chapter 40: Overview of Muscle Types and Their Functions
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary, Conscious control
Skeletal Muscle Structure
Striated, long multinucleated (cells fuse during embryonic development)
Fibers, cells, bound together by connective tissue (fascia)
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, autoregulatory
cardiac muscle structure
Striated, branched, uni-or binucleated
Cells smaller than skeletal
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary, ANS control
smooth muscle structure
Nonstriated, spindle shaped cells, central nucleus
Sheets of cells
Muscle Basics
Presence of contractile proteins and muscle tissue (phylogeny).
Animals with Muscle Tissue
All metazoans except cnidarians.
Animals with Contractile Proteins
All metazoans (porocytes in sponges regulate water flow).
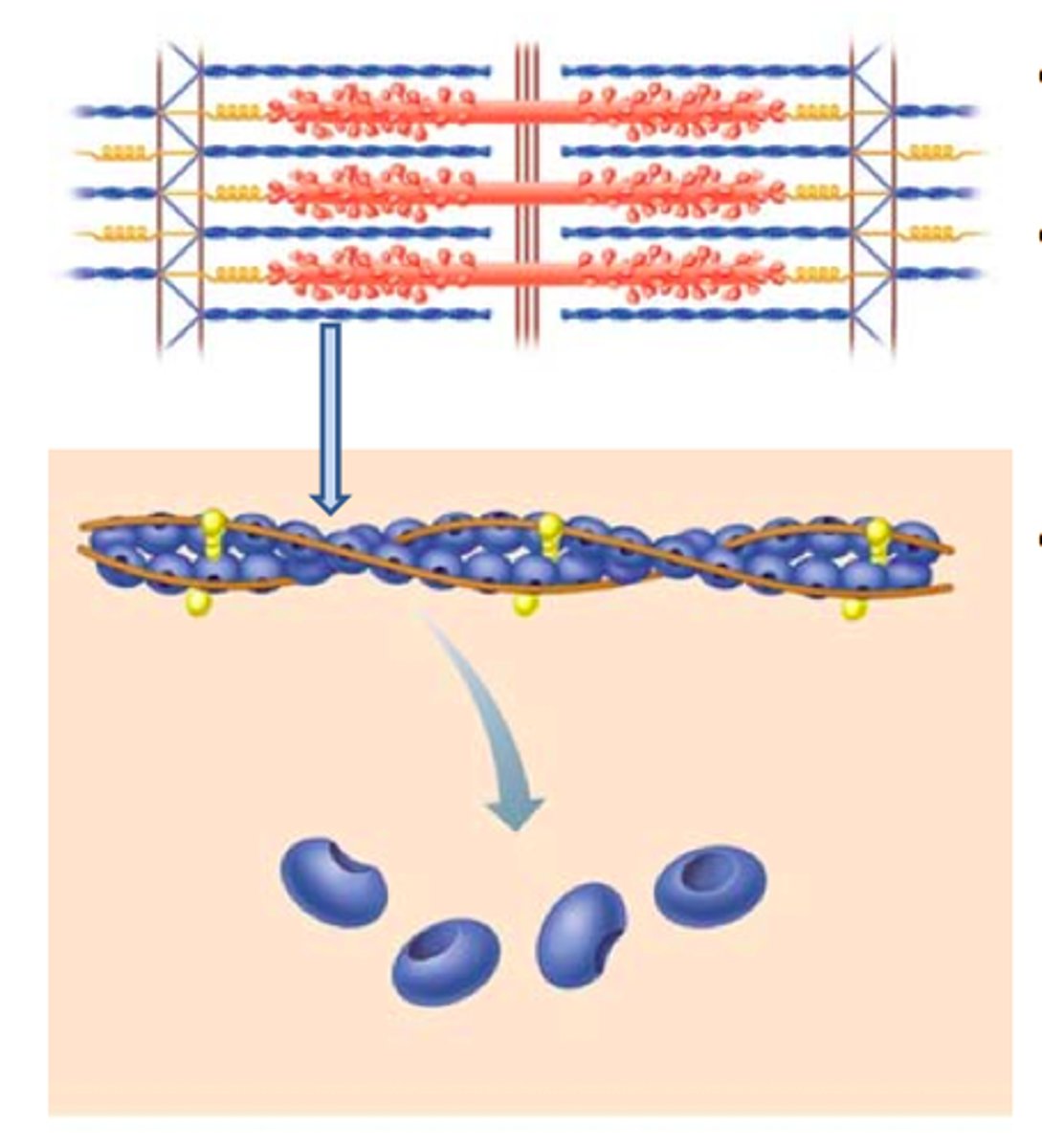
Actin
Thin filaments
tropomyosin and troponin
calcium binding site
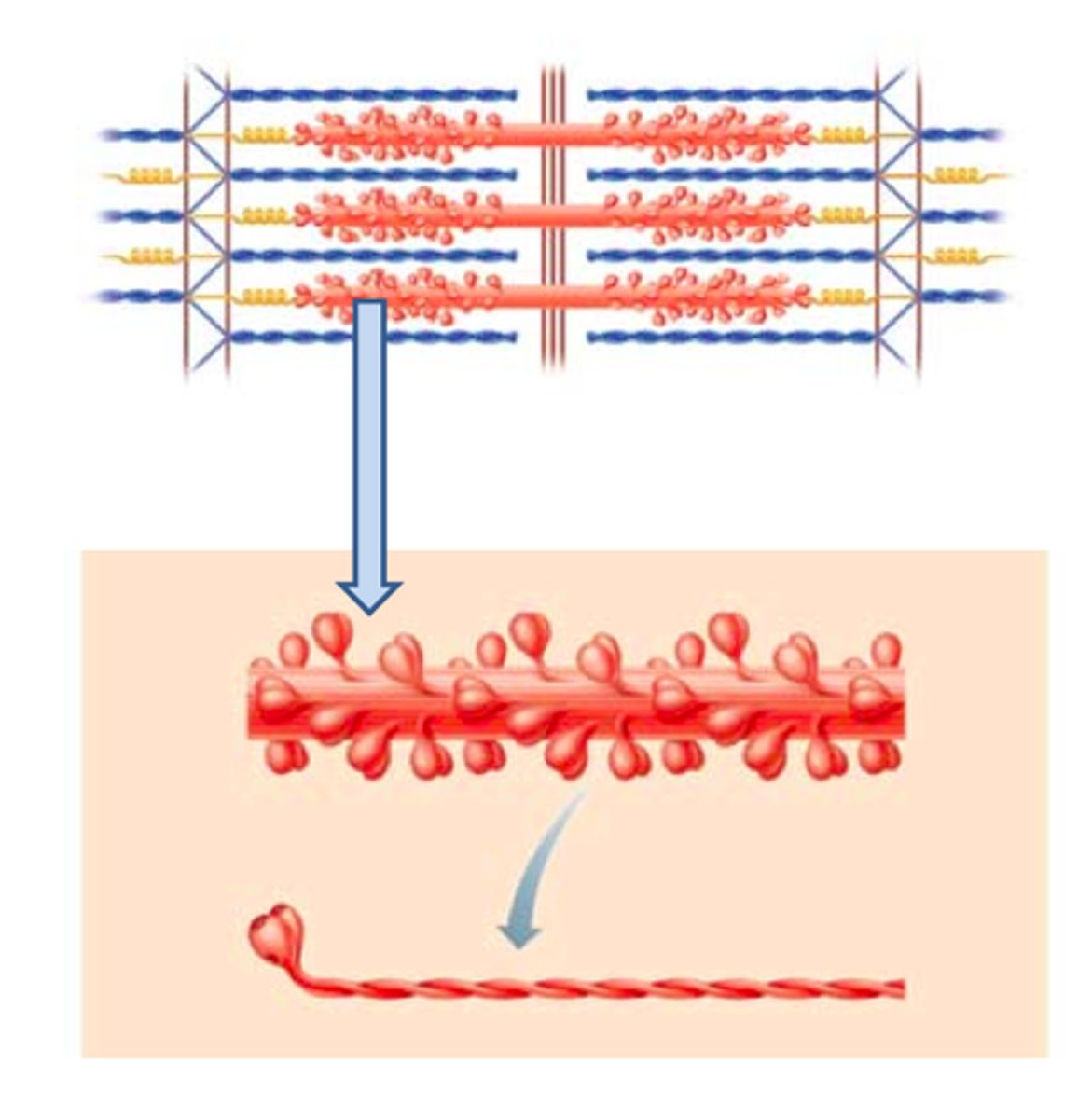
Myosin
Thick filaments
two interwoven protein chains, each head can hydrolyze ATP and can bind an actin monomer
Muscle Function
Convert chemical energy, ATP, into mechanical energy.
movement (body and internally) and manipulation
Muscle Activity: Contraction
Shortens when stimulated - electrical impulse, hormones.
Muscle Activity: Relaxation
Elongates when stimulation ceases; actin and myosin fibers return to resting position.
Agonist muscle
contract together producing a motion - biceps
antagonist muscle
contraction opposes motion of agonists - triceps
connective tissue: skeletal muscle
surround and hold groups of muscle fibers (cells) together
Endomysium
Around individual muscle fiber
Perimysium:
Around bundle of fibers
Epimysium:
Around entire muscle.
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane
Sarcoplasm:
Cytoplasm
Sarcoplasmic reticulum:
Endoplasmic reticulum
T tubule:
Transverse tubules.
Triad
SR T-tubule, SR.
Myofibril
Threadlike structures that run lengthwise through sarcoplasm and contain myofilaments.
Myofilaments
Contractile proteins: produce tension; regulatory proteins: control when contraction occurs; structural proteins: produce myofilament structural stability.
Skeletal Muscle Unit
A contractile unit with a structure with repeating sarcomeres.
Z Line
Defining point of a sarcomere; beginning and end of sarcomere
sarcomeres connect and actin is anchored here
I Band
Z line and actin only; part of 2 sarcomeres.
goes from the end of myosin in one to end of myosin in the other
A Band
Runs length of myosin; includes actin overlap with myosin.
H Band
Zone within A band that contains myosin only.
M Line
Proteins that provide sarcomere stability; hold myosin in place and anchor elastic filaments.
Skeletal Muscle Contraction steps
1. Action potential and stimulation of contraction; nerve impulse travels along sarcolemma and down T-tubule - stimulates release of Ca from S, Ca enters cytoplasm
2. Ca bind to troponin, changes shape and causes tropomyosin to roll and exposed myosin - binding sites for actin
3. myosin head energized by ATP, forms cross bridge with exposed binding sight
4. power stroke is initiated, contraction (shortening) begins, flexion
5. ATP binds myosin site and cross bridge is broken (at end of contraction cycle)
Muscle Tone
Muscles are in a state of partial contraction - such as sitting or standing.
sarcomere shortens
happens during a contraction cycle
active and myosin filaments move past one another - sliding filament
Overlap
Increases; I band and H zone decrease in length
actin and myosin do not change in length
Power for muscle contraction
Immediate use of ATP; preformed ATP is rapidly depleted.
Maintaining ATP availability
Creatine phosphate: Phosphate transferred to ADP making ATP - rapidly depleted.
Without sufficient O2 pyruvate and lactic acid formed - fermentation
Glycogen
Stored in muscle and liver.
Oxygen debt
Metabolism of build up lactic acid.
Sarcomere length
Influences strength of contraction; mouth of actin and myosin overlap determines the number of cross bridges that can form
the longer = more strength
shorter it gets = less strength
Motor unit
Defined as the nerve and muscle fibers (cells) it innervates.
Recruitment of motor units
motor units and muscle strength
Single stimulus
Brief electrical stimulus produces a twitch; muscle contraction followed by relaxation - single quick simple twitch.
time for contraction is longer than
action potential
Action potential
Lasts 1-2 seconds; finished before contraction begins.
Summation of multiple stimuli
Separate stimuli arrive very close together - twitches can fuse together.
Unfused tetanus
Occurs when twitches do not completely fuse.
Fused (complete) tetanus
Occurs when twitches completely fuse.
Smooth muscle
Surrounds tubular (hollow) organs; regulates diameter of bronchioles and arterioles.
Skeletal muscle
Attached to bones; responsible for whole body movement.
Regulation of contraction: smooth
myosin linked - contraction initiated by change in myosin
Regulation of contraction: skeletal
actin linked - contraction initiated by change in actin
Initiation of contraction: smooth
autonomic nerve impulse (neurogenic) or self-generated action potential (myogenic)
Initiation of contraction: skeletal
motor nerve impulse.
Strength of contraction
Smooth muscle is stronger than skeletal muscle.
amount of contraction
Smooth shortens more than striated muscle
Myosin head along length
Type of contraction
Smooth muscle contraction is slow and sustained, cycles Ca slowly, use less ATP
gap junctions
Pass electrical signals rapidly between fibers
Gap junctions present: smooth
yes, contract as a sheet
Calcium source: smooth
extracellular and from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Initiates cascade leading to activation of myosin ATPase
Gap junctions present: skeletal
individual cells stimulated
Calcium source: skeletal
sarcoplasmic reticulum binds troponin - none in smooth
Sarcomeres
Present only in skeletal and cardiac muscle.
contractile myofilaments: smooth
myosin to actin ratio of 1:10 to 1:15
contractile myofilaments: skeletal
myosin to actin ratio of 1:2 to 1:4
Smooth muscle contraction
Absence of striated does not mean no actin or myosin; there is just a different arrangement.
Cnidarians
no muscle fibers and contractile proteins in bundles as a part of non muscle cell layers
epithelia muscular cells
nematodes
single layer of muscle cells running longitudinally
Mollusks
Good example of long, sustained contraction in smooth muscle; keeps the shell tightly closed.
Annelids
Coordinated circular and longitudinal contraction in individual segments for movement.
more and thicker myosin fibers
Arthropods
Use skeletal muscle for fast movements and along the digestive tract.