Basics of Edema and Glomerular Filtration
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
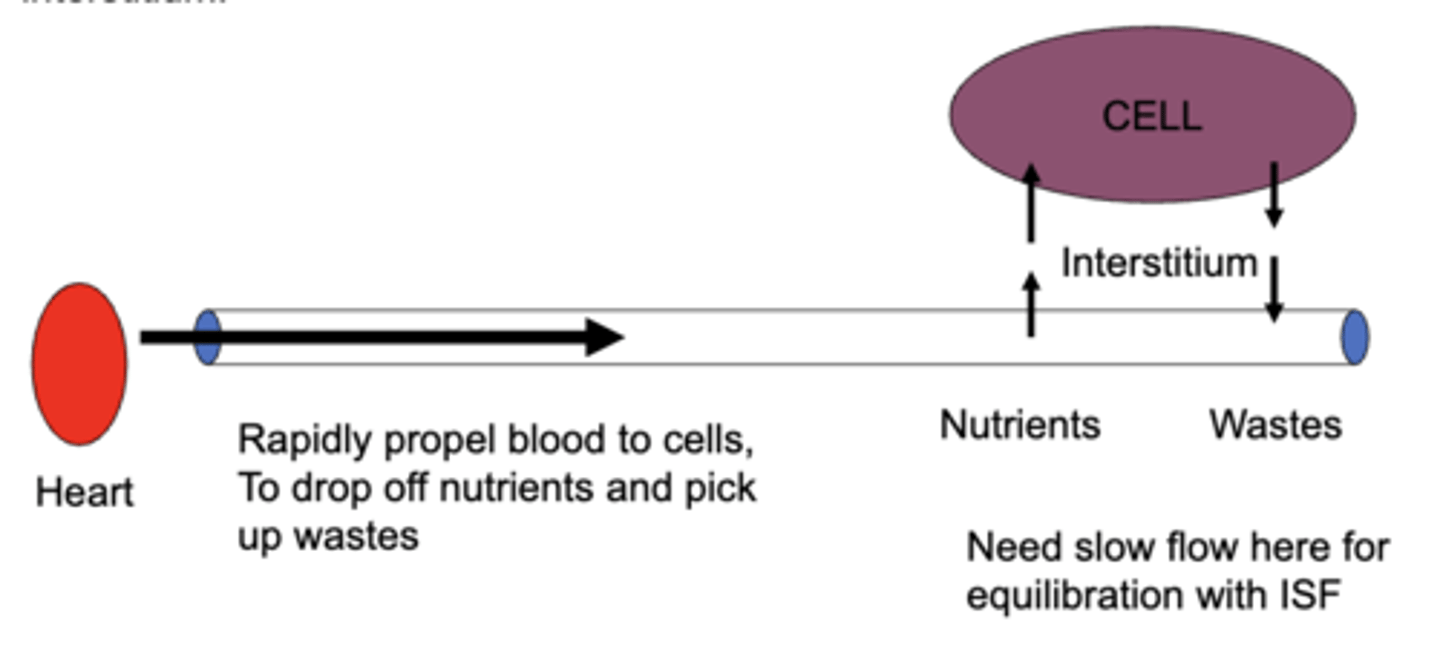
(t/f) blood should be propelled to cells without needing to slow down at the capillaries
false; the blood needs to slow down at the capillaries in order to equilibrate with the interstitium fluid
what will facilitate the reduction of resistance in capillaries for small molecules to diffuse between capillaries and the interstitium?
clefts/pores
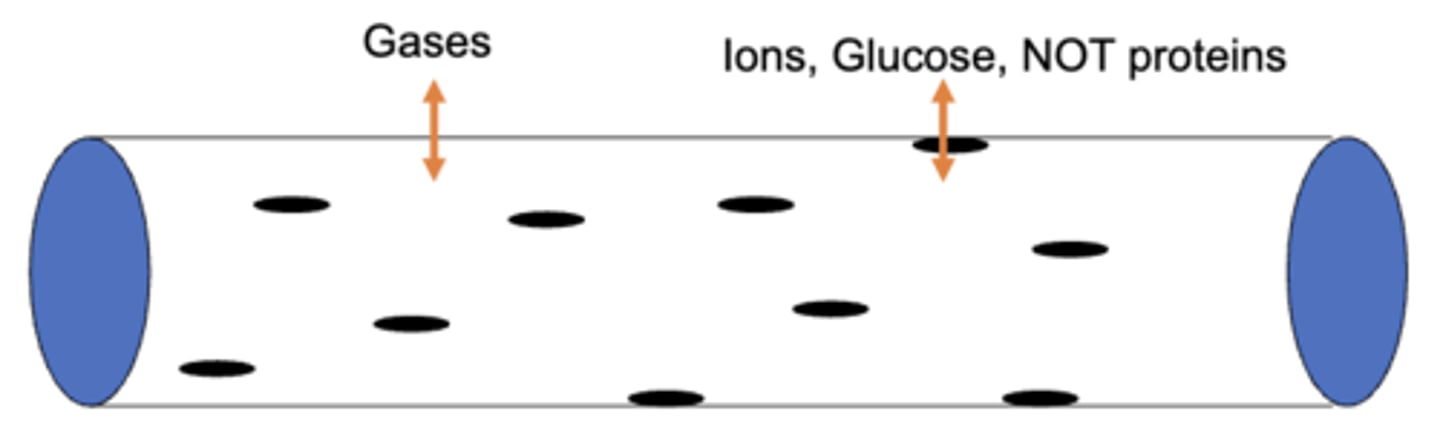
(t/f) pores of the capillary walls allow for the free movement of small non-lipid molecules, ions, glucose, amino acids, and plasma proteins
false; plasma proteins are too large and CANNOT pass through the pores
the amount of time spent by blood in a systemic capillary (at rest) is about _____ times longer than necessary for equilibration of ions with the interstitium
80
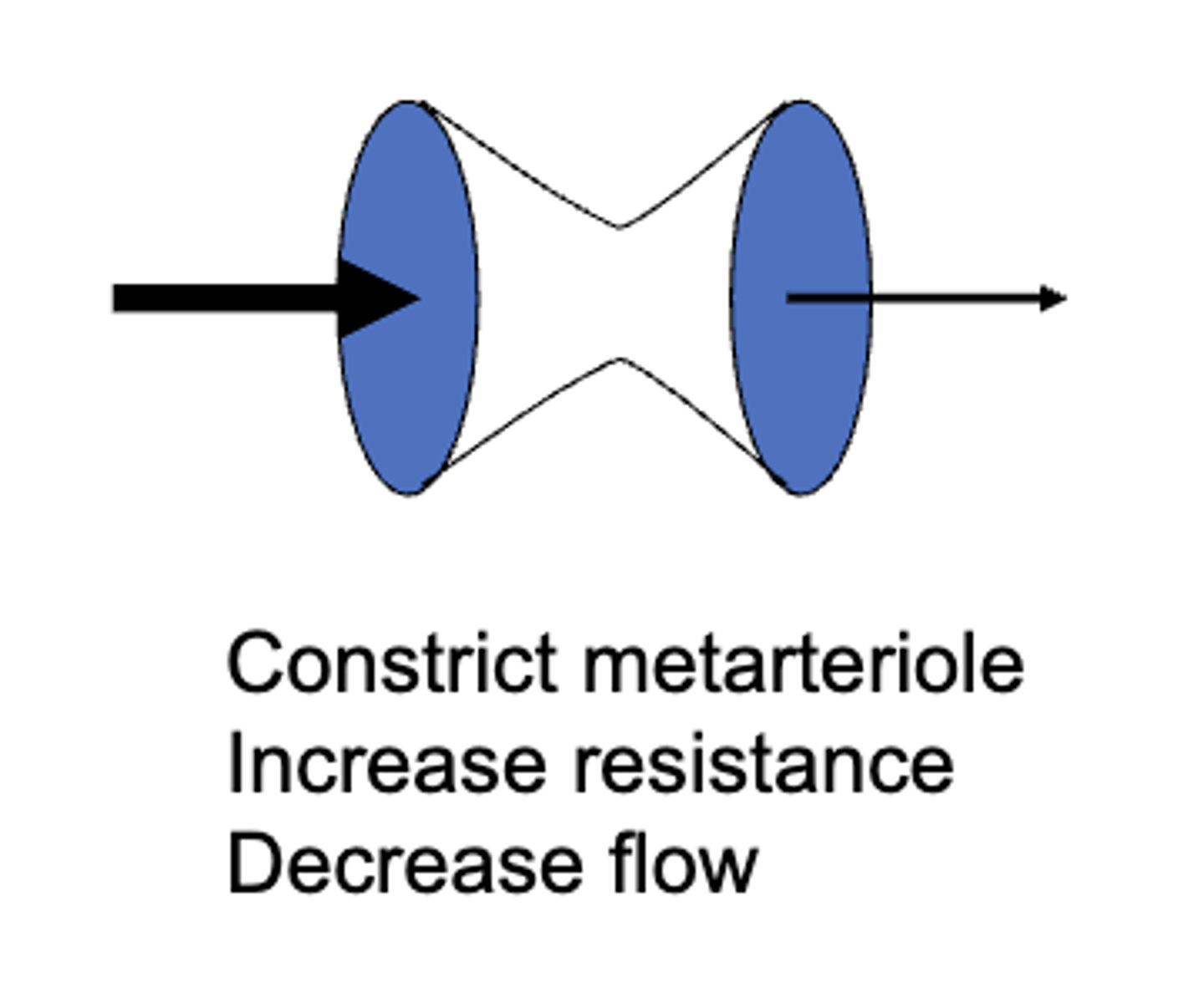
constriction of the metarterioles results in a(n) (decrease/increase) in resistance and a(n) (decrease/increase) in flow
increase, decrease
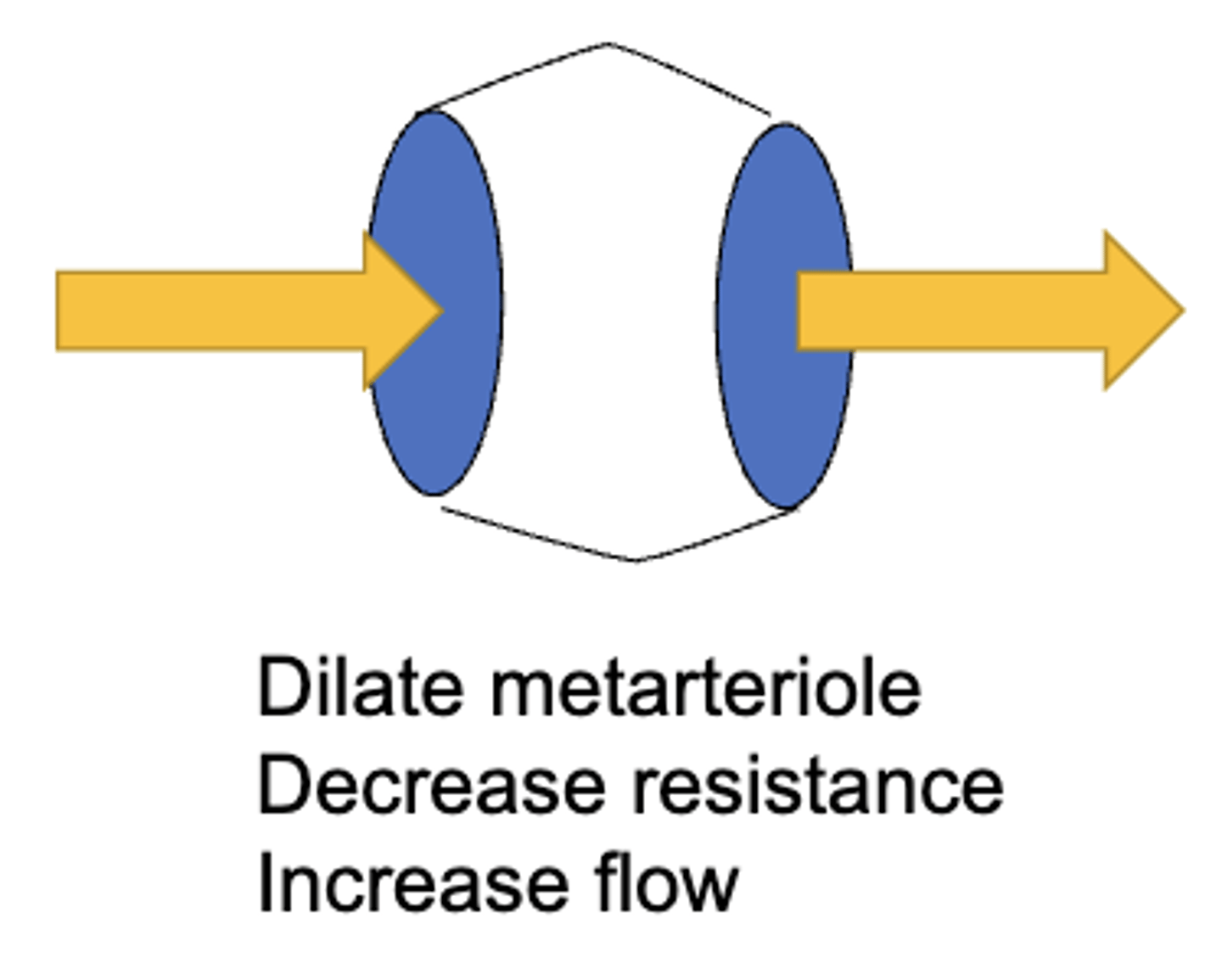
relaxation of the metarterioles results in a(n) (decrease/increase) in resistance and a(n) (decrease/increase) in flow
decrease, increase
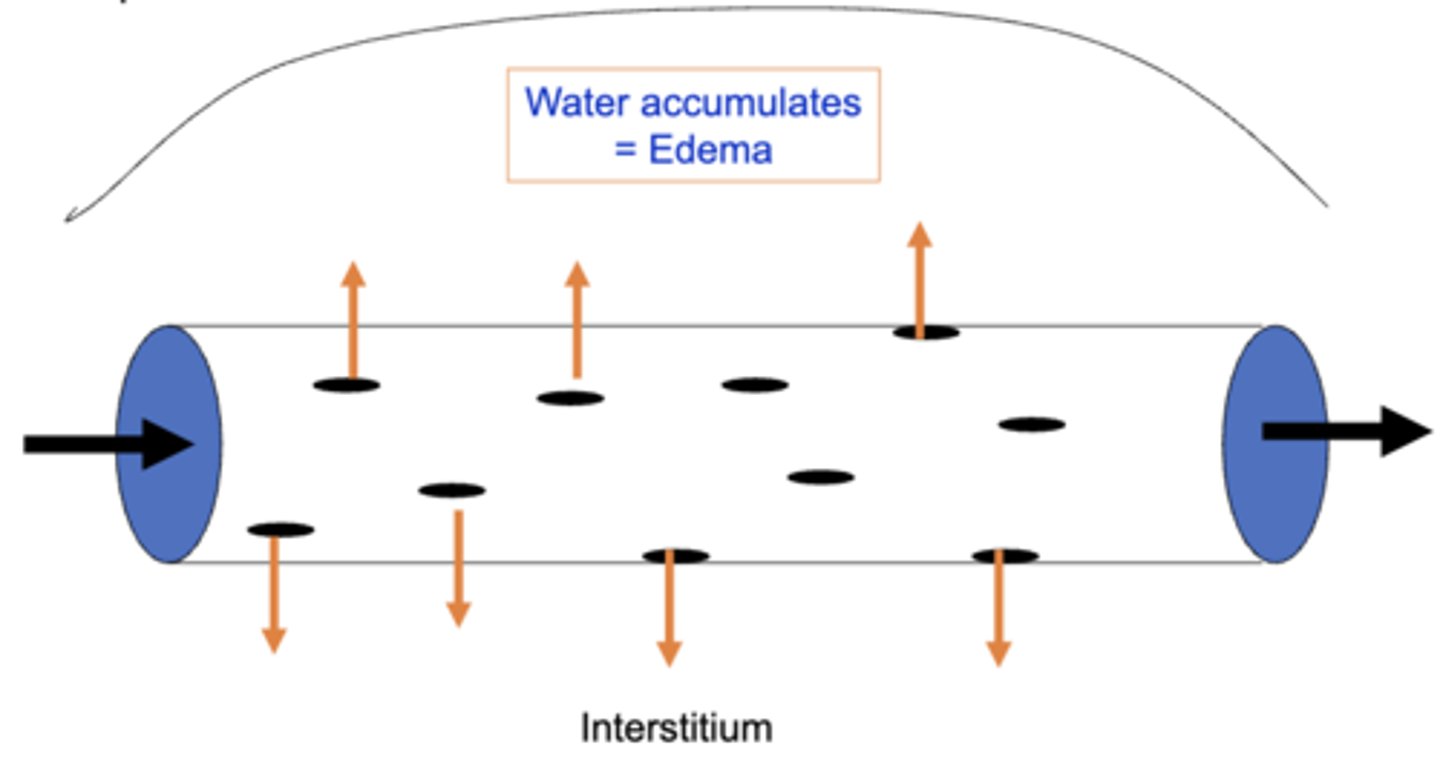
what is a potential issue with the positive hydrostatic blood pressure moving plasma not only forward, but sideways?
water from the plasma is forced into the interstitium which can accumulate and cause edema
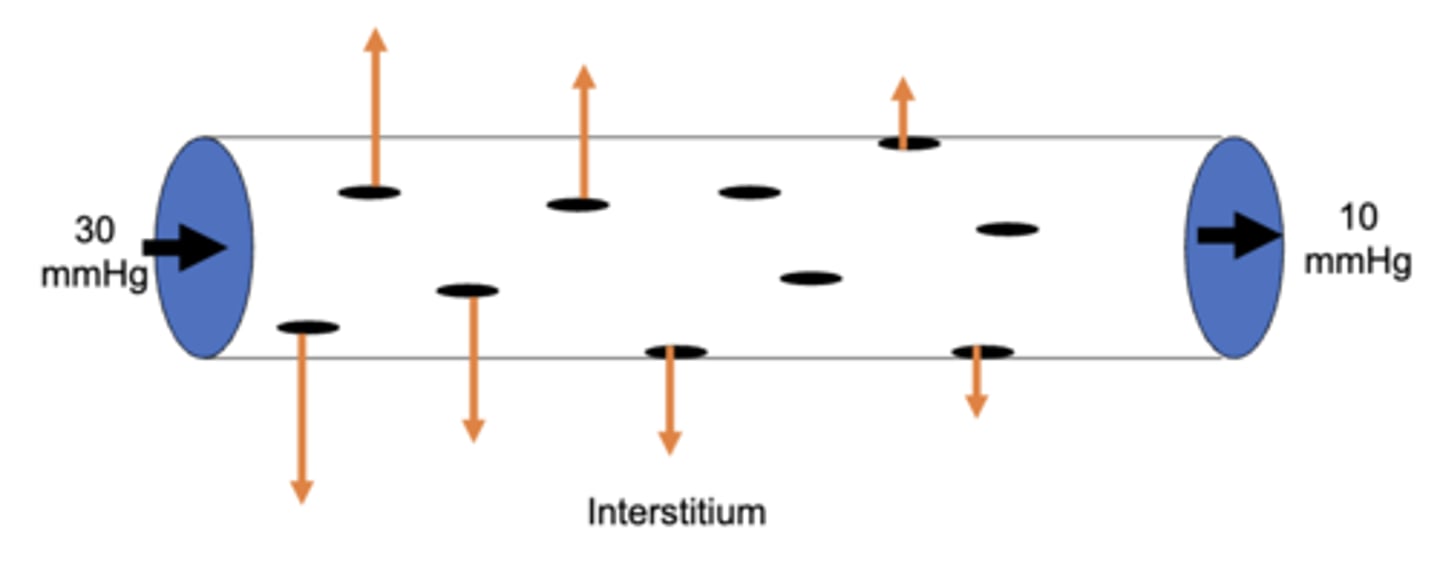
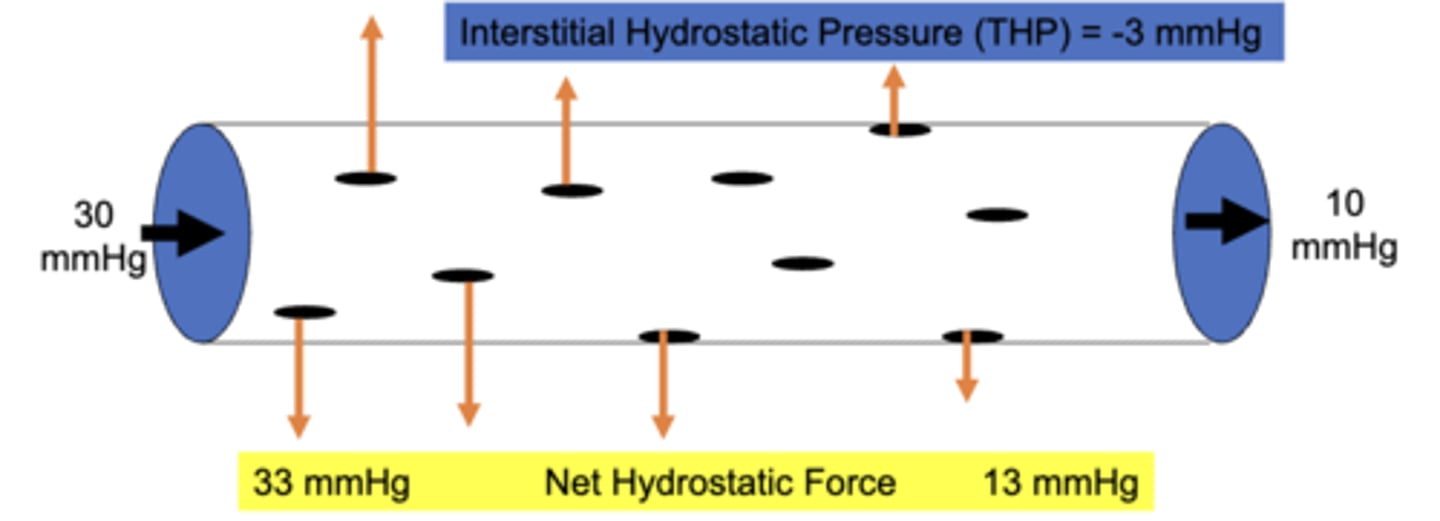
the capillary hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end is typically ___ mmHg and then decreases to ___ mmHg at the venous end
30, 10
the systemic tissue hydrostatic pressure is ____ mmHg. what does this mean?
-3; this means the tissue is hydrostatically sucking water out of the plasma
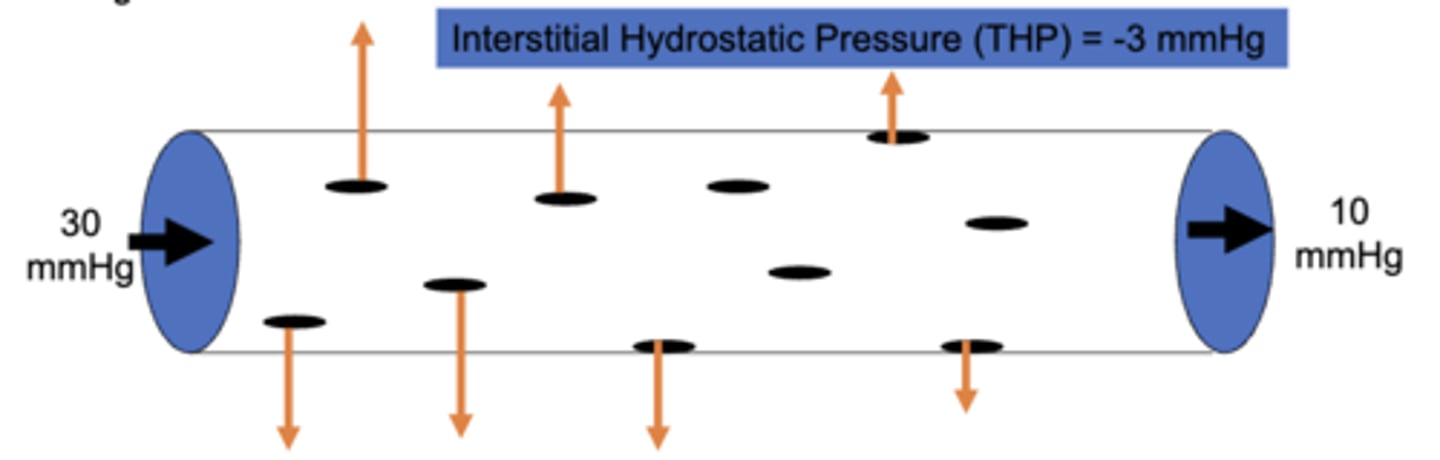
what causes the tissue hydrostatic pressure to be negative?
due to the presence of lymphatics which drain more fluid from the tissues than normally accumulates
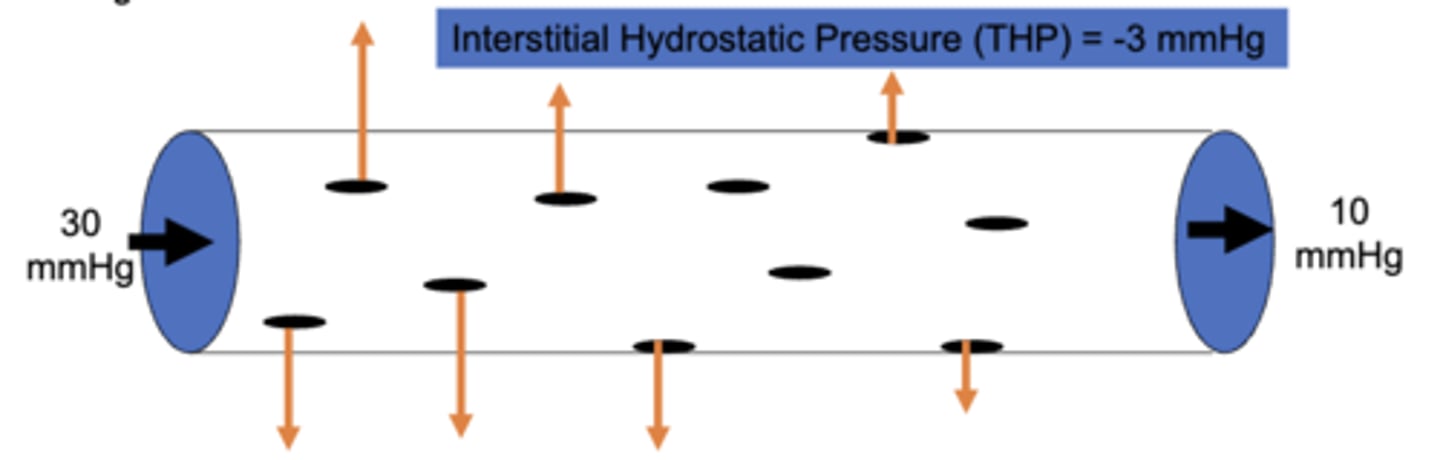
the net hydrostatic force at the arterial end of a capillary is ____ mmHg and decreases to ____ mmHg at the venous end
33, 13
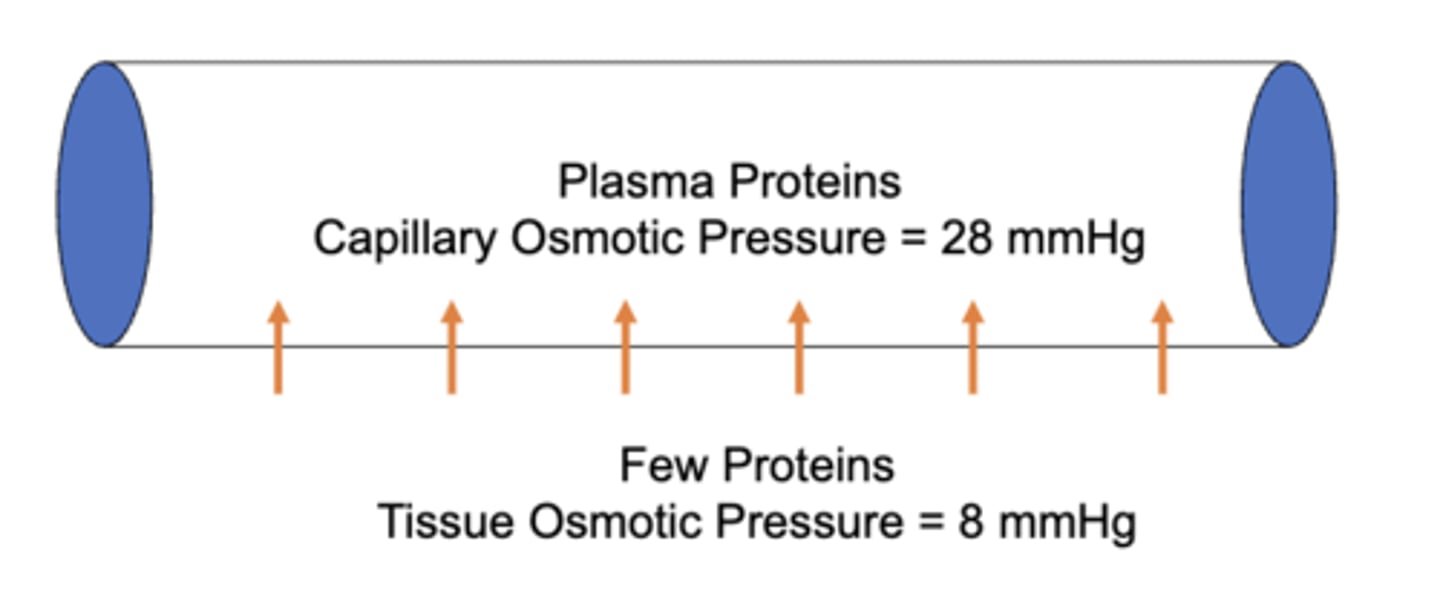
what are the major structures that cause the osmotic pressure differences between the capillary and interstitium?
plasma proteins

the capillary osmotic pressure is _____ mmHg while the tissue osmotic pressure is only _____ mmHg. this means the oncotic (or colloid osmotic) pressure into the capillary is _____ mmHg.
28, 8, 20;
20 mmHg into the capillary
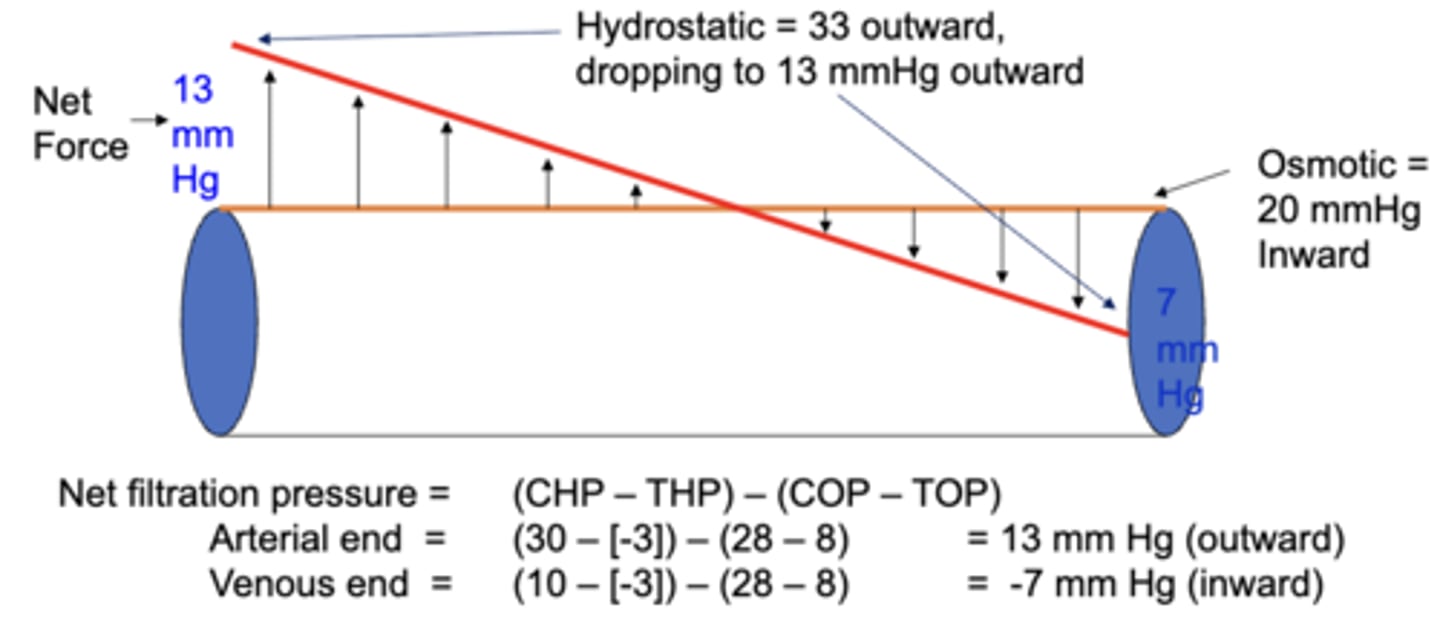
the net filtration pressure of a capillary at the arterial end is _____ mmHg and then decreases to _____ mmHg at the venous end
13, -7;
this explains how water will exit the capillary at the arterial end, but is then sucked back in at the venous end
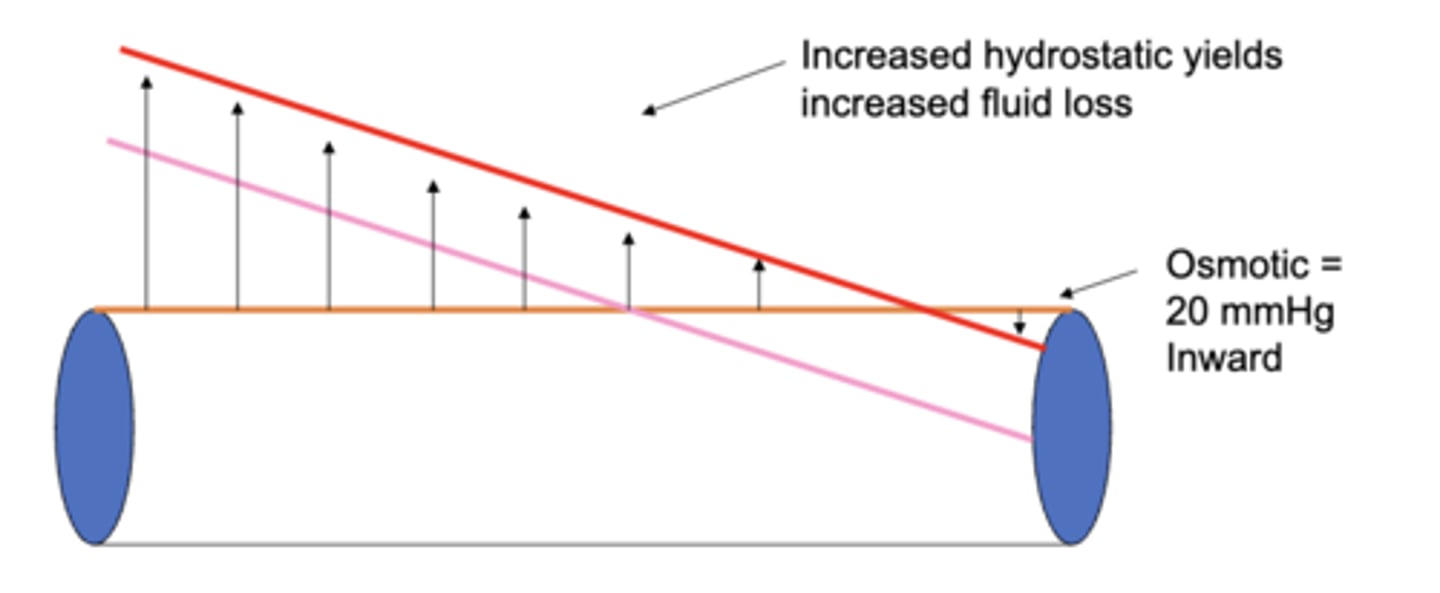
edema will be promoted by (decreasing/increasing) capillary hydrostatic pressure
increasing
edema will be promoted by (decreasing/increasing) capillary osmotic pressure
decreasing
edema will be promoted by (decreasing/increasing) tissue osmotic pressure
increasing
edema will be promoted by (decreasing/increasing) tissue hydrostatic pressure
decreasing
what can be a result of a lymphatic blockage that stops the lymphatic system from draining?
edema
edema can be done in Bowman's capsule by regulating (capillary/tissue) (hydrostatic/osmotic) pressure
capillary, hydrostatic
(constriction/dilation) of the efferent arteriole will increase capillary hydrostatic pressure (and filtration pressure) resulting in edema
constriction
(constriction/dilation) of the afferent arteriole will increase capillary hydrostatic pressure (and filtration pressure) resulting in edema
dilation
only ___-___ ml of fluid per minute exits the collecting duct and leaves the body as urine
2-3
an average male has a renal blood flow of 1.2 L per min. this is _____% of the total cardiac output.
25
the average rate of plasma through the kidneys is _______ ml per min, but the average renal plasma flow filtered by the glomerulus is _____%. so, _______ ml per min of plasma enters Bowman's capsule and proceeds into the proximal convoluted tubule
625, 20, 125
___-___ L of fluid is collected by lymphatics per day
2-3