MLS 220 Chemistry Exam 4 Terms & Definitions Study Set
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
LECTURE 17: INSTRUMENTATION – LIGHT ENERGY
Light
Type of electromagnetic radiant energy that travels in waves
Wavelength
Distance between two peaks as light travels in wavelike manner
determines the color seen by the human eye (every wavelength is a particular color)
expressed in nanometers
Electromagnetic radiation
Spectrum of energy
-long wavelength of radio frequencies to highly energetic gamma rays and x rays
Visible light
380-750 nm
UV light
10-400 nm
Color of light seen by naked eye is _______
Transmitted
All other wavelengths that are not transmitted are absorbed.
Planks Equation
Shows relationship between wavelength and energy
Frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength (Ex. ↑Frequency ↓Wavelength )
Energy of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional wavelength ( Ex. ↑Energy ↓Wavelength)

Planks Equation
E = hv = (hc)/λ
E: Energy
h: plank's constant (6.62x10^-27)
V: frequency
c: concentration
Frequency is ____ proportional to wavelength.
inversely
V = C/λ
V= frequency
C= speed of light
λ= wavelength
Energy of electromagnetic radiation is ______ proportional to wavelength
Inversely
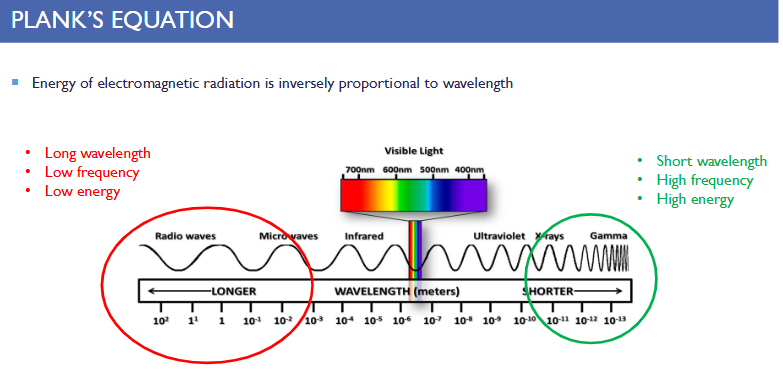
Long wavelength =
-Low frequency
-Low energy
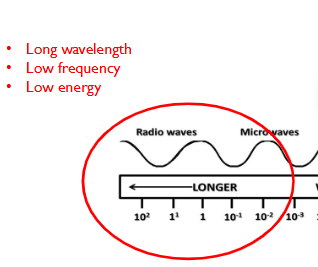
Short wavelength =
-high frequency
-high energy
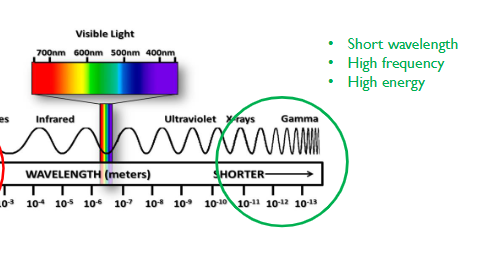
Wavelengths and color observed
380-440: Violet
440-500: Blue
500-580: Green
580-600: Yellow
600-620: Orange
620-750: Red
Beer's law
↑concentration ↑light absorbed
The amount of light absorbed by a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of a solution
The logarithm of the transmitted light of a substance is ___________proportional to its concentration
Inversely
Absorbance equation
A = εbc
A: absorbance
ε: absorptivity
b: length of light path (cm)
c: concentration
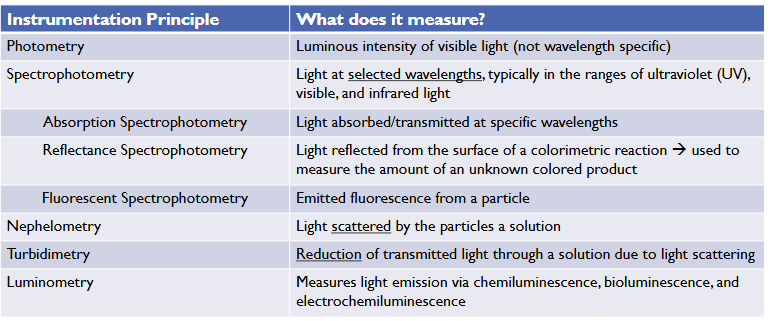
Photometry
-Determine concentration of a substance
-Measures intensity of light ->color
Wavelength of light is not taken into account
Only measures visible light
T or F? Photometry only measures visible light
True
In Photometry, is wavelength taken into account?
No
Spectrophotometry
The measurement of light at selected wavelength
-in ranges of UV, visible, and infrared (colorimetry)
Spectrophotometry uses what type of measurement? Qualitative or quantitative or both?
Qualitative and quantitative
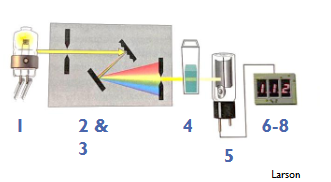
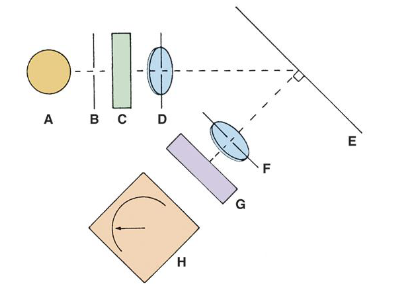
Spectrophotometry components (single beam)
1. Light source
2. Spectral Isolation device (monochromator)
3. Fiberoptics
4. Cuvette
5. Photodetector
6. Read out device
7. Recorder
8. Microprocessor
(Spectrophotometry) Light source include
-Incandescent lamps
-hydrogen lamps
-deuterium lamps
-laser
(Spectrophotometry) Spectral Isolation Device (Monochromator)
Isolated radiant energy of desired wavelengths (ex: 340 nm) while excluding other unwanted wavelengths
-filters
-prisms
-refraction gratings
(Spectrophotometry) Fiberoptics
Improve directional control of the light beam within the instrument using glass fibers
Bundles of thin, transparent fibers of glass, quartz, or plastic “flexible light pipes
(Spectrophotometry) Cuvette
Small vessel designed to hold liquid in the light
Square or rectangular → plane-parallel optical surfaces and constant light path
❖ Glass, quartz, or plastic
(Spectrophotometry) Photodetector
Convert light into measurable electrical signal by detecting photons (electrons are released)
❖ Electrons are released in proportion to the number of photons that strike
(Spectrophotometry) Readout device/computer
amplifies and mathematically manipulates the electrical signal produced and converts it into a convenient format
Absorbance Spectrophotometry
Concentration of an unknown sample is determined by measuring its absorption of light at a particular
- Measures the light absorbed/transmitted by a solution
- Quantitative Measurement
↑ Color Intensity (brightness of color) ↑ Concentration of Substance
Is absorbance Spectrophotometry quantitative or qualitative?
Quantitative
In absorbance spectrophotometry, can the samples be colored?
Samples must be naturally colored or capable of being colored
In absorbance spectrophotometry. Color intensity is _________ proportional to the concentration of the substance
Directly
Absorbance (A)
Expression of the amount of light absorbed by a solution
Percent Transmittance (%T)
Amount of light that passes through a colored solution compared with the amount of light that passes through a blank or standard solution
Blank
contains all of the reagents used in the procedure w/o the unknown substance
Absorbance equation
A = 2 - log10 %T
Amount of light absorbed by a solution
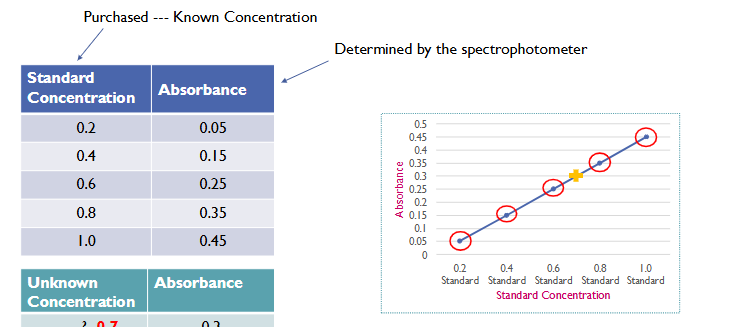
Standard curve
Graphical representation of the relationship between concentration and absorbance or %transmittance
Beer’s Law

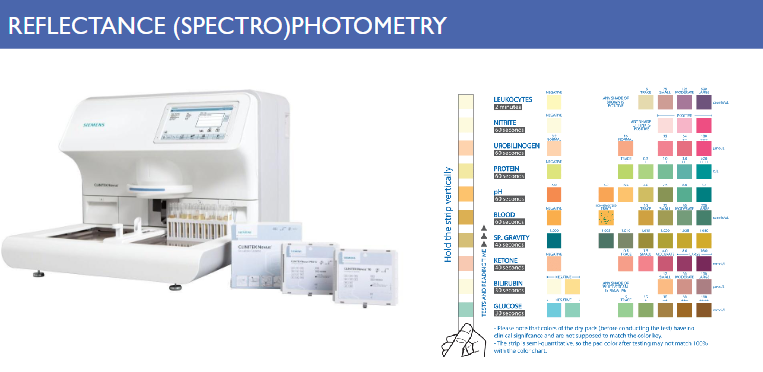
Reflectance spectrophotometry
Light reflected from the surface of a sample is used to measure the amount of unknown colored product (quantitative)
Sample concentration ↑ Intensity of the color ↑ Amount of light reflected ↓
(Amount of light absorbed ↑)
specular reflectance:
The amount of light reflected by a colored reaction product on a reflective surface composed of paper or plastic (smooth or mirror like surface)
Reflectance density:
The amount of light absorbed by the colored reaction product on the smooth surface
-inversely proportional to the light intensity reflected by the sample
Reflectance spectrophotometry relationship
Sample concentration ↑ intensity of the color ↑ amount of light reflected ↓ (amount of light absorbed ↑)
Fluorescent spectrophotometry
Uses a beam of light, typically UV light, to excite electronsin molecules causing them to emit light of a different wavelength
Fluorimetry
The measurement of emitted fluorescence
Fluorescence
When a molecule absorbs light at one wavelength and remits light at a longer wavelength
Fluorphore
An atom or molecule that fluoresces
-frequently used as tags/labels in immunoassays and flow cytometry
Which is more sensitive and specific? Absorption spectrophotometry or fluorescent spectrophotometry?
Fluorescent spectrophotometry
-emitted fluorescent signal comes directly
From sample
FLUORESCENT SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
▪ Disadvantages
▪ Sensitive to environmental changes
▪ pH, temperatures, contaminants
▪ Loss of excitation due to environmental factors → quenching
Fluorometer
Measures fluorescent intensity
How is fluorometer different than spectrophotometer?
Fluorometer measures the fluorescent intensity of light source, sample cell, and detector.
Light source in fluorescent spectrophotometry must be
High intensity lamp or laser producing light in the UV and short wavelength
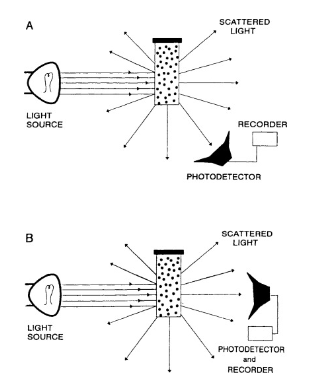
Nephelometry
Scattered light towards a detector not the direct path of transmitted light
-used to assay larger particles at lower concentration
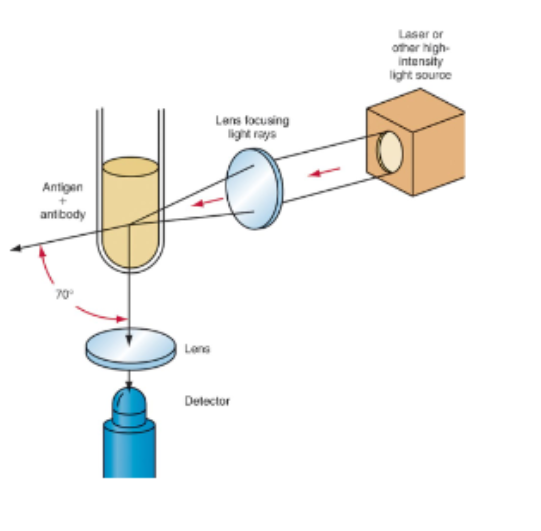
Turbidimetry
measures the reduction of light transmitted through a homogenous solution due to the light's scattering (solution becomes turbid)
-used to assay smaller particles at higher concentrations
Luminometer
Measures light emission via chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, and electrochemiluminescence
Chemiluminescence
Chemical reaction that produces light without producing heat
Ex: luminol, glow sticks, etc.
Bioluminescence
Form of chemiluminescence found in biological system
Ex: firefly glow
Electrochemiluminescence
Differs from chemiluminescence -> occurs at the surface of an electrode
Summary of Chapter 17

Chapter 18
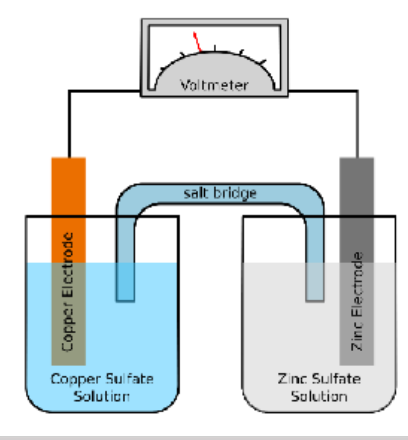
Electrochemistry
chemical energy is converted to an electric current (a flow of electrons) in a galvanic cell
In Electrochemistry, what is chemical energy converted to?
An electrical current or flow of electrons in galvanic cell
Galvanic cell
two half cells ->each contain a metal in a solution of one of its salts.
Components
Two half-cells
Salt Bridge
- Can be liquid or solid
- Helps keep the positive/negative balance between the two cells
Two Electrodes
- Cathode (-) and Anode (+)
Voltmeter
OILRIG
Oxidation is Loss of Electrons
Reduction Is Gain of Electrons
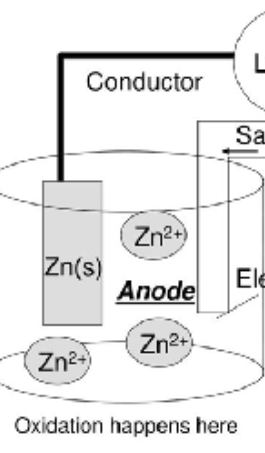
Anode
-Positive pole
-oxidation reaction
-loss of electrons

Cathode
-negative pole
-reduction reaction
-Gain of electrons
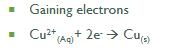
What does electrochemistry measure?
-ions
-drugs
-hormones
-metals
-gases
techniques used to measure electrochemistry
1. potentiometry
2.amperometry
3.conductometry
4.coulometry
Potentiometry
Measurement of voltage potential difference between two electrodes immersed in a
solution under zero current conditions
o Direct measurement of electrical potential due to the activity of free ions
- H+, Na+, K+
- Nernst equation relates the measured electrical potential
to the concentration (or activity) of ions
o Voltage also sometimes referred to as potential or electromotive force (EMF)
o Difference is measured using a voltage or pH meter
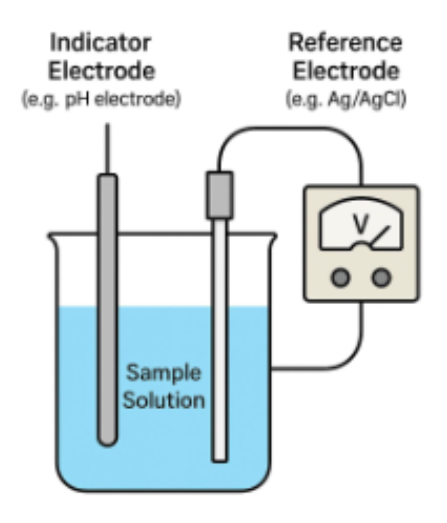
Two electrodes utilized in potentiometry
1. indicator electrode
2. reference electrode
*Need both need the the reference to measure against the reference solution
1. indicator electrode
measure analyte in your sample
ex. ion selective electrode
reference electrode
used as fixed reference (qc)
-most common: silver or silver chloride like a
-ph electrode is 7 the reference compared to your solution
ELECTROCHEMISTRY & CHEMICAL SENSORS POTENTIOMETRY
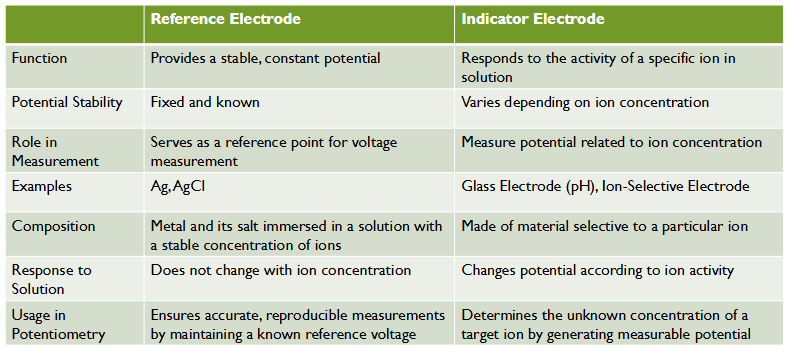

Ion – Selective Electrode (ISE) (indicator electrode)
o Membranes selectively permeable to certain ions (H+, K+, Na+, Mg2+)
o Interaction with the membrane creates a potential difference
• Polymer membranes → most prominent class of potentiometric ISE used in chemical analyzers
• Glass membranes (silica dioxide) → pH electrode
• Glass membrane permits interaction with H+ ions
PH
Measure of H+ ions (protons)
pH = log(1/[H+]) = -log[H+]**
what is attached to ISE probe?
Electrical read out
how is pH meter used?
1. Immersed pH in solution #1 of known pH
2.Immerse pH electrode in solution #2 of known pH
3.A slope is calculated by the pH meter based on the two values assigned to the known pH standards.
Amperometry
measures current flow through electrochemical cells between two electrodes while a constant external voltage is applied
Clark Electrode->platinum cathode is surrounded by_____
tubular silver anode
Clark Electrode” → pO2 electrode
Platinum cathode surrounded by tubular silver anode
Oxygen diffuses through polymeric membrane to internal electrolyte solution, reduced at the
platinum cathode
Measures the amount of current flow in a circuit that is related to the amount of oxygen being
reduced at the cathode
Cathode (Red Cat)
• Negative Pole
• Reduction Reaction
• Gain of Electrons
Conductometry
Measurement of electrolytic conductivity
Electrolytes in solution carry a current by migration of ions
- Current is proportional to concentration of the ions

Current is ___________to concentration of the ions ( for conductometry)
proportional
Coulemetry measures
the amount of charge(in coulombs) passing between two electrodes at a FIXED POTENTIAL (based on amperometry) as a result of chemical reaction
Coulometry
Technique in which the charge required to completely electrolyze a sample is measured; measures amount of current passing between two electrodes in an electrochemical cell
- Determines the amount of analyte consumed or produced by measuring the amount of electricity (in coulombs)
- Based on a chemical reaction
Number of coulombs = direct measurement of quantitative oxidation or reduction of an electroactive species at one
of the electrodes
The more of an analyte is present, the higher charge measured
Produces an insoluble product
Number of coulombs
Direct measurement of quantitative oxidation or reduction of an electroactive species at one of the electrodes
The more of an analyte is present, the higher charge measured
Produces an insoluble product
LECTURE 19:
INSTRUMENTATION – CHROMATOGRAPHY
Chromatography
Physical separation technique that separates solutes dissolved in a common solvent
Particles in the mobile phase with higher affinity for the stationary phase migrate slower than those with a lower affinity (migrate faster)
A Mobile and Stationary Phase
Mobile Phase
phase that carries the sample through a stationary phase; usually gas or liquid
Stationary Phase
a fixed phase through/over which the mobile phase (sample) passes; usually solid
How are the analytes separated ?
Affinity, Size Exclusion
Where is the Stationary Phase ?
Column, Planar (flat)
Retention Factor (R f )
Distance leading edge of component moves/ Total distance solvent front moves
Find Unknown Components
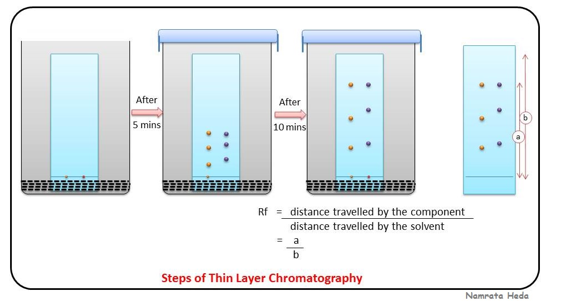
Planar Chromatography
Stationary phase is planar (flat)
Paper layered with stationary phase (paper chromatography)
Solid phase on glass plate support (thin layer chromatography)
Column Chromatography
Stationary phase coated onto particles which are placed in or coated onto a tube or column
Two Main Types
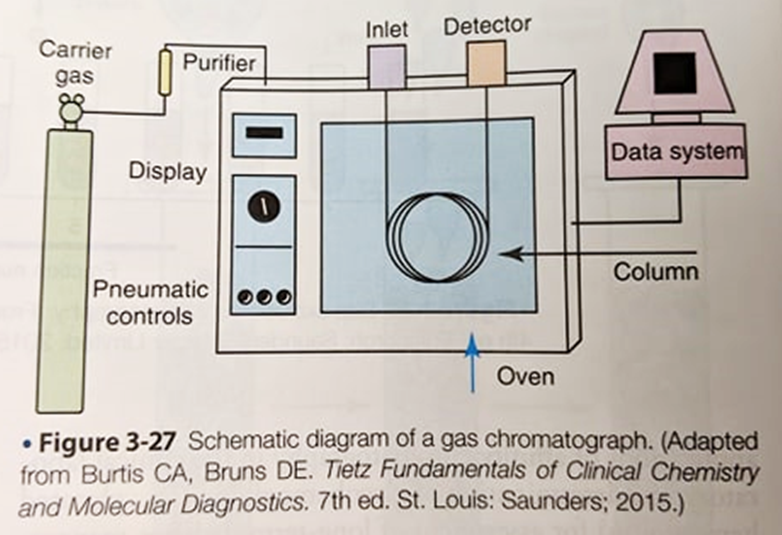
Gas Chromatography
Liquid Chromatography
Gas Chromatography
Mobile phase = carrier gas (helium, hydrogen, or nitrogen)
Moves volatile sample through the column stationary phase
Solutes separated based on differences in vapor pressure and interactions with the stationary phase
More volatile/Less interactive solute will elute faster than a less volatile/more interactive one
Gas Chromatography - Components
oCarrier gas
oSample injector
Heated
oColumn/Oven
Components separated based on their abilities to bind to stationary phase
oTemperature control
oDetector
oComputer
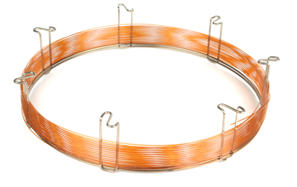
Packed Column
Filled with support materials that are used uncoated
Gas-Solid Chromatography (GSC)
Capillary Column
Non-volatile liquid is coated or chemically bonded with the support particles or directly onto the wall
Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC)
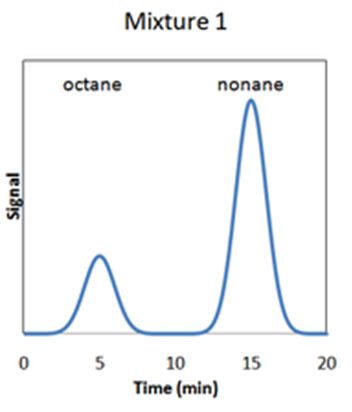
Resolution
How well that analytes are separated by chromatography
Measured betweentwo peaks on chromatogram
Peaks characterized based on retention time and width
Column - Liquid Chromatography (LC)
Liquid mobile phase
Components similar to GC but LC requires a solvent reservoir and pump
Columns much smaller diameter
Capillary columns <1 mm à fused silica
Detectors: Fluorometer, UV Vis Spectrophotometer, electrochemical
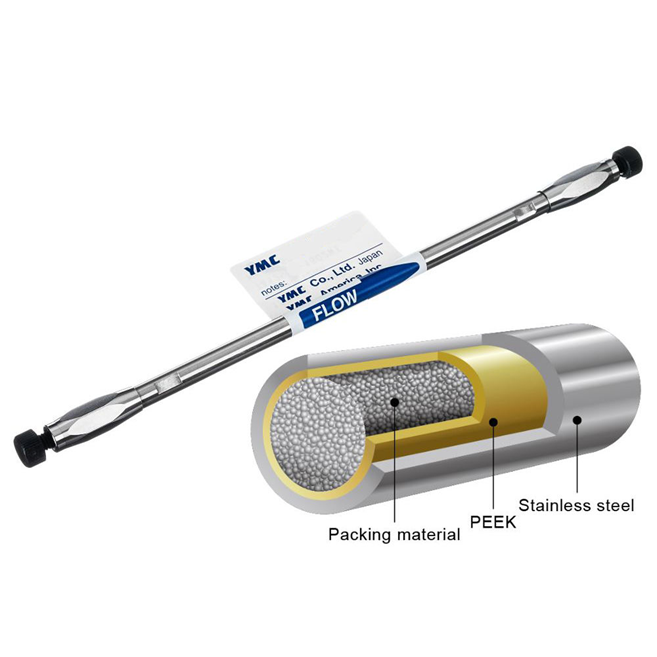

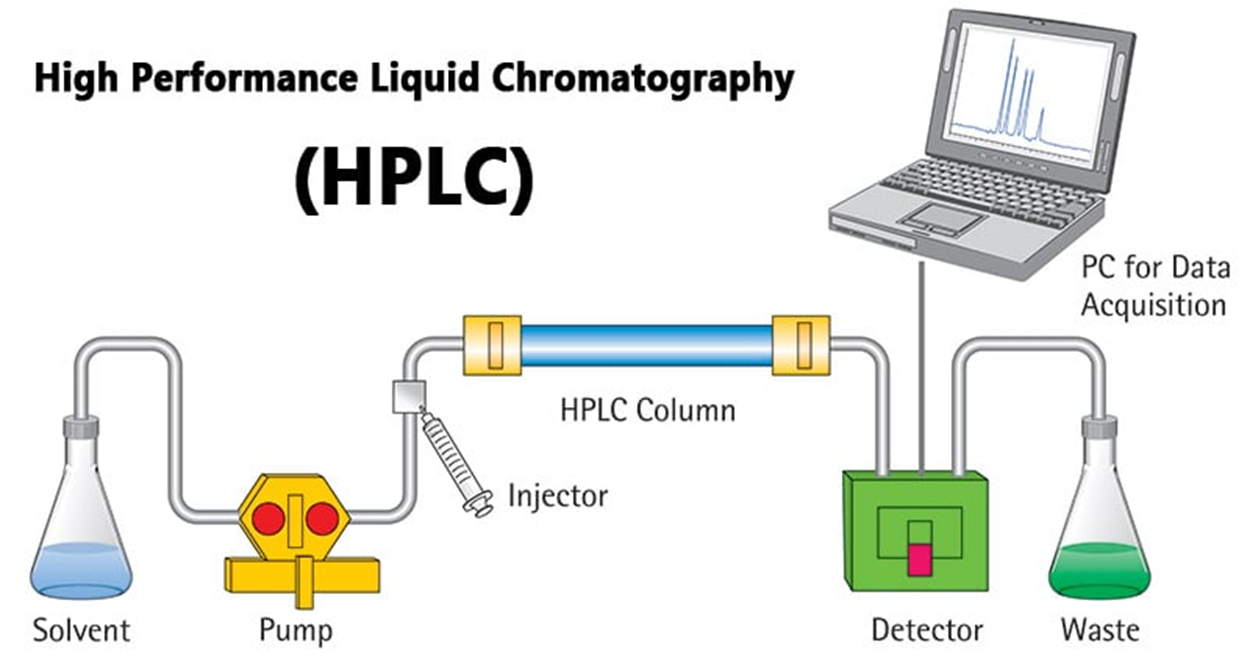
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Uses pressure for faster separations