BYU Cell 220 Lecture Exam 3 (Gonda)
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
331 Terms
What does blood transport?
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and waste products
Blood and lymph is what type of tissue?
fluid connective tissue
How does blood regulate the body
Absorbs and distributes heat, regulates body pH and fluid levels
How does blood defend the body?
Protects from infection, transports infection-fighting antibodies, forms blood clots
What percentage of blood is plasma?
55%
What percentage of blood is buffy coat?
less than 1%
What is the buffy coat made up of?
leukocytes (white blood cells) and platelets
What percentage of blood is erythrocytes
about 44%
What percentage of plasma is water by weight?
92% by weight
What percentage of plasma is proteins by weight?
7%
What are the proteins in plasma
Albumins
Globulins
Fibrinogen
Regulatory proteins
other solutes in plasma
electrolytes, nutrients, respiratory gases, waste products
What are erythrocytes?
red blood cells (RBCs)
- Small biconcave discs -allows gases to be loaded and unloaded efficiently.
- no nucleus or organelles
- they bend as they pass through vessels
What do erythrocytes do?
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
What are erythrocytes filled with?
hemoglobin
What do regulatory T cells do
suppress immune response to keep it under control and turn it off when infection is over
What happens when B cells become activated
They divide and either become plasma cells or memory B cells
What do plasma cells do (B lymphocytes)
Produce immunoglobulins (antibodies) and those antibodies bind to antigens to take them for destruction
What do memory B cells do
Patrol body after an attack and are easily activated if infected again
What is the life cycle of a erythrocyte?
- Form in red bone marrow
- Circulate in bloodstream for up to 120 days
- Phagocytized in liver, spleen, and bone marrow
- Broken down and reused
What does the heme in a erythrocyte get converted into?
Bilirubin and secreted in bile by the liver
What is polycythemia
Too many erythrocytes (RBC) in the blood, increasing the viscosity of blood and placing strain on the heart
What is anemia
Low levels of erythrocytes (RBCs) or hemoglobin, leading to low oxygen levels
What is another name for leukocytes
White blood cells
What do leukocytes do
Initiate the immune response and defend against pathogens (larger than erythrocytes and contains a nucleus & organelles)
What is diapedesis
WBCs leave the bloodstream and enter tissues
What is chemotaxis
WBCs are attracted to site of infection by damaged cells, dead cells, or invading pathogens
What are the two types of leukocytes?
granulocytes and agranulocytes
What are the three types of granulocytes (leukocyte)
Neutrophil, eosinophil, and basophil
What are the two types of agranulocytes (leukocyte)
Monocyte and lymphocyte
What is the function of a Neutrophil (granulocyte leukocyte)
Phagocytizes pathogens
What is the function of a Eosinophil (granulocyte leukocyte)
Destroys parasites and is important in allergies
What is the function of a Basophil (granulocyte leukocyte)
Promotes inflammation by releasing histamine and heparin
What is the function of a Monocyte (agranulocyte leukocyte)
Exits bloodstream and becomes a macrophage; phagocytizes pathogens and debris
What is the function of a Lymphocyte (agranulocyte leukocyte)
Resides in lymphatic tissue. Coordinates immune response (T, B, and natural killer cells)
What is leukocytosis
High WBC count that results from infection, inflammation, or extreme stress
What is leukopenia
Low WBC count that results from certain types of viral or bacterial infections (HIV and AIDS)
What is leukemia
Cancer in the leukocyte forming cells in the bone marrow; proliferation of abnormal leukocytes (cancer takes over bone marrow and slow production of erythrocytes and platelets, causing bleeding and anemia)
What is another name for platelets
Thrombocytes
Where do platelets come from
Cell fragments of megakaryocytic
How long do platelets live for
8 to 10 days
What do blood clots consist of
Fibrin, platelets, and trapped erythrocytes
What is thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count from damage to bone marrow, chemotherapy, leukemia, or overactive spleen
What is thrombocytosis
High platelet count from disease of blood or bone marrow, cancer, removal of spleen, or an infection
What type of antigens does type A blood have?
Antigen A
What type of antigen does blood type B have?
B antigen
Antigen for AB blood
AB antigen
Antigen for O blood
None
What type of antibody is in blood type A plasma
Anti-B
What type of antibody is in blood type B plasma
Anti-A
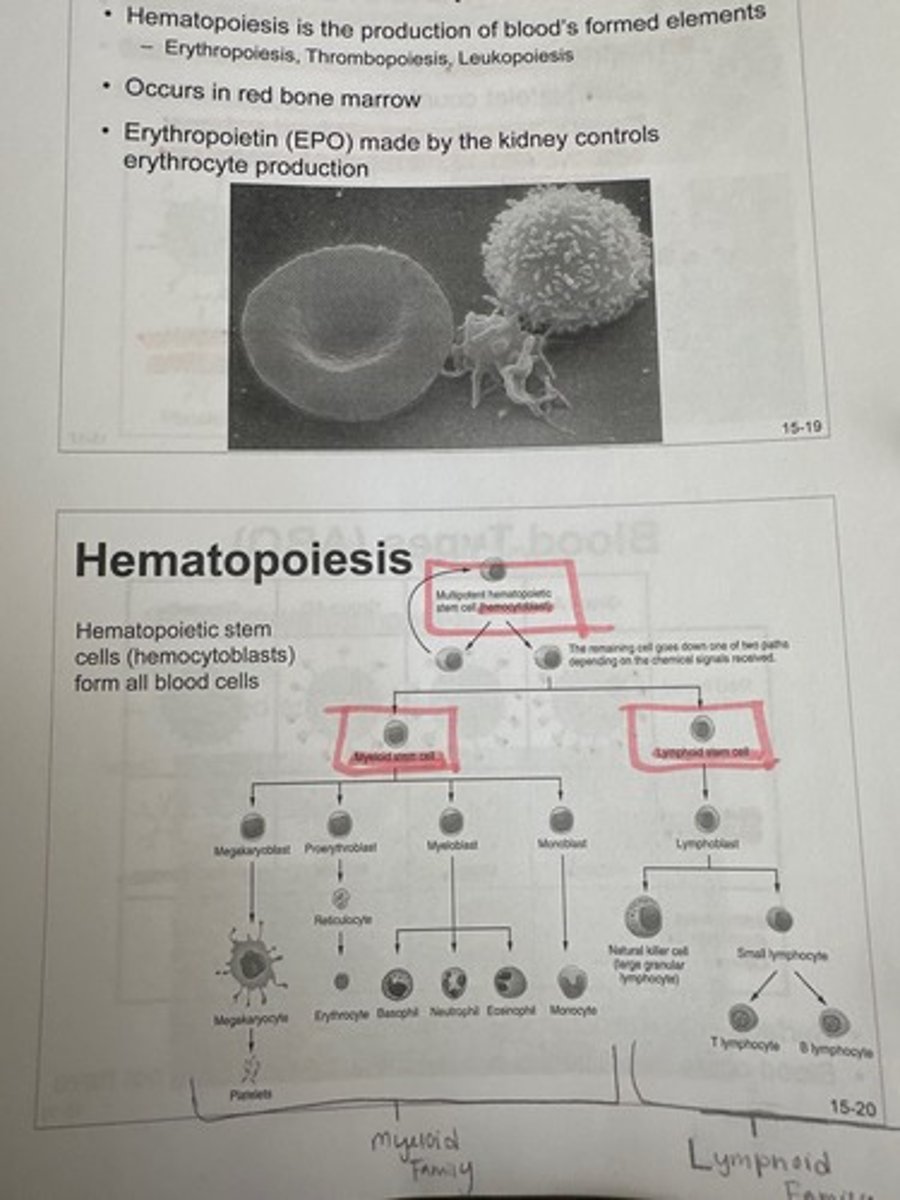
Erythropoietin
Made by the kidney to control RBC formation in the bone marrow.
Chart
What type of antibody is in blood type AB plasma
None
What type of antibody is in blood type O plasma
Anti-A and Anti-B
What do natural killer cells do
Respond to multiple antigens to kill a wide variety of infected cells and some cancerous cells
What is lymphoma
Cancer of the lymphatic cells, often presents as an enlarged lymph node
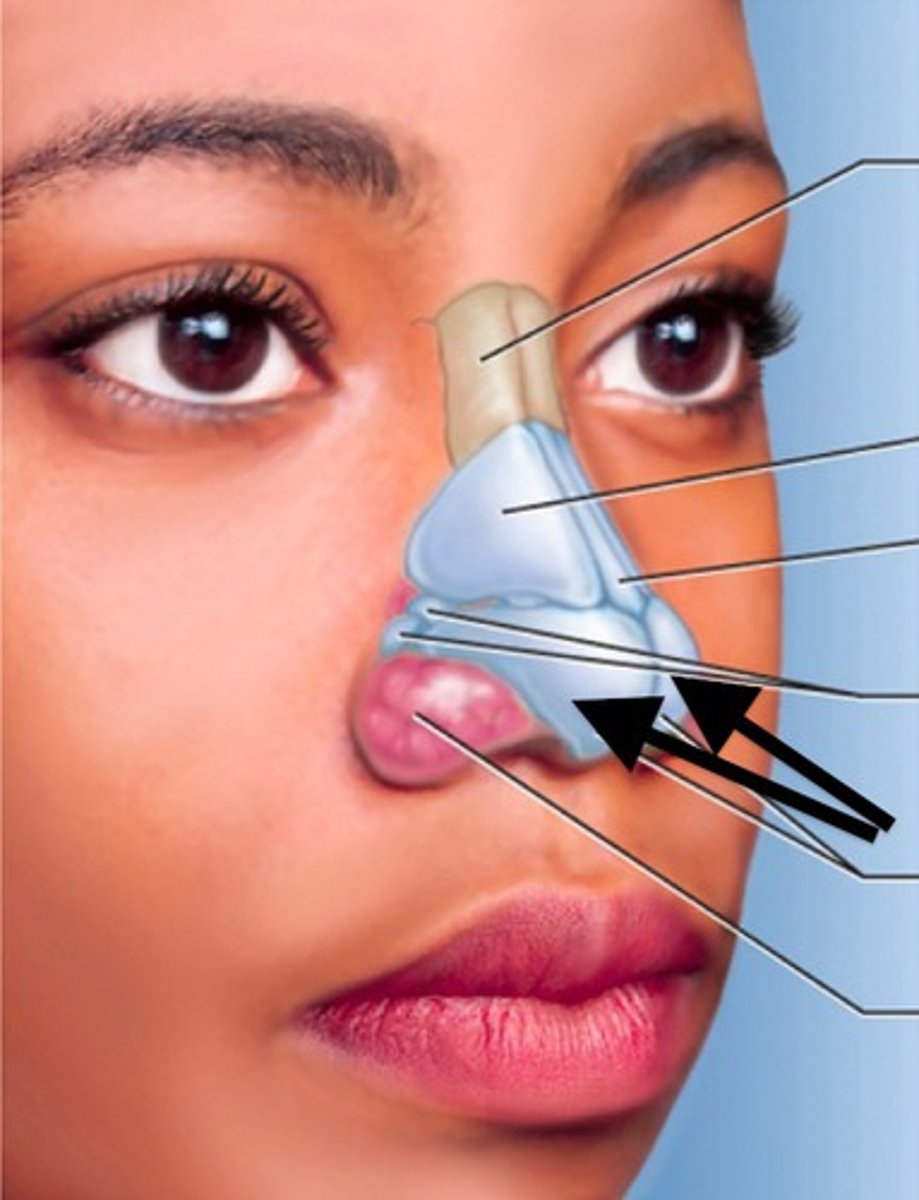
What does the upper respiratory tract consist of
Sinuses, nasal cavity, and pharynx
What does the lower respiratory tract consist of
Parynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lung alveoli
What is hematopoiesis
The production of the bloods formed elements (erythropoiesis, Thrombopoiesis, leukopoiesis)
Where does hematopoiesis occur
Red bone marrow
Functions of the respiratory system
- Breathing
- Gas exchange
- Gas conditioning (warm, humidify, and cleanse air)
- Sound production
- Olfaction
- Defense
Alar cartilage
What is the average cardiac output
5.25 L/min
Heart beats 75/min, 108000/day
Functions as a dual pump
Heart is oriented
Within the mediastinum
Lies on the diaphragm, posterior to the sternum
Base: posterior and superior surface of the heart
Apex: anterior and inferior, points to the left hip
What are the layers of the pericardium
fibrous and serous (parietal and visceral)
What does the pericardial cavity contain
Serous fluid
What are the functions of the pericardium
-prevents undesired movement
-prevents overfilling of the heart
-reduces friction
What are the three layers of the heart wall
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
What type of tissue is the epicardium and endocardium made up of
Simple squamous epithelium
What does the pulmonary circuit of the heart entail
Carrying of blood to and from the lungs with the right ventricle as the pump
What does the systemic circuit of the heart entail
Transportation of blood to and from body tissues with the left ventricle as the pump
Coronary sinus
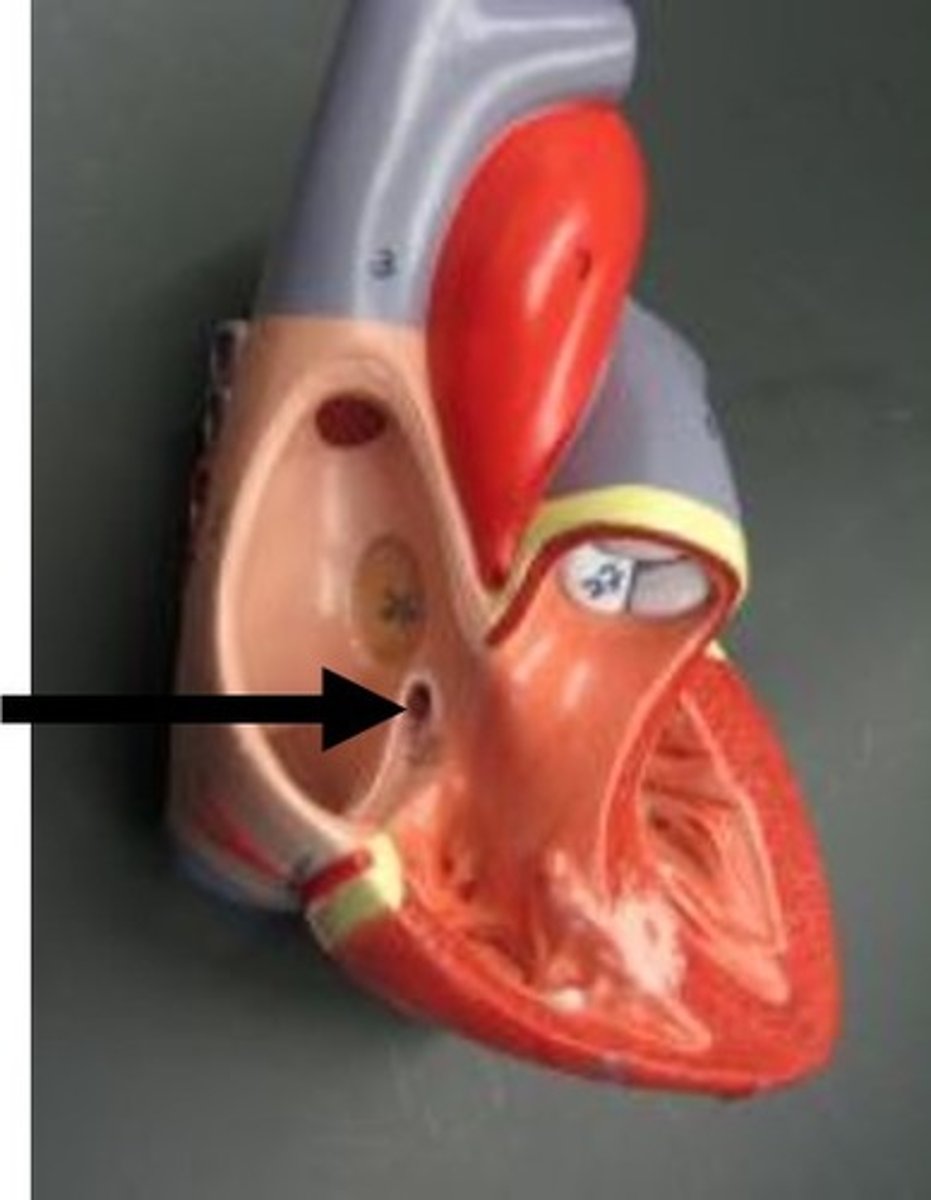
fossa ovalis
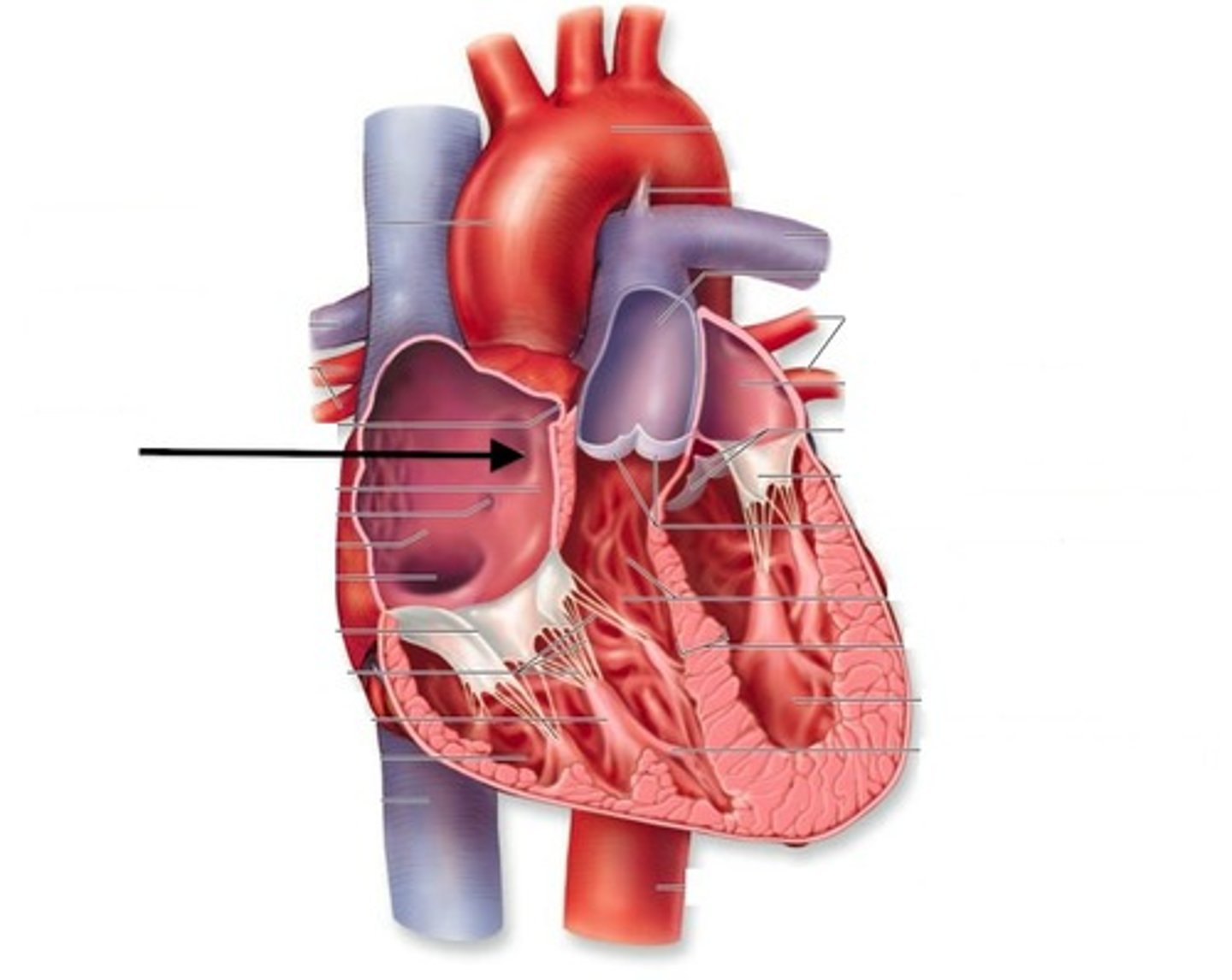
What is the fossa ovals during fetal circulation
Foramen oval
Sinoatrial node
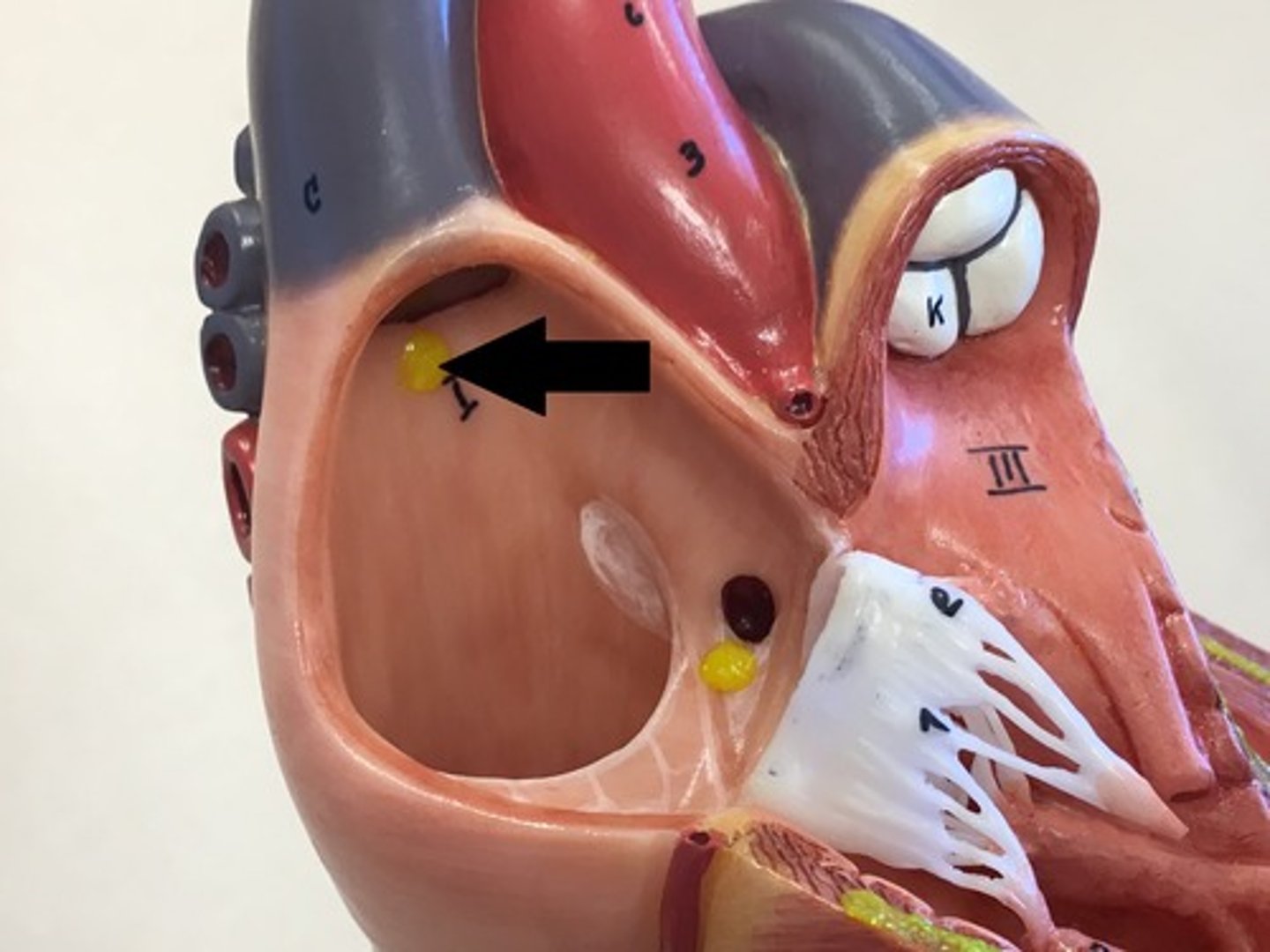
Atrioventricular node
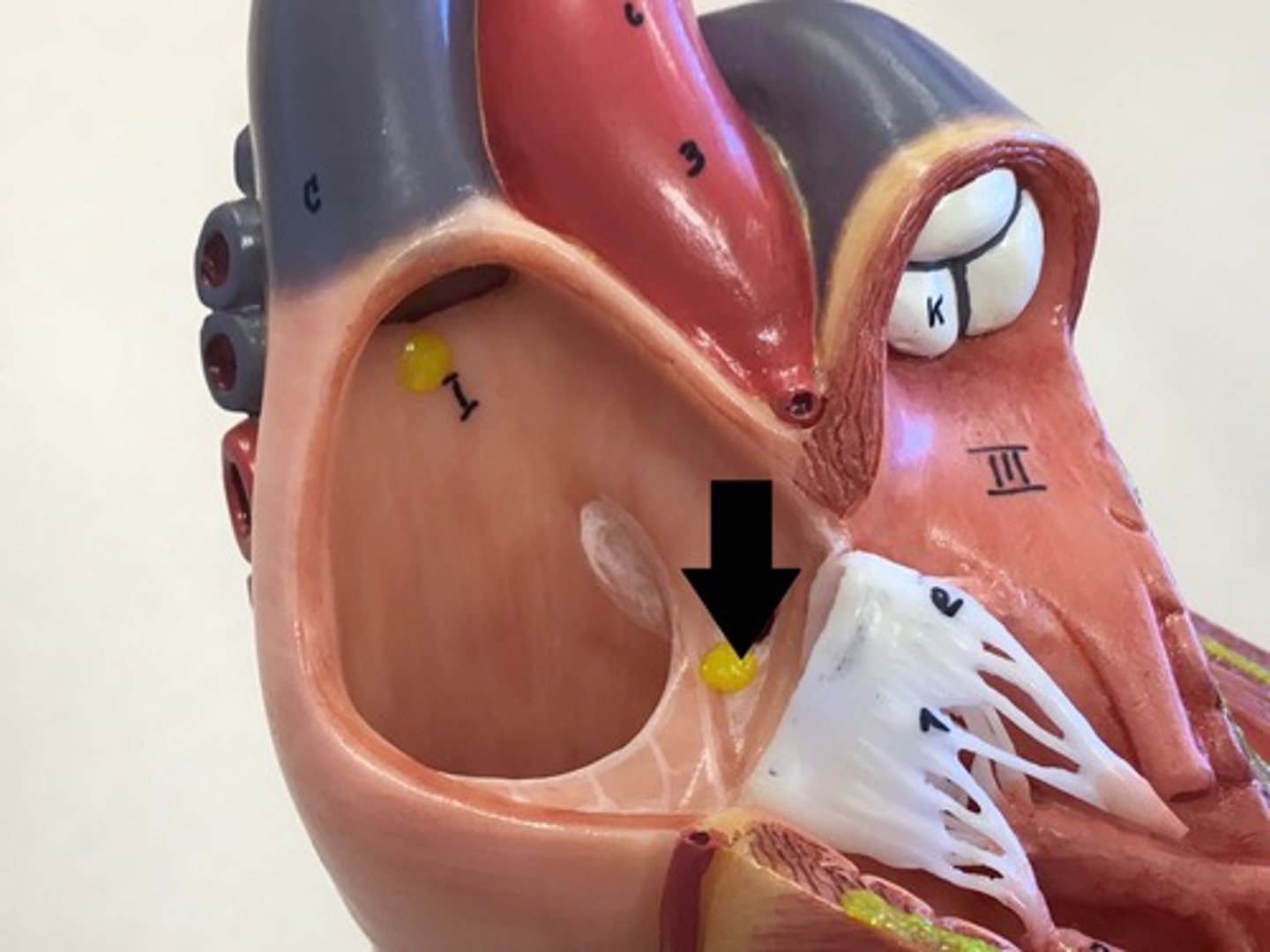
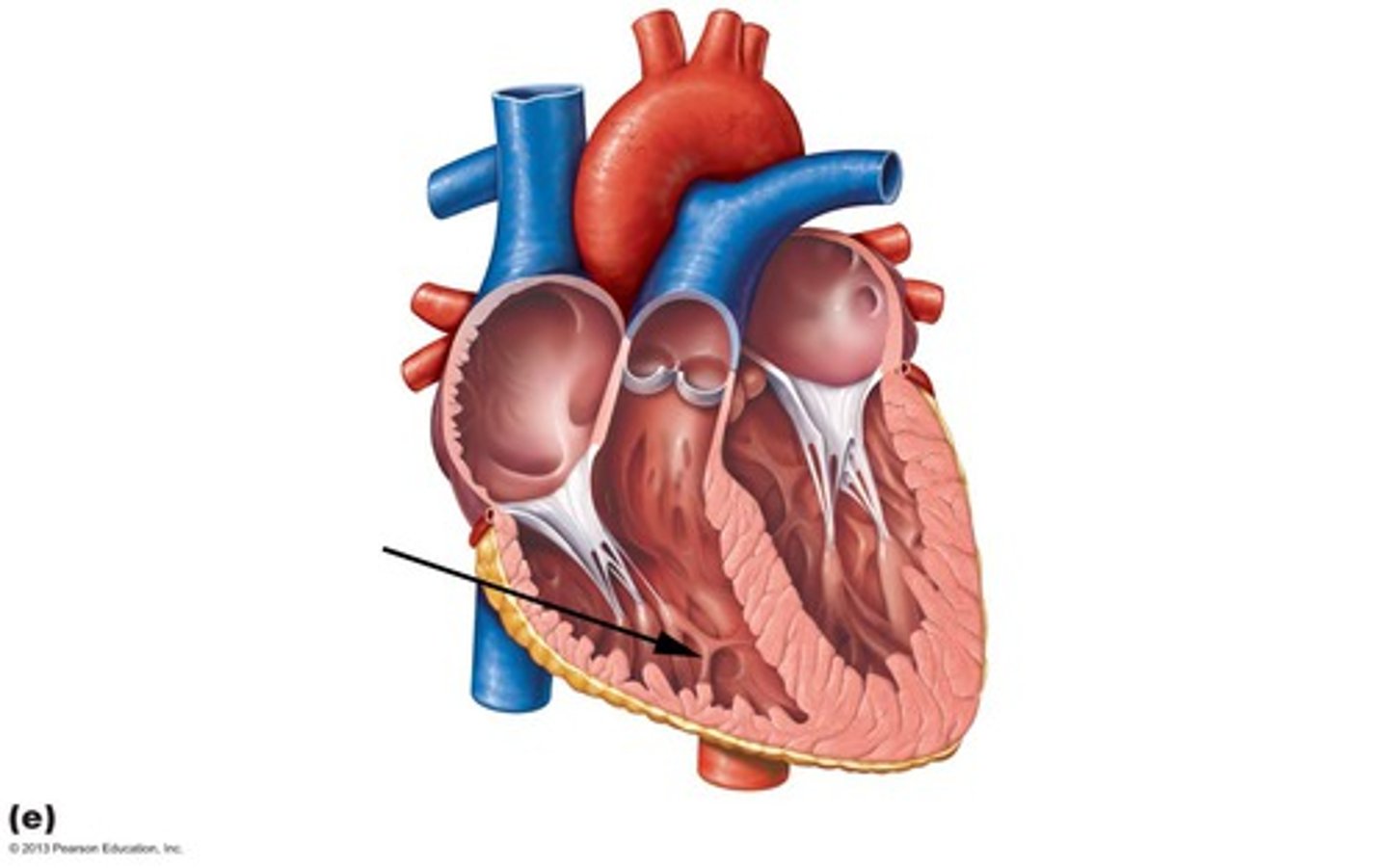
trabecular carneae
Fibrous skeleton
Dense connective tissue located between the atria and the ventricles
Functions:
- separates the atria and ventricles (structurally and electrically)
- anchors heart valves
- framework for cardiac muscle attachment
Characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue
striated and involuntary, 1-2 nuclei
How are cardiac muscle cells joined
Intercalated discs
What do gap junctions in cardiac muscle cells do
Increase flow of electrical current
What do desmosomes in the cardiac muscle cells do
prevent cardiac muscle from pulling apart
Cardiac muscle has...
More mitochondria and ATP than skeletal muscles
What is another name for the sinoatrial node
Pacemaker
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system emerge for the heart
Medulla
Which parasympathetic nerve is in charge of the cardiac plexus
Vagus nerve X, decreases heart rate
Where does the sympathetic nervous system emerge for the heart
Thoracic spinal cord
Where does the sympathetic nervous system synapse for the heart
Sympathetic chain ganglia
Coronary circulation
Brings nutrients and oxygen to the heart wall
What does inadequate coronary circulation result in
Heart attack or myocardial infarction
What is heart failure
Progressive weakening of the heart, meaning the heart can no longer pump enough blood to meet the ends of the body
Weakened ventricles fail to empty completely and blood backs up
May result in edema (congestion) in the tissues outside the pulmonary or systemic circuits
What do arteries do
Always transports blood away from the heart
Carry oxygen rich blood in the systemic circuit
Carry oxygen poor blood in the pulmonary circuit and umbilical arteries
What do veins do
Transport blood to the heart
Carry oxygen poor blood in the systemic circuit
Carry oxygen rich blood in the pulmonary circuit and umbilical vein
What happens in the capillaries
Gas and nutrient exchange between blood and tissues
What is the most inner tunic of vessels
Lumen (the space)
Vessel Tunics image
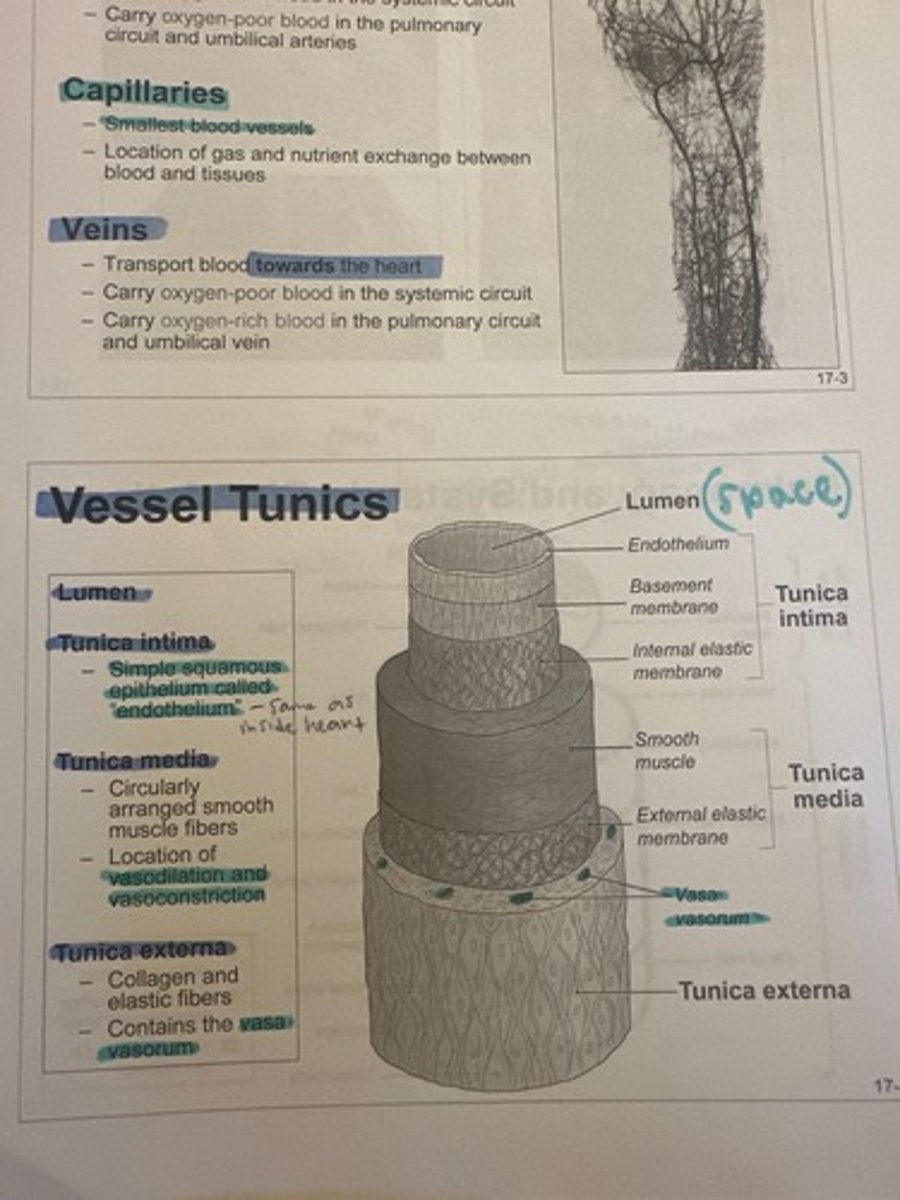
What type of tissue is the tunica intima
simple squamous epithelium (endothelium)
What is the composition of the tunica media
Circularly arranged smooth muscle fibers
What takes place in the tunica media
Vasodilation and vasoconstriction
What is the tunica external composed of
Collagen and elastic fibers; contains the vasa vasorum