bio 221 final
1/377
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
378 Terms
In Pasteur's famous experiment that finally disproved spontaneous generation, bacteria grew ________________________.
A. in all flasks regardless of how they were treated experimentally
B. only once media had been boiled
C. only in flasks with a swan neck
D. only in media that came in contact with other bacteria
E. only in media that came in contact with air
D. only in media that came in contact with other bacteria
A C-C bond in molecule A undergoes a random charge fluctuation. As molecule A comes close to a C-C bond in molecule B, what will happen to molecule B?
A. Nothing will happen. These molecules cannot interact.
B. It will form a polar covalent bond with molecule A.
C. A dipole will be induced which will weakly attract molecule B to molecule A
D. It will form a hydrogen bond with molecule A.
E. It will form a covalent bond with molecule A.
C. A dipole will be induced which will weakly attract molecule B to molecule A
Proteins with the amino acid valine on their surface often stick together when placed in water.
Why? On the right, is the structure of the amino acid valine with its R-group highlighted in pink.
A. Valine is attached to other valine by very strong van del Waals interactions.
B. Valine's R-group forms covalent bonds with other valine R-groups.
C. Valine forms H-bonds with water.
D. Valine forms H-bonds with water.
E. Due to the hydrophobic effect, H2O forms a network of H-bonds around collected valines.
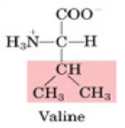
E. Due to the hydrophobic effect, H2O forms a network of H-bonds around collected valines.
Viroids are ____________________.
A. small pieces of RNA without a protein coat
B. small virus-like particles
C. another name for a plant virus
D. empty protein coats without any nucleic acid
E. infectious proteins that serve as folding templates for other proteins
A. small pieces of RNA without a protein coat
Which of the following is NOT true of cellulose?
A. It is branched.
B. It is considered biodegradable even though humans cannot digest it.
C. It has intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
D. It is linked ꞵ-1,4.
E. It contains just one glucose monomer.
A. It is branched.
Two molecules are composed of the same atoms, but the molecules have different molecular weights. This can be explained by the existence of ______________.
A. dipole moment
B. ions
C. isomers
D. isotopes
E. sp3 orbital hybridization
D. isotopes
You are examining an organism under the microscope. It is about 15 micrometers (μm) in diameter. A chemical analysis shows that it contains DNA, RNA and protein, as well as other macromolecules. You grow it on a petri dish to get a pure culture, but this time when you look at under the microscope it consists of filaments 100 μm long and 8 μm wide. Explain this.
A. It is diffusion-limited when it is growing on the petri dish.
B. You were looking at a virus that became contaminated with rod-shaped bacteria.
C. You are looking at eukaryotic algae, with long flagella.
D. You are looking at a culture of ciliated protozoan.
E. You are looking at a fungal culture.
E. You are looking at a fungal culture.
Which of the following can serve as a hydrogen bond donor?
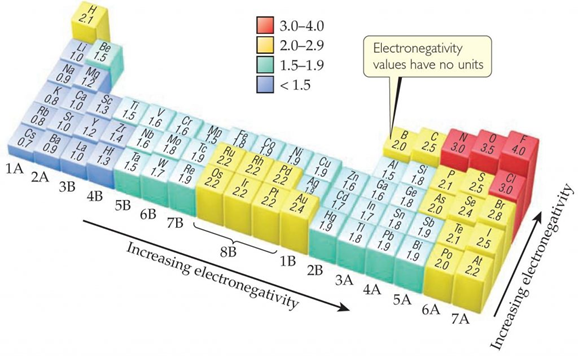
A. The O in a C=O bond.
B. The H in a C-H bond.
C. The O in a P=O bond
D. The H in a B-H bond.
E. The H in a N-H bond.
E. The H in a N-H bond.
What type of microscope would you use to examine a biofilm that was 2 mm thick?
A. Transmission electron
B. Confocal scanning laser
C. Atomic force
D. Phase contrast
E. Interference (Nomarski)
B. Confocal scanning laser
Mycolic acids cause mycobacteria to _______________________.
A. be toxic to humans
B. stick to surfaces
C. be Gram positive
D. resist chemical damage
E. be shapeless
D. resist chemical damage
The acid-fast stain is an example of a differential stain. What makes it "differential"?
A. It stains positively charged molecules in the cell rather than negatively charged molecules.
B. It stains special bacterial structures called differentials that are present in some cells
C. It uses two stains, along with a solvent that removes stain from some cells but not all.
D. It stains positively charged molecules in the cell rather than negatively charged molecules.
E. It uses a special differential dye during the staining process.
C. It uses two stains, along with a solvent that removes stain from some cells but not all.
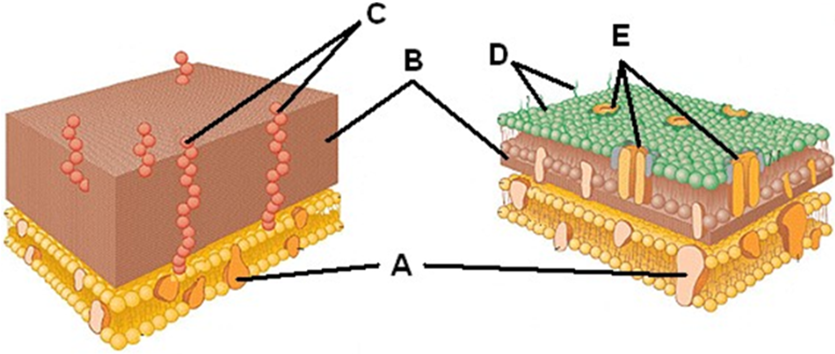
In the following depiction of a phospholipid membrane, what represents the fatty acid component of the membrane?
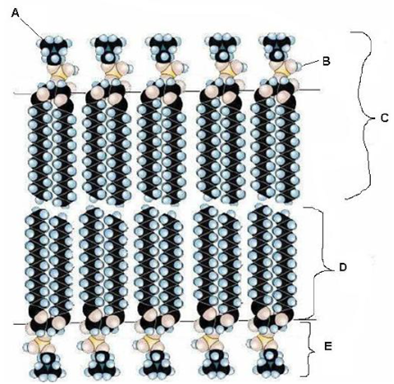
D
What type of microscope views a specimen with light reflected from the specimen rather than passed through the specimen?
A. dark field
B. bright field
C. interference (Nomarski)
D. phase contrast
E. confocal scanning laser
A. dark field
Some bacterial cells can synthesize osmoprotectants to avoid ___________________.
A. plasmolysis in a hypotonic environment
B. lysis in a hypotonic environment
C. lysis in a hypertonic environment
D. plasmolysis in a hypertonic environment
E. turgor pressure against their cell walls
D. plasmolysis in a hypertonic environment
How does the MFS antiport pump Na+ out of the cell?
A. It uses energy from ATP hydrolysis.
B. It uses both the membrane potential and proton gradient energy.
C. It uses the membrane potential (charge component of the PMF).
D. It uses the energy of the proton gradient.
E. It uses energy in the Na+ gradient.
D. It uses the energy of the proton gradient.
How can an E. coli cell move toward a point source of a molecular attractant?
A. It cannot. E. coli can only move toward attractant that is evenly distributed in a solution.
B. The cell follows signals from other cells that are nearer to the attractant than it is.
C. A protein at one end of the cell acts like an "eyespot" to "see" the attractant.
D. E. coli can tumble less frequently if it is moving towards a continually increasing attractant concentration.
E. There is a higher attractant concentration at one end of the cell than at the other, and E. coli can move forward or backward toward the higher concentration.
D. E. coli can tumble less frequently if it is moving towards a continually increasing attractant concentration.
This reaction is an example of ____________________.
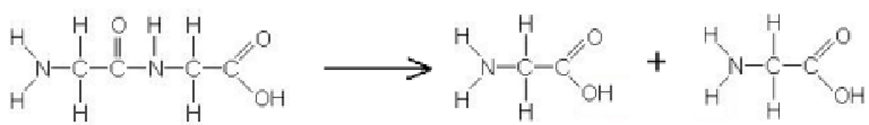
A. Reduction
B. Hydrolysis
C. Oxidation
D. Transpeptidation
E. Condensation
B. Hydrolysis
An atomic force "microscope" is different enough that some people do not consider it a microscope at all. What is so different about it compared to other microscope types?
A. It uses a rotating illuminating beam to image the sample at multiple angles.
B. It produces an image that must be stacked together with other images in a computer.
C. There is no true magnification system. It just has a sensitive electrical probe and amplifier.
D. It has complicated electronic components to control the focus.
E. It does not use light.
C. There is no true magnification system. It just has a sensitive electrical probe and amplifier.
What will happen when cells of the bacterium Mycoplasma are placed in distilled water?
A. They will lyse.
B. They will swell with turgor pressure but will not burst.
C. These are very robust cells, and they will grow in distilled water.
D. They will synthesize osmoprotectants so that they do not plasmolyze.
E. They will plasmolyze.
A. They will lyse.
What do bacterial ABC drug efflux pumps and Type III secretory systems have in common?
A. Neither involves a periplasmic intermediate.
B. Both allow transport of fully folded proteins.
C. Both are structurally related to flagella.
D. Neither requires contact with another cell to initiate transport.
E. Both make use of a needle complex.
A. Neither involves a periplasmic intermediate.
The presence of carboxysomes in a bacterial cell indicates that the cell ________________.
A. is a phototroph
B. is an autotroph
C. is an auxotroph
D. can store carbon reserves
E. can use organic electron donors
B. is an autotroph
The purpose of an enrichment culture is to ____________________.
A. grow fastidious bacteria or auxotrophs
B. prevent or inhibit growth of many bacteria in a sample
C. grow obligate intracellular parasites
D. grow lots of different cells in an enriched medium
E. allow better growth of one type of bacteria than others from an environmental sample
E. allow better growth of one type of bacteria than others from an environmental sample
Which of the structures below most accurately represents a porin?
E
The most evolutionary primitive rocker-switch model for transport proteins requires __________________________.
A. Solute gates to prevent reverse transport.
B. A transporter with a periplasmic binding protein.
C. A transporter with two alternative conformations.
D. A proton motive force to provide energy.
E. ATP hydrolysis to provide energy.
C. A transporter with two alternative conformations.
The protein coat of an endospore ______________________.
A. is deposited between the membranes of the forming endospore and the mother cell
B. is a thin layer of protein crosslinked with glycosidic bonds
C. is formed very early in the sporulation process
D. is involved in drying out the spore core
E. is the structural equivalent of the Gram-negative outer membrane
A. is deposited between the membranes of the forming endospore and the mother cell
Superoxide dismutase is _________________.
A. an enzyme that allows autotrophs to reduce CO2
B. an enzyme that allows thermophiles to survive high temperatures
C. a storage granule for lithotrophic electron sources
D. one of the components of the electron transport system
E. an enzyme that allows aerobes to survive in oxygen
E. an enzyme that allows aerobes to survive in oxygen
Based on what you know about the following methods for bacterial growth enumeration work, you should be able to classify one of them as a direct method. Which one?
A. Most Probable Number estimation
B. Measurement of bacterial turbidity with a spectrophotometer
C. Gas production measured in a Durham tube
D. Using the luciferase assay
E. Acid production measured on a nanochip
B. Measurement of bacterial turbidity with a spectrophotometer
Why is the phosphorelay mechanism involved in sugar transport in bacteria?
A. The phosphorelay can be used to make a PMF which can then be used to make ATP.
B. Each protein in the relay can be used to regulate other cell processes based on the presence or absence of sugar in the environment.
C. Each protein in the relay can receive a phosphate from a different phosphate carrier, either ATP, ADP, or PEP.
D. The energy from the phosphate is increased slightly at each step until it is enough to open the transport channel.
E. Each protein in the phosphorelay can transport a different sugar molecule.
B. Each protein in the relay can be used to regulate other cell processes based on the presence or absence of sugar in the environment.
Capsules or slime layers are wholly or partly responsible for all of the following EXCEPT _______.
A. biofouling of filters
B. formation of biofilms
C. avoiding phagocytosis
D. surface adhesion
E. motility
E. motility

The ingredients list for a biological medium is shown at the right. This medium is __________.
A. complex and differential
B. complex
C. defined and selective
D. selective
E. defined
A. complex and differential
A competitive inhibitor of an enzyme _______________.
A. can only inhibit enzymes in anabolic pathway
B. inhibits an enzyme even at a much lower concentration than the substrate
C. binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme
D. must structurally resemble the substrate of the enzyme it inhibits
E. works by denaturing or modifying the shape of the active site
D. must structurally resemble the substrate of the enzyme it inhibits
Which of the following equations would be used to solve this problem?
“How many bacteria would you need to start with in order to have as many cells as the Earth’s population (6 billion) within 12 hours. The bacterium divides in 30 minutes.
A. x = (6 X 109) e(1.39)(12)
B. (6 X 109) = x e(0.5)(12)
C. (6 X 109) = x e(1.39)(12)
D. (6 X 109) = e12 x
E. x = (6 X 109) e(2)(12)
A. x = (6 X 109) e(1.39)(12)
Whether a eukaryotic cell will use the TCA cycle depends on how much O2 is present in the environment. What determines whether a bacterium will use its TCA cycle or not?
A. Whether there is excess glucose in the cell
B. The need the cell has for reducing power
C. An excess of NADH in the cell
D. The need the cell has for ATP
E. Still the amount of O2 in the environment
C. An excess of NADH in the cell
The Most Probable Number (MPN) method _______________.
A. is used for very large sample volumes
B. requires multiple culture tubes, but no petri dishes
C. is considered to be a direct cell count, even though it is statistically based
D. is usually performed by pouring a sample of the culture through a filter
E. is a rough estimate of the actual titer based on optical density
B. requires multiple culture tubes, but no petri dishes
Given their particular lifestyle, thermophilic bacteria must have evolved specialized mechanisms to guard against ___________________.
A. plasmolysis of their cytoplasm
B. development of too large a PMF
C. plasmolysis of their cytoplasm
D. solidification of their membranes
E. denaturation of their enzymes
E. denaturation of their enzymes
One advantage of growing cells in continuous culture is that _________________.
A. you can make the cells grow as fast or as slowly as you want
B. there is no special equipment required
C. you can get them to produce more secondary metabolites, such as antibiotics
D. you can count them more easily than in batch culture
E. their growth rate constant (μ) is higher than in batch culture
A. you can make the cells grow as fast or as slowly as you want
Much of the bacterial cell membrane is made of lipids. Where do lipids come from during bacterial metabolism?
A. By catabolic reactions from glucose.
B. Bacteria must ingest lipids in their diet. They cannot be synthesized.
C. From fermentation of pyruvate.
D. They are built from glycerol and acetyl-CoA.
E. hey are made by oxidative phosphorylation.
D. They are built from glycerol and acetyl-CoA.
How could you best determine whether an unknown respiratory chain was from a bacterium or from a eukaryotic mitochondrion?
A. Whether a different magnitude of PMF can be produced under different conditions
B. Whether it produced ATP directly or indirectly
C. Whether it used NADH as an electron donor or not
D. Whether it involved a quinone loop or not
E. Whether cytochrome c were an electron acceptor or not
A. Whether a different magnitude of PMF can be produced under different conditions
Which of the following reactions is carried out by methanogenic Archaea?
A. CO2 is reduced to CH4 using electrons from light
B. CH4 is oxidized to CO2 using electrons from light
C. CO2 is reduced to CH4 using electrons from H2
D. CH4 is oxidized to CO2 using an organic electron donor
E. glucose is hydrolyzed to CO2 using energy from CH4
C. CO2 is reduced to CH4 using electrons from H2
A mouthwash called “Hexodent” lists the following ingredients: 8% alcohol, 0.2% chlorhexidine, mint flavor. How does this mouthwash kill bacteria?
A. The chlorhexidine oxidizes proteins.
B. The chlorhexidine dissolves cell membranes.
C. Chlorhexidine + ethyl alcohol → ethylene oxide, which oxidizes DNA.
D. The alcohol damages DNA.
E. The alcohol denatures proteins.
B. The chlorhexidine dissolves cell membranes.
The chemical DCCD binds irreversibly to the proton binding site of the FOF1 ATP Synthase. What is the most likely consequence if DCCD is added to a culture of a facultative anaerobe?
A. The cell would be OK, since the H+ binding site is not the place where ATP is made.
B. The flagellar rotation speed would briefly increase due to a larger PMF.
C. The cells will die because they cannot produce ATP.
D. The cell would produce much less of a PMF.
E. The ATP Synthase would rotate passively but would not produce ATP.
B. The flagellar rotation speed would briefly increase due to a larger PMF.
Agrobacterium tumifaciens is especially important to plant scientists. What is so special about it?
A. It forms cysts that help to aerate the soil.
B. It can be used to insert foreign DNA into plant cells.
C. It is an excellent bacterial model for the plant type of photosynthesis.
D. It makes a carbon source that plants can use to grow.
E. It fixes nitrogen in plant root nodules.
B. It can be used to insert foreign DNA into plant cells.
Which of the following is NOT a part of the updated (modern) “Central Dogma” of Biology?
A. RNA makes protein
B. DNA makes DNA
C. RNA makes DNA
D. Protein makes RNA
E. DNA makes RNA
D. Protein makes RNA
During a reaction in the electron transport chain, an electron acceptor ______.
A. must be a protein
B. must also accept H+
C. must be reduced by the electron donor
D. must be able to synthesize ATP
E. must have more energy than the electron donor
C. must be reduced by the electron donor
Compared to a dry surface, an oily surface ________________.
A. should have about the same properties as far as disinfection is concerned
B. will be more susceptible to dry heat than to steam
C. is easier to pasteurize but harder to sterilize
D. will probably require cleaning with antiseptics rather than with disinfectants
E. is likely to require a longer decimal reduction time for disinfection
E. is likely to require a longer decimal reduction time for disinfection
The following segment of double stranded DNA is transcribed using the sigma factor σ70, which recognizes as a consensus “TTGACA” at -35 and “TATAAT” at -10.
5’---TAGTGTATTGACATGATAGAAGCACTCTTACTATAATCTCAATAGCTACG---3’
3’---ATCACATAACTGTACTATCTTCGTGAGAATGATATTAGAGTTATCGATGC---5’
Which strand is the template, and in which direction is it read?
A. Either strand could be the template, read to the right.
B. Bottom strand, read to the left.
C. Bottom strand, read to the right.
D. Top strand, read to the left.
E. Top strand, read to the right.
C. Bottom strand, read to the right.
Which of the following bacteria both carry out fermentation reactions that are used in the preparation of important food products?
A. Leuconostoc and Deinococcus
B. Lactococcus and Propionibacterium
C. Streptomyces and Pseudomonas
D. Caulobacter and Bacillus
E. Clostridium and Corynebacterium
D. Lactococcus and Propionibacterium
There are 61 coding codons, but only 45 tRNAs. How can 45 tRNAs recognize 61 codons?
A. The tRNA anticodons do not have to base-pair precisely with the codons.
B. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases allow the appropriate tRNA to match each codon.
C. The 5' end of the codon can shift by one base to match the tRNA in the A site.
D. The 45 tRNAs still have 61 different anticodons.
E. The reading frame can vary to allow the same tRNA to read multiple codons.
A. The tRNA anticodons do not have to base-pair precisely with the codons.
Which of the following medical instruments is NOT matched properly with an antimicrobial method that could be used to cleanse it?
A. Examination table - Phenolic (e.g. Lysol)
B. Central venous (in vein) catheter - Ethylene oxide
C. Tracheal (lung) endoscope - Glutaraldehyde
D. Gastric (stomach) endoscope - Hydrogen peroxide
E. Surgical sponge - Quaternary ammonium salt (QUAT)
E. Surgical sponge - Quaternary ammonium salt (QUAT)
The enzyme DNA polymerase __________________.
A. adds a new nucleotide to the 5' end of an existing nucleotide
B. begins replication by binding its sigma factor to a promoter
C. requires the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP in order to carry out its reaction
D. reads a template strand in either direction, depending on the direction of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence
E. requires a short sequence of bases with a 3' OH to initiate its reaction
E. requires a short sequence of bases with a 3' OH to initiate its reaction
The protein TrmB binds to the promoter region of the malE gene. The sugar trehalose binds to TrmB. In the presence of trehalose, the binding of TrmB to the malE gene is inhibited, and the malE gene is transcribed. TrmB is an example of _____.
A. a repressible gene
B. an operator
C. a repressor
D. an inducer
E. a positive control protein
C. a repressor
Which of the following is true about the translocation reaction during protein translation?
A. It moves a ribosome so that a tRNA is in the A-site.
B. It moves an amino acid to the A-site and a tRNA to the E-site.
C. It moves an amino acid onto the tRNA in the A-site.
D. It moves a ribosome so that a tRNA is in the P-site.
E. It moves an amino acid onto a tRNA in the P-site.
D. It moves a ribosome so that a tRNA is in the P-site.
Which of the following sequences is considered a palindrome?
A. 5'-CGATCG-3'
B. 5'-AGAAGA-3'
C. 5'-TATAAT-3'
D. 5'-CCCAAA-3'
E. 5'-GGAGG-3'
A. 5'-CGATCG-3'
Why must the lagging strand at a replication fork be replicated in short fragments?
A. The slower replication requires DNA polymerase to start at several different places.
B. There are several DNA polymerase molecules on the lagging strand.
C. It is being replicated 3’ to 5’, which is backwards and slower than 5’ to 3’.
D. DNA is always replicated in short fragments.
E. It is replicated toward the origin, but the fork is opening away from the origin.
E. It is replicated toward the origin, but the fork is opening away from the origin.
What is the correct order for the three steps in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), starting with a double stranded DNA sequence?
A. anneal probes, clone the DNA, isolate the clone
B. digest the DNA, run electrophoresis, probe the gel
C. replicate the DNA, anneal primers, clone the DNA
D. denature the DNA, anneal primers, replicate the DNA
E. anneal primers, replicate the DNA, denature the DNA
D. denature the DNA, anneal primers, replicate the DNA
The active site of an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase recognizes ________________.
A. An amino acid's R-group and a tRNA anticodon
B. A tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon
C. The charge on an amino acid and on RNA
D. An amino acid and an mRNA codon
E. A DNA codon and an RNA anticodon
A. An amino acid's R-group and a tRNA anticodon
A probe can be used in all of the following procedures EXCEPT _______________.
A. altering the DNA sequence of a gene
B. joining restriction-digested DNA fragments
C. amplifying the number of copies of a selected DNA fragment
D. detecting a DNA sequence at a crime scene
E. diagnosing a genetic disease in a patient
B. joining restriction-digested DNA fragments
Gene regulation achieved by moving a gene from a silent (cryptic) site to an expressed site near a promoter is called ____________.
A. gene dispersal
B. quorum sensing
C. response regulation
D. cassette switching
E. two component regulation
D. cassette switching
What sort of medical problem is caused by pinworms?
A. Growth of a massive ball of worms can block and eventually rupture the intestine.
B. Intense itching around the anus as the worms crawl from the intestine.
C. Taking essential nutrients from the infected person, causing malnutrition.
D. Blockage of blood vessels in the heart, leading to heart failure.
E. Liver damage from an immune response to the worm eggs in the liver.
B. Intense itching around the anus as the worms crawl from the intestine.
How does an inducer induce a gene without being present inside the cell?
A. The inducer must be phosphorylated so it can phosphorylate the DNA.
B. By phosphate transfer between a membrane sensor kinase and a cytoplasmic regulatory protein.
C. By binding a repressor and preventing the repressor from entering the cell.
D. It cannot. The inducer must at least be able to enter the cell to induce a gene.
E. By altering the lipid bilayer which then alters the DNA around a gene.
B. By phosphate transfer between a membrane sensor kinase and a cytoplasmic regulatory protein.
A chronic virus _____________.
A. usually lyses an infected host cell quickly
B. causes a new infection after a long time without symptoms
C. uses reverse transcriptase
D. continually buds from the host cell for a long time period
E. replicates very slowly over a long time period
D. continually buds from the host cell for a long time period
Place in order the following steps used to create a cloning library and find a specific gene in the library. (Some of the steps may not be used.)
1. Clones are transferred to filter paper
2. Library is plated on agar
3. Clones are screened by colony hybridization
4. DNA is isolated and restricted
5. Cloned DNA is inserted into cloning host
6. DNA is ligated into cloning vector
7. Electrophoresis separates DNA
A. 2 – 1 – 3 – 4 – 7 – 6 – 5
B. 7 – 4 – 5 – 2 – 3
C. 4 – 7 – 3 – 6 – 5
D. 4 – 6 – 5 – 2 – 1 – 3
E. 4 – 7 – 5 – 1 – 3 – 2
D. 4 – 6 – 5 – 2 – 1 – 3
How do some algae cause paralytic shellfish poisoning in humans?
A. They are mechanical vectors that transmit diseases from other microbes.
B. They produce a neurotoxin that is ingested when people eat shellfish.
C. They differentiate into motile zoospores that enter the body through damaged skin.
D. They colonize the digestive tract and overcome the native flora.
E. They produce larvae that can invade the brain and cause abscesses.
B. They produce a neurotoxin that is ingested when people eat shellfish.
What happens after prions cause protein misfolding?
A. Neurons can proliferate uncontrollably, resulting in a tumor.
B. The growth of the infected host can become stunted.
C. Protein synthesis in a host cell is inhibited.
D. Death of infected cells leads to inflammation of tissues.
E. Neuron death leads to brain tissue becoming porous.
E. Neuron death leads to brain tissue becoming porous.
The first antibiotic to be used commercially is a competitive inhibitor of bacterial folic acid biosynthesis. What antibiotic is this?
A. Polymyxin
B. Sulfanilamide
C. Cephalosporin
D. Tetracycline
E. Penicillin
B. Sulfanilamide
Which of the following is NOT part of the Schistosome life cycle?
A. Eggs are ingested by humans who eat contaminated food
B. Adult flukes mate in human blood vessels and lay eggs
C. Cercarial larvae burrow into a human host
D. Miracidial larvae hatch from eggs released in human feces
E. Miracidial larvae are ingested by a snail
A. Eggs are ingested by humans who eat contaminated food
Which of the following is prescribed to treat both anaerobic bacterial infections and infections caused by flagellated protozoans such as Giardia?
A. Penicillin
B. Artemisinin
C. Sulfa drugs
D. Metronidazole
E. Neuraminidase inhibitors
D. Metronidazole
This plant is most likely infected with a _________.
A. prion
B. mosaic virus
C. wilt virus
D. stunt virus
E. phage

B. mosaic virus
Which of the following is NOT a part of the inflammatory response?
A. Activation of B cells to secrete cytokines
B. Secretion of proteins that affect the hypothalamus
C. Increased blood flow to the affected area
D. Diapedesis of neutrophils
E. Adhesion of phagocytes to capillary walls
A. Activation of B cells to secrete cytokines
Which of the following would NOT be a good bacterial target for an antibiotic with a high therapeutic index?
A. Folic acid synthesis
B. Peptidoglycan synthesis
C. Protein synthesis
D. DNA synthesis
E. Lipid synthesis
E. Lipid synthesis
Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are both __________.
A. nucleocytes and lymphocytes
B. granulocytes and phagocytes
C. lymphocytes and monocytes
D. macrophages and dendritic cells
E. antigen presenting cells and macrophages
B. granulocytes and phagocytes
A cutaneous case of tinea corporis could best be treated with ____________.
A. Fluconazole
B. Mupirosin
C. Bacitracin
D. Ivermectin
E. Penicillin
A. Fluconazole
Which of the following does not describe a role the complement system plays in your body’s response to an infection?
A. Complement proteins enhance new capillary growth to promote wound healing
B. Complement proteins make invading bacteria easier to phagocytize.
C. Complement proteins induce B cells to become plasma cells.
D. Complement proteins lyse invading bacteria.
E. Complement proteins induce inflammation.
C. Complement proteins induce B cells to become plasma cells.
Which part of the virus can be either icosahedral or helical?
A. the part labeled A
B. the part labeled E
C. the part labeled D
D. the part labeled C
E. The entire virus is either helical or icosahedral.
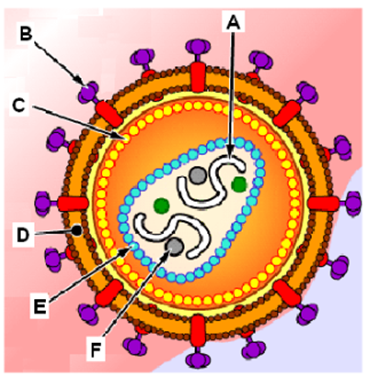
B. the part labeled E
How is interferon produced during an infection?
It is produced when MHC-I phosphorylates a response regulator in infected cells.
TH cells produce it when they bind to MHC-II that is displaying viral antigens.
A second-messenger pathway induces it when viral RNA binds to an RLR receptor.
Bacteria produce it in response to the phagocyte oxidative burst.
It is produced by induction of viral genes in the phagolysosome.
C. A second-messenger pathway induces it when viral RNA binds to an RLR receptor.
Granuloma formation involves all of the following EXCEPT ______________________.
antibodies
bacteria
cytokines
T cells
macrophages
A. antibodies
Which antibody can cross the placenta to protect the fetus?
IgD
IgE
IgM
IgA
IgG
D. IgG
A B cell recognizes an antigen, but there is no TH cell that also recognizes the antigen. What will happen?
The TH cell will kill the B cell.
The B cell will internalize the antigen.
The TH cell will secrete cytokines to activate the B cell.
The B cell will become anergic.
The B cell will begin producing antibodies.
D. The B cell will become anergic.
One of the complement activation pathways is called the “alternate” pathway. What is different between this pathway and the “classical” pathway?
It kills bacteria in a different manner than the classical pathway.
It can be activated even before the humoral immune response is active.
It only kills infected “self” cells, rather than pathogenic bacteria.
It alternates between inducing inflammation and keeping fever from getting too high.
It requires a bacterial surface to be coated with lectins.
B. It can be activated even before the humoral immune response is active.
What is the role of Treg cells in the immune response?
They secrete regulatory antibodies that limit the body's autoimmune responses
They produce the cytokine IL-2 to stimulate TC cell differentiation.
They regulate the interaction between TC cells and NK cells.
They regulate B-cell clonal expansion in the absence of nearby macrophages.
They produce the cytokine IL-10 to reduce the effectiveness of TH and TC cells.
E. They produce the cytokine IL-10 to reduce the effectiveness of TH and TC cells.
What parts of antibodies have great variability due to somatic recombination?
variable and constant regions
the Fab part only
alpha and beta chains
the Fc part only
the heavy chain only
B. the Fab part only
Which of the following is true about T cells that recognize self-antigens?
They are responsible for Type III hypersensitivity reactions.
They form because V-J joining is random, but they apoptose in the thymus
They can activate macrophages even in the absence of protein B7.
The second signal that activates them is antibody binding to MHC-II on their surface.
They never form.
B. They form because V-J joining is random, but they apoptose in the thymus
Which of the following statements about antibody types is TRUE?
IgE is produced by class switching of the genes that encode the Fab part of IgM.
Most B-cells produce IgG as soon as they detect an infection.
The role of IgD is not clear, but it is involved in the allergic response.
IgA can cross the placenta to protect the baby for a few months after birth.
The most effective antibody for agglutinating antigens is IgM.
E. The most effective antibody for agglutinating antigens is IgM.
Which of the following statements about live attenuated vaccines (LAV) and inactivated vaccines (INV) is correct?
INV fail to induce B-cell responses, and so very low antibody titers are produced.
LAV contain the actual disease agent, which can induce a strong immune response.
LAV must always be given with adjuvants to maximize the humoral response.
INV allow a patient to translate antigens from injected pathogen DNA.
LAV can be either orally administered or injected, whereas INV must be injected.
E. LAV can be either orally administered or injected, whereas INV must be injected.
What is the role of the B7 protein in the immune response?
It is secreted by TH cells to stimulate B cell clonal expansion and differentiation.
It is a type of antibody produced by effector B cells.
It is a receptor on macrophages that recognizes pathogens.
It is produced by infected macrophages to help stimulate T cells.
It is a protein on TC cells that allows them to bind to TH cells.
D. It is produced by infected macrophages to help stimulate T cells.
In the disease Lupus, autoantibodies are directed against ________________.
the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
almost anything you touch or eat
DNA
epithelial cell receptors
B cells
C. DNA
How do you know that a person has been exposed to a particular pathogen within the past year or so?
If the person produces monoclonal antibodies against the pathogen.
If the person's antibody titer against the pathogen, which was 1:8, is now 1:128.
Filtering the blood and adding a dye to it.
You'd have to perform an immunoelectrophoresis test.
If the well of a direct ELISA microtiter plate turns red.
B. If the person's antibody titer against the pathogen, which was 1:8, is now 1:128.
The most common immune disorder in the US is selective IgA deficiency. People who suffer from this will be more likely to get ______________ than other people.
respiratory and digestive illnesses
viral infections
blood-borne illnesses
systemic lupus erythematosus
allergies
A. respiratory and digestive illnesses
You are testing antibiotics in a mouse model of a new bacterial disease. You have determined the MIC for the antibiotics from an E-test and administered each antibiotic to several mice at greater than the MIC dose. But all the mice still die. Which of the following would be a logical conclusion from the results of this experiment?
You should look for the production of a toxin by the new bacterium.
You shouldn't have used an E-test to determine the MIC of the antibiotics.
You should have administered the antibiotics at a dose less than the MIC, not more.
This new disease is probably polymicrobial.
Animal models are not valid for study of human diseases.
A. You should look for the production of a toxin by the new bacterium.
Which of the following is true for a direct ELISA, but not for an indirect ELISA?
The test can be made more sensitive by conjugating latex beads to the known antigen.
To begin the test, known antibodies are bound to the bottom of a microtiter well.
The test uses an enzyme reaction to visualize antibodies.
The test can be used to detect a latent infection.
Anti-FC secondary antibodies are used to detect the primary antibodies.
B. To begin the test, known antibodies are bound to the bottom of a microtiter well.
During vaccine clinical trials, it was discovered that a vaccine antigen could bind to a
receptor on the patient's epithelial cells. The vaccine development was cancelled. Why?
IgG bound to the vaccine antigen might direct ADCC against the patient's own cells.
The vaccine antigen might activate a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
The vaccine might prevent the disease agent from being recognized by phagocytes.
The patient's TC cells might destroy the vaccine antigen, making it ineffective.
The patient could not make antibodies to this sort of antigen.
A. IgG bound to the vaccine antigen might direct ADCC against the patient's own cells.
What would be the most effective way to protect a patient against bacterial endotoxin?
Test to see if intravenous fluids given to the patient coagulate Limulus blood cells.
Autoclave all intravenous fluids that might be given to the patient.
Use a Western Blot to screen any intravenous fluids given to the patient.
Passively immunize the patient against bacterial endotoxin.
Vaccinate the patient with an endotoxoid vaccine.
A. Test to see if intravenous fluids given to the patient coagulate Limulus blood cells.
What happens when an effector TC cell binds to an antigen on an epithelial cell’s MHC-1?
The TC cell becomes anergic.
The TC cell releases cytokines that activate TH cells.
The TC cell kills the epithelial cell.
The TC cell recruits B cells to the site of the infection.
The epithelial cell produces cytokines to activate the TC cell.
C. The TC cell kills the epithelial cell.
A TB test involves a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction. If you have been sensitized to TB before you take such a test _________________.
your macrophages will have TB living inside them, and this will cause a positive test
it will not matter, since sensitization is not required for Type IV hypersensitivity
anti-TB antibodies circulating in your body will cause the test to be positive
mast cells in your body will be coated with antibodies against TB
Tmemory cells in your body that recognize TB will cause the test to be positive
E. Tmemory cells in your body that recognize TB will cause the test to be positive
Most of the really dangerous pathogenic fungi can do which of the following?
Escape the immune system by living inside red blood cells
Grow as yeast in an environmental reservoir outside the host
Produce endotoxin
Get inhaled as mold spores and transition to yeast in the host’s body
Produce spores within the host’s body
D. Get inhaled as mold spores and transition to yeast in the host’s body
What is the function of the Staphylococcal protein A?
Fc receptor
IgA protease
adhesin
activates complement C5a
prevents phagosome / lysosome fusion
A. Fc receptor
A flight lands at O'Hare with a passenger who has a respiratory disease. A week later, there are 155 cases of the disease in Chicago. By the second week, there are 6,000 cases and an epidemiologist is consulted. He would most likely consider this to be ________________.
a common-source epidemic
a propagated epidemic of an airborne disease
a person-to-person epidemic with multiple index cases
an example of an emerging disease
a disease transmitted by respiratory droplets
B. a propagated epidemic of an airborne disease
The most effective way to reduce the incidence of nosocomially spread infections is to ________.
use more antibiotics in hospitals
fit HEPA filters in all patient rooms
have health care workers wash their hands between each patient they touch
disinfect operating rooms better between surgeries
separate patients into wards grouped by the disease they have
C. have health care workers wash their hands between each patient they touch
Acute rheumatic fever is caused by which of the following?
Antibodies for Strep M recognize an autoantigen in heart muscle, leading to induced autoimmune disease.
Parasites living in red blood cells release A-B toxins, leading to gradual worsening of the condition.
Exposure to aflatoxin leads to destruction of liver tissue.
Syncytia formation clogs arteries leading to heart failure.
A massive inflammatory response is mounted in response to a superantigen toxin.
A. Antibodies for Strep M recognize an autoantigen in heart muscle, leading to induced autoimmune disease.
Which of the following is a childhood disease that is potentially serious because it leaves a patient immunocompromised? It is now rare in the United States because of an effective vaccine.
Group A Streptococcus
German Measles
Measles
Zoster
Chickenpox
C. Measles