ENVI
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
Application of scientific principles to improve the natural environment for the development and benefit of the society.
ETHICS
Define the code that a society or group of people adhete to
Moral
Delve into right and wrong at a much deeper level, which is about personal and spiritual
Environment
refers to the surroundings in which a person, animal,plant and other microorganisms live or operate.
Engineering
refers to the application of scientific principles for the planning, design, operation and maintenance of structures, equipment or systems for the development and benefit of the society
Biotic Environment
It compose of plants, animals, microorganisms, and human beings
Abiotic Environment
It compose of land, water and air
Synergism
The process where more harmful substance are produced from less harmful ones
Mesosphere
Part of the atmosphere where most of the photochemical reactions take place
Herbivores
Organisms that belong to the second trophic level
Niche
It is identified as the role of the organisms in the community
Ammonification
This is the process where decomposers return back the nitrogen to the soils through the remains and waste of plants and animals
Biomagnification
This involves the accumulation of trace metals through each species of the food chain
Nitrogen Fixation
The process of converting nitrogen gas to ammonia is called
Detritivores
These types of organisms feed on the waste of the ecosystem
Dominant plant life
Biomes are distinguised or identified by its
Anaerobic Bacteria
Denitrification is carrried out when bacteria break down nitrates and release nitrogen gas. What are these bacteria?
Bioaccumulation
The total uptake of chemicals by an organism from food items as well as via mass transport of dissolved chemicals
20
The permissible color for domestic water supply in ppm is
Turbidity
The resistance of water to the passage of light through it is a measure of the water’s
Suspended and dissolved solids
The total solids in water are due to the presense of
Hardness
Which of the following is not a physical characteristic of waste water?
Hydrogen Sulfide
This is the gas responsible for the rotten egg odor of waste water
Cadmium
A trace metal which causes Itai-itai disease
Eutrophication
It is a phenomenon that results in the overabundance of algae growth in bodies of water. It is also the natural process of nutrient enrichment that occurs over tim in a body of water
Iron and Manganese
The red brownish color of water is due to the presence of dissolved impurities of
Dissolved CO2
The alkalinity of waste water is due to the presence of the following except
CaCo3
The hardness of water is usually expressed as parts per million of
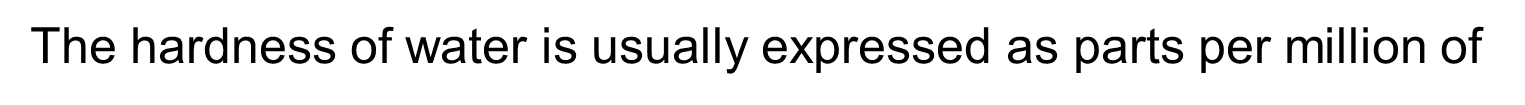
BOD - BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND
Which of the following can be used to measure the assimilative capacity of a stream?
Primary Treatment
Type of wastewater treatment that employs physical and chemical treatment methods to remove or reduce a high percentage of suspended solid and toxic materials
Screening
This is a process whereby coarse matter ( suspended or floating) of a certaing size can be strained out of flowing water with the aid of bars, fine wires or rocks.
Sedimentation
The removal of all settable particles rendered settable under the influence of gravity, basically the theory of gravity under the influence of which all particles heavier then water tend to settle down
Water
Which of the following is not used as an adsorbent material?
Mud Balls
Insufficient washing of sand grains in a rapid sand filter causes
Sulfuric Acid
Which of the following is not use for the disinfection of water
pH = 6-9
Most aquatic organisms can survive in a pH range of about
Aluminum Sulfate
which of the following is the most commonly used coagulating agent?
Mathenoglobenemia
Nitrates more than 50 ppm in water leads to a disease called
Sterilization
The process of disinfecting bacteria is called
Residual Chlorine
The amount of chlorine available in water after disinfection is called___
Temporary Hardness
What substance in water is removed in the Lime Soda Process?
Coagulation
An electrochemical process used in the removal of colloidal matter in wastewater through reduction of electrostatic charges surrounding the solids is_____
Sludge
These are accumulated solids removed from separation equipment such as settling tanks and clarifiers.
Chlorination
Water treatment that destroys disease-causing bacteria, nuisance bacteria, parasites and other organisms and removes soluble chlorine, manganese and hydrogen sulfide from water
Minamata
A neurological diesease characterized by trembling, inability to walk and speak, serius combulsions that can lead to death due to ingestion of mercury
Tertiary Treatment
Type of wastewater treatment that employs biological methods to remove fine suspended colloidal and dissolved organics by biochemical oxidation
Biological treatment is most practical
A wastewater with a BOD/COD = 1 indicates that ____
Activated Sludge Process
A continuous re-circulating aerobic biochemical process that keeps cells in a suspended growth
Total Count Test
When a sample of water is added to a medium of agar and incubated at 37oC for 24 hours, colonies of bacteria formed are counted. This test is called____
Dissolved Gases
Aeration of water is done to remove
DENR Administrative Order No. 34
It is the legislation that presents the revised water usage and classification
Class B
The class of water intended for primary contact recreation such as bathing, swimming,skin diving, etc.
Kyoto Protocol
A global treaty that aims to regulation emissions of greenhouse gases
Superadiabatic
What is the atmospheric condition when the lapse rate > 10oC /km
Agenda 21
This provides the blue print action towards sustainable development
Fly Ash
It is a generic term used to describe the particulate matter carried in the effluent gas from furnaces buring fossil fuels.
NOx
These are reddish brown oxides in concentrated form which may produce an abnormal accummulation of fluids in the lungs
Settling Chamber
These are closed compartments that use gravitational force to extract dust and mist and typically used only for larger particles
Montreal Protocol
A global treaty that aims to diminish and eventually phase out CFCs
ozone
t is a very unstable gas use for disinfection, a very powerful oxidant capable of oxidizing 200 t0 300 times more that chlorine and can reduce complex taste and odor in water.
Thermal Inversion
A phenomenon where a cold layer of air becomes trapped by a layer or warmer air above due to a lack of wind circulation or the presence or certain tropographical features such as mountains that results to air pollution being trapped in the lower, cooler laters of the troposphere
SMOG
This is described as the cloud of air pollution trapped by thermal inversion
Stockholm Convention
A global treaty that aims to protect human health and environment from POPs
Peroxiacetylnitrate
PAN is a powerful lachrymator or tear producer formed from unburned hydrocarbons, aldehydes, nitrogen oxides and oxygen. PAN stands for____
CHLORINE
Component of CFC’s that causes destruction of 100,000 molecules ozone
FORMALDEHYDE
It is used as a bonding agent in building and furniture construction which may cause drowsiness, nausea and headaches when exposed to low level concentration
Leachate
The liquid produced when water perculates through any permeable material. It can contain either dissolved or suspended material, or usually both, anoxic, acidic, rich in organic acid groups, sulfate ions and with hihg concentration of common metal ions especially iron
PVC
Recyclable Material Labelled as 3
composting
It is defined as the controlled decomposition of organic materials, such as leaves, grass, and food scraps
Tertiary
This is the type of recycling that involves recovery of chemicals and energy from post consumer
RA 9003
Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000 is otherwise known as ________________.
forestry projects
Which of the following is not classified as a heavy industry in the list of environmentally critical projects?
RA - REPUBLIC ACT
A piece of legislation used to create a policy in order to carry out the principles of the constitution
Crafted and passed by the congress of the Philippines and approved by the President of the Philippines
PD - Presidential Decree
an innovation made by President FEM with the proclamtion of Martial Law
EO - Executive Order
acts of the President providing for rules of a general or permanent character in implementation or execution of constitutional or statutory powers
DAO - DENR ADMINISTRATIVE ORDER
enforceable order issued by the Department of Environment and Natural Resources to the public to take certain corrective action or to refrain from any activity
CCO - CHEMICAL CONTROL ORDER
laws that are meant to control and regulate the use and disposal of asbestos into the environment to avoid the adverse consequences
IRR - IMPLEMENTING RULES & RRGULATIONS
- very specific policies and often address highly technical details of legislation.
- facilitate the implementation of a legislation
RA NO. 3931
•An act creating the National Water and Air Pollution Control Commission (NWAPCC)
July 10, 1967
PD 1251
Imposing a fee on Operating Mining Companies to be known as Mine Wastes and Tailing Fee to compensate for Damages to Private landowners and for other purposes
PD 1151
Philippine Environmental Policy
Defines the general policies on the pursuit of a better quality of life for the present and future generations
It mandates the undertaking of EIA for all projects which may significantly affect the environment
June 6, 1977
PD 1152
PHILIPPINE ENVIRONMENTAL CODE
It defined the objectives of the policy and strategies for various aspect of environmental management, such as air, water quality, natural resource development, land and waste management
It tells about how to implement /enforce PD 1151
PD 984
POLLUTION CONTROL LAW - AUGUST 8, 1976
It seeks to prevent , abate, and control pollution of water, air, and land for a more effective utilization of the resources of the country
RA 6969
•An act to control toxic substances, hazardous, and nuclear wastes
•This Act shall cover the importation, manufacture, processing, handling, storage, transportation, sale, distribution, use and disposal of all unregulated chemical substances and mixtures in the Philippines, including the entry, even in transit, as well as the keeping or storage and disposal of hazardous and nuclear wastes into the country for whatever purpose
DENR Administrative Order 29 series of 1992 (DAO 92-29)
•IRR of RA 6969
•regulate the importation, manufacture, processing, distribution, use and disposal of chemical substances and mixtures that present unreasonable risk and/or injury to health or the environment
Republic Act 8749
•Clean Air Act of 1999
Provides for a comprehensive air pollution control policy
•Stipulates the development of an integrated air quality improvement framework, standards on ambient air quality from mobile and stationary sources and mitigation of all sources of air pollution
PD 953 & 1153
•Laws penalizing illegal cutting of trees
•PD 953 – planting of trees on certain areas and restriction of illegal logging
•PD 1153 – requires all citizen to PLANT A TREE PER MONTH FOR FIVE CONSECUTIVE YEARS
PD 953
planting of trees on certain areas and restriction of illegal logging
PD 1153
requires all citizen to PLANT A TREE PER MONTH FOR FIVE CONSECUTIVE YEARS
RA 9275
Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004 (PCWA)
An act providing for a comprehensive water quality management and for other purposes
RA 7586 – National Integrated Protected Areas System Act of 1992 (NIPAS)
Set forth in detail the processes by which DENR and other concerned institutions and agencies will establish and manage the NIPAS
DAO 2019 – 05 & DAO 1992 – 25 (IRRs of RA 7586)
RA 7942
•Philippine Mining Act of 1995
•An act instituting a new system of mineral resources exploitation, development, utilization and conservation
•DAO 2010 – 21 (Revised IRR)
–All mineral resources in public and private lands within the territory and exclusive economic zone of the Republic of the Philippines are owned by the State. It shall be the responsibility of the State to promote their rational exploration, development, utilization and conservation through the combined efforts of the Government and private sector in order to enhance national growth in a way that effectively safeguards the environment and protects the rights of affected communities.
RA 9175 CHAINSAW LAW
Regulates ownership, possession, sale, importation and use of chainsaw
Chainsaw must be registered before using
RA 1586 EIA (ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT)
before undertaking environmentally critical projects or operating in environmentally critical areas, ensuring environmental protection alongside socio-economic development.
RA 1067 - PHILIPPINE WATER CODE
This decree provides a comprehensive framework for the management of all water resources in the Philippines, including their conservation and protection.
RA 8749
Republic Act in the Philippines that converts the Cawayanan High School in Tubigon, Bohol, into a national high school, renaming it the Cawayanan National High School.
RA 856
refers to the Republic Act No. 856, an act amending the Private Employment Agency Law to provide added protection to applicants for employment, not the Code on Sanitation of the Philippines, which is P.D. 856. The Philippine government has also proposed legislation to amend P.D. 856, also known as the Code on Sanitation of the Philippines, to strengthen sanitation laws.
TROPHOSPHERE
1ST LAYER OF THE ATMOSPHERE
CLOSEST TO EARTH, WHERE WEATHER OCCURS
STRATOSPHERE
2ND LAYER OF ATM
CONTAINS OZONE LAYER