature of human behaviour using introspection
-Thoughts images sensations, standardised
-Structuralism
Wundt and Introspection Evaluation
+SCIENTIFIC
>some methods were scientific and well-controlled
>frontrunner to later approaches
-SUBJECTIVE DATA
>self reporting mental processes
>doesnt meet scientific criteria
The emergence of psychology as a science
1900s - behaviourists
1950s - cognitive
1980s - biological
The emergence of psychology as a science EvaluatioN
+MODERN PSYCHOLOGY
>same aims, understanding, scientific methodology, unbiased and controlled
-SUBJECTIVE DATA
>not all approaches use scientific methods, humanistic, psychodynamic
>humans mean demand characteristic
The Behaviourist Approach
A way of explaining behaviour in terms of what is observable and in terms of learning. We are a blank slate at birth.
Classical Conditioning- Pavlov's dog, NS US CR CS
Operant Conditioning- Skinner Box PR NR PUN
The Behaviourist Approach Evaluation
+WELL-CONTROLLED RESEARCH
>controlled lab setting, other variables removed so cause-effect more likely
COUNTER
>may as a result have oversimplified learning processes, human thought involved
+RW APPLICATION
>token systems, phobia treatment
-ENVIRONMENTAL DETERMINISM
>ignores any possibility of free will
Social Learning Theory
we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished. Vicarious reinforcement- seen to be rewarded
Mediational Processes:
Attention Retention Motor Reproduction Motivation
More likely to occur if there is identification
Banduras doll
Social Learning Theory Evaluation
+COGNITIVE FACTORS
>recognises cognitive factors, neglected by other learning approaches
COUNTER
>biological factors ignored, mirror neurons bandura
-CONTRIVED LAB STUDIES
>many studies it is based on suffer demand characteristics due to contrived nature, bandura kids thought the expectation was to strike it
+RW APPLICATION
>shows how cultural norms are transmitted through societies through the media
The Cognitive Approach
An approach to psychology emphasizing the mental processes involved in knowing: how we direct our attention, perceive, remember, think, and solve problems.
-Role of Schema
-Theoretical and computer models, msm, wmm, artificial intelligence
Cognitive Neuroscience:
influence of the brain structures on mental processes
uses fmri pet etc to map diefferent sections to functions
The Cognitive Approach Evaluation
+SCIENTIFIC METHODS
>lab studies
>cognitive neuroscience uses biological methods
COUNTER
>reliant on inference, can be too abstrct/theoretical
>artificial stimuli
+RW APPLICATION
>important contribution to ai
-MACHINE REDUCTIONISM
>similarities but ignores emotion and motivation, anxiety on ewt
The Biological Approach
Neurochemical Basis- neurotransmitters, dopamine on schizo, seretonin in ocd
Genetic Basis- twin studies, concordance rates
Genotype and Phenotype
Evolution and Behaviour- natural selection
The Biological Approach Evaluation
+RW APPLICATION
>antidepressant drugs via knowledge of neurotransmitters etc
COUNTER
>drugs dont work for all, modest effect, therefore chemistry cant fully account for this
+SCIENTIFIC METHODS
>fmri, eeg
-BIOLOGICAL DETERMINISM
>ignores environmental effects + free will
The Psychodynamic Approach
Role of Unconscious
Defence Mechanisms (repression denial displacement)
Id (bad) Ego (mediator) Superego (morality)
Psychosexual Stages:
Oral 0-1
Anal 1-3
Phallic 3-6
Latency
Genital
The Psychodynamic Approach Evaluation
+RW APPLICATION
>psychoanalysis and psychotherapy, counselling
COUNTER
>not successful for serious disorders eg schizo
+EXPLANATORY POWER
>controversial and bizarre, however, influential in drawing attention to unconscious and chilhood experience
-UNTESTABLE CONCEPTS
>doesnt meet the criterion of falsification, occurrance at an unconscious level
Humanistic Psychology
-Free Will
-Self Actualisation
The self, congruence and worth: concept of self must be somewhat aligned with ideal self, if gap exists, self actualisation isnt possible
counselling reduces gap
issues rooted in unconditional positive regard in childhood
-Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
Maslow's Hierarchy
physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, self-actualization
Humanistic Psychology Evaluation
+NOT REDUCTIONIST
>holistic approach, considers meaning in a real world environment
COUNTER
>less scientific as a result
+POSITIVE APPROACH
>optimism, freud says prisoners of past, humanistic are free to work towards their ideal self
-CULTURAL BIAS
>collectivist cultures emphasise needs of the group
Experimental Method
Aim
Hypotheses
Method
Type of Hypothesis
IV DV CV
Levels of IV- INDEPENDENT OR REPEATED
Operationalised variables
Research Issues
- Extraneous variables - Confounding variables - Demand characteristics - Investigator effects - Randomisation - Standardisation
Independent Groups Evaluation
- participant variables not controlled (use random allocation)
- less economical (more ppts needed), no order effects (guessing aims)
Repeated Measures Evaluation
- Order effects
- Demand characteristics
- No participant variable problems
- More economical
Matched Pairs Evaluation
+ pps only take part in a single condition so order effects and demand characteristics less of a problem
- although participant variables reduced, pps can never be matched exactly. even when identical twins are used as matched pairs, there will still be important differences that may effect DV.
- matching may be time-consuming and expensive especially if a pre-test is required, less economical than other designs
Lab Experiments Evaluation
High internal validity (control)
Low external validity (low realism)
Cause and effect
Replication
Demand characteristics
Field Experiments AO1 AND 3
IV manipulated in a real world setting
+authentic behaviour, covert possibility
-ethical issues, replication is hard, cause-effect
Natural Experiments AO1 AND 3
No control over IV eg natural disaster, childs age
+opportunity for research which may usually be avoided due to practicality and ethics, high ext validity as it is real world as it happens
-no random allocation
Quasi-Experiments
IV is based on an existing difference (ie age), the DV is measured by the researcher, can be in lab or natural settings
+often in lab conditions so variables controlled
-confounding variables, cause effect as IV is not manipulated by researcher
Sample Types PSYCHOLOGY
Random
Systematic
Stratified
Opportunity
Volunteer
Ethical Issues
informed consent
deception
harm
confidentiality
Dealing With Ethical Issues
BPS Code of Conduct
Consent letter
Debrief
Right to withhold
Anonymity
Aims of Pilot Studies
-Remove Ambiguous Questions
-Identify issues
Pilot Studies Other Stuff
Single Blind: ppts not made aware
Double Blind: researcher and ppts not aware
Control Groups: used for comparison
Types of Observation
-naturalistic (take place where behaviour would usually occur)
-controlled
-covert
-overt
-participant
-non-participant
Types of Observation Evaluation
-Causal relationships
-Observer Bias
rest are fairly self explanatory in an exam eg demand characteristics
Ways of recording data
Unstructured (write all)
Structured (target criteria)
Behavioural Categories
When a target behaviour is broken up into components that are observable and measurable
Event and Time Sampling
Counting the number of times a particular behaviour occurs (event) or recording behaviour within a pre-established time-frame (time).
Questionnaires
self-administered, written sets of questions
Open and Closed
Questionnaires Evaluation
+more responses
+easy to analyse closed
+easy to replicate
-social desirability bias
-can misinterpret qs
-restricted to qs closed
-tendency to just put yes
Interviews Evaluation
Structured:
+replicate
+differences in interviewers
-richness of data
Unstructured:
+flexibility and insight
-interviewer bias
Self Report Design Q
Likert (agreement)
Rating (eg 1-5)
Fixed Choice
Correlations Evaluation
+ easily displayed in graphs
+ allows to see relationships between 2 co-variables
+ easy and quick to carry out
+ quantative data - easy to analyse
- correlation is NOT causation
- extraneous variables can have an impact
REMINDER TO WATCH HOW TO DO THE SIGN TEST
DO IT
Aims of Peer Review
1) To allocate funding properly and appropriately. It stops researchers spending lots of money on investigations which may encounter problems. Also it helps to develop the areas of psychology that need to be developed,
2) To validate the quality of research. It establishes more accurate to inter-observer reliability. Additionally it makes sure that you are measuring what you set out to measure.
3) To suggest amendments and improvements. It allows researchers to get more accurate results as it eliminates potential problems.
Evaluation of Peer Review
- Anonymity > revenge > some journals favour open reviewing
- Publication bias > only interesting/successful research published > file drawer problem
- Burying ground breaking research > research which challenges established order isn't passed
Case Studies
a research method that involves the intensive examination of unusual people or organizations
+rich insights on atypical behaviour
+generate hypotheses for future studies
-generalisation of findings
-prone to inaccuracy
Coding and Quantitative Data
- initial stage of content analysis
- some data sets to be analysed may be extremely large and so there is a need to categorise this information into meaningful units
- may involve counting up the number of times a particular word or phrase is said to form quantitative in an interview
Thematic analysis and qualitative data
Recurrent ideas that keep 'cropping up' in the communication are described.
Content Analysis Evaluation
+get around ethical issues as info may be in the public domain
+external validity
-indirect study so communications are analysed outside the content they occurred
-subjective assumptions made
Types of Validity
Does it produce a genuine result?
Internal Validity- whether effects are due to IV
External Validity- generalisation to other settings
Ecological Validity- application to real life
Temporal Validity- hold true over time
Reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, on alternate forms of the test, or on retesting
Ways of Assessing Reliability
Test-retest: same test given to same person on different occasions, 2 sets of scores are correlated if correlation is significant the reliability of the measuring tool is good
Inter-observer: for observations, inter-rater for content analysis, inter-interviewer for interviews, correlation of +0.8
Improving Reliability
questionnaires: test retest, rewrite if bad
interviews: use same interviewer each time, less leading questions, ambiguous questions, maybe even closed
experiments and observations: ensure proper operationalisation, no overlap, training in observation, standardised procedures for experiments
Choosing A Statistical Test
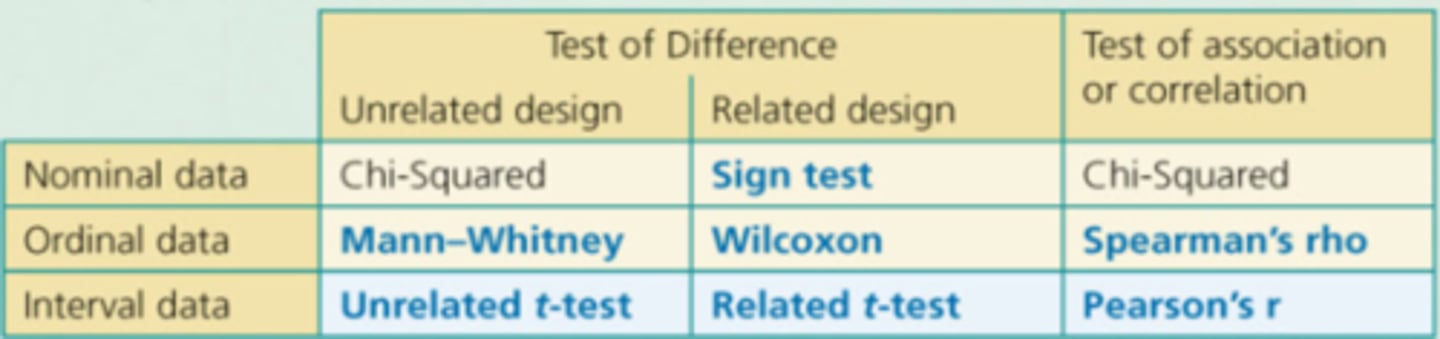
Features of science
Paradigms & paradigm shifts (assumptions and agreements)
Theory construction
Falsifiability (ability to be proved untrue)
Replicability
Objectivity
Empirical method (based on evidence through direct observation and experience)
Sections of a scientific report
Abstract (short summary)
Introduction (detail relevant theories and studies, start broad narrow down to aim and hypothesis)
Method (design, sample, apparatus, procedure, ethics)
Results
Discussion
Referencing