Reproductive 2 - Spermatogenesis, Regulation, Seminal Fluid
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Where does spermatogenesis occur
Occurs in the space between adjacent sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubles
Male teste germ cell
Spematogonium
Are spermatogonia haploid or diploid
diploid
Steps of spermatogenesis
1. Spermatogonium undergoes mitosis, creating 1 cell that will remain spermatogonium (rejoins pool), and one cell that becomes a primary spermatocyte
2. Primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I, splitting into a secondary spermatocyte which is haploid with 2 copies of DNA (23 pairs of chromatids)
3. Secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis 2 to be come a haploid spermatid
4. Spermatids mature/differentiate into spermatozoa
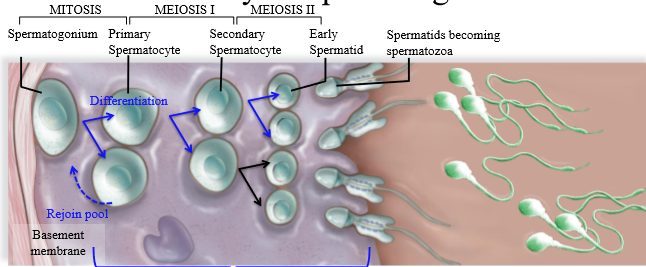
Are primary spermatocytes haploid or diploid
Diploid (2n x 2) - 2 copies of genetic DNA
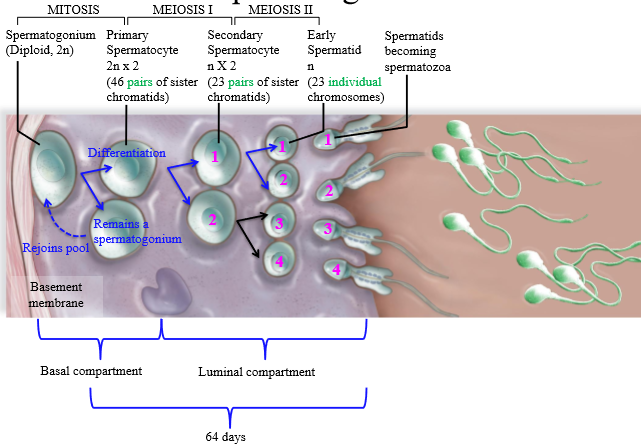
Are secondary spermatocytes haploid or diploid?
Haploid (1n x2) - 2 copies of genetic DNA
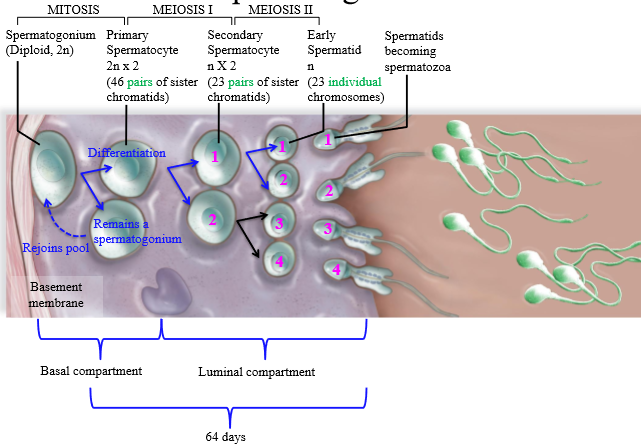
Are spermatids haploid or diploid
Haploid (1n)
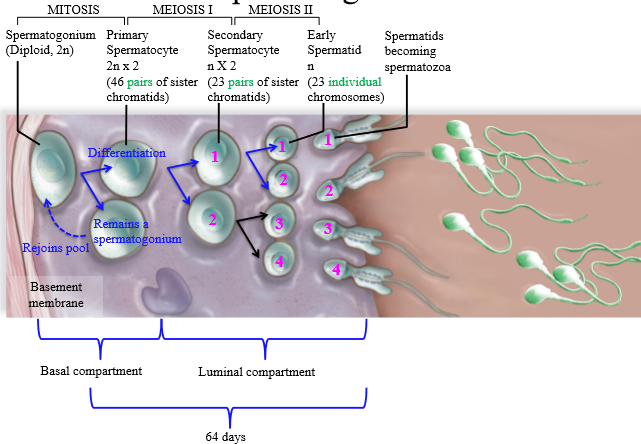
From 1 spermatogonium, how many sperm are made?
4
Location of Spermatogenesis mitosis
Basal compartment of the seminiferous tubule
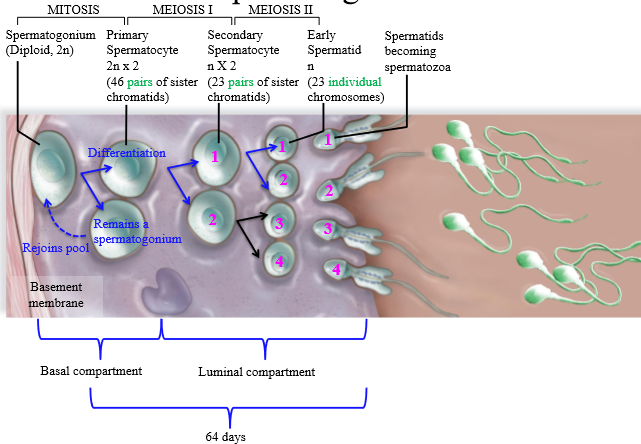
Location of Spermatogenesis meiosis I
Luminal compartment of the seminiferous tubule
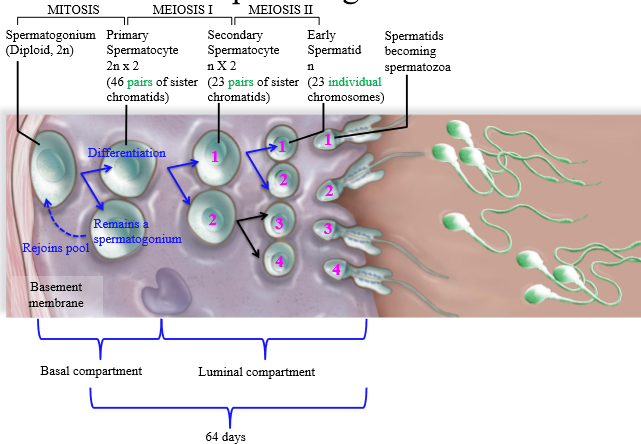
Location of spermatogenesis meiosis II
luminal compartment of seminiferous tubule
How many days does spermatogenesis take?
64 days
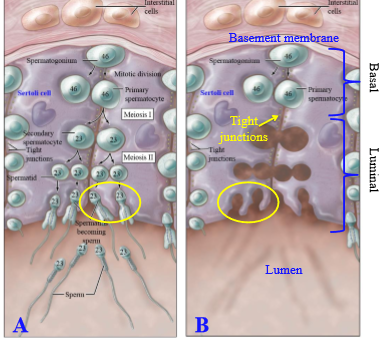
How do primary spermatocytes move from the basal compartment to the luminal compartment of the seminiferous tuuble
Tight junctions between sertoli cells open up to permit primary spermatocytes to move
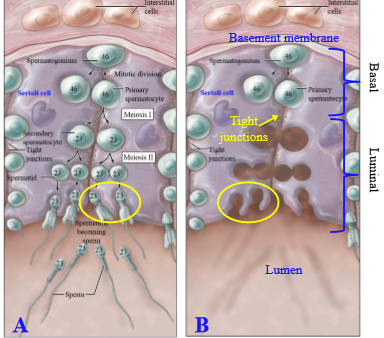
Location of maturing spermatids
Create cavities in the luminal surface of certoli cells
What is spermiogenesis
Maturation of spermatids into spermatozoa
How long does spermiogenesis take
24 days (part of the 64 it takes for spermatogenesis)
What happens during spermiogenesis
Spermatids become sperm: produce a flagellum, an acrosome, and lose most cytoplasm and organelles
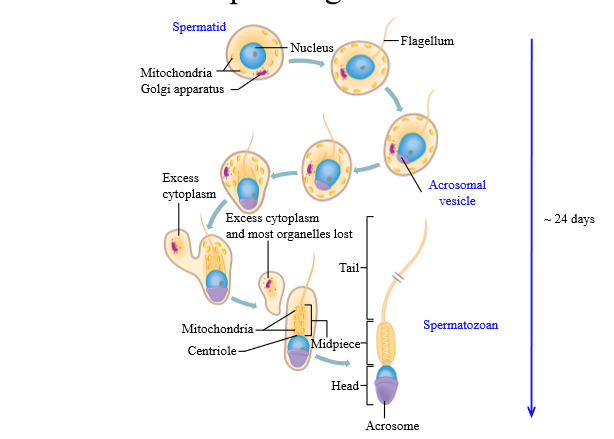
What happens to the mitochondria during spermiogenesis
They aggregate and become the neckpiece for spermatozoa
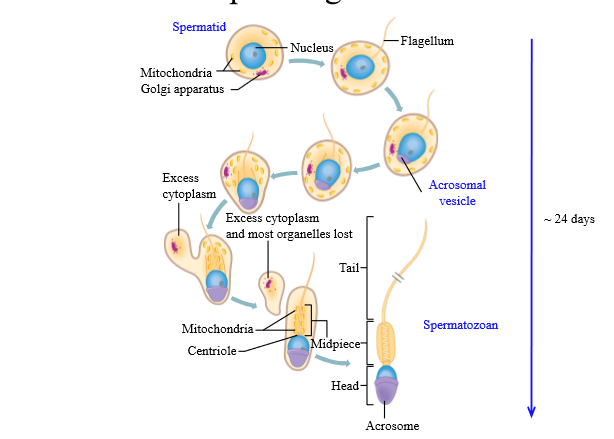
Components of a sperm cell
Head, Midpiece, Tail
Sperm head composition
Nucleus: chromosomes must be passed on to the egg
Acrosome - tip (cap) on the head, contains enzymes necessary for fertilization
Sperm midpiece
location of mitochondria = ATP generation. Required for flagellar motion
Sperm tail composition
Tail made by microtubules - use whip live movements to propel
By the time sperm are moved from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis, are they mature?
No - they are non-motile
How are sperm moved from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis
Pressure generated by fluid secreted from Sertoli cells
How long do sperm stay in the epididymis, and what do they do there?
Stay for 6-12 days, and they mature until they acquire motility
What happens to surrounding sperm fluid in the epididymis
Most fluid is reabsorbed (stereocilia), sperm is concentrated
How does sperm move from epididymis to vas deferens
Via peristalsis (remains in vas deferens until ejaculation)
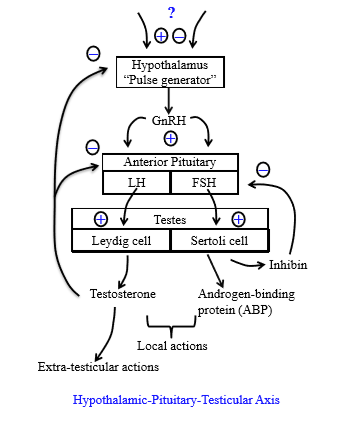
What do Sertoli cells secrete
Androgen binding protein and inhibin
Role of inhibin
Regulates the anterior pituitary do help decrease FSH secretion. Does not work on hypothalamic level
What is inhibin made of
Peptide
How does testosterone regulate male reprodction
Inhibits both the anterior pituitary from releasing LH and from the hypothalamus from releasing GnRH pulses
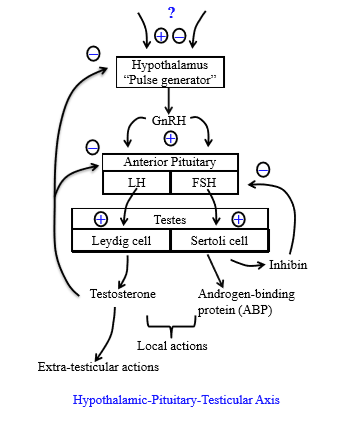
Role of androgen binding protein
Concentrates testosterone in seminiferous tubules
= enables spermatogenesis
Role of testosterone in sperm production
Stimulates spermatogenesis
Where does sperm move after the vas deferens
Common urethral tract
How does the body prevent urine from entering the semen
Valve in urethral tract closes when sperm moves into urethra
3 functions of seminal fluid
1. Dilution of sperm
2. Provision of energy (fructose)
3. Formation of semen clot
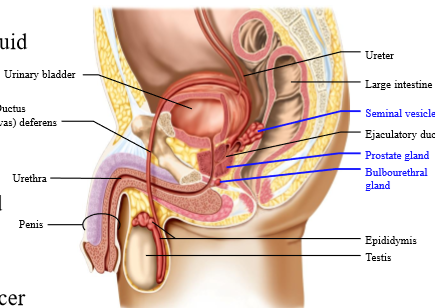
What male reproductive accessory gland secretes the most seminal fluid
Seminal vesicles
Function of seminal vesicles
Secretions - it secretes
- Fructose (energy)
- Enzymes (form semen clot)
- Prostaglandins (causes contraction of female tract for forward movement)
What pH is semen
Alkaline - neutralize the acidic female genital tract
Location of prostate gland
inferior to the bladder
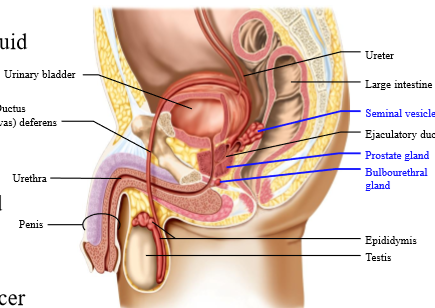
Role of the prostate gland
Secretions = it secretes:
- Citrate (energy): required when sperm are sitting in fluid
- Prostate specific androgen (PSA) - breaks down protein in semenal clot
Use of prostate specific androgen as a biomarker
Works as a biomarker for cancer
- Increased with prostate gland benign growth or cancerous
Role of bulbourethral gland
Secretes viscous fluid with mucus - joints with common urogenital tract that ends up in penile tissue
What are the accessory male reproductive glands
seminal vesicle, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands
What is semen composed of
Sperm + Seminal fluid
What nervous system controls male sexual response
Autonomic nervous system
3 phases of male sexual response
3 E's
- Erection
- Emission
- Ejaculation
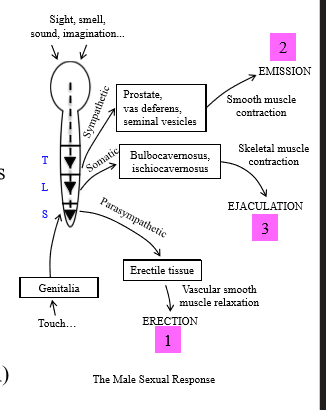
What controls an erection
Parasympathetic nervous system
What controls emission
sympathetic nervous system - thoracolumbar region (sacral region is PSNS)
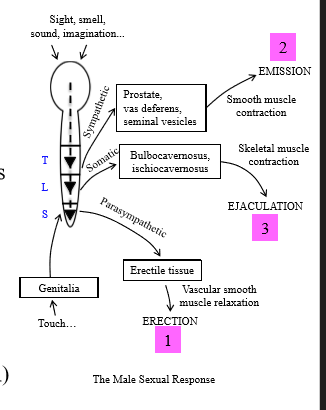
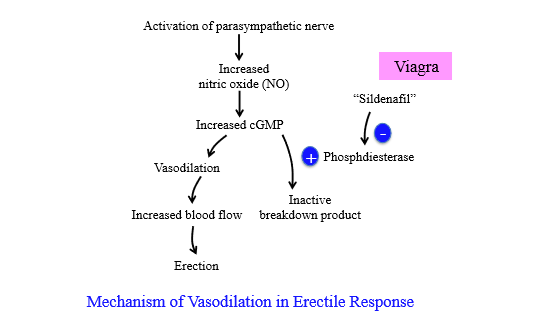
How does the PSNS cause erection
Under mechanical stimulation or neural inputs, PSNS is activated and causes relaxation of the penis arteries for increased blood flow = erection
How does the SNS cause emission
SNS causes smooth muscle contraction of vas deferens, leading to movement of sperm from the vas deferens and mixing of seminal fluid in urogenital tract
How does ejaculation occur
Rapid contraction of skeletal muscle for semen expulsion (somatic control)
How is blood flow increases in an erection
PSNS nerve activation increases nitric oxide, which increases cGMP. cGMP causes vasodilation for increased blood flow = erection
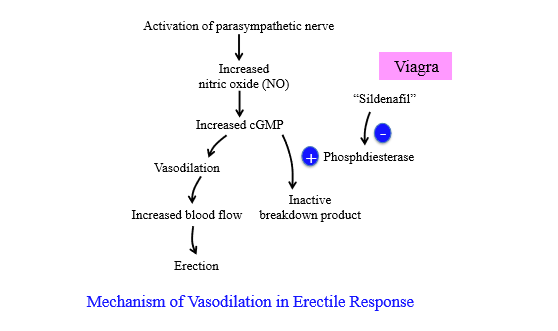
How is cGMP broken down during an erection
Phosphodiesterase breaks down cGMP to stop erection
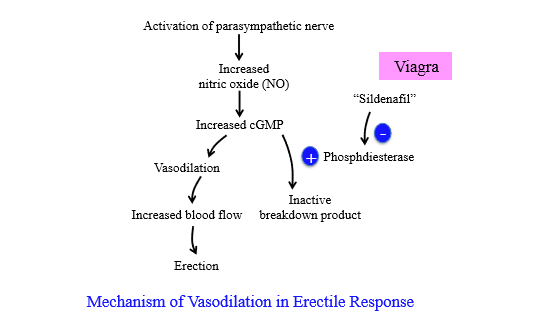
What enzyme produces cGMP
guanylate cyclase - converts GTP to cGMP
What is erectile dysfunction, and how is it caused
Erectile dysfunction - inability to get an erection. Possible causes include diabetes, alcohol, or depression
How to treat erectile dysfunction
Sildenafil (Viagra)
How does Sildenafil (viagra) cause an erection
Inhibits cGMP breakdown by inhibiting phosphodiesterase
How many sperm are deposited into the vagina during ejaculation, how many get past the cervical area, and how many get past the fallopian tube?
200-300 million sperm are ejaculated, 100 000 get past the cervical area, 100 get past the fallopian tube
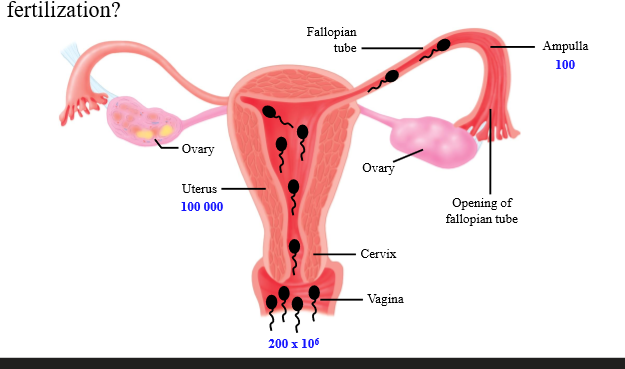
What accounts for the low number of sperm to reach fertilization site
Acidic pH of vagina kills sperm
Where does the final stage of sperm maturation occur
Inside the female reproductive tract
What are the final stages of sperm development
Capaciation and the Acrosome reaction
Capaciation
Receptors are made available for removal of ova glycoprotein layer, and sperm become fully motile (whiplash movement instead of gentle wave)
Zona pellucida
A thick coating rich in glycoproteins that surrounds an oocyte.
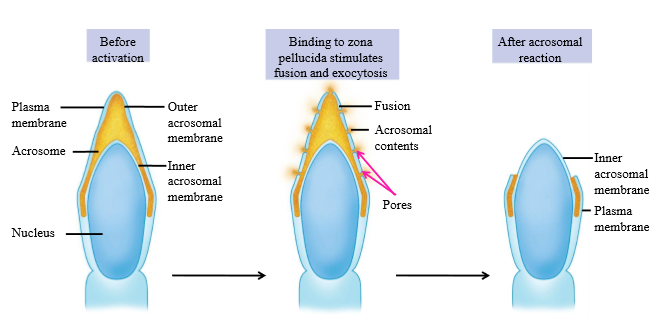
What causes activation of the acrosome reaction
Binding of sperm to zona pellucida
Acrosome reaction
When sperm binds to zona pellucida, Pores are made in acrosome, and acrosomal contents are released. Acrosomal enzymes digest zona pellucida for sperm to fertilize ova.