Soil 1/19/23
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
primary succession
Water, air, and living organisms break down parent material in the lithosphere
2
New cards
parent material (R Horizon)
1. Hardened lava or ash
2. Sediment deposited by glaciers or water
3. Windblown dunes
4. Bedrock is the solid rock that makes the earth’s crust
3
New cards
what breaks down parent material?
weathering
4
New cards
humus
partially decomposed matter on top of soil
5
New cards
parent material + weathering
creates smaller particles of parent material
6
New cards
how many types of weathering are there?
Three
7
New cards
physical weathering
wind, rain, thermal expansion and contraction, water freezing
8
New cards
chemical weathering
water and gases
9
New cards
biological weatherings
tree roots and lichens
10
New cards
particle size
Determines the amount of air & water contained in the soil
11
New cards
Scale (From Largest to Smallest)
Large, Coarse pebbles→
Medium, coarse pebbles→
small, fine pebbles→
finest pebbles→
quartz sand
Medium, coarse pebbles→
small, fine pebbles→
finest pebbles→
quartz sand
12
New cards
soil horizons
a distinct layer of soil
13
New cards
soil profile
the cross-section of soil as a whole, including all soil horizons from the surface to bedrock
14
New cards
leaching
the process by which minerals are dissolved in a liquid and transported to another location
15
New cards
Soil Profile
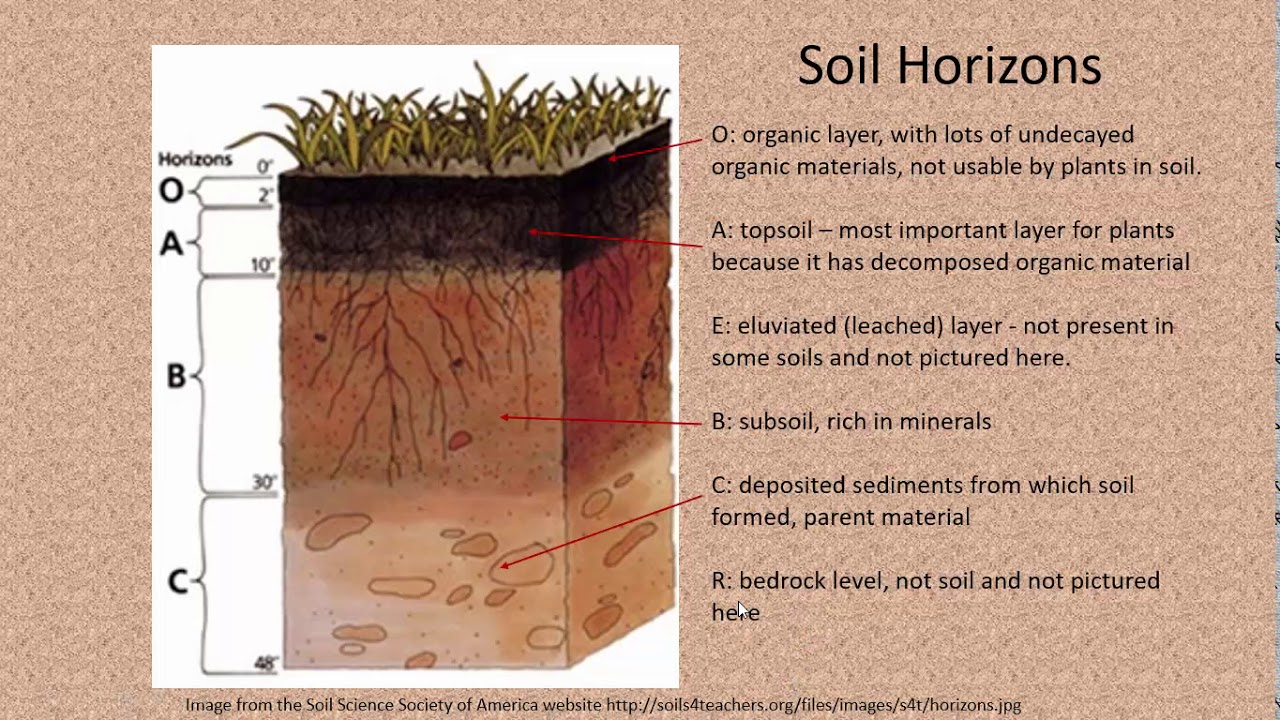
16
New cards
O Horizon (Litter Layer)
organic matter deposited by organisms
17
New cards
A Horion (Topsoil)
organic material mixed with mineral components (salt, etc.)
18
New cards
E Horizon (Eluviated, leaching layer)
minerals and organic matter tend to leach out of this horizon
19
New cards
B Horizon (Subsoil)
minerals and organic matter accumulate here
20
New cards
C Horizon (Weathered parent material)
initial step in soil formation
21
New cards
R Horizon (Rock, parent material)
bedrock, lava, etc.
22
New cards
Soil Texture Chart
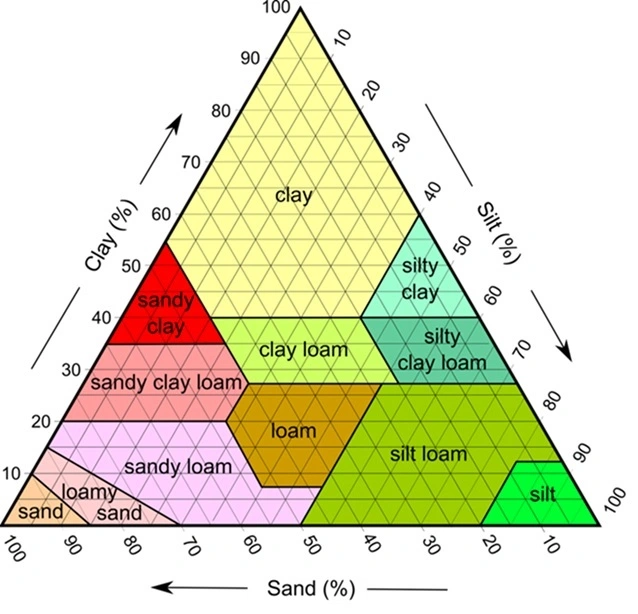
23
New cards
soil texture
determined by percentage of sand, silt, and clay
24
New cards
clay (smallest)
few pore spaces, sticky, difficult for air and water to pass through
25
New cards
silt
more pore spaces than clay, less pore spaces than sand
26
New cards
sand (largest)
water passes through quickly
27
New cards
loam
even mixture of sand and clay, best for agriculture
28
New cards
porosity
the pore space within a soil (more sand, more porous)
29
New cards
permeability
how easily water drains through the soil
30
New cards
H2O holding capacity
how well water is retained, or held by a soil
31
New cards
effects on soil fertility
different soil textures have different effects on soil fertility
32
New cards
when soil is too sandy
drains water too quickly for roots and dries out
33
New cards
when soil has too much clay
doesn’t let H2O drain to roots, or waterlogs (suffocating them)
34
New cards
when soil is just right (loam)
The ideal soil for most plant growth is loam, which balances porosity with H2O holding capacity
35
New cards
soil fertility
soil’s ability to support plant life
36
New cards
factors that increase soil nutrients
* Organic matter
* Humus
* Decomposer activity
* Clay
* bases
* Humus
* Decomposer activity
* Clay
* bases
37
New cards
factors that decrease soil nutrients
* Acids leach positve Charge nutrients
* Excessive rain/irrigation Leeches nutrient
* Excessive farming depletes nut.
* Topsoil erosion
* Excessive rain/irrigation Leeches nutrient
* Excessive farming depletes nut.
* Topsoil erosion
38
New cards
factors that increase H2O holding capacity
* Compacted soil
* Topsoil erosion
* Sand
* Root loss
* Topsoil erosion
* Sand
* Root loss
39
New cards
nutrients for plants can be provided by
1. Inorganic fertilizers
2. Organic fertilizers (compost)