infectious disorders of the pulmonary system III
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
laryngitis
-upper airway inflammatory disorder
-MCC: viral infection
-< 3 weeks
laryngitis etiology/RF
-viral: rhinovirus, influenza, adenovirus, RSV
-smoking, allergy
-recent URI
-vocal overuse or abuse
-GERD for chronic cases
laryngitis sx
-primary sx: hoarseness or voice change
-throat pain, dry cough, fullness, fever
-hoarse, raspy, weak voice
-vocal cord edema, erythema
-red flag sx: SOB, dysphagia, odynophagia, drooling, tripod
laryngitis dx/tx
-clinical
-sx >3 weeks = direct laryngoscopy
-tx: self limited in 3-7d, vocal rest, supportive care (OTC)
viral upper respiratory tract infections (URIs)
-common cold
-MCC: rhinovirus
-viral invasion of respiratory epithelium leading to inflammatory response > vascular permeability
-kids can have up to 12/year
URI sx
-begin gradually, peak early, can last up to 14 days
-nasal fullness, rhinorrhea, sore throat, laryngitis, lymphadenopathy
-cough, low grade fever, myalgia, epistaxis, headache, malaise
-conjunctivitis
-pharyngeal erythema, cobblestoning
-diffuse wheezing and bronchial breath sounds, lung sound should NOT be focal
URI dx/tx
-clinical
-PCR: only order tests if it will change tx or concerned for complications
-tx: self limiting 5-10d, up to 14d
-supportive care (OTC), anti-tussives, mucolytics, decongestant
-secondary infections: abx
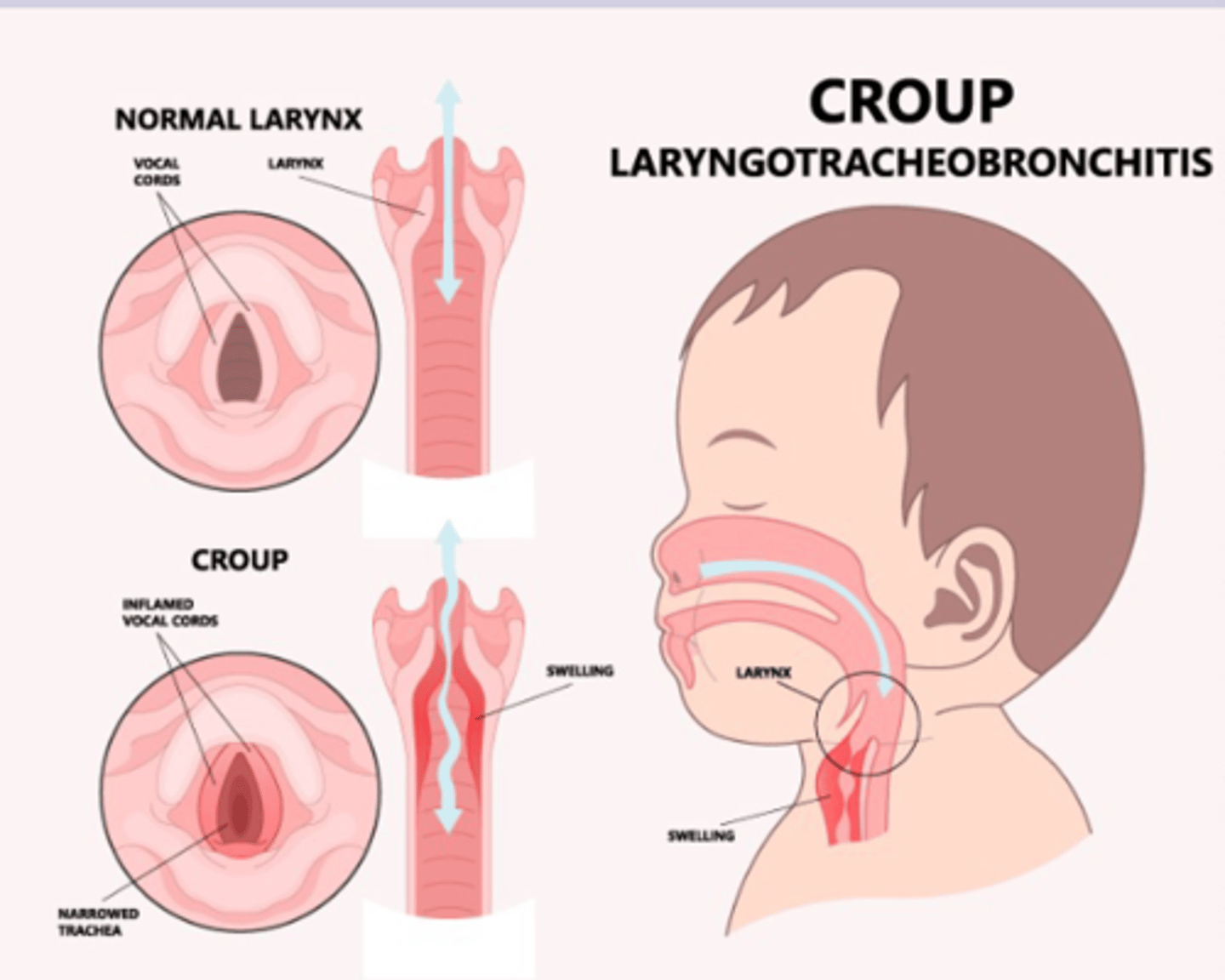
Croup- laryngotracheobronchitis
-viral infection of upper airway > edema
-MCC: parainfluenza virus
-sx occur from edema
-6mon to 3yrs
croup patho
infection leads to inflammation and edema in subglottic space > upper airway obstruction
croup etiology/RF
-parainfluenza
-influenza A and B, RSV, adenovirus, rhinovirus
-6mon-3yrs
-male
-hx
-GERD hx
-recurrent URI
-second hand smoke exposure
croup sx
-mild URI 1-3 days > seal-like barking cough
-cough is worse overnight
-hoarse voice
-stridor can hear without stethoscope
-severe: vital abnormalities, stridor at rest, tachypnea, nasal flaring, belly breathing, lethargy
croup dx
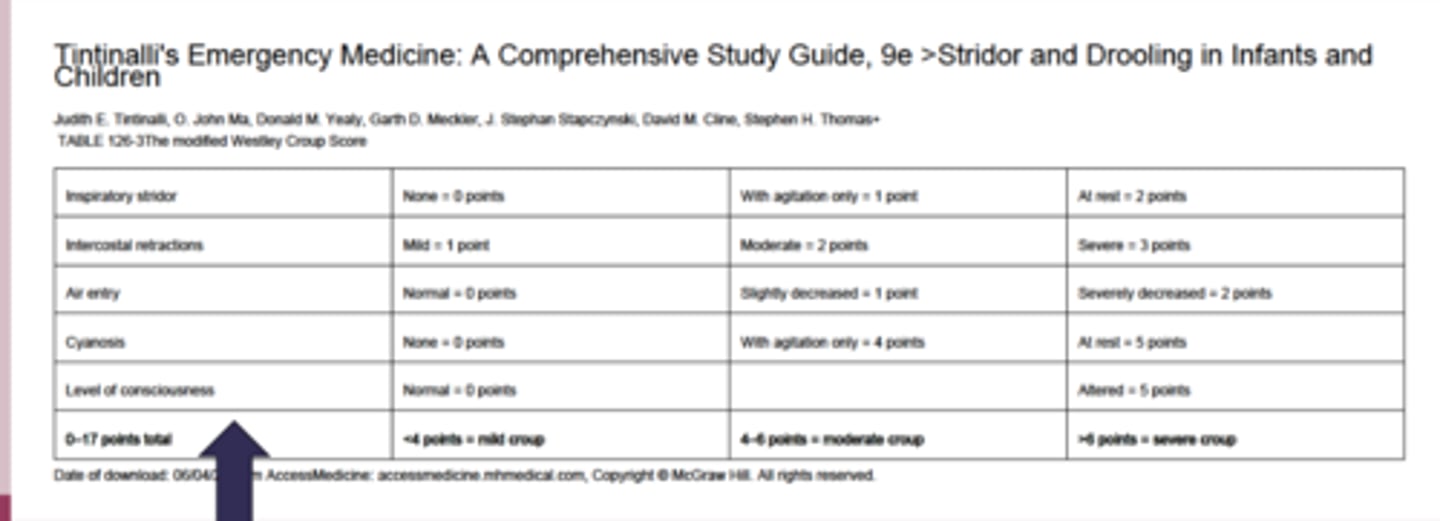
-clinical: westley croup severity score
-XR of neck: steeple sign
-lateral neck radiograph different croup from epiglottitis
croup tx
most self limiting within 3 days
-mild: supportive care, one dose oral dexamethasone
-moderate: supportive care, one dose oral dexamethasone, nebulized epinephrine, watch for 3hrs
-severe: supportive care, one dose oral or IV dexamethasone, nebulized epinephrine, hospital admission, intubation
bronchitis
-self limited respiratory infection of the large airways
-cough without evidence of pneumonia
bronchitis patho
infection of the bronchi > inflammation and thickening of bronchial mucosa > airflow obstruction and bronchial hyperresponsiveness
-secondary bacterial infection is uncommon
-MCC: viruses
bronchitis sx
-hallmark= acute cough 1-3 weeks
-viral URI sx for >5 days to qualify for bronchitis may last 4 weeks
-sputum clear or white, can be yellow or green
-chest discomfort
-dyspnea with exertion
-vital signs normal
-rhonchi or wheezing that clear w coughing
-NO focal adventitious sounds
bronchitis dx/tx
-clinical
-CXR (rule out): fever, tachy, dyspnea, hypoxia, altered mental, focal abnormalities
tx: supportive care, antitussive, expectorants, antihistamines, mucolytics
-benzonatate and guaifenesin for cough relief
-smoking cessation
acute bronchiolitis
-inflammatory process that affects the bronchioles (lower respiratory tract)
-MCC: RSV
-most common cause of hospitalization <1yo
acute bronchiolitis sx
-URI, LRTI sx, peak at 3-5 days
-wheezing diffuse and non-focal
-crackles less common
-cough, clear rhinorrhea
-low fever, tachypnea, tachycardia
-severe: ill, toxic, O2 sat <95%, RR >70, cyanosis
acute bronchiolitis dx
-clinical
-confirmatory- nasal PCR
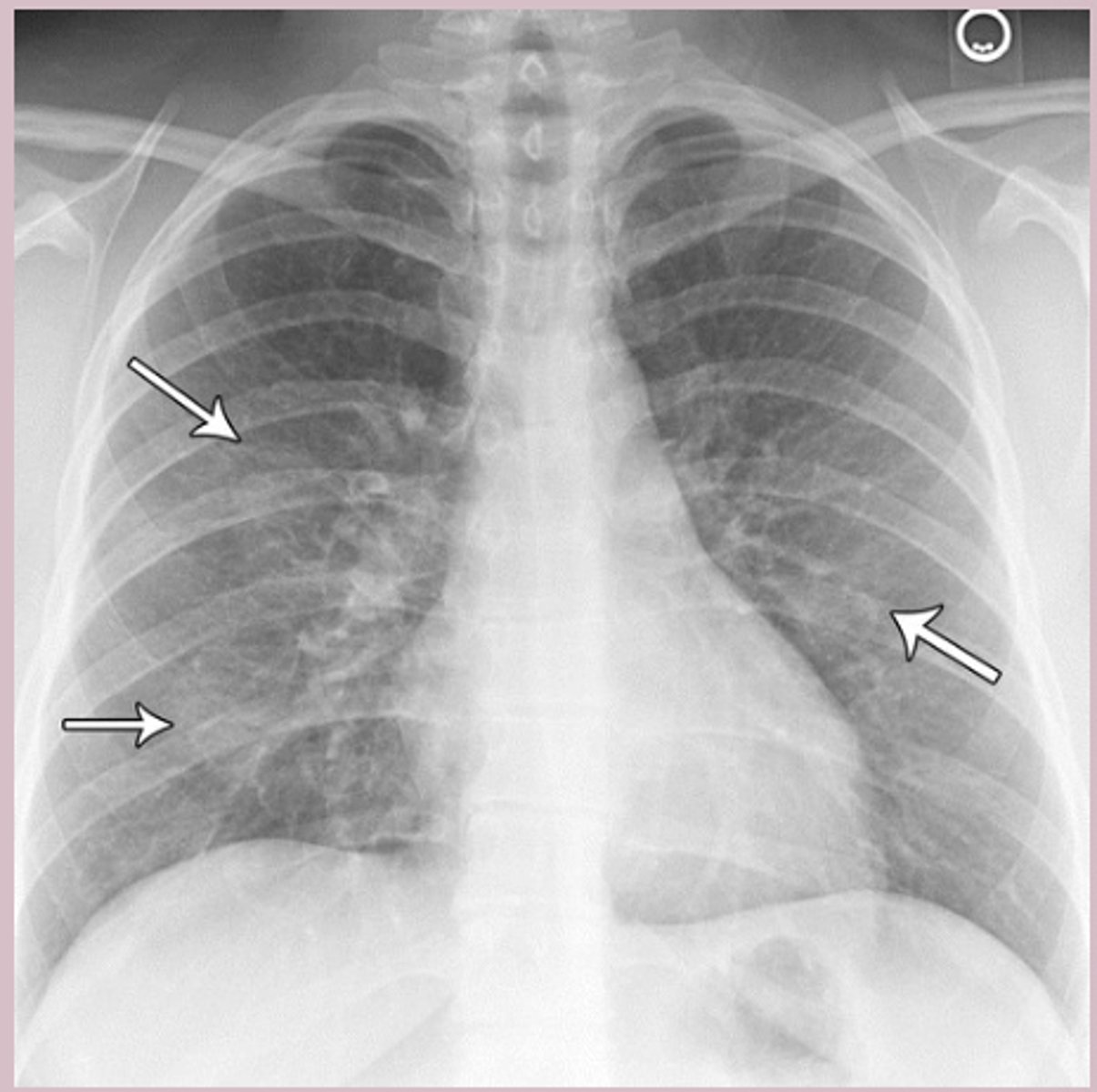
-CXR (rule out): patchy atelectasis, patchy interstitial infiltrates, peribronchial cuffing, hyperinflation
acute bronchiolitis tx
-supportive care: nasal suctioning, antipyretic, fluids, humidified air
-DO NOT USE SABA AND CORTICOSTEROIDS
-ribavirin: high risk patients
-RSV vaccination: abrysvo (maternal 32-36weeks), nirsvimab (8-19mon infants)
-prophylaxis: palivizumab 1/mon high risk infants 0-24 mons during RSV season
pertussis
-whooping cough
-MCC (bacteria): bordetella pertussis
-infants <1 year
pertussis patho
-bordetella pertussis attaches to ciliated epithelium
-toxin prevents immune cell recruitment, progressive damage, impair mucus clearance
-paroxysmal coughing fits result
pertussis sx
-catarrhal stage (1-2w): URI sx, most contagious
-paroxysmal stage (2-6w): paroxysmal coughing fit followed by inspiratory whoop, post tussive vomiting, cyanosis during episodes, NO fever
-convalescent stage (weeks to mon): gradual resolution of cough, may recur with viral infection
pertussis dx
-confirmatory:
-first 2 weeks: PCR + culture
-2-4 weeks: PCR
->4 weeks: serology
pertussis tx
-supportive care
-hospitalize <6 mon or severe
-isolate for 5 days after antibiotics
-first line: azithromycin 10-12mg/kg/day for 5 days
-most effective in catarrhal stage
-prevention: 5 dose DTaP vaccine
-6-10 weeks to resolve
antitussive- dextromethorphan
-cough
-OTC
-delsym, robitussin
-MOA: decrease sensitivity of cough receptors and interrupts cough impulses
-can use in pregnancy
antitussive- benzonatate
-cough
-prescription only
-MOA: suppresses cough by topical anesthetic action on respiratory stretch receptors
-ADR: chest discomfort
antitussive- codeine
-opioid
-prescription only
-dosing is lower for cough
-ADR: somnolence, dysphoria, respiratory depression
mucolytics + expectorants- guaifenesin
-mucinex
-OTC
-chest congestion
-MOA: increases hydration of mucus and can cough it out better
decongestant: pseudoephedrine
-nasal congestion and rhinorrhea
-sudafed
-MOA: stimulate alpha adrenergic receptor of respiratory mucosa causing vasoconstriction
-avoid use in cardiovascular disease, DM
decongestant- phenylephrine
-nasal congestion and rhinorrhea
-OTC
-sudafed PE
-MOA: systemic arterial vasoconstriction
nasal decongestant- oxymetazoline
-nasal congestion and rhinorrhea
-afrin
-OTC
-MOA: nasal mucosa to produce vasocontriction
-rebound congestion if use for >5 days
rhinitis medicamentosa
-nasal inflammation and congestion from overuse of topical nasal decongestants
-develope 3 days after use
-nasal obstruction
-boggy, swollen, leaky nasal mucosa
-tx: oral corticosteroids