Invertebrates #19
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Flagellum
the motor appendage of motile cells
its location defines if the organism is a Fungi or an Animal
Metazoa
Animals
evolved 1 bill yrs ago
characteristics:
multicellular heterotrophs
cell that lack a cell wall, and are held together with collagen
embryonic development includes a blastula stage
many of the major evolutionary steps in animals are defined by embryology
Embryology
the study of early organismal development
process of an organism growing from a zygote to a fetus
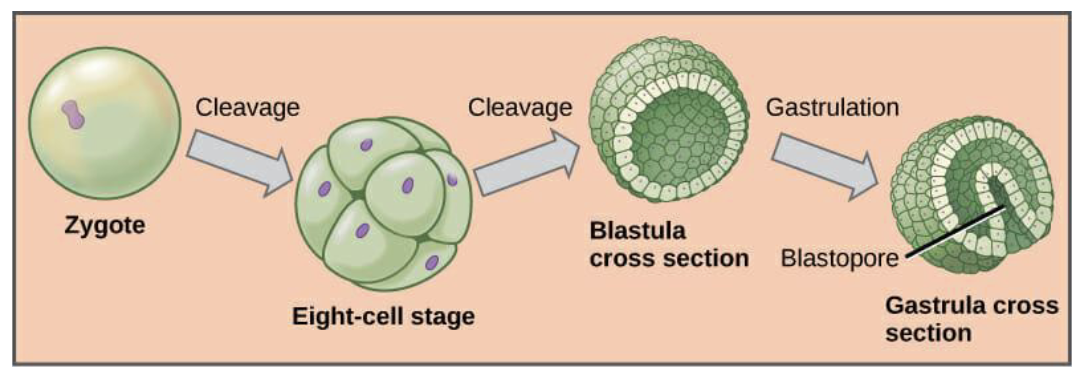
Blastula
the stage through which all animal embryos develop
embryo forms a circular form that is hollow on the inside
Cambrian Period
when all extant animal phyla evolved
when animal diversity exploded (cambrian explosion)
540 mill yrs ago
predominantly marine animals
animals began to venture onto land
Ordovician Period
arthropods now completely living on land
Arachnids, Myriapods, & Hexapods independently became land-dwelling around the same time as plants
460 mill yrs ago
Tetrapod
dont make it onto land until the Devonian period (after the Ordovician Period and the Cambrian period)
Denonvian Period
360 mill yrs ago
when tetrapods get to land
Porifera
sponges
sessile animals that lack tissues
cells are differentiated into different roles, but they do not work together for a specific function
suspension feeders
primarily marine
Cnidaria
Hydras, Corals, Jellyfish
symmetrical (1 gastrovascular cavity - mouth & anus use same hole)
have a top and bottom but not lateral differentiation
Predatory:
use tentacles tipped with spear-like stinging cells to capture prey
2 Subhyla:
Medusozoa - jellyfish & hydra
Anthozoa - corals & anemones
Mollusca
evolved eyes multiple times within the phylum
major subgroups:
Bivalvia - clams, mussels, scallops, oysters
Gastropoda - snails, slugs
Cephalopoda - octopus, squid, nautilus
Annelida
segmented worms
3 subgroups:
Polychaetes, Oligoshaetes, Hirudinea
earthworms
decomposers
leeches (hirudinea)
parasitic or predatory
Platyhelminthes
flatworms
free-living predators
parasites
lack circulatory and respiratory systems
species important medically:
trematoda
cestoda (tapeworms)
Nematoda
Roundworms
found everywhere on earth
Hugely important to humans, both as a research subject,
as agricultural pests, and as insect pest-control
diverse, thread-like worms found in almost every habitat, from soil and water to parasites in plants and animals
Arthropoda
5 groups:
Chelicerata
spiders, scorpions, ticks
marine, freshwater, and terrestrial
predators, parasites, and decomposers
8 walking legs + 2 pairs of feeding limbs
Myriapoda
millipedes - predators & 1 pair of legs per body segment
centipedes - decomposers & 2 pairs of legs per body segment
terrestrial
Crustacea
crabs, lobster, shrinp
marine, freshwater, and terrestrial
Insects
3 body segments: head, thorax, abdomen
3 pairs of legs & 2 pairs of wings
terrestrial & freshwater
NO MARINE bc their respiratory systems requires oxygen/air, and their exoskeletons (hardened with oxygen) aren't suited for saltwater
Echinodermata
starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers
strictly marine
adults are 5-sided (pentaradial)
larvae are bilateral (2 sided)
have a unique water vascular system that powers their tube feet
Chordata
an animal phylum containing all vertebrates (like humans, fish, birds) and two invertebrate groups (tunicates/sea squirts & lancelets)
Bilateria
Bilateral symmetry
most animals
have a top and bottom, a front and back, and a left and right
Gastrulation
a process when the embryo starts to form a pouch
3 layers of cells form in the embryo which get locked into a developmental pathway for tissues
Germ Layers
3 layers in embryonic development
determine the developmental fate of tissues
Endoderm
innermost layer (yellow) of the embryo
will go on to become:
digestive system (liver, pancreas, bladder)
Lungs
Thyroid & parathyroid
Mesoderm
middle layer (blue) of the embryo
will go on to become:
muscles (cardiac, skeletal etc.)
bone, cartilage, and connective tissues
fat tissues
circulatory system
lymphatic system
dentine of teeth
spleen
genitals & reproductive tissue
Ectoderm
outermost layer (brown) of the embryo
will go on to become:
the external surface of the body (skin, hair, etc.)
the Nervous system (nerves, brain, spinal cord)
Blastopore
the depression/pouch formed in gastrulation
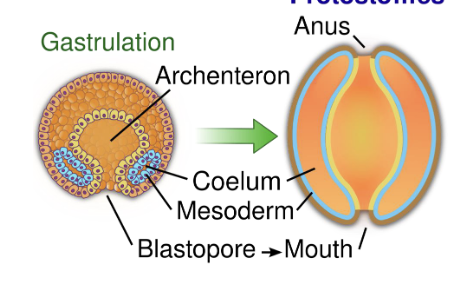
Protostome
Blastopore becomes the mouth of the organism
& a second opening develops to become the anus
2 major groups:
Lophotrochozoa
Ecdysozoa
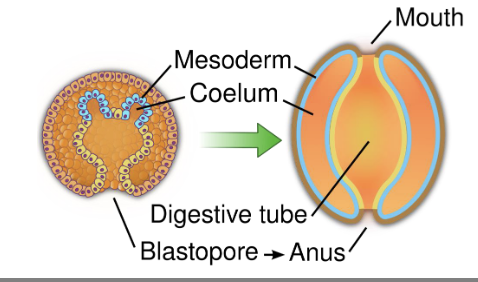
Deuterostome
Blastopore becomes the anus of the organism
& a second opening develops to become the mouth
Ecdysozoa
a type of Protostomes
have a tough cuticle that they shed in order to grow
most diverse group of organisms on the planet