HSF Exam 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Simple Squamous Epithelia
locations: lining of ventral body cavities, endothelia lining heart and blood vessels, portions of kidney tubules, inner lining of cornea, alveoli of lungs.
functions: reduces friction, controls vessel permeability, performs absorption and secretion
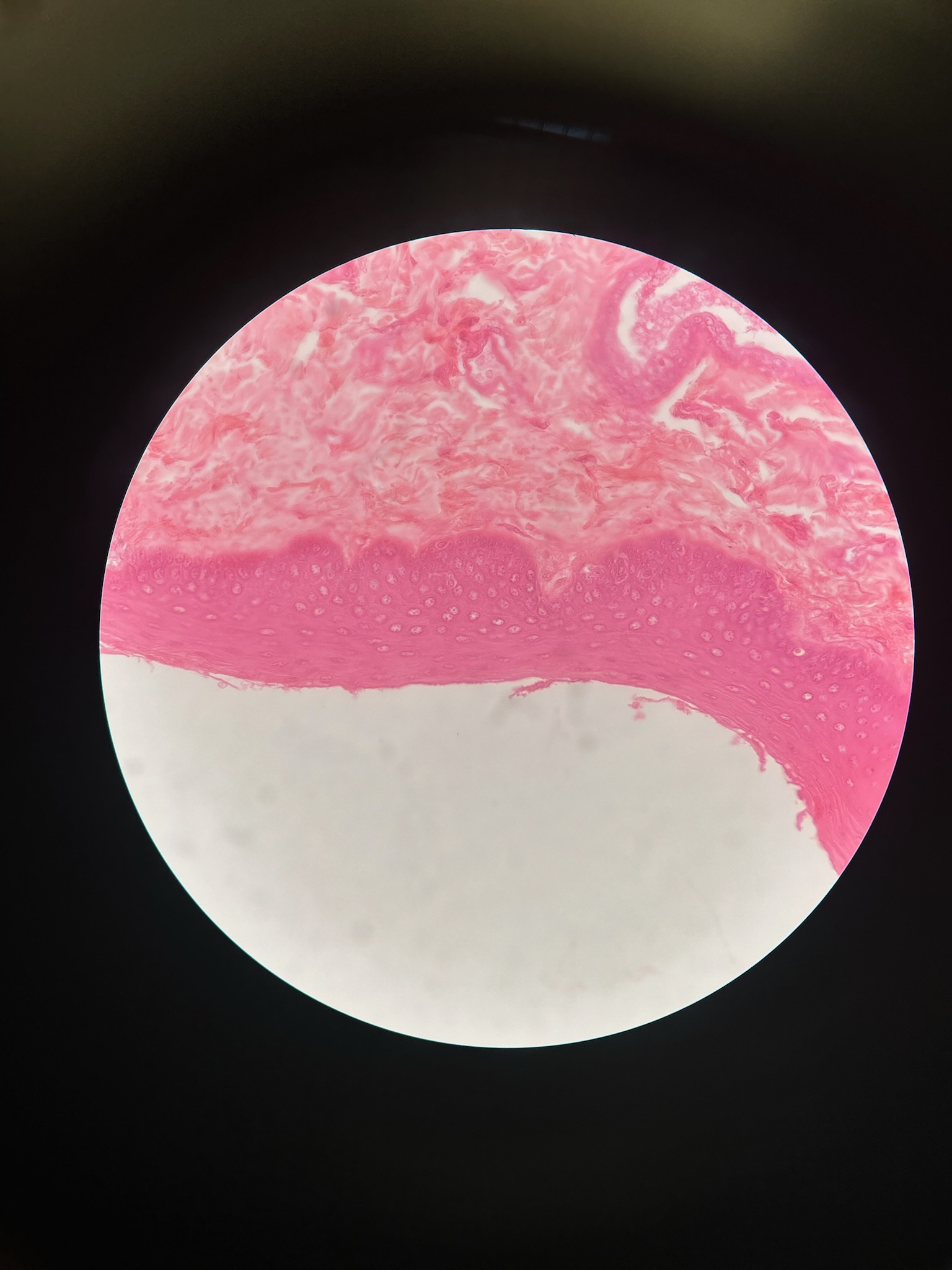
Stratified Squamous Epithelia
locations: surface of skin, lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, and vagina
functions: provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemicals
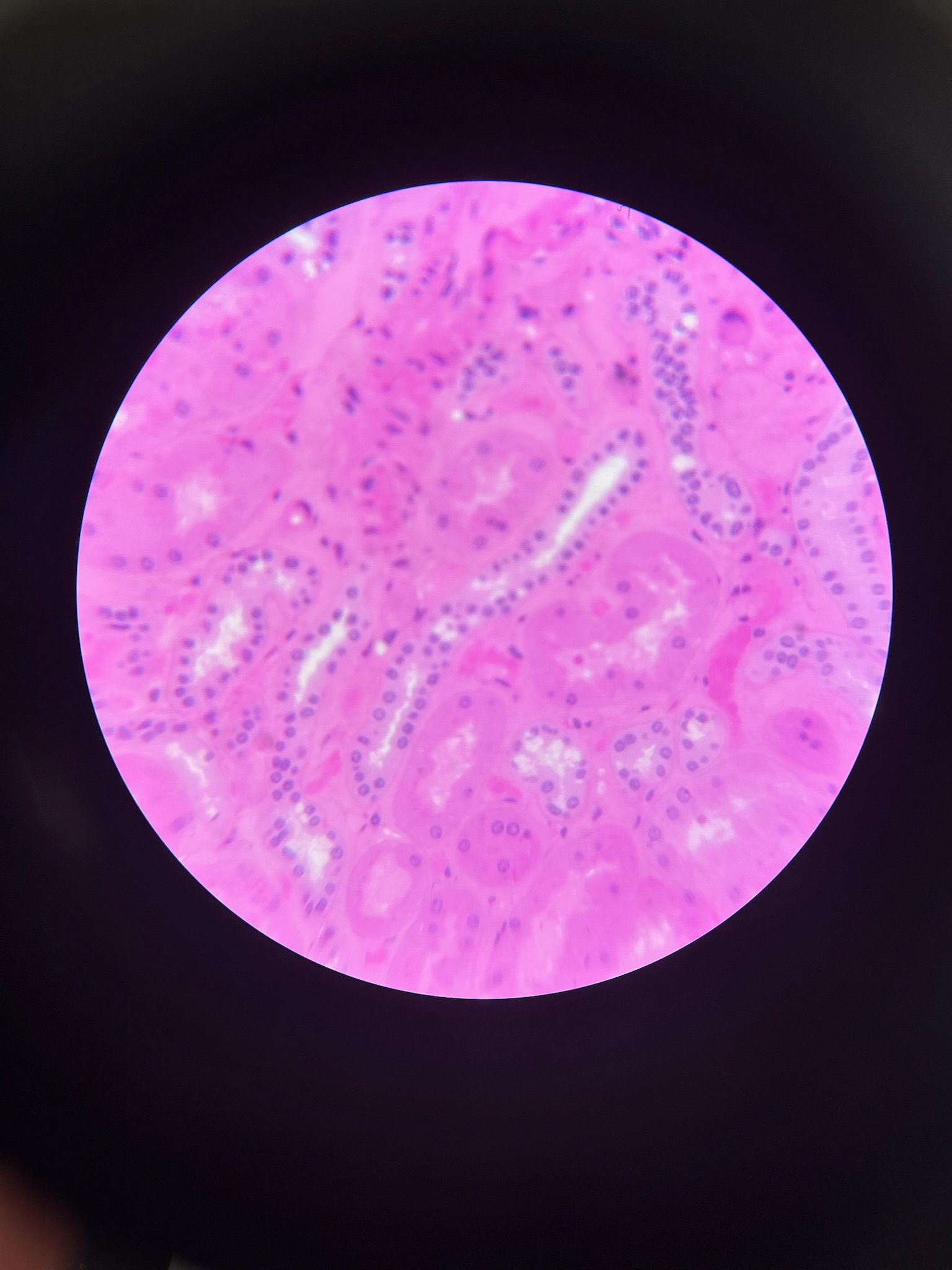
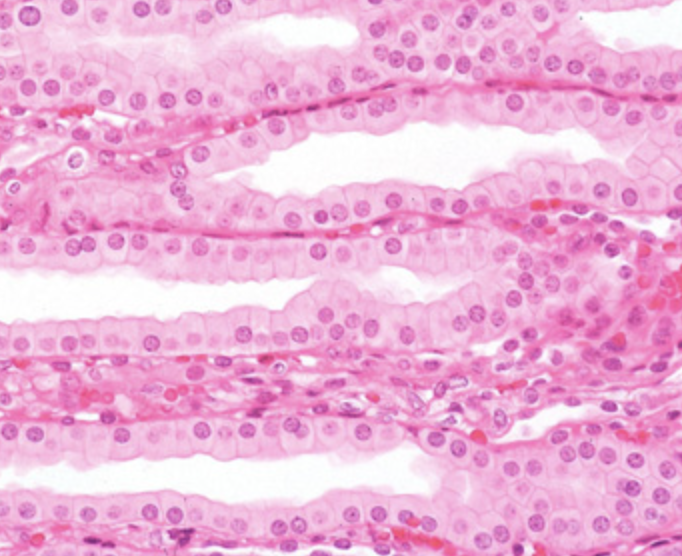
Simple Cuboidal Epithelia
locations: glands, ducts, portions of kidney tubules, thyroid glands
functions: limited protection, secretion, absorption
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
locations: lining of some ducts (rare)
functions: protection, secretion, absorption
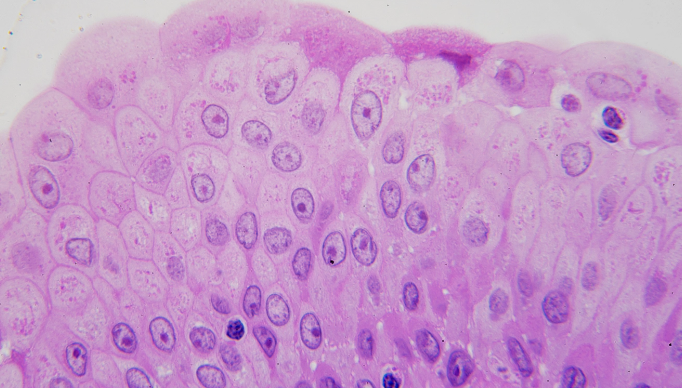
Transitional Epithelia
locations: urinary bladder, renal pelvis, ureters
functions: permits expansion and recoil after stretching
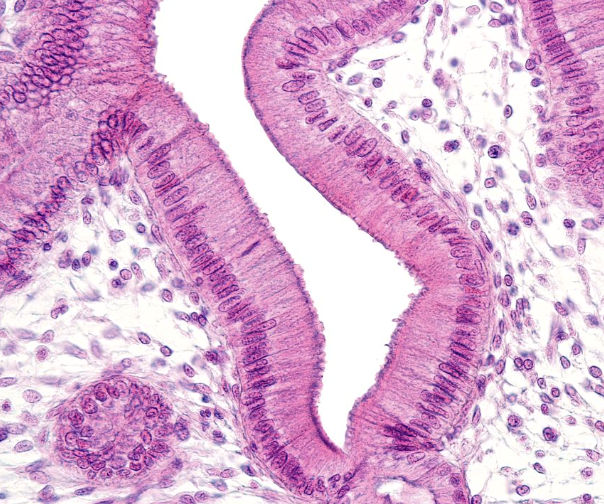
Simple Columnar Epithelia
locations: lining of stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kindeys
functions: protection, secretion, absorption
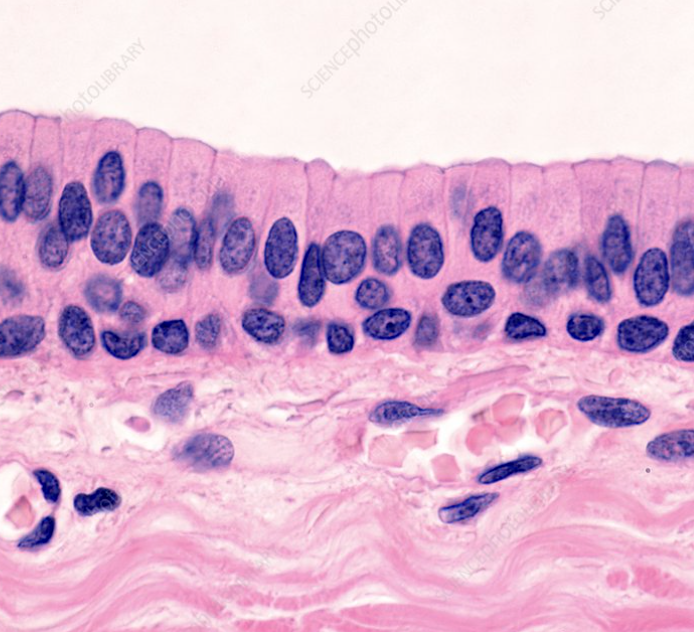
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelia
locations: lining of nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi. portions of male reproductive tract
functions: protection, secretion, move mucous with cilia
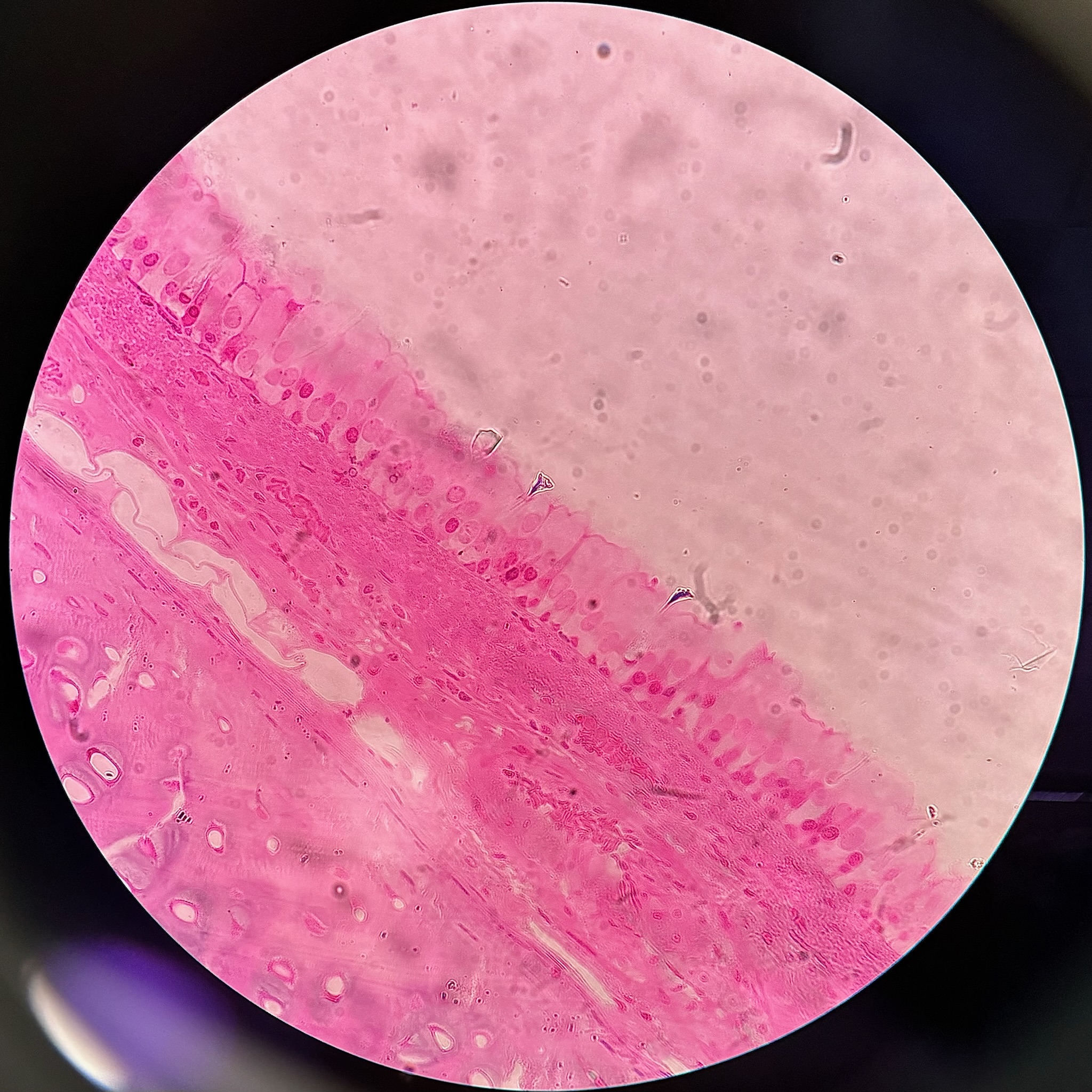
Stratified columnar epithelia
locations: small areas of pharynx, epiglottis, anus, mammary glands, salivary glands ducts, and urethra
function: protection
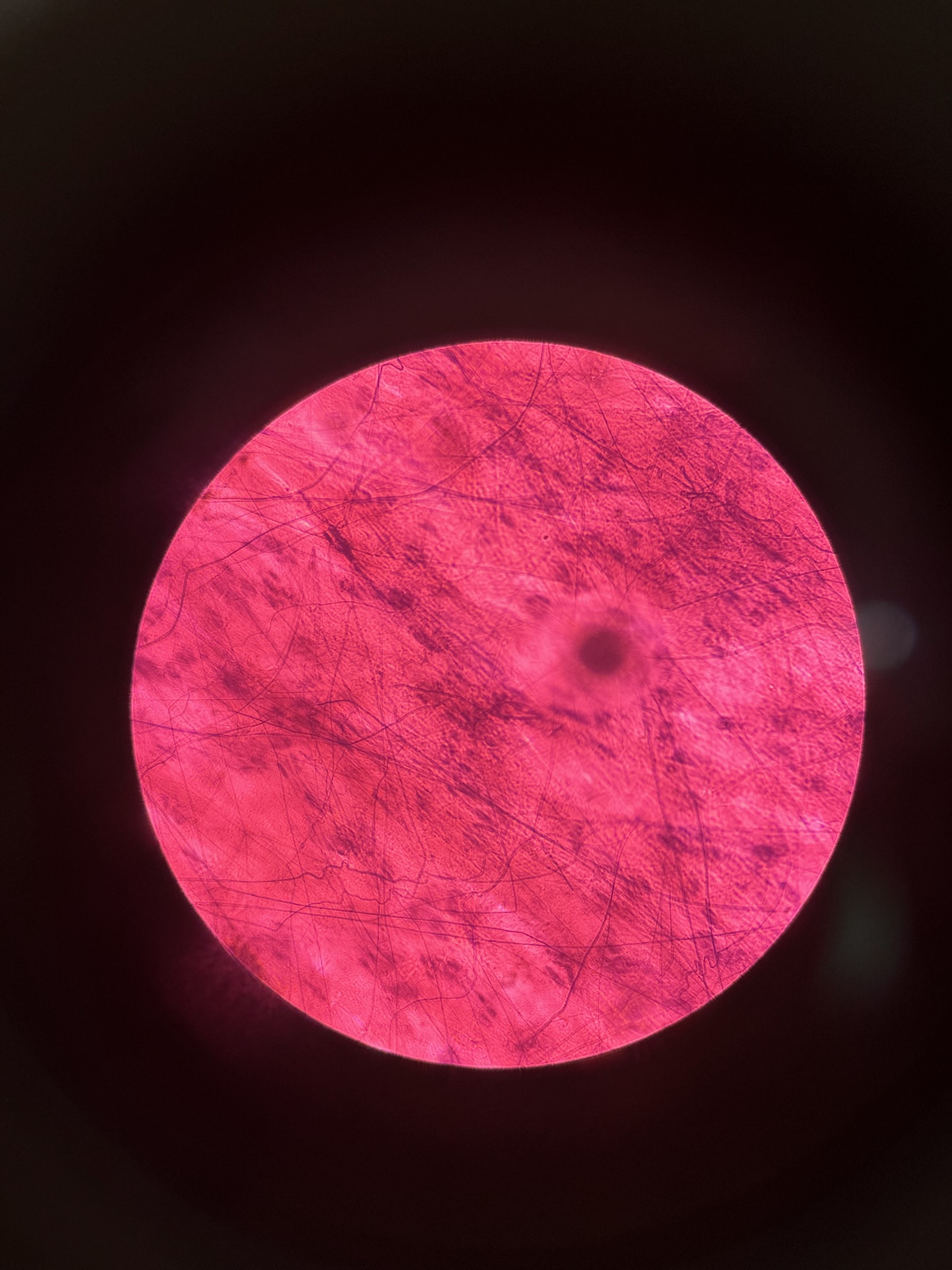
Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
Has all 3 fibers (elastic, collagen, reticulum)
fills nooks and crannies throughout body
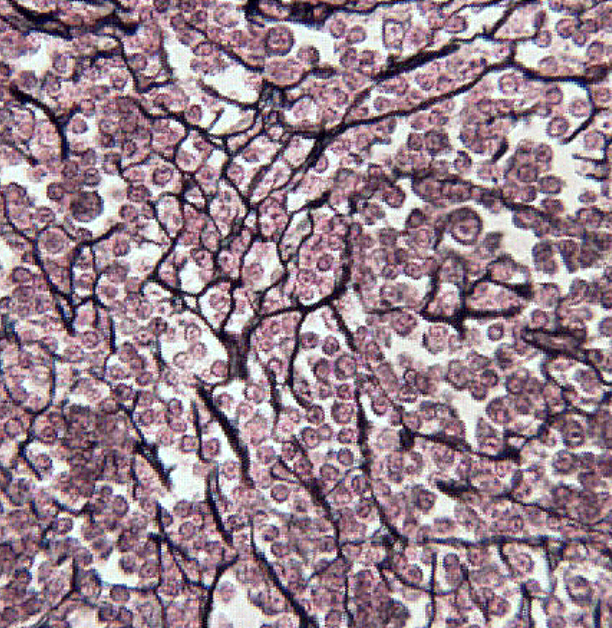
Loose reticular connective tissue
locations: liver, kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow
functions: supporting framework
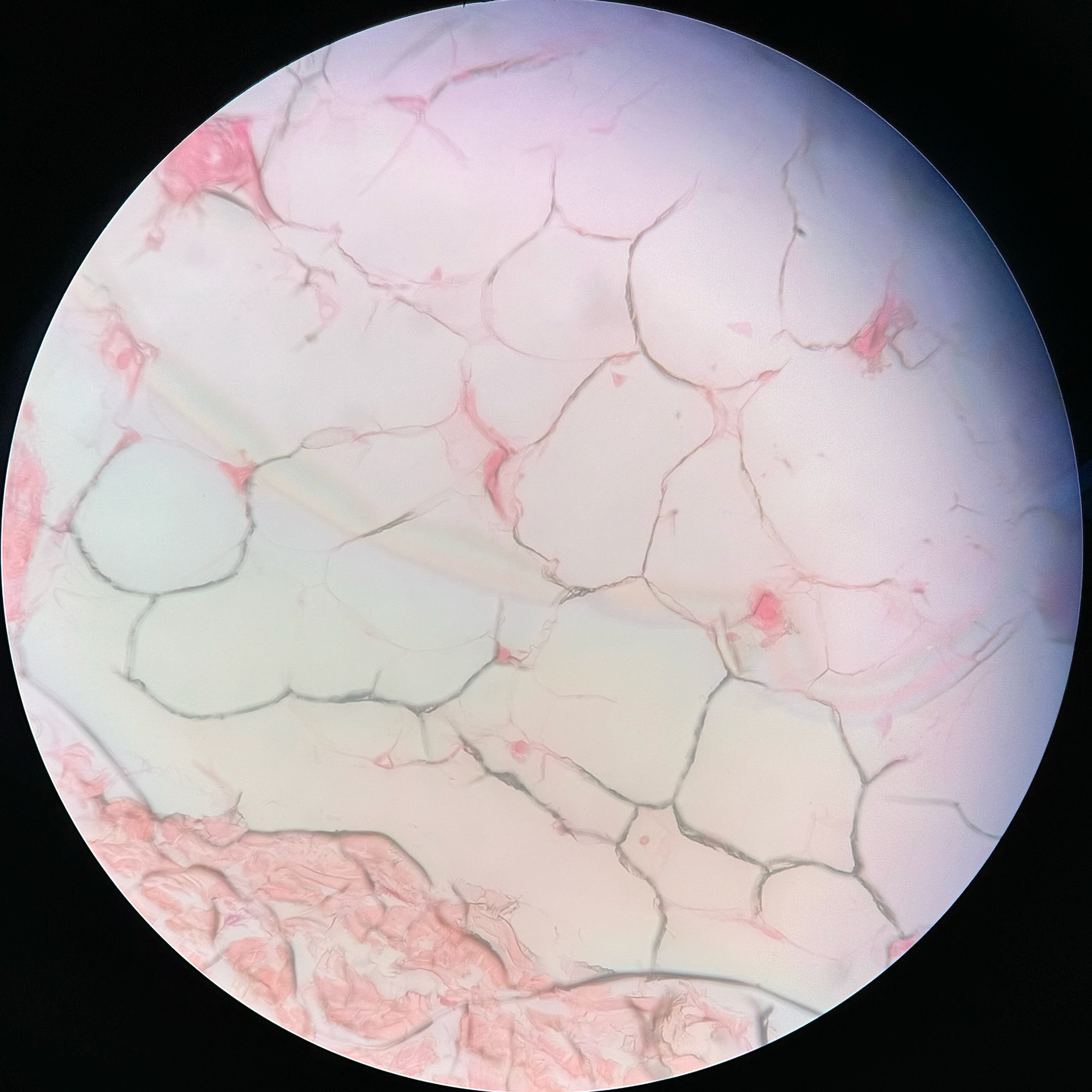
Loose adipose connective tissue
locations: deep to the skin, especially at sides, buttocks, breaks, padding around eyes, and kidneys
functions: provides padding and cushion shocks; insulates, stores energy
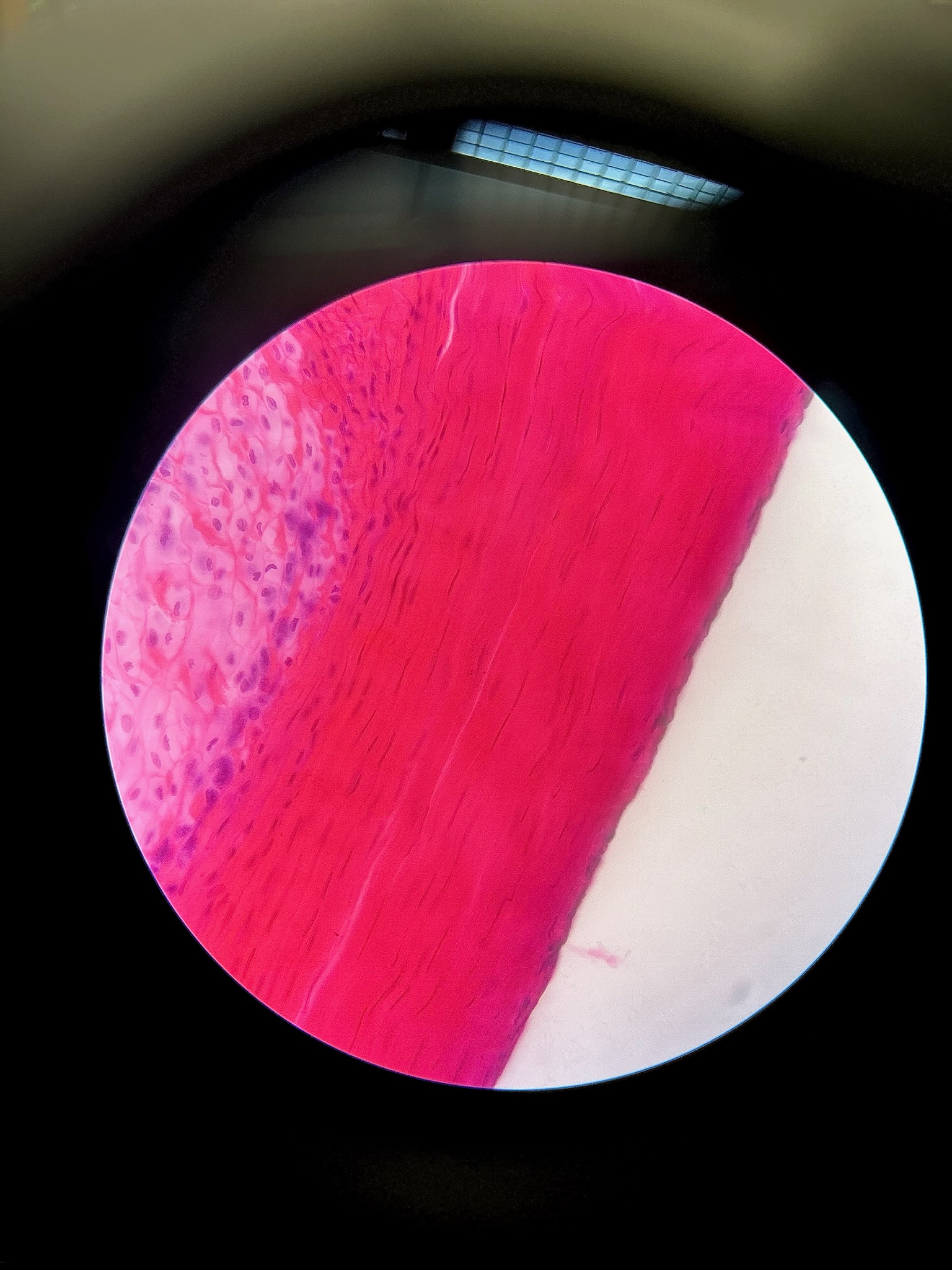
Dense regular connective tissue
locations: tendons and aponeuroses, ligaments, covering skeletal muscles
functions: provide firm attachment, conducts pull of muscles, reduces friction between muscles, stabilizes relative position of bones
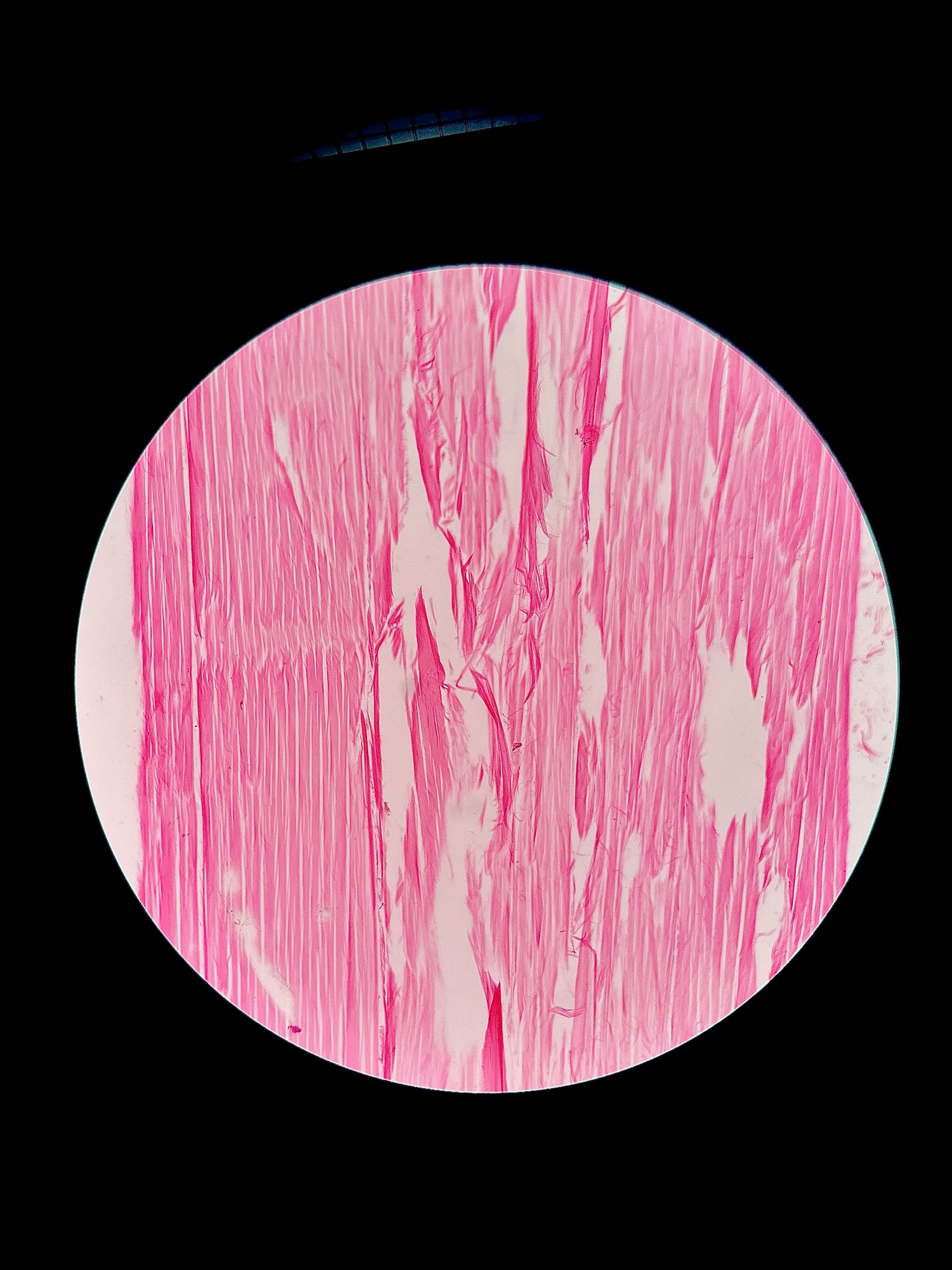
Dense regular connective tissue
locations: tendons and aponeuroses, ligaments, covering skeletal muscles
functions: provide firm attachment, conducts pull of muscles, reduces friction between muscles, stabilizes relative position of bones
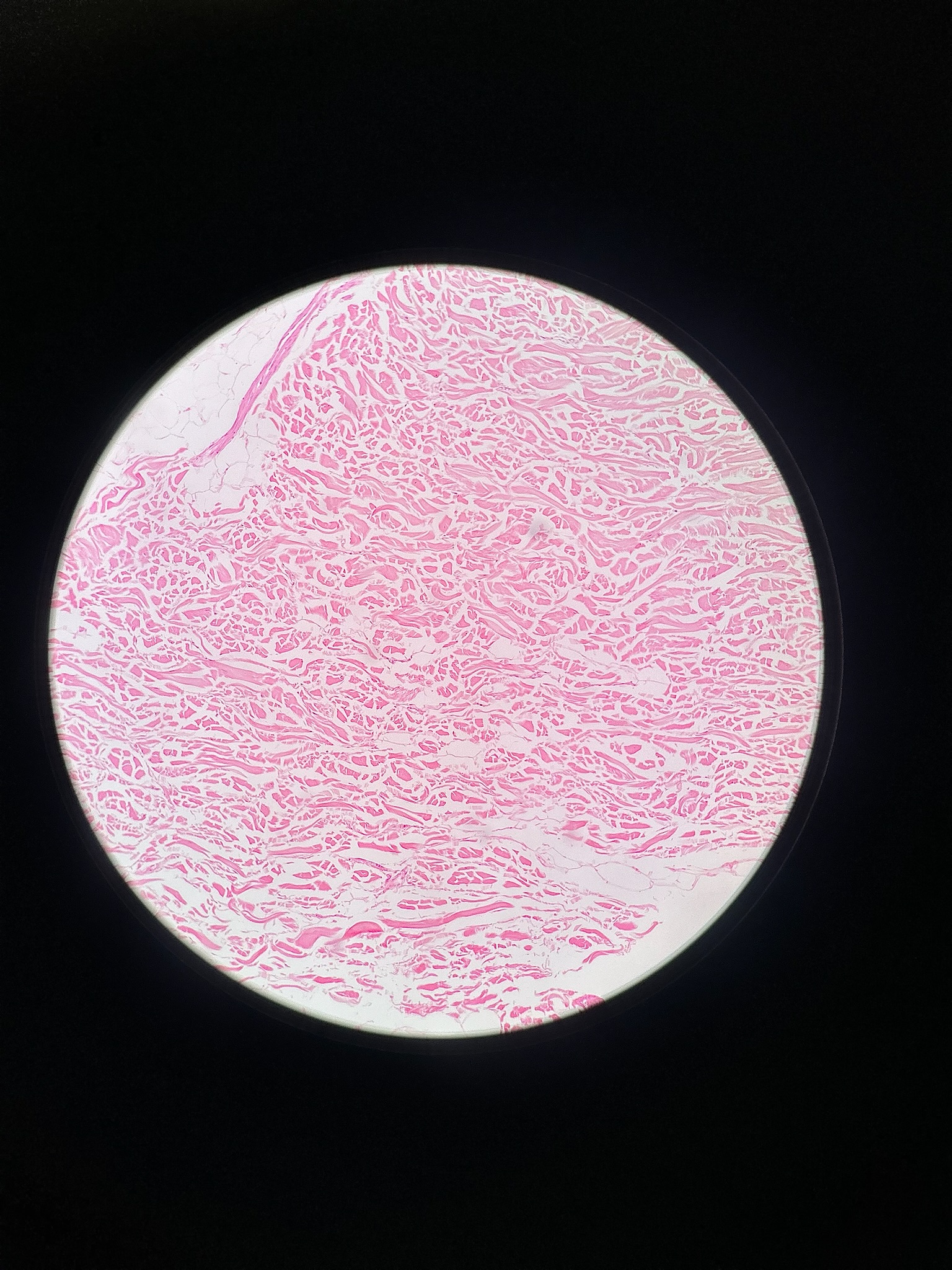
Dense irregular connective tissue
locations: capsules of visceral organs, periostea and perichondria, nerve and muscle sheaths, dermis
functions: provides strength to resist forces applied from many directions, helps prevent overexpansion of organs such as the urinary bladder
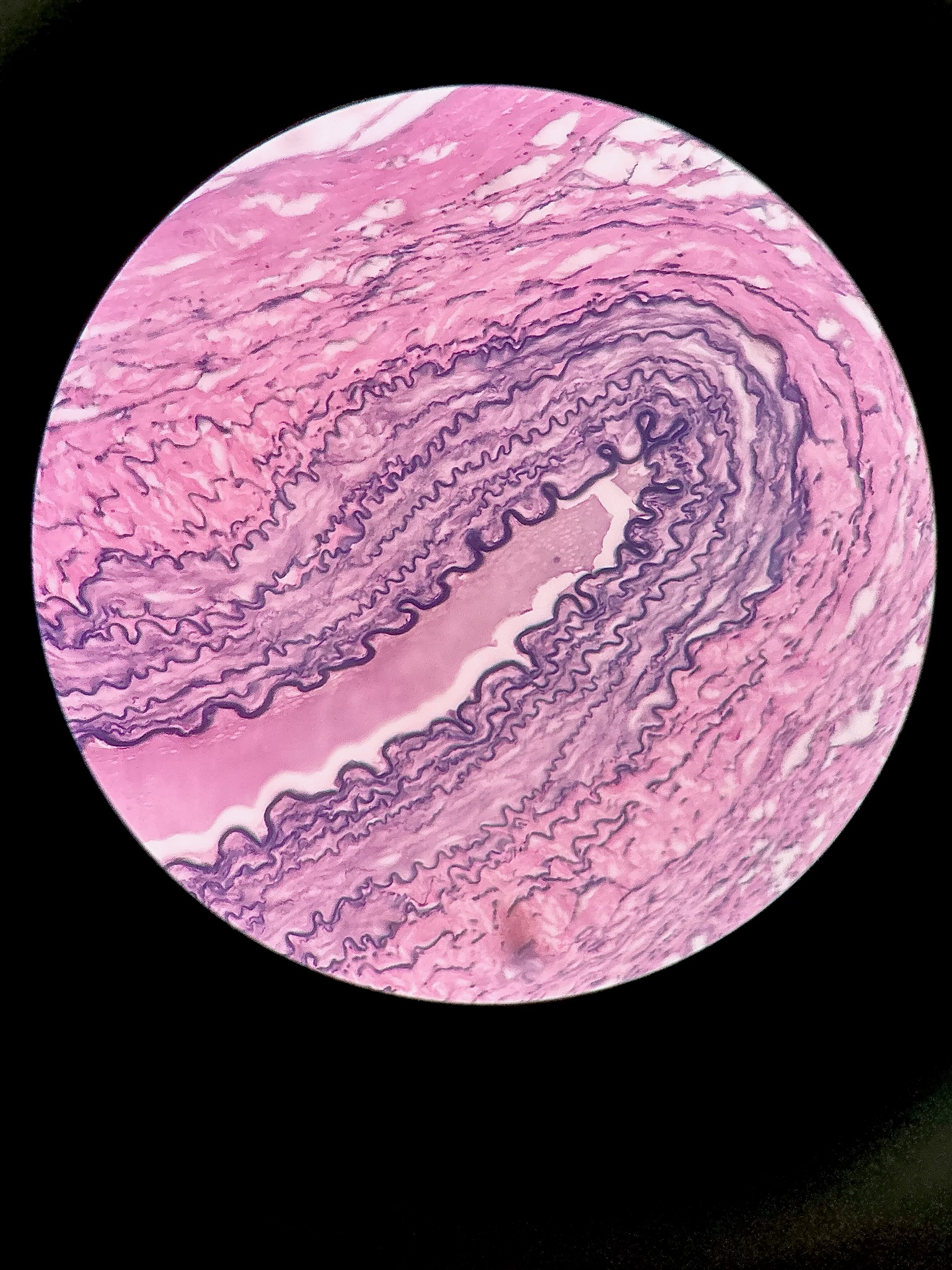
Elastic connective tissue
locations: between vertebrae of the spinal column, ligaments supporting penis, ligaments supporting transitional epithelia
functions: stabilizes positions of vertebrae and penis, cushions shocks, permits expansion and contraction of organs
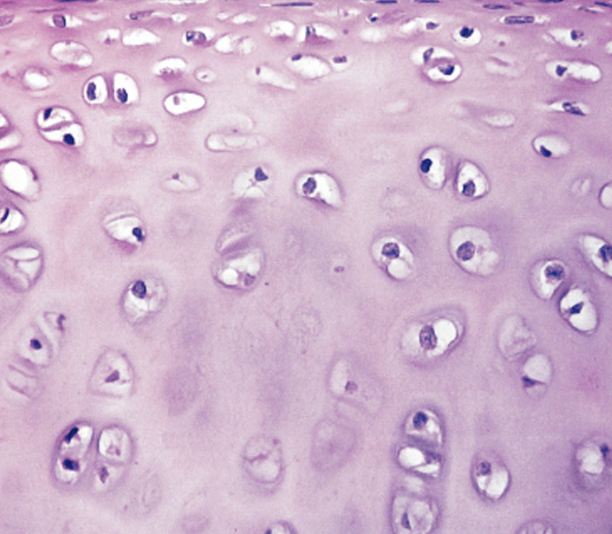
Hyaline Cartilage
locations: between tips of ribs and bones of sternum, covering bone surfaces at synovial joints, supporting larynx (voice box), trachea, and bronchi
functions: somewhat flexible support, reduces friction between bony surfaces
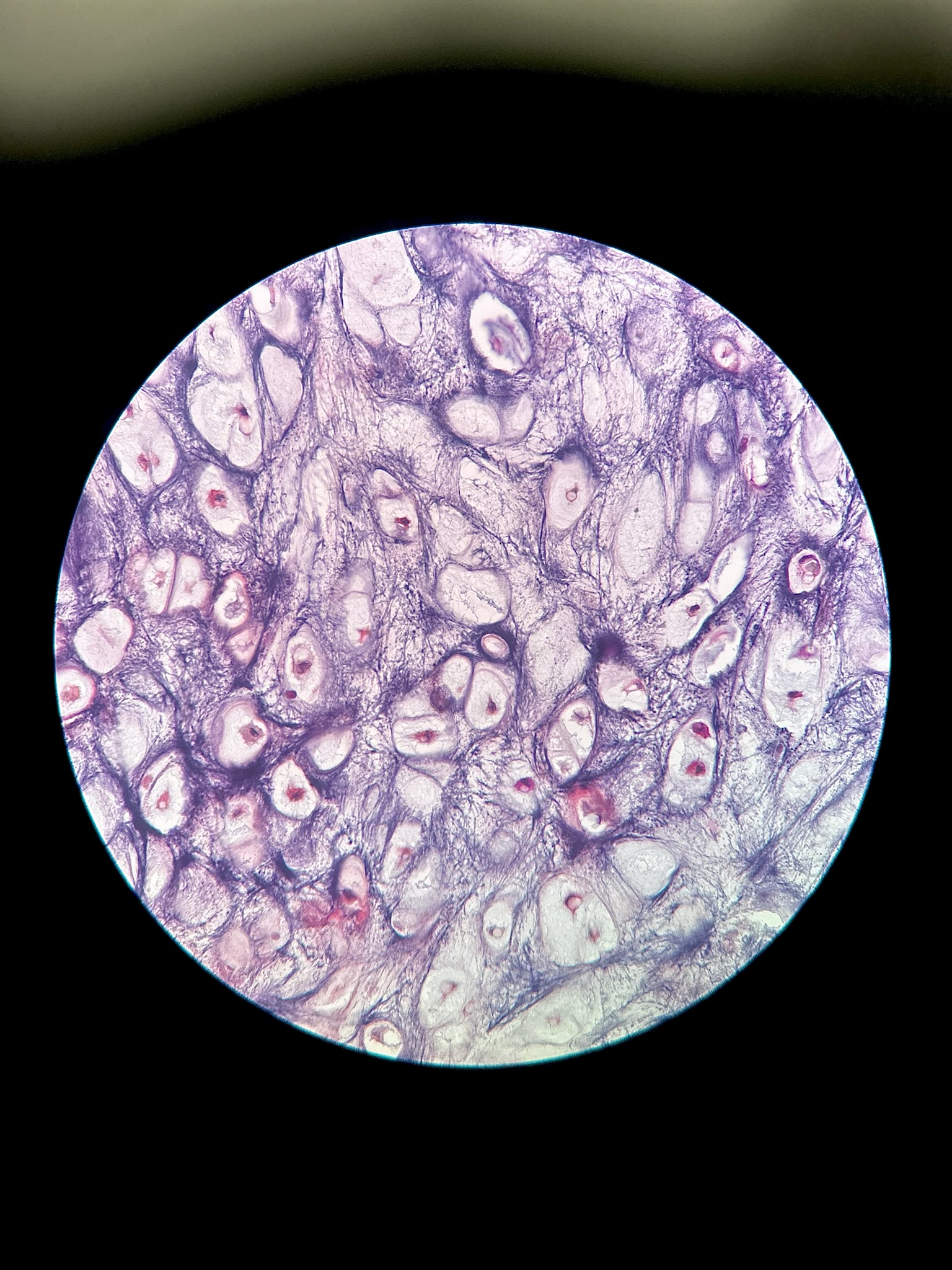
Elastic Cartilage
Locations: pinna, epiglottis, auditory canal, cuneiform cartilages of larynx
functions: maintains the shape of the structure while allowing flexibility
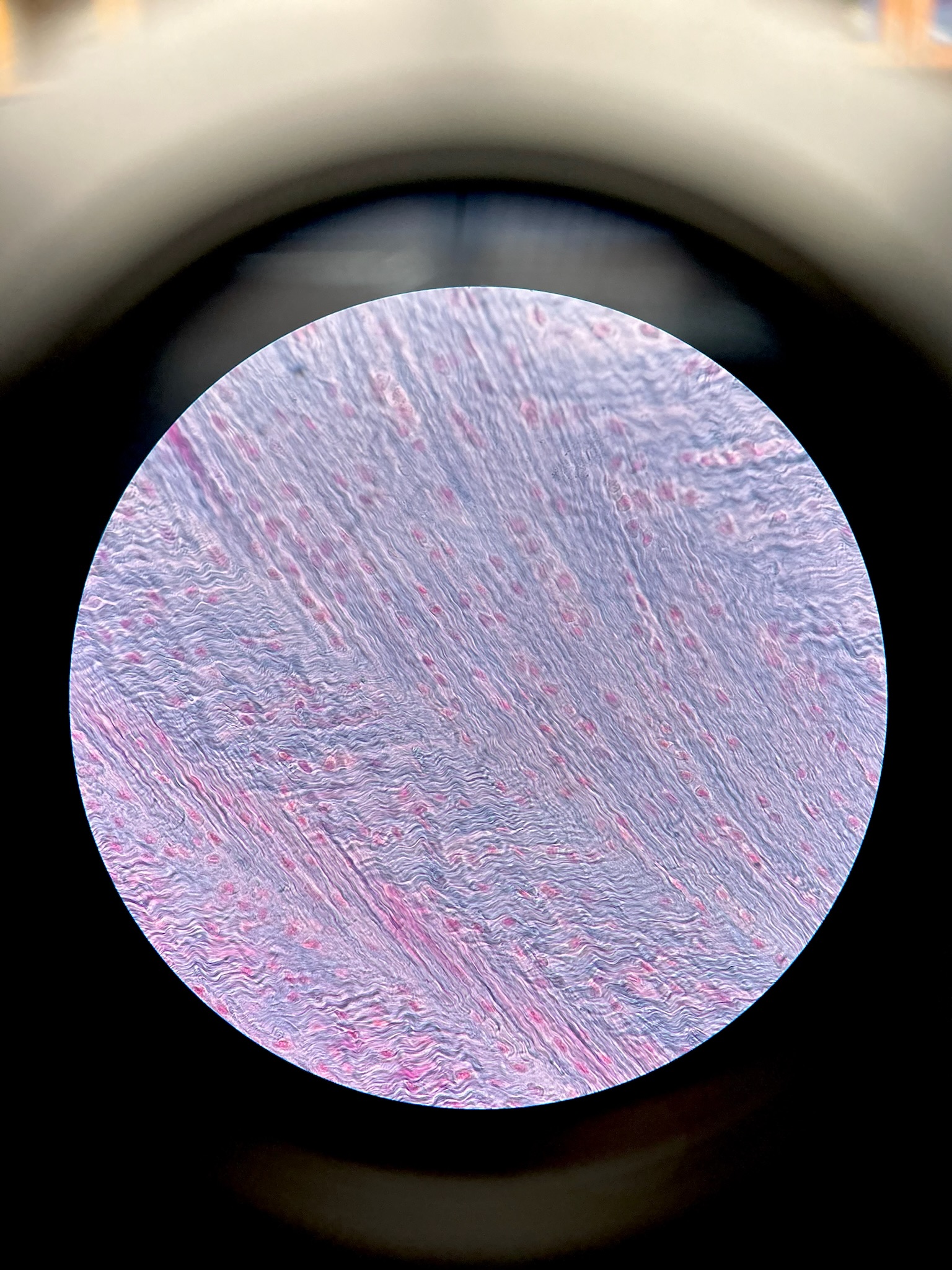
Fibrocartilage
locations: pads within knee joint, between pubic bones of pelvis, intervertebral discs
functions: resists compression, prevents bone to bone contact, limits movement
Bone
compact and spongy
has lacuna, inside has osteocytes
matrix is solid due to salts of calcium and phosphate
Blood
Liquid. No fibers, fibers only become active with clotting
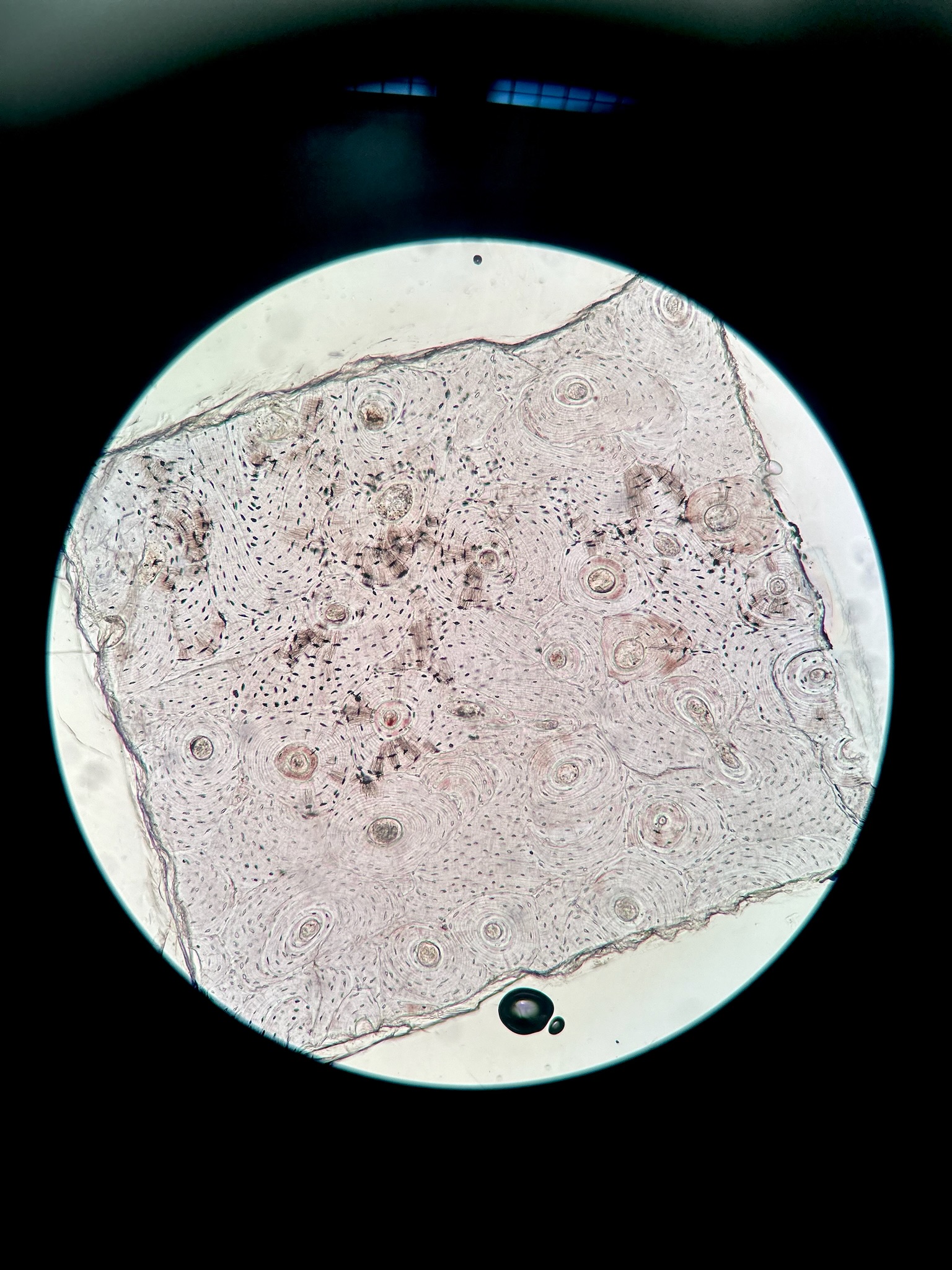
Bone
Location: bones
function: supports and protects, provide levers, stores calcium and other minerals and fat, marrow inside bone is site of blood cell formation
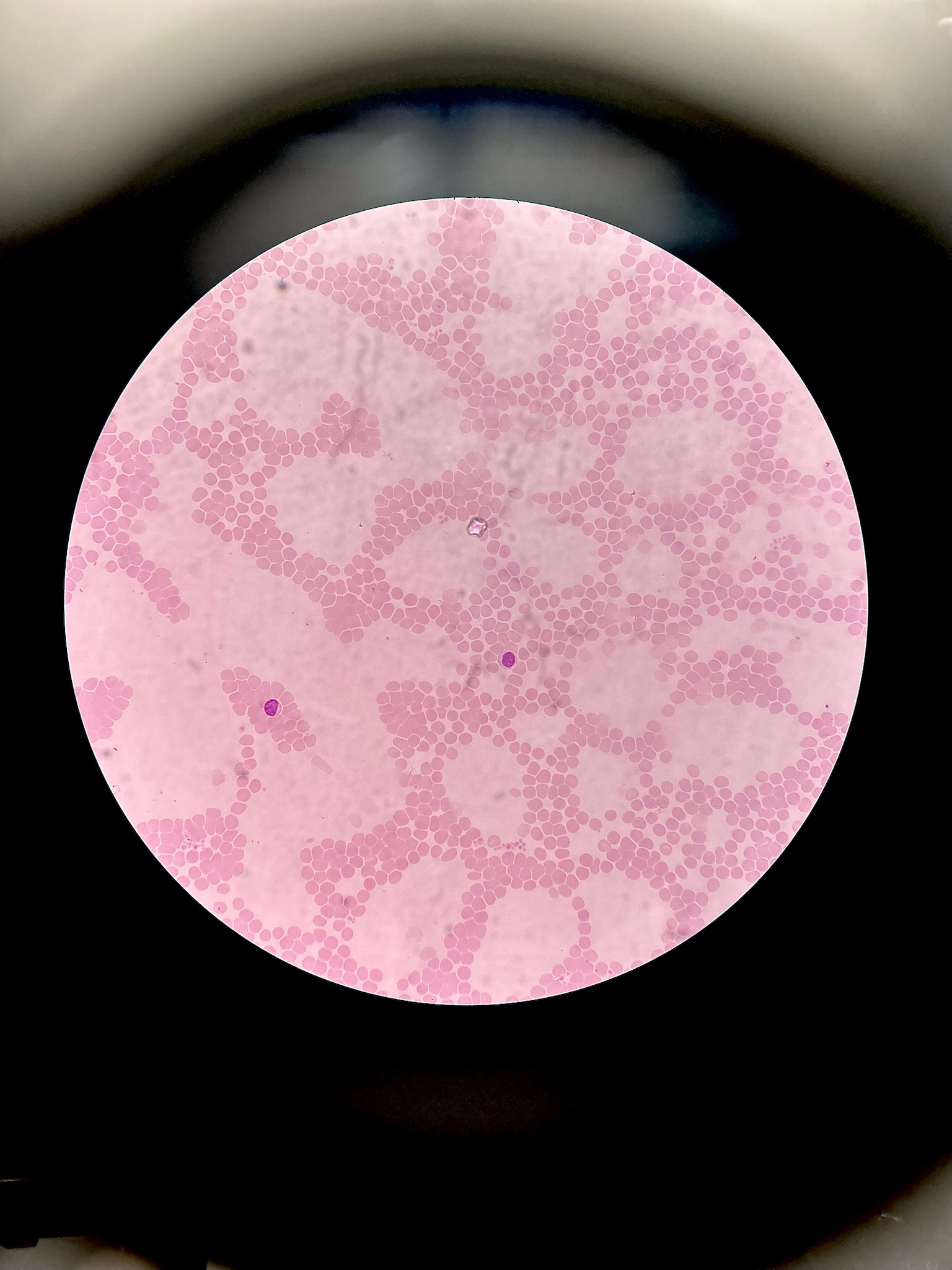
Blood
RBC - no nucleus WBC - nucleus
Location: blood vessels
function: transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
Nervous Tissue
Neurologia and Neurons
Neurologia
supporting cells that protect, support, and insulate delicate neurons
Neurons
Highly specialized to receive stimuli and conduct waves of impulses to all parts of the body
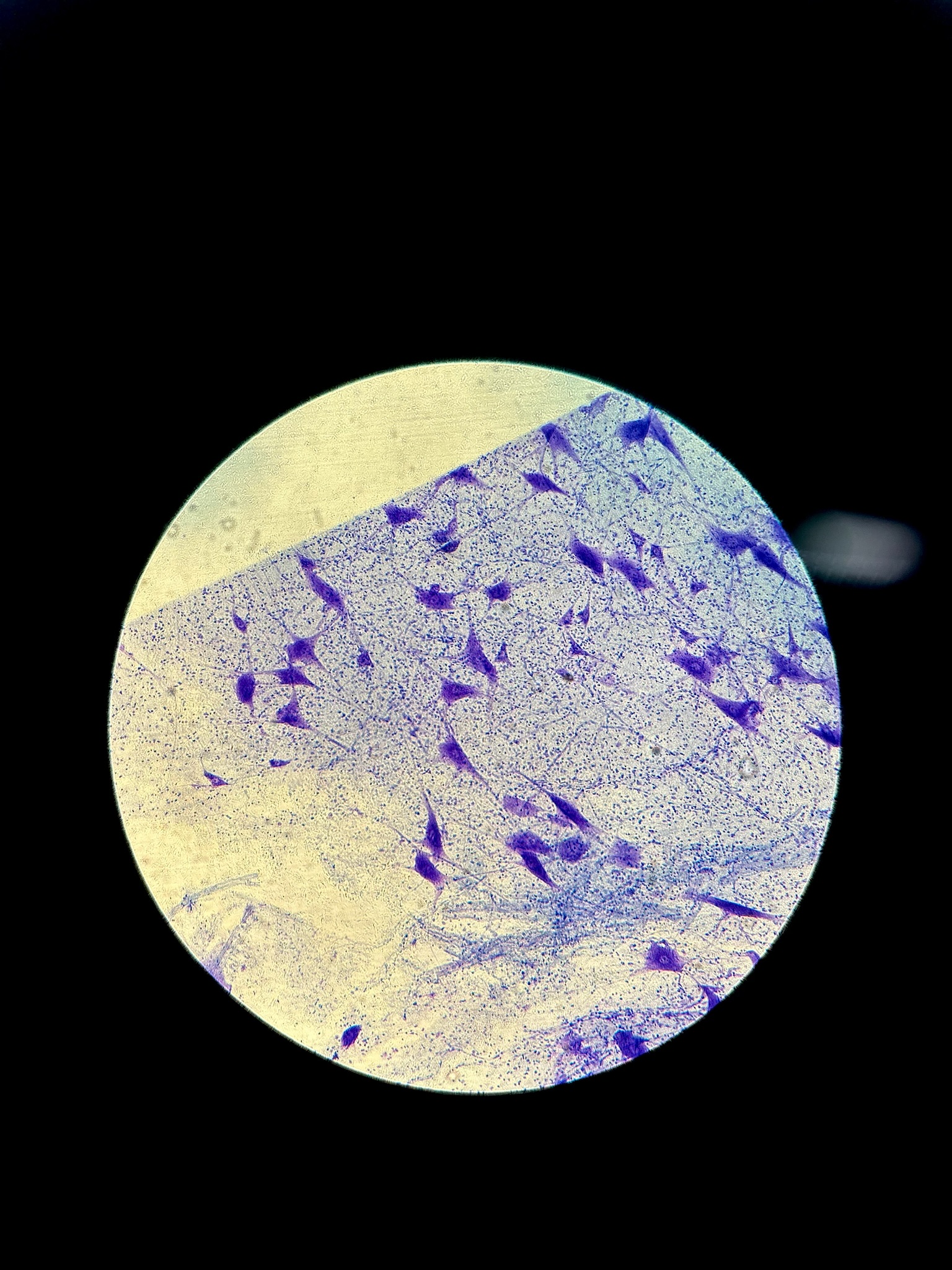
Nervous tissue. big black: neurons
Location: brain, spinal cord, nerves
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors which control their activity
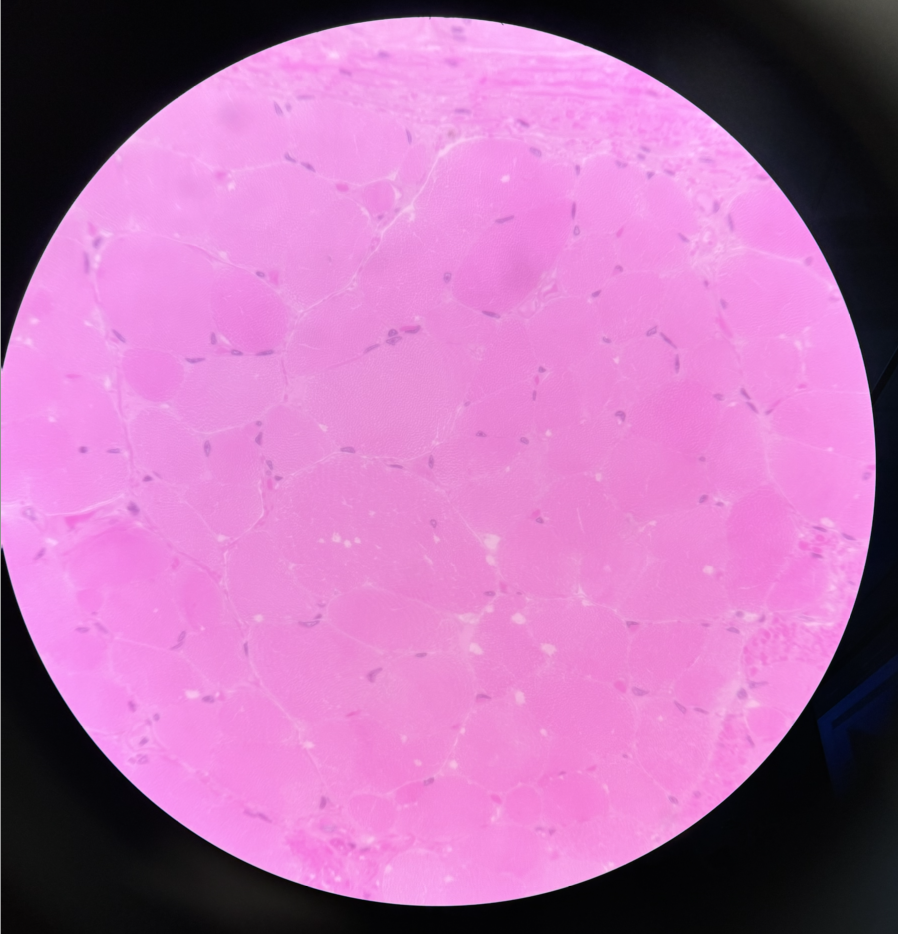
Muscle
Contact and produce most body movement
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Smooth Muscle
No striations. Nuceli are in the center of the cell
Skeletal Muscle
Striated muscle
many nuceli and are pushed to the side
Cardiac
Striated muscle cell. Are branched
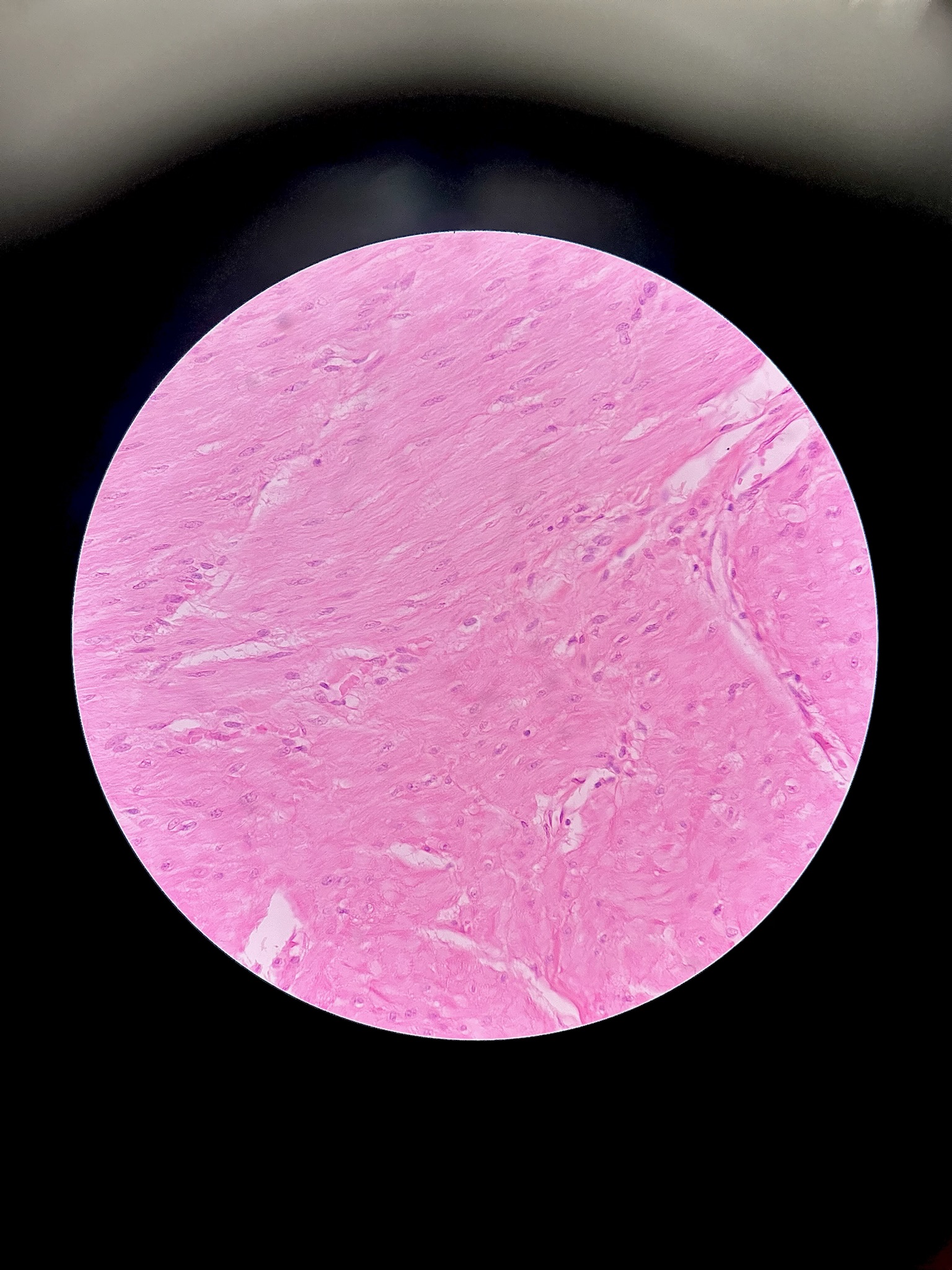
Smooth muscle
location: mostly walls of hollow organs
functions: propels substances or objects along internal passageways, involuntary control
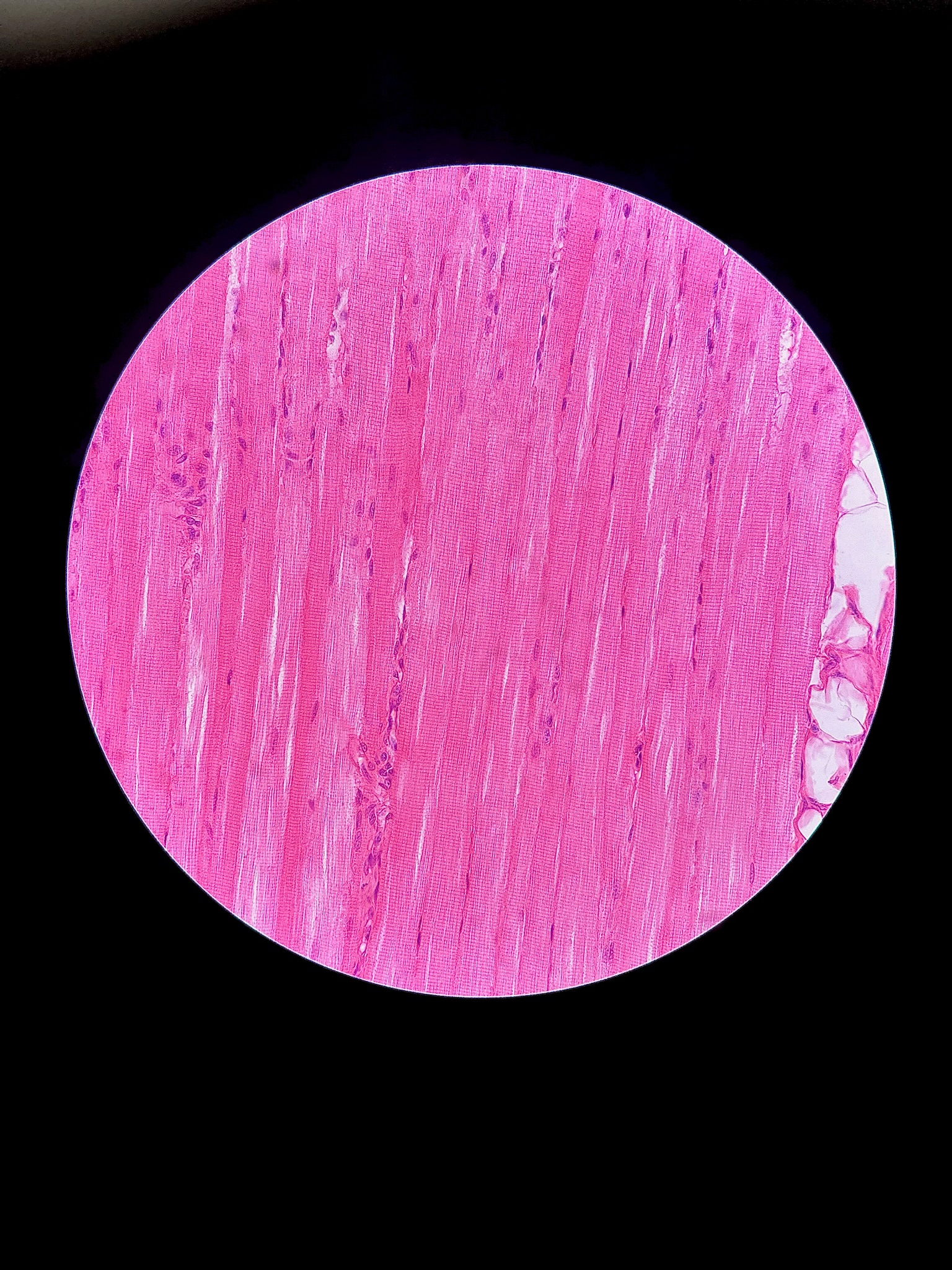
Skeletal muscle
location: in skeletal muscles attached to bones
function: voluntary movement, locomotion, manipulation of environment, facial expression
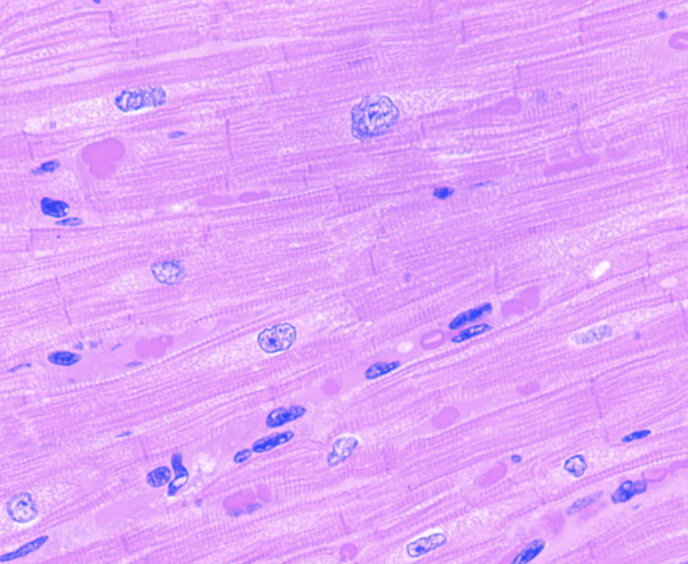
Cardiac muscle. Look for intercalated disc
location: walls of heart
function: as it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation, involuntary control
Skin
Epidermis + dermis
Epidermis
5 Layers: stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
Stratum basale
Closest to dermis. Constantly dividing
Stratum spinosum
Appear spikey. Weblike bundles of intermediate filaments
Stratum granulosum
Thin layer with granules
Stratum lucidum
Thin translucent layer with flattened dead keratinocytes. Not in thin skin
Stratum corneum
outermost layer
Dermis
Papillary layer (areolar connective tissue) and reticular layer (dense irregular layer)
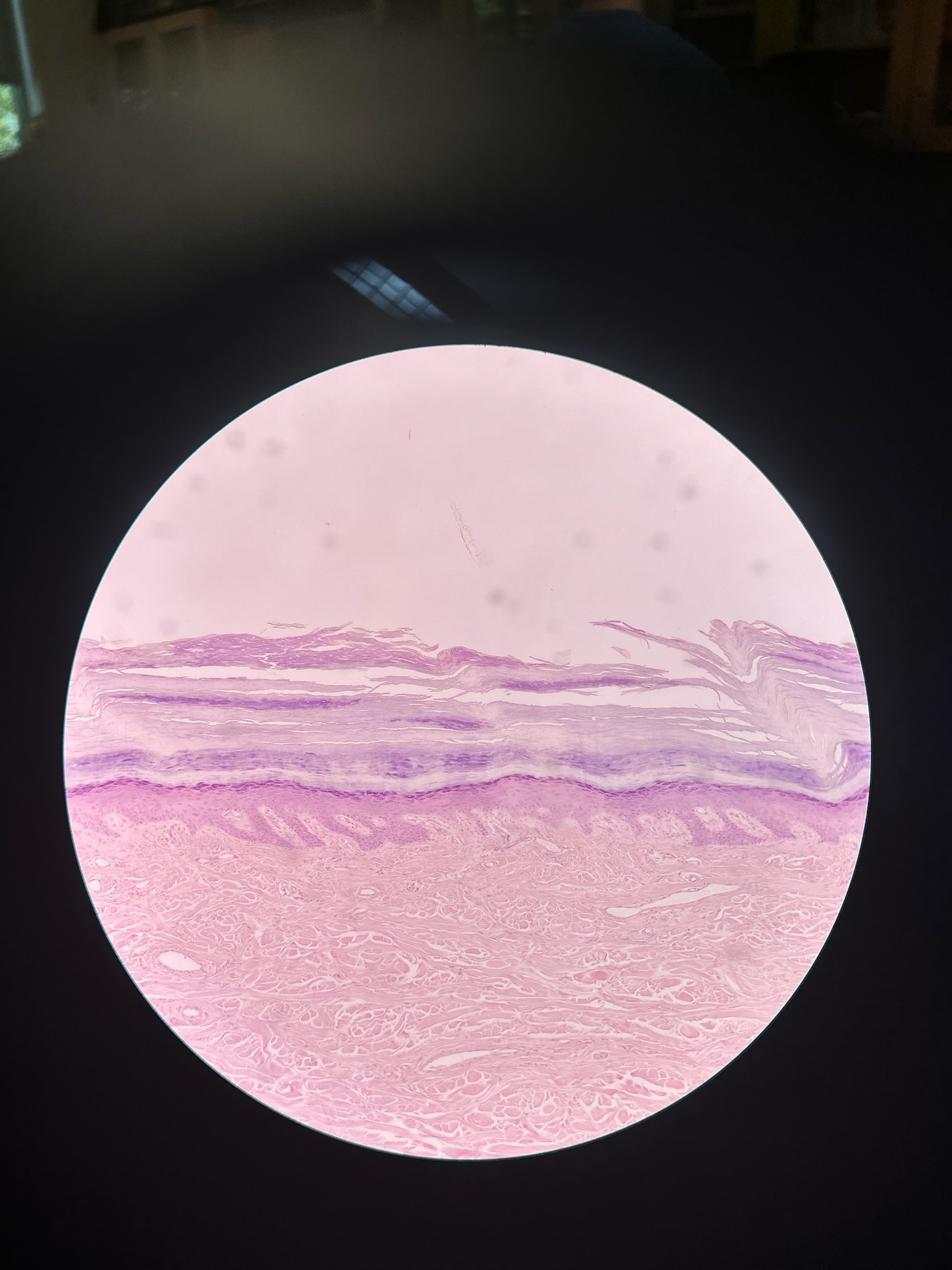
thick skin
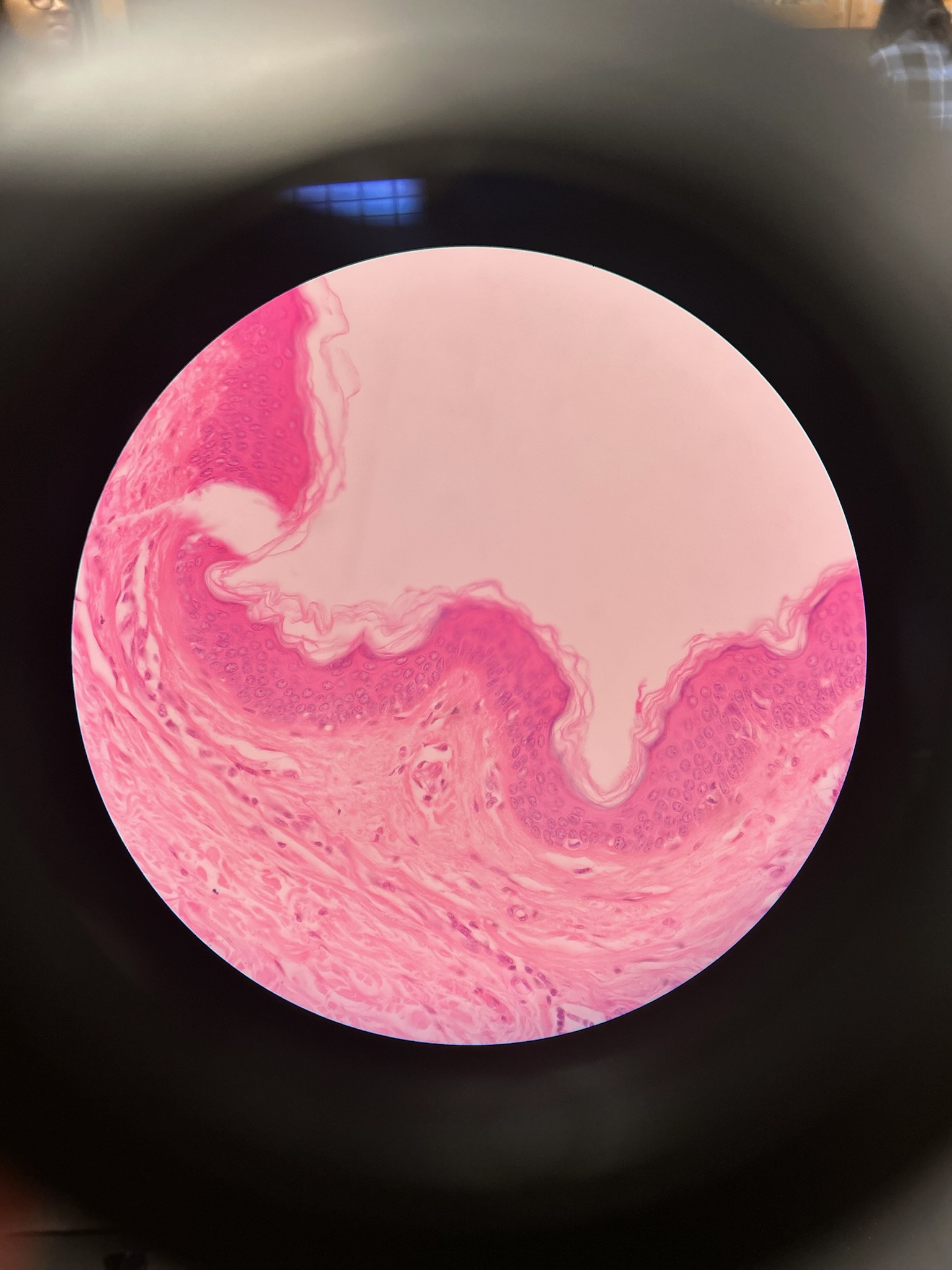
thin skin