Honors Bio Final
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
342 Terms
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells break down glucose using oxygen to release energy (ATP).
Photosynthesis
The process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using light energy.
Overall Balanced Equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy)
Energy Requirement in Cells
Cells need energy to live, grow, repair themselves, and respond to their environment.
Breathing and Cellular Respiration
Breathing gets oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide; cellular respiration uses oxygen to make energy and creates carbon dioxide as a waste product.
Redox Reactions
A chemical reaction in which electrons are lost from one substance (oxidation) and added to another (reduction).
Oxidation
The loss of electrons from a substance.
Reduction
The gain of electrons by a substance.
Stages of Cellular Respiration
The stages include glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Reactants of Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Products of Photosynthesis
Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Reactants of Cellular Respiration
Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Products of Cellular Respiration
Carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and ATP (energy).
Location of Photosynthesis
Occurs in chloroplasts.
Location of Cellular Respiration
Occurs in mitochondria.
Light Energy in Photosynthesis
Requires light energy from the sun.
Energy Release in Cellular Respiration
Releases energy stored in ATP.
Equation for Photosynthesis
Sunlight + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Waste Product of Cellular Respiration
Carbon dioxide (CO2).
Support of Breathing for Cellular Respiration
Breathing supports cellular respiration, and cellular respiration depends on breathing.
Chemical Reaction in Redox
Involves the transfer of electrons between substances.
Glycolysis
The metabolic process that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH.
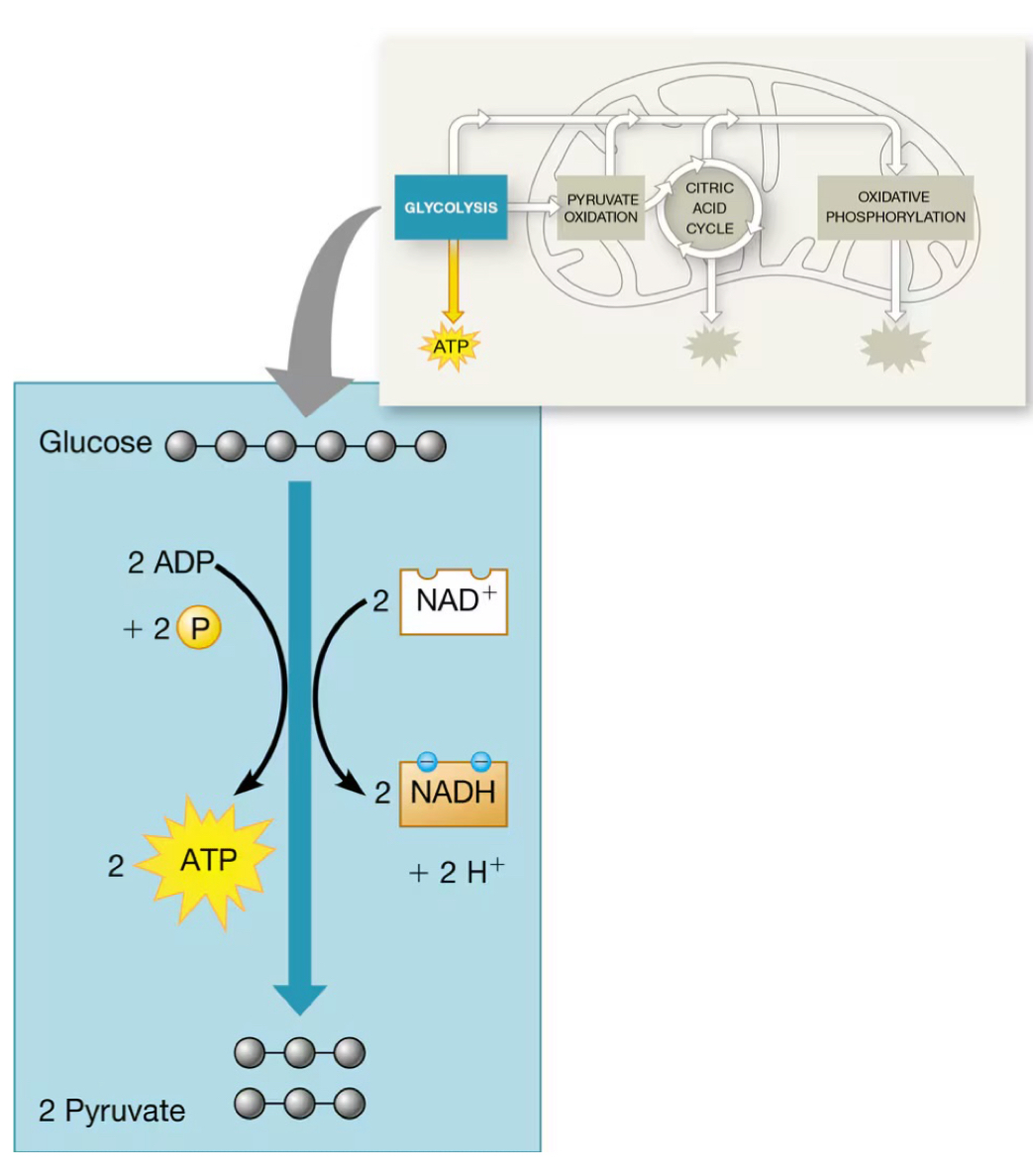
What process is demonstrated in this image?
Glycolysis, in cellular respiration
Cytosol
The fluid portion of the cytoplasm in cells where glycolysis occurs.
Net production of ATP from each glucose
2 ATP (Net gain); 4 ATP produced, but to ATP are used during earlier steps
NAD+
An electron carrier that is reduced to NADH during glycolysis.
NADH
The reduced form of NAD+, produced when NAD+ gains electrons and hydrogen.
Glucose oxidation
The process by which glucose loses electrons, resulting in the production of NADH.
Pyruvate
The end product of glycolysis, formed from the splitting of a 6-carbon glucose molecule.
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions
The 9 reactions that occur during glycolysis as glucose is converted to pyruvate.
Cleavage
The step in glycolysis where glucose is split into two 3-carbon molecules (G3P).
Energy Payoff Phase
The phase of glycolysis where each 3-carbon molecule is converted into pyruvate, producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
Initial energy source
Glucose, which contains chemical energy and is used at the start of glycolysis.
ATP investment
2 ATP are invested early in glycolysis to activate glucose.
High-energy electrons
Electrons stored in NADH, produced during glycolysis when NAD+ is reduced.
ATP generation
4 ATP are generated during the conversion of 3-carbon sugars in glycolysis, resulting in a net gain of 2 ATP.
Mitochondria
The organelle where pyruvate can enter for further ATP production via aerobic respiration.
Oxidation of pyruvate
The process that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix after glycolysis, producing acetyl-CoA and NADH.
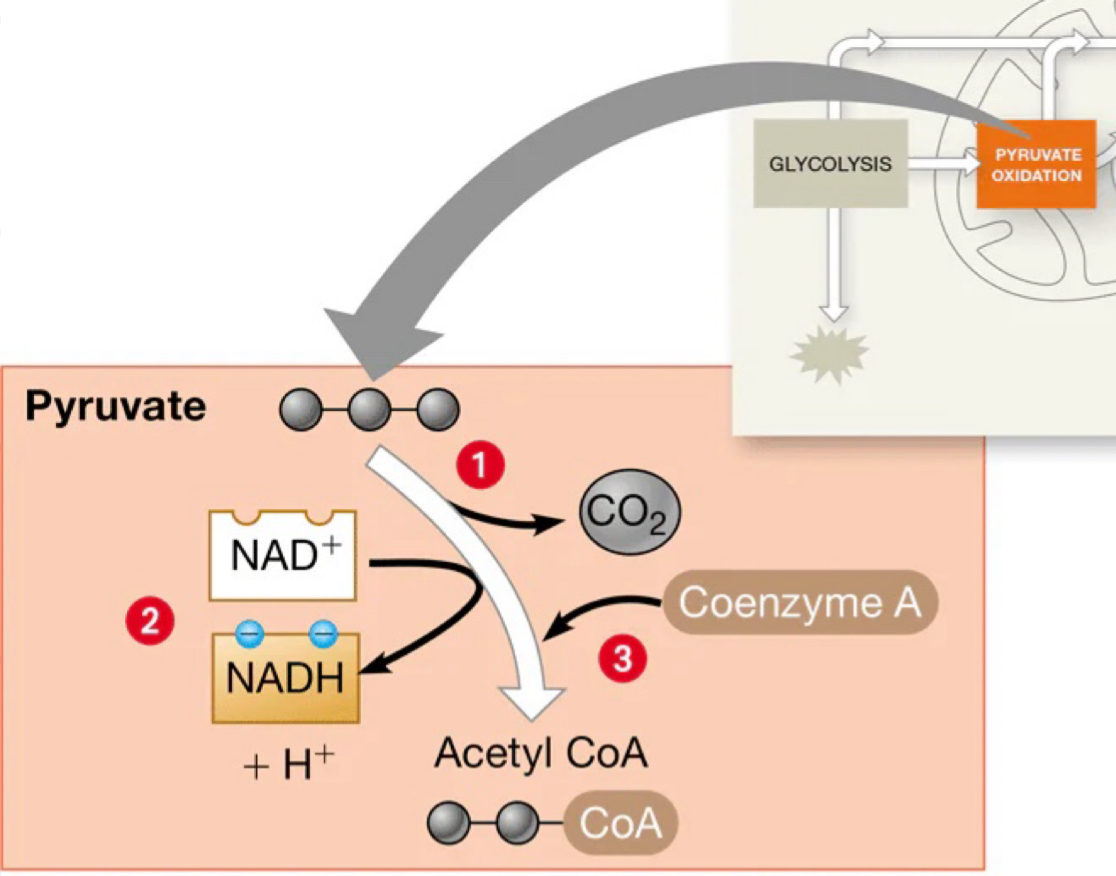
The process outlined in the image
Oxidation of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA, in cellular respiration
Acetyl-CoA
The product formed from the oxidation of pyruvate, which enters the citric acid cycle.
Twice per glucose
The oxidation of pyruvate occurs twice for each glucose molecule, as glycolysis produces two pyruvate.
Decarboxylation
One carbon atom is removed from the pyruvate (a 3 carbon molecule) as CO2, leaving a 2 carbon fragment.
Coenzyme A
The oxidized 2-carbon unit is attached to Coenzyme A, forming acetyl-CoA.
Citric Acid Cycle
A cycle that starts and ends with oxaloacetate (a 4-carbon molecule), allowing it to combine with another acetyl-CoA.
Mitochondrial Matrix
The location where the Krebs cycle takes place.
Oxaloacetate
Regenerated at the end of the citric acid cycle, ready to combine with another acetyl-CoA.
Citric Acid (Citrate)
A 6-carbon molecule formed from the combination of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
2 CO2 are released as waste from carbon oxidation during the citric acid cycle.
FADH2
1 FADH2 is produced from the reduction of FAD, also carrying electrons.
ATP
1 ATP is formed by substrate-level phosphorylation during the citric acid cycle.
Oxylactate
Regenerated during the cycle, enabling it to repeat.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A series of proteins in the inner membrane of mitochondria that transfer electrons and pump H+ ions.
Inner Membrane
Location of the ETC and ATP synthase.
Intermembrane Space
The space between inner and outer membranes where H+ ions accumulate.
Matrix
The innermost space of the mitochondrion where the Krebs cycle occurs.
Proton Gradient
Created by pumping H+ ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space.
ATP Synthase
An enzyme that uses the flow of H+ ions to phosphorylate ADP + P to ATP.
Oxygen's Role
Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the ETC, combining with low-energy electrons and H+ to form water (H2O).
Cyanide Poisoning
Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain, preventing ATP production and leading to cell death.
Cyanide
A poison that blocks the electron transport chain (ETC) in mitochondria, halting ATP production and causing cells to die from energy failure.
Cell death
Occurs quickly after ATP depletion, leading to organ failure and death within minutes in high doses.
Alcoholic Fermentation
A type of fermentation that occurs in yeast and some bacteria, producing 2 ethanol and 2 CO2 from glucose.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
A type of fermentation that occurs in mammalian muscle cells and some bacteria, producing 2 lactic acid from glucose.
Fermentation Overview
An anaerobic process that occurs in the cytosol, begins after glycolysis when oxygen is not available, and regenerates NAD+.
NAD+ Regeneration
Occurs via conversion of pyruvate in fermentation and via the electron transport chain (ETC) in aerobic respiration.
ATP Yield in Fermentation
2 ATP is produced per glucose during fermentation.
ATP Yield in Aerobic Respiration
About 30-32 ATP is produced per glucose during aerobic respiration.
End Products of Fermentation
Lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 are produced in fermentation.
End Products of Aerobic Respiration
CO2 and H2O are produced in aerobic respiration.
Location of Fermentation
Occurs only in the cytosol.
Location of Aerobic Respiration
Occurs in the cytosol (glycolysis) and mitochondria (ETC).
Organism Examples for Fermentation
Mammal muscle cells (lactic acid), yeast (alcoholic), lactic acid bacteria (lactic acid), certain prokaryotes (either type).
Elements of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
Structural Formula of Glucose
C6H12O6 is the structural formula of glucose, a monosaccharide.
Importance of Glucose
Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for cells and is essential for the proper functioning of every organ system.
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides are single sugar units, disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides, and polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides.
Monosaccharides
The simplified form of carbohydrates, simple sugar units.
Disaccharides
Made by joining two monosaccharides together through a dehydration reaction (which removes a water molecule).
Polysaccharides
Long chains of many monosaccharides linked together.
Dehydration synthesis
Two monosaccharides (for disaccharides) or many monosaccharides (for polysaccharides) join together.
Hydrolysis
A water molecule is added to break a glycosidic bond.
Starch
Found in: Plants.
Glycogen
Found in: Animals (especially liver and muscles).
Cellulose
Found in: Plant cell walls.
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food using light or chemical energy.
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food and must consume organisms for energy.
Chloroplast
An organelle in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs.
Grana
Stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids in chloroplasts.
Thylakoid
Membrane-bound compartment within chloroplasts where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place.
Thylakoid membrane
Site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll, photosystems (I and II), electron transport chains, and ATP synthase.
Thylakoid Space (Lumen)
Interior space enclosed by the thylakoid membrane where the proton gradient builds up to power ATP production.
Stroma
Located inside the chloroplast, but outside the thylakoid membranes; site of the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide (CO2) is fixed into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, allowing scientists to follow atoms through complex pathways.
Overall equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Redox reactions in photosynthesis
Involves the oxidation of water and reduction of NADP+; essential for energy transfer in light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
Water (H2O)
Oxidized in photosynthesis; source of electrons and protons; releases O2.
NADP+
Reduced in light reactions; final electron acceptor that forms NADPH.
CO2
Reduced in the Calvin Cycle; becomes part of glucose.
NADPH
Oxidized in the Calvin Cycle; donates electrons to reduce CO2.
Pigments
Molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light; capture light energy for photosynthesis.