chap 9 nervous system
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
crashing out rn
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
axon hillock
where axon originates
gyrus
ridges
sulci
shallow grooves
fissure
deep grooves
corticospinal (pyramidal)
originates in the cortex of the brain and conducts impulses that control skeletal muscle movements (passes through medulla oblongata)
ganglion
masses of cell bodies
tracts
bundles of myelinated axons
Which three regions of the brain process sensory information?
diencephalon, cerebellum, and cerebrum
extrapyramidal tract
control movements associated with balance, posture and muscle tone
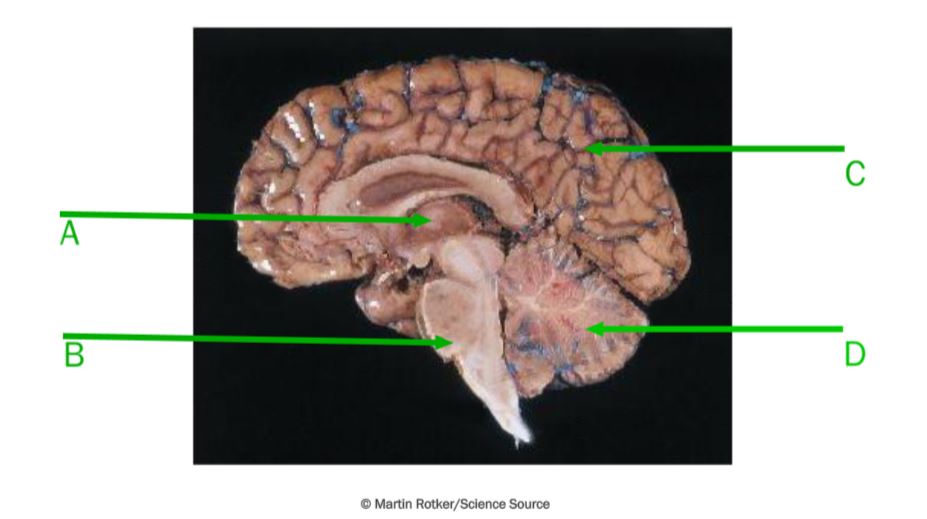
a - diencephalon; b - brainstem; c - cerebrum; d - cerebellum
The left and right cerebral hemispheres are connected by a broad, flat bundle of axons called the
corpus callosum
falx cerebri
part of the dura mater, separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
What does the longitudinal fissure separate?
right and left cerebral hemispheres
transverse fissure
separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum
cerebral cortex
The thin layer of gray matter that forms the outermost layer of the cerebrum
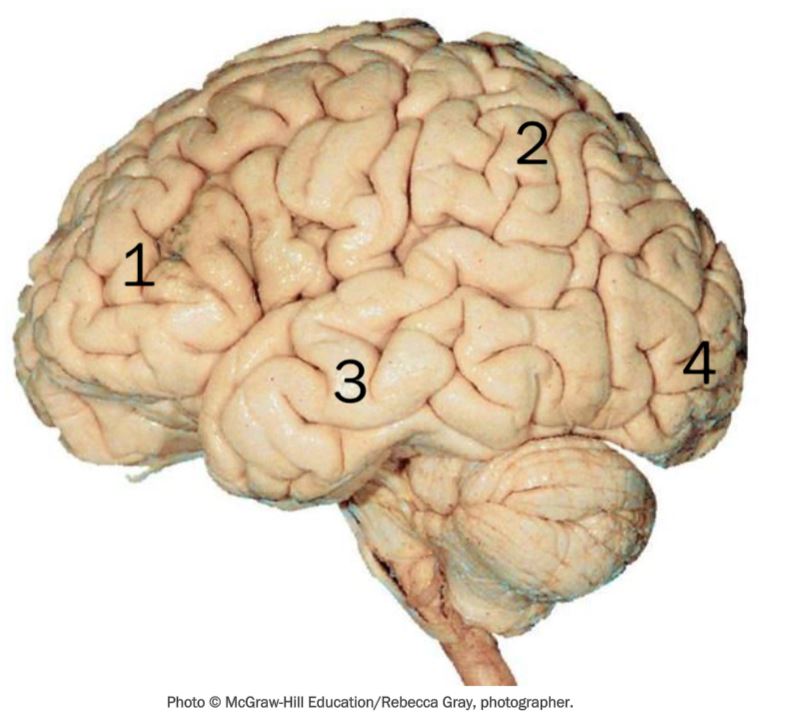
1 - frontal, 2 - parietal, 3 - temporal, 4 - occipital
cutaneous senses
anterior parietal lobe
visual senses
posterior occipital lobe
auditory senses
posterior temporal lobe
taste
base of central sulcus & insula
smell senses
deep in temporal lobe
white matter
myelinated axons
gray matter
unmyelinated axons
The cerebral cortex is divided into what THREE functional areas?
sensory, association, & motor
What makes up the bulk of the cerebrum and provides connections between different parts of the brain?
white matter
basal nuclei (or ganglia)
Masses of gray matter deep within each cerebral hemisphere that facilitate voluntary movement.
basal nuclei
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
A withdrawal reflex involves contraction of ____ muscles and reciprocal inhibition of _____ muscles
flexor, extensor
Where is the epidural space located?
Between vertebrae and dura mater
dorsal root ganglia
masses of cell bodies for sensory neurons
dorsal root
Carries sensory (afferent) impulses from the body to the spinal cord.
dorsal root
Carries motor (efferent) impulses from the spinal cord to the body.
central canal
surrounded by gray commissure and contains CSF
gray commissure
connects left and right gray matter
Broca’s area
frontal lobe, usually on the left side; controls muscles that function in speaking
what inhibitory neurotransmitter does basal ganglia secrete?
Produce the inhibitory neurotransmitter, dopamine.
function of basal nuclei
Relay motor impulses from the cerebrum, and help control motor activities by interacting with the motor cortex, thalamus, and cerebellum.
left hemisphere dominance
language-related activities of speech, writing, and reading, as well as complex intellectual functions.
nondominant hemisphere
specializes in nonverbal functions, such as body orientation in space, and controls emotions and intuitive thinking.
Wierncke’s area
understanding of written & spoken language. located in temporal lobe
What is the name of the neurons that leave the spinal cord and synapse with skeletal muscle fibers?
lower motor neurons
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons (LMNs) located?
In the ventral horn of the spinal cord or the cranial nerve nuclei in the brainstem
What is the function of lower motor neurons (LMNs)?
LMNs transmit impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles, directly stimulating muscle contraction. They serve as the final common pathway in the motor system.
Where are the cell bodies of upper motor neurons (UMNs) located?
In the motor cortex or the brainstem.
What is the function of upper motor neurons (UMNs)?
UMNs send motor signals from the brain to the spinal cord or cranial nerve nuclei, coordinating voluntary movement by regulating lower motor neurons.
The motor area responsible for voluntary movements of the eyes and eyelids is located in the
frontal lobe
True or false: Because of their location, the pyramidal cells of the motor cortex are also called upper motor neurons.
true
The area of the brain responsible for the voluntary movements of the eyes and eyelids is called the:
eye field
basal nuclei function
facilitate voluntary movement
Parkinson and Huntington disease are disorders associate with altered activity from what area of the brain?
basal nuclei
cerebral aqueduct
Which ventricle is located on the midline of the brain beneath the corpus callosum and surrounded by the diencephalon?
third
What structure connects each lateral ventricle to the third ventricle?
interventricular foramen
The cavities in the brain that store cerebrospinal fluid are the ______.
ventricles
Which ventricle is in the brainstem anterior to the cerebellum?
fourth
Which ventricle is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord and have openings leading to the subarachnoid space?
fourth
Which of the following are functions of CSF?
protection, buoyancy, stable ionic concentration
Flow of CSF proceeds through the ventricles and channels in this order:
2 Lateral ventricles.
Interventricular foramina.
Third ventricle.
Cerebral aqueduct.
Fourth ventricle, which is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord and the subarachnoid space of the meninges.
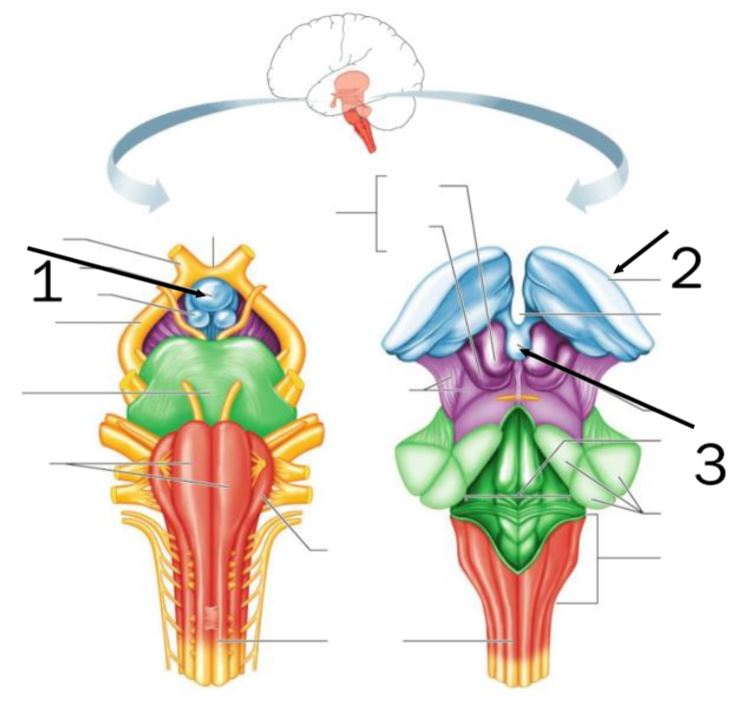
1 - pituitary gland; 2 - thalamus; 3 - pineal gland
limbic system
connected structures in the brain that produce emotion
optic chiasma
(op'tik ki-az'mah) X-shaped structure on the underside of the brain formed by optic nerve fibers (axons) that partially cross over to the visual cortex on the opposite side.
posterior pituitary gland
(pos-tēr'e-or pĭ-tu'ĭ-tār"e) Rear (posterior) lobe of the pituitary gland. It secretes oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone.
mammillary bodies
two rounded structures behind infundibulum
infundibulum
conical process behind optic chiasma where pituitary gland attaches
pineal gland
cone-shaped structure attached to the upper part of the diencephalon
Midbrain
Located between the diencephalon and pons.
Contains bundles of myelinated nerve fibers that convey impulses to and from higher centers of the brain.
Contains masses of gray matter that serve as centers for auditory and visual reflexes.
Contains main motor pathways between cerebrum and lower portions of the nervous system.
pons
Lies between the midbrain and medulla oblongata.
Transmits impulses to & from medulla oblongata and cerebrum.
Also conducts impulses from cerebrum to cerebellum.
Contains centers that help regulate the rate and depth of breathing.
reticular formation
Complex network of nerve fibers in the brainstem that arouses the cerebrum to a wakeful state.
What part of the brain acts as a gateway for sensory impulses and channels them to appropriate regions of the cortex for interpretation?
thalamus
The ______ of the brain maintains homeostasis by regulating visceral activities and controlling the endocrine system.
hypothalamus
The ______ is not a distinct structure; it includes parts of the cerebral cortex, diencephalon, and the basal nuclei.
limbic system
The optic nerves cross over at this structure called the _______ ________.
optic chiasm
two functions of thalamus
Relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex
Control of emotional experience and expressions
The brain area that regulates visceral activities, maintains homeostasis and links the nervous and endocrine systems is called the
hypothalamus
Which of the following parts of the brain compose a complex called the limbic system?
thalamus
temporal lobe of cerebrum
frontal lobe of cerebrum
What is the infundibulum?
A process that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
In what part of the brain are the nuclei responsible for visual and auditory reflexes located?
midbrain
functions of pons
Relay impulses between medulla and cerebrum
Nuclei that control rhythm of breathing
Relay impulses to the cerebellum
The medulla oblongata contains nerve fibers that connect what structures?
spinal cord & brain
Which of the following centers or reflexes have their nuclei located within the midbrain?
visual reflex center
auditory reflex center
medulla oblongata houses what reflexes?
coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting.
Where is the reticular formation located?
through the brainstem
A structure called the vermis connects the two hemispheres of the
cerebellum
cerebellar penducles
nerve tracts via which the cerebellum communicates with other parts of the CNS
A complex network of gray matter found within all levels of the brainstem is called the:
reticular formation
The ______ nerve originates at the medulla oblongata and extends into the neck, chest and the abdomen.
vagus
List the effectors for the autonomic motor fibers of the vagus nerve.
Smooth muscle of viscera of thorax and abdomen
The accessory nerve (CN XI) has two branches. Indicate the name of the two branches.
Spinal branch
Cranial branch
List the effectors for the somatic motor fibers of the vagus nerve.
Muscles for speech and swallowing (in tongue, pharynx, larynx)
Indicate the cranial nerve that has both cranial and spinal branches.
Accessory Nerve (XI)
The spinal nerve are ______ nerves.
mixed
Spinal nerve C5 emerges ______ vertebra C5 and spinal nerve L5 emerges _____ vertebra L5.
above, below
The spinal cord has ____ pairs of cervical nerves, ____ pairs of thoracic nerves and ____ pairs of sacral nerves.
8, 12, 5
What areas of the body do spinal nerves innervate?
upper limbs, trunk, lower limbs
The thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spinal nerves are associated with (named for) the vertebra that are ______ the nerve's point of emergence from the vertebral column.
superior to
what is the cauda equina?
Lumbar and sacral nerves that extend inferior to the spinal cord but within the vertebral column