Foundations of Biology Exam 5: Chapter 22
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
populations
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same geographic area at the same time
theory
explanation for a broad class of phenomena that is supported by a wide body of evidence; serves as a framework for the development of hew hypothesis; have two components: pattern and process
pattern
a component of a theory; a statement that summarizes a series of observations about the natural world; about facts- how things are in natures
process
a component of a theory; a mechanism that produces that pattern or set of observations
Plato
claimed the every organism was an example of a perfect essence, or type, created by God, and these types were unchanging
typological thinking
way way of thinking of that claims organisms were all created by a divine entity
Aristole
proposed that species were fixed types organized into a sequence based on increasing size and complexity; humans were at the top and only surpassed by angels or God
Lamarck
proposed the first formal theory of evolution; claimed that simple organisms originate at the base of the scale by spontaneous generation and then evolve by moving up the scale over time, always producing "better" species. contended that species changeDar via inheritance of acquired characters
evolution
the theory that all organisms on Earth are related by common ancestry and that they have changes over time, and continue to change via natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation; any change in the genetic characteristics of a population over time, especially change in allele frequency
Darwin and Wallace
emphasized that the process responsible for change through time- natural selection- occurs because traits vary among individuals in a population; the opposite of typological thinking, which ignores variation or considers it unimportant
reasons the theory of evolution by natural selection was revolutionary
1. it overturned the idea that species are static and unchanging; instead, it suggested that species change through time and are related by common ancestry
2. it replaced typological thinking with population thinking
3. it was scientific; it proposed a mechanism that could account for change through time and made predictions that could be tested through observation and experimentation
descent with modification
the phrase used by Darwin to describe how species that lived in the past are the ancestors of species existing today, and that species change through time; the pattern component of Darwin's theory
fossil
any physical trace of on organism that existed is the past; includes tracks, burrows, fossilized bones, casts, ancient DNA (aDNA), and so on
fossil record
all of the fossils that have been found anywhere on Earth and that have been formally described in the scientific literature
extant species
a species living today
the vastness of geologic time
evidence one for change through time; knowing that sedimentary rock forms in layers allows us to date fossils based on the age of the rock, creates a geologic time scale
geologic time scale
the sequence of eons, eras, and periods used to describe the geologic history of Earth; gives fossils relative ages
radioactive decay
acts as a "natural clock" in which the decay of different elements can be used to give absolute ages to fossils
extinction changes the species present over time
evidence 2 for change of over time; if species have gone extinct, then the array of species living on Earth has changed through time; 99% of all species that once lived are now extinct
extinct species
a species that no longer exists
transitional features link older and younger species
evidence four for change over time; through the observation of fossils we can find transitional features linking ancestral species to their derived species; ex. limbs turning into fins on fish
transitional feature
a trait that is intermediate between a trait observed in ancestral (older) species and the homologous trait observed in derived (younger) species
vestigial traits
evidence four for change through time; the presence of vestigial traits in current species; change over time is logical because environments change drastically overtime; what once was useful lost its purpose
species can be observed changing today
evidence five for change through time; antibiotic resistant bacteria or finch beaks shape changing
similar species are found in the same geographic area
evidence one for descent from a common ancestor; ex. finches from the Galapagoes islands were similar because they had descended from the same ancestor on the mainland but then evolved different traits as they colonized the island
pylogenic tree
a branching diagram that depicts the evolutionary relationship among species; shows ancestor to descendant relationship
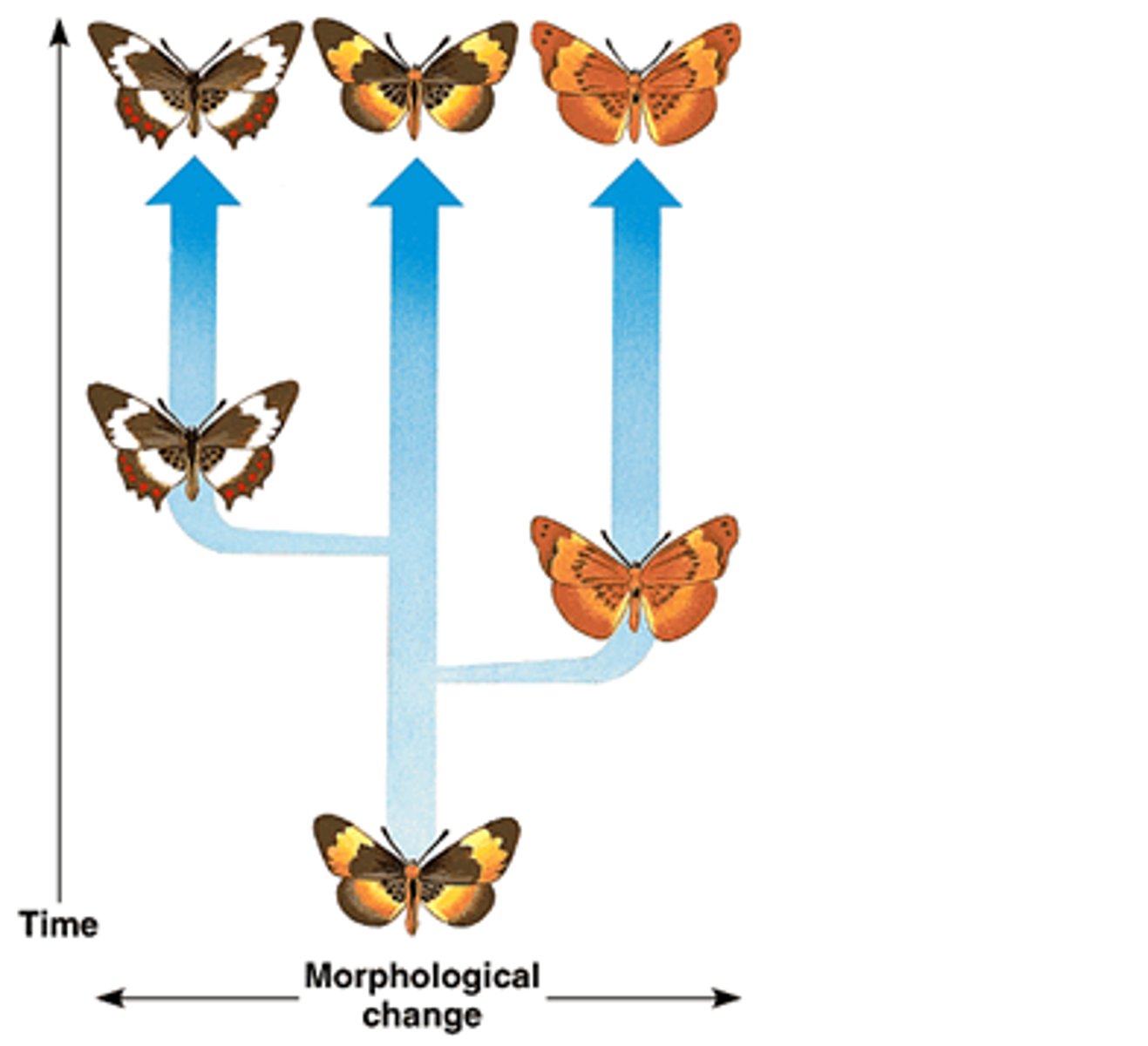
related species share homologies
evidence two for descent from a common ancestor; ex. human hair and dog hair are shared traits because they descended from the same common ancestor
genetic homology
similarity in DNA nucleotide sequences, RNA sequences, or amino acid sequences due to inheritance from a common ancestor
developmental homology
similarity in developmental structures or processes, embryonic form; due to inheritance from a common ancestor
structural homology
similarities in adult organismal structures that are due to inheritance from a common ancestor
independently
if species were created ___________, homologies would not occur
formation of new species from pre-existing species can be observed today
evidence three for descent from a common ancestor; ex. killer whales, some populations so different in prey choice and social behavior now that they can no longer interbreed like they used to in the past
internal consistency
the observation that data from independent sources agree in supporting predictions made by a theory
artificial selection
deliberate manipulation by humans, as in animal and plant breeding, of the genetic composition of a population by only allowing certain individuals with desirable traits to reproduce
struggle for existence
coined by Darwin, since there are many more individuals born than can survive due to limited resources, this occurs as people compete for food and places to live
Darwins four postulates
1. variation exists among individual organisms that make up a population
2. some of the trait differences are heritable, passed on to offspring
3. survival and reproductive success are highly variable
4. the subset of individuals that survive best and produce the most offspring is not a random sample of the population
natural selection
the process by which individuals with certain heritable traits tend to produce more surviving offspring than do individuals without those traits, often leading to change in the genetic makeup of the population; a major mechanism of evolution; the only evolutionary process that produces adaptation
fitness
in evolutionary biology, the ability of an individual to produce viable offspring relative to others of the same species
adaptation
a heritable trait that increases fitness in an individual in a particular environment relative to individuals lacking the trait
selection
a passive process; differential reproduction as a result of heritable variation; not a purposeful choice