VMED Small Animal Physical Diagnosis II Final Exam
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What does POMR stand for? What does SOAP stand for?
Problem oriented medical record
Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan
A SOAP is just a _________ _______ ________ _________.
POMR
What are the goals of a SOAP?
–Approach case in logical manner
–Work through problems systematically
–Communicate case in a thorough and concise manner
–Establish a legal record
What does the "subjective" part of SOAP consist of?
Information that you CANNOT put a number or rigid descriptor on.
Signalment, complaint, history, and mentation.
Immeasurable
What does the "objective" part of SOAP consist of?
Information that you CAN put a number or rigid description on.
Physical exam findings - TPR, BCS, Pain score, hydration status
Measurable
S/O is your ________ ________. The more you collect and the more accurate itis, the better your assessment and plan will be.
Data collection
What does the "assessment" part of SOAP consist of?
Analysis of the subjective and objective data
Problem list and Differentials
What is the most important step of the SOAP?
Assessment
What does DAMNITV stand for?
D-degenerative, developmental
A-allergic, anomalous, auto-immune
M-metabolic, mechanical, mental
N-neoplasia, nutritional
I-inflammatory, infectious, immune mediated, iatrogenic, ischemic, idiopathic
T-trauma, toxin
V-vascular
What does the "plan" part of SOAP consist of?
What do you want to do, or what are you going to do?
Diagnostics/ Treatments/ Differential
Client communication important here!
End of Lecture One
:)
Routes of administration:
Enteral
Parenteral
E - given via GI tract
PE - NOT given via GI tract
How are oral meds - Liquid - properly administered in dogs?
- Grasp upper gums caudal to the canines with non-dominant hand over the muzzle and lift
- Slide syringe between cheek and teeth and slowly give
- Alternatively grasp over the muzzle with non-dominant hand but place thumb on the roof of the mouth
How are oral meds - Pill - properly administered in dogs?
- Grasp and lift with non-dominant hand as described
- With middle finger on dominant hand pull the mandible down
- Place pill as far aboral as possible with pointer finger
What are the two tricks to use when pilling a dog?
- Get over the hump
- Lick their nose
How are oral meds - Liquid - properly administered in cats?
- Same technique as dogs except I don't use the thumb on roof of mouth
- Have to go slower with cats if large volume
- Normal for cats to spit and foam
How are oral meds - Pill - properly administered in cats?
- More important to lift nose
- Some cats do fine with finger technique
- Nothing wrong with a pill popper
- Watch front feet!
Angles of injection insertions.
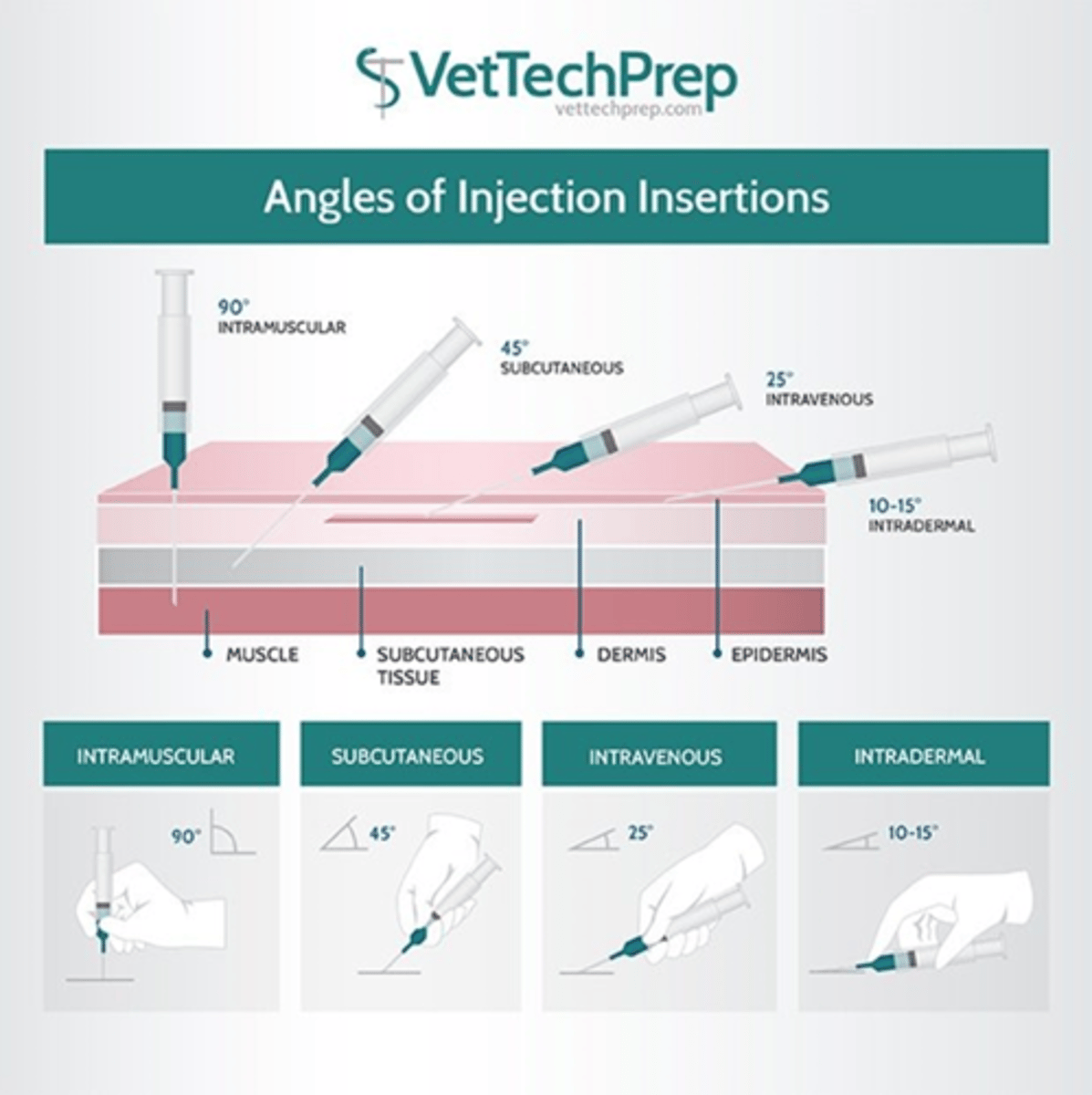
Rules for intradermal injections. Used for? Needle size?
Local block and allergy testing.
25-27 gauge needle.
Tense skin, insert, and inject.
Should feel resistance to injection and should get a 'bleb'
What is the most common route of giving an injection? Why?
Subcutaneous
Larger volumes, less painful, and less restraint.
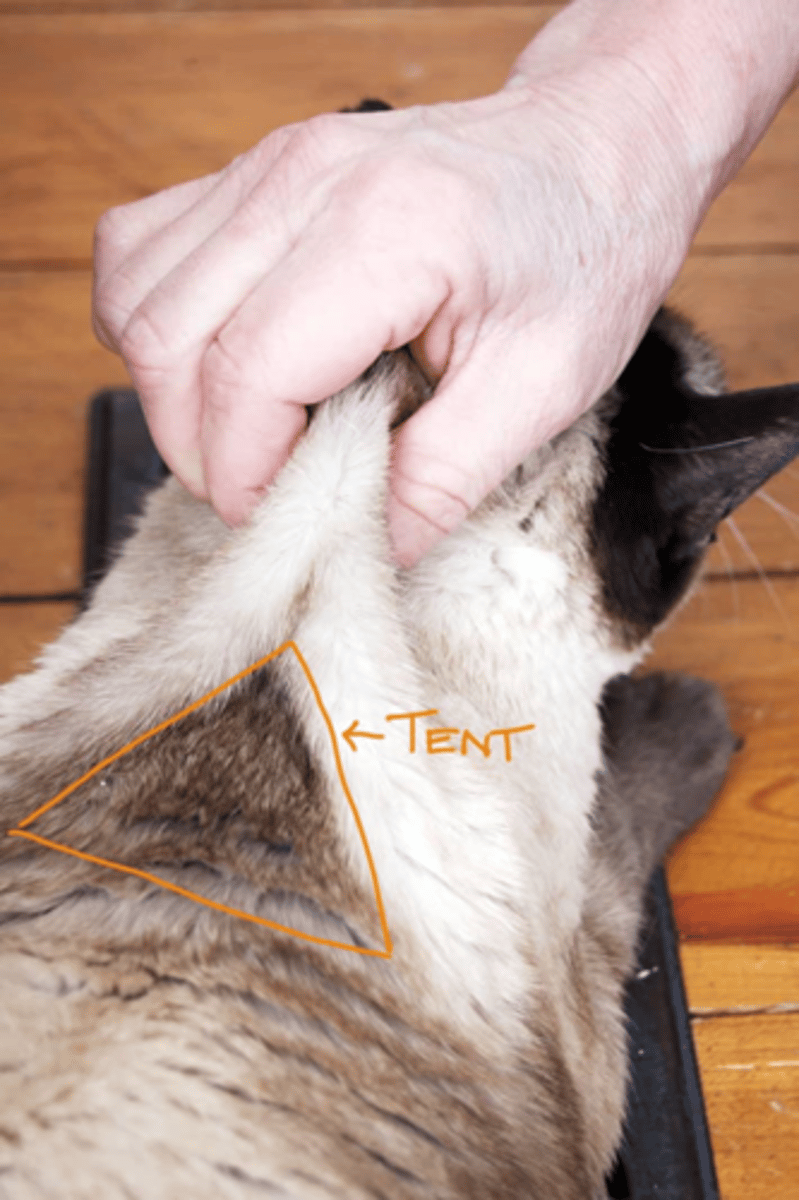
Subcutaneous injections. Needle size? Technique?
18-25 gauge
- Pick up an area of loose skin typically over shoulders, neck, or lateral thigh
- Insert needle at base of skin tent and aspirate
- Inject if no blood and negative pressure
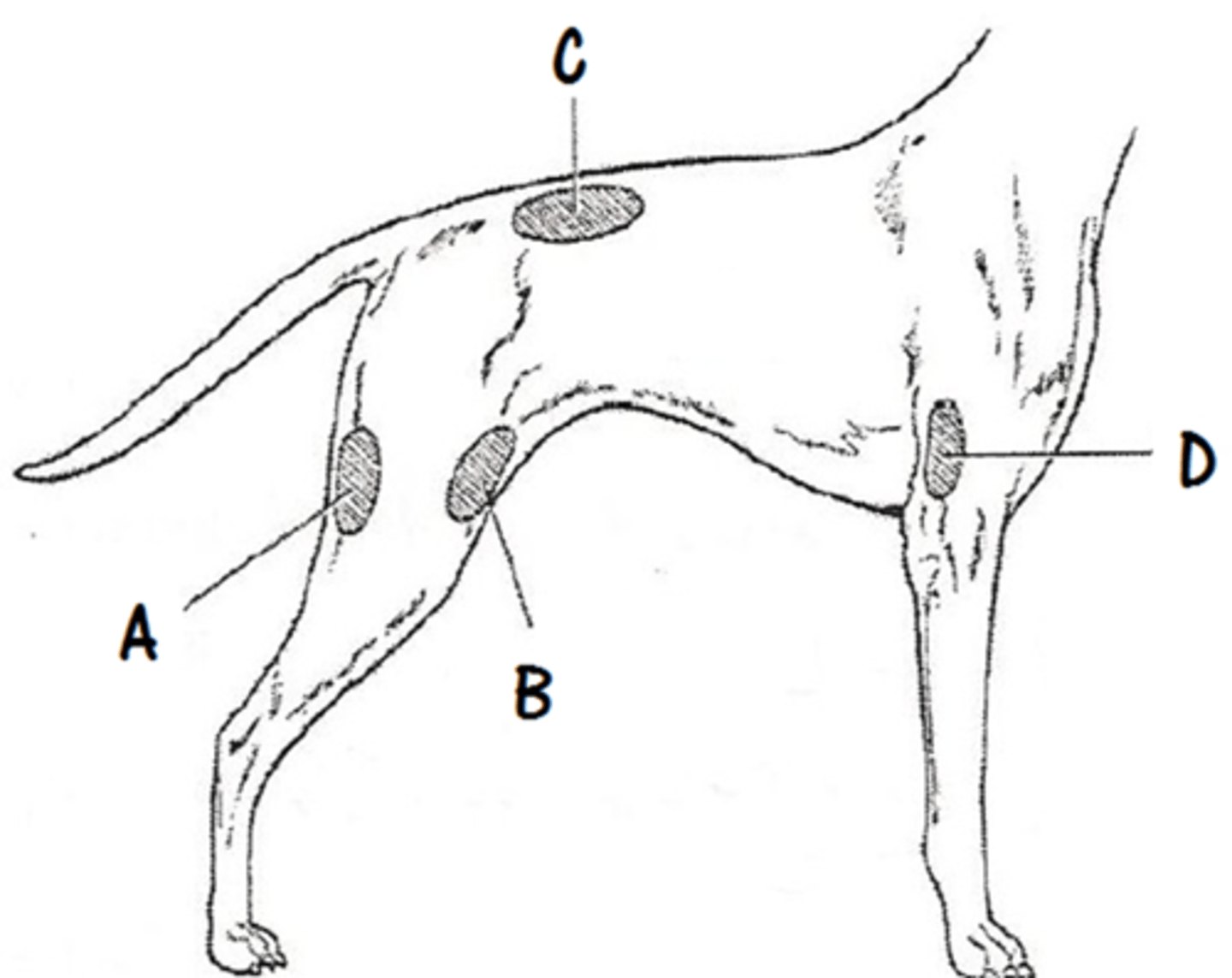
Vaccination sites dogs:
- AAHA Recommendations
- Rabies
- DAPPv
- Lepto
- Lyme/influenza/bordetella
- Core on?
-Right rear
-Right fore
-Left rear
-Left fore
Right side
Vaccination sites of cats:
- AAFP Recommendations
- Rabies
- FVRCP
- FeLV
- Location on the leg, above or below the stifle/elbow? Why?
-Right rear
-Right fore
-Left rear
Distal to elbow and stifle due to fibrosarcoma
Intramuscular injection are commonly used for? Needle size? Most common sites?
Sedation, pain meds, and melarsomine
20-22 gauge
Hamstring, epaxial, quadriceps, and triceps
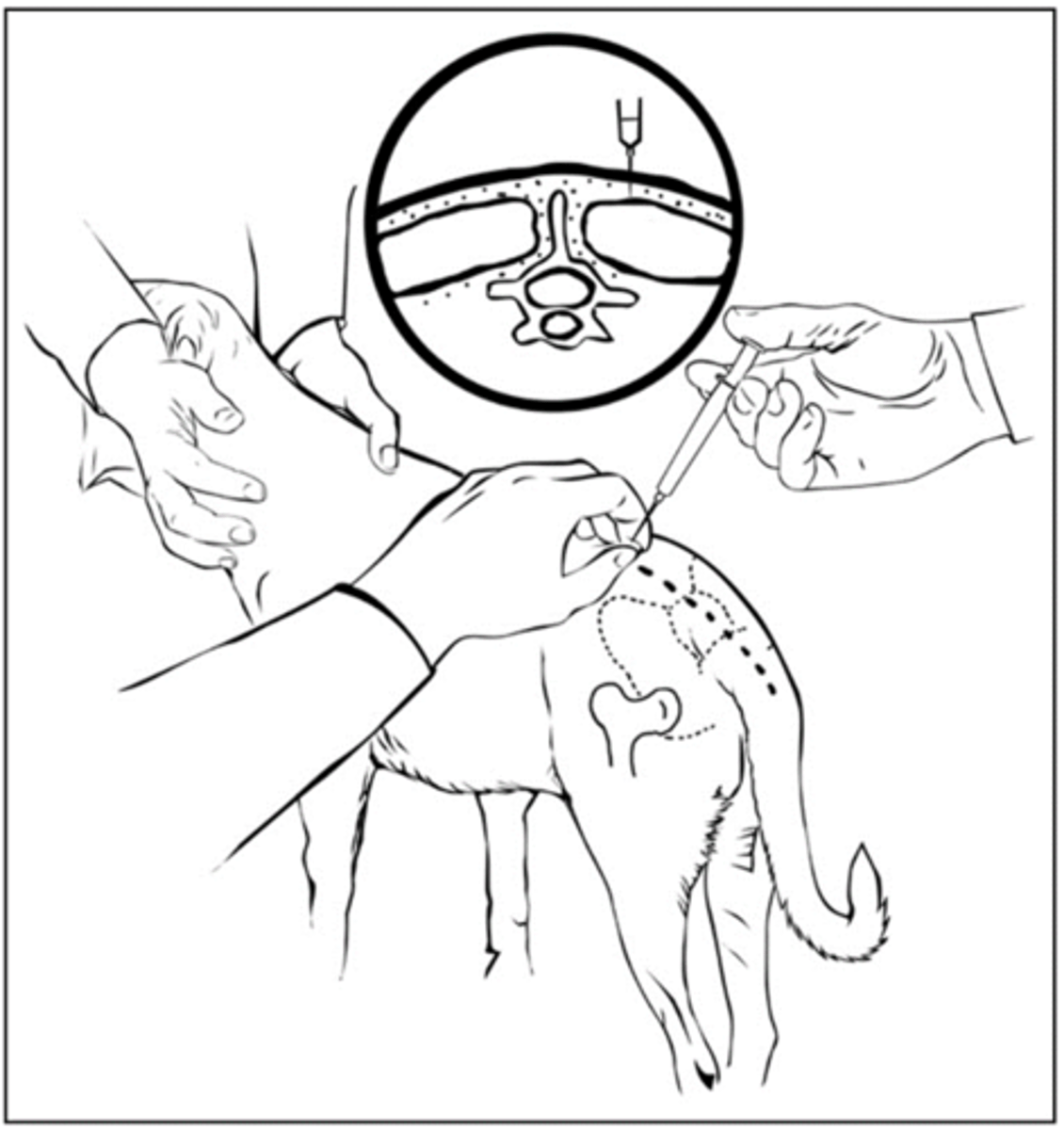
Epaxial injection, advantages? Disadvantages?
Advantages:
- Easy to locate
- Can handle larger volumes
- Less chance of complications
Disadvantage:
- Seems more painful
- Slower onset
Hamstring injection, advantages? Disadvantages?
Advantages:
- Probably safest for personnel
- Seems less painful
- Faster onset
Disadvantages:
- Slightly smaller volumes
- Sciatic nerve!
Intravenous injections, advantages? Disadvantages?
Advantages:
- Most rapid onset
- Allows for prolonged administration
Disadvantage:
- Takes the most skill
- More risk of serious complications
T/F: Match your needle to your patient and your drug.
True
End of Lecture Two
:)
Triage is based on a scale of __________.
Urgency
Triage patients are sorted into 3 groups, what are they?
- Likely to live no matter what
- Likely to die no matter what
- More likely to live if something is done
Three group system?
Emergent
Urgent
Delayed
Steps to triage?
1. Very BRIEF history (<1min). DON'T get trapped!!!
2. Perfusion Parameters and Respiratory
3. CODE STATUS
4. Primary Survey
5. Secondary Survey
6. Full assessment
7. Re-assess everything
What are the six perfusion parameters?
- Mentation
- Mucous membrane color
- Capillary refill time
- Pulse quality
- Heart rate
- Distal extremity temperature
Patients that are stable but need to be moved to the back anyways?
Messy
Unusual appearance
Uncontrolled pain
Potentially infectious
Generally, all cats should be triaged in?
Triaged in the treatment area for patient and staff safety.
After getting Code status, what is completed?
Primary Survey (1-2min):
Primary Surveys include?
Airway
Breathing
Circulation
Disability
Extremities
Airways surveys include?
Patent or moving
Breathing surveys include?
- Rate and effort.
- Pattern and posture.
- Mucous membranes.
- Auscultation
What are some breathing auscultations that can be heard?
- Decreased dull sounds
- Increased sounds or crackles
- Gut sounds
Shock in trauma may be caused by?
Hypovolemia
Vasodilation
Cardiac failure
T/F: Shock state can result in depressed mentation.
True
Pulse quality is dictated by?
Pulse pressure
Prolonged CRT? Shortened CRT?
>2sec, reflects decreased peripheral perfusion from vasoconstriction
<1sec, may reflect increased peripheral perfusion/vasodilation
___________: primary focus is evidence of traumatic brain injury. Mentation.
Disability
Secondary surveys include?
- Repeat your primary survey assessment
- Complete head to toe exam
- Prioritize treatments and diagnostics
T/F: Every patient WITHOUT exception.
True
In a full assessment be methodical, how?
Speed
Accuracy
Consistency
Memory
T/F: Re-assess EVERYTHING.
True
End of Gerken Lecture
:)
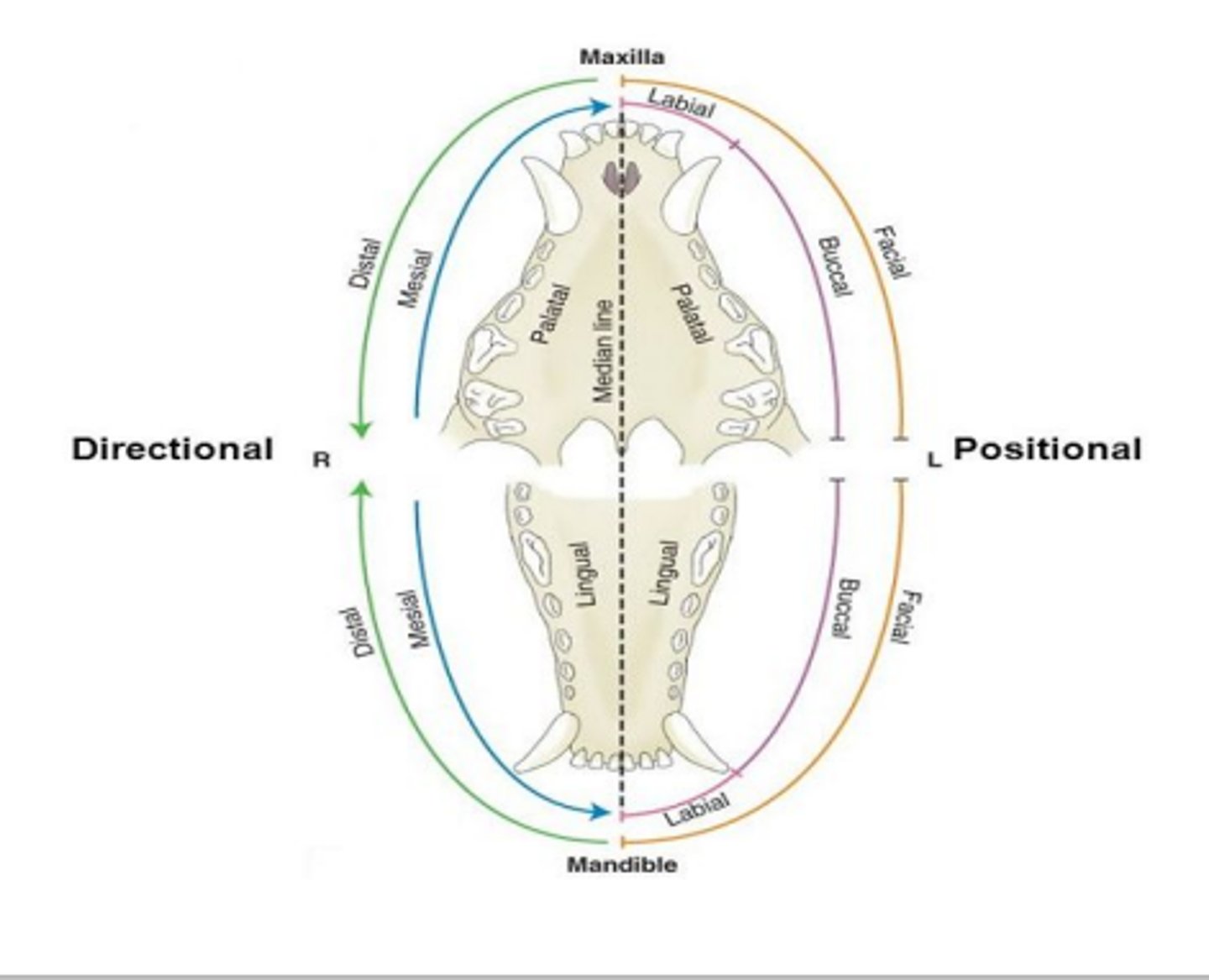
Directional terms in the mouth:
__________ – toward the front/rostral
__________ – away from the front
__________ – toward the cheek
__________/____________ – toward midline
____________– between teeth _____ – natural gap between teeth to allow normal occlusion
Mesial
Distal
Buccal
Lingual/palatal:
- Mandible – lingual
- Maxilla – palatal
Interdental
Diastema
Numbering system for teeth
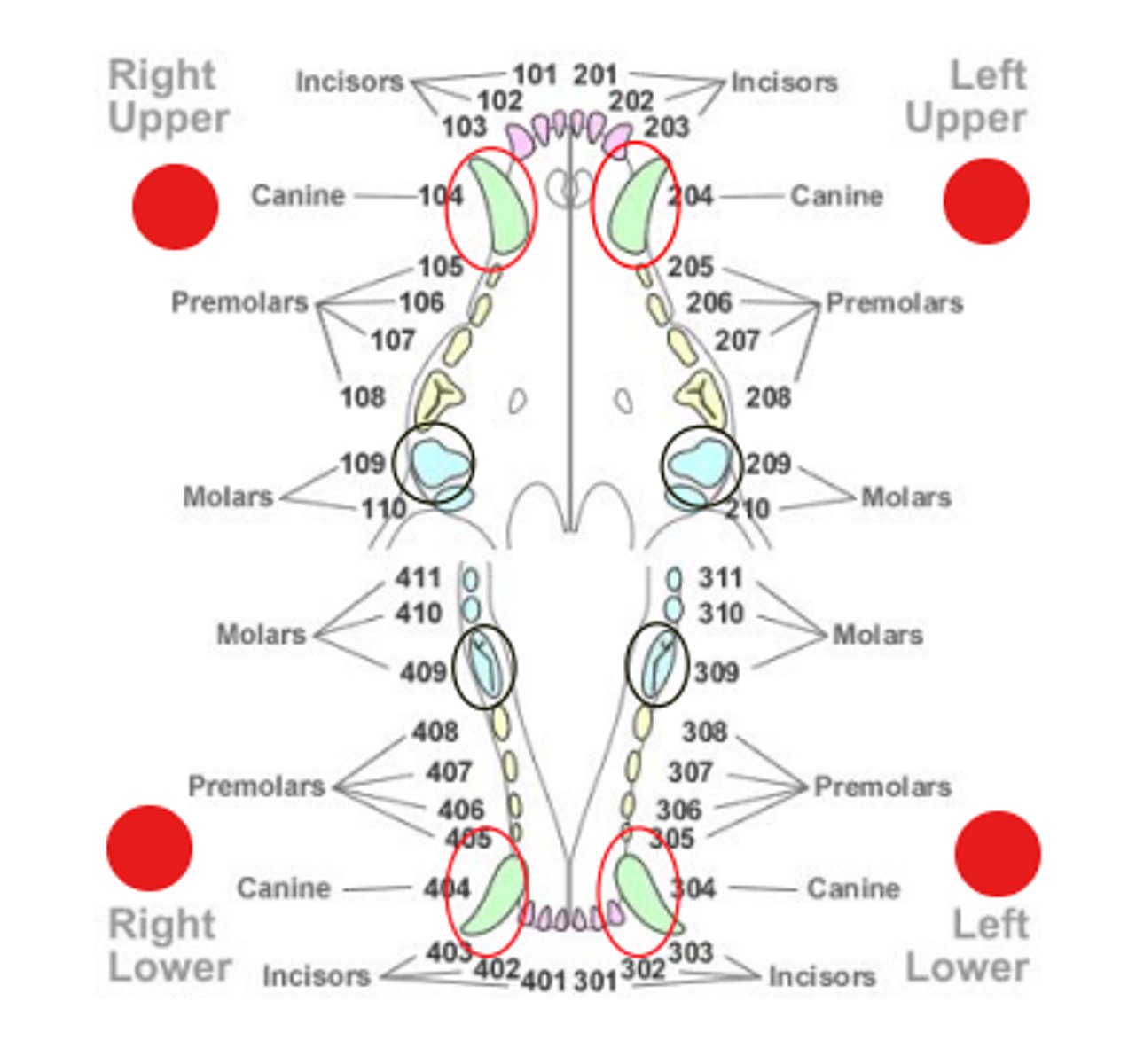
Canine teeth are always __________.
-04
First molars are always the ___________.
-09
___________ ____________: Large upper 4th premolar (P4) and 1st lower molar (M1) teeth of dogs and cats, adapted for shearing flesh - commonly fractured.
Carnassial teeth
Approximate ages of deciduous tooth eruption:
Puppy
Kitten

Deciduous tooth eruption is normally complete by?
8 weeks of age
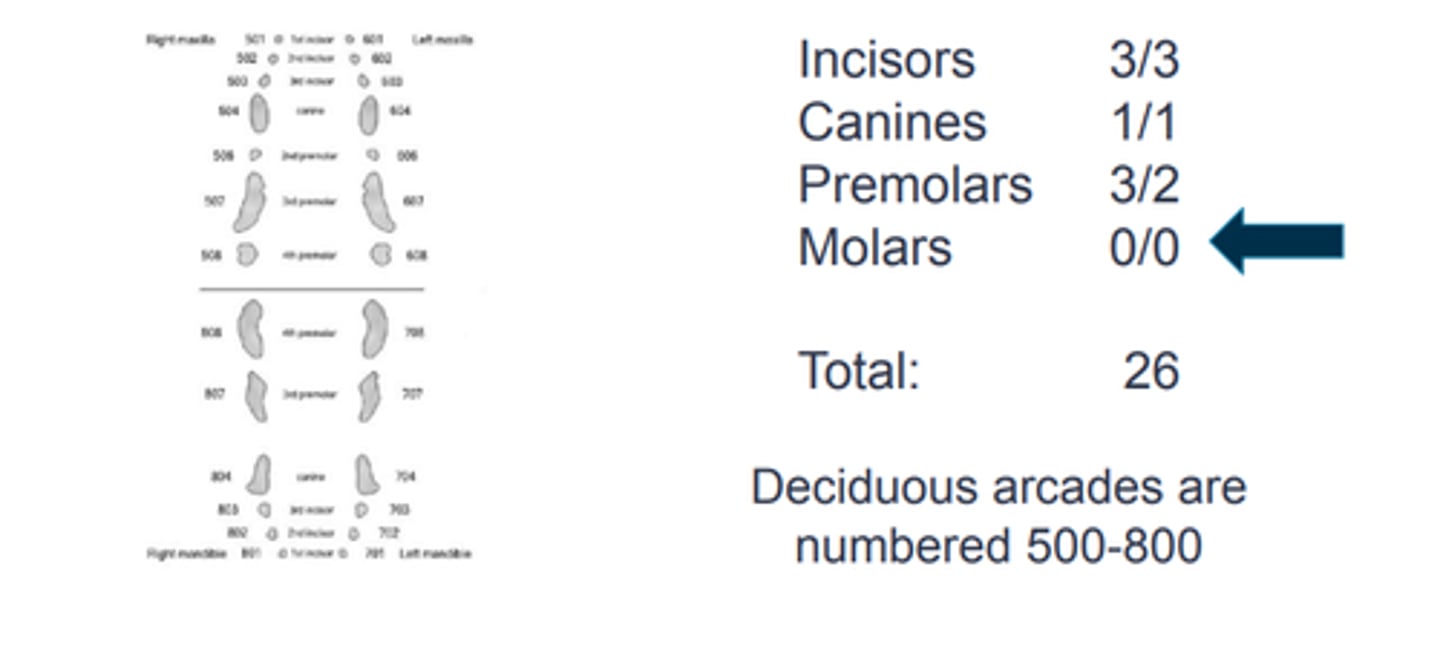
Deciduous arcades are numbered?
500-800
Canine dental formula: deciduous
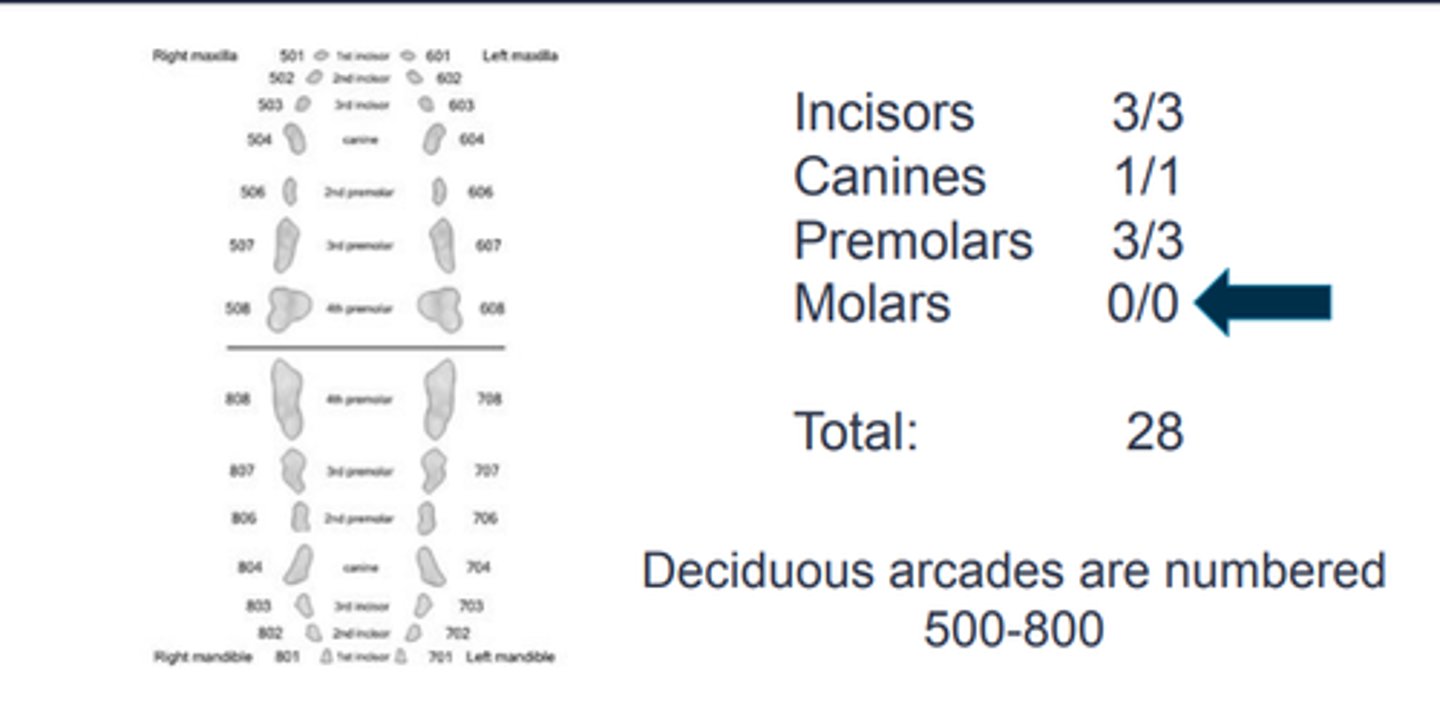
Feline dental formula: deciduous
Approximate ages for permanent tooth eruption:
Dog
Cat
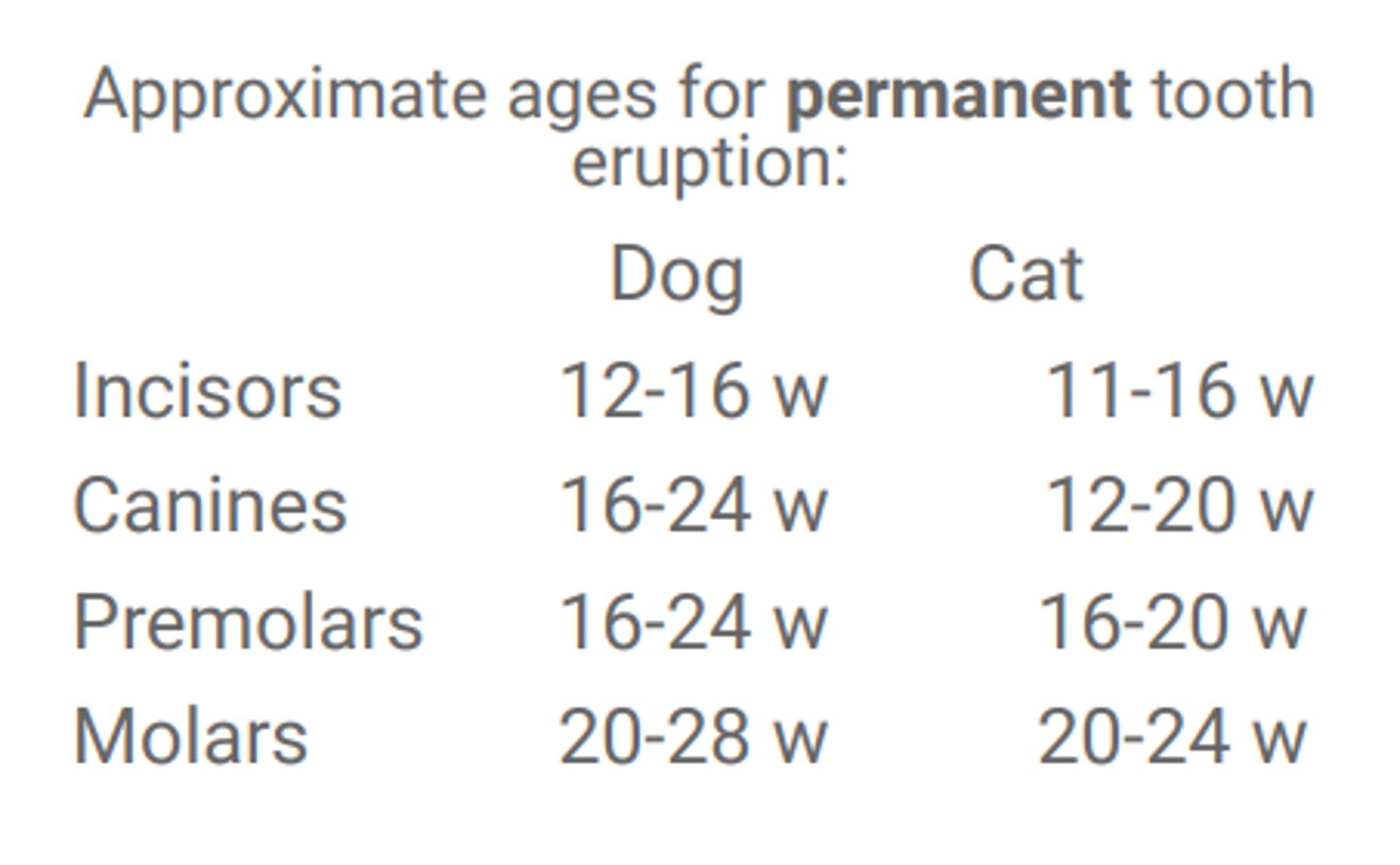
Permanent tooth eruption is normally complete by ______ __________ of age.
7 months
Canine dental formula: Adult
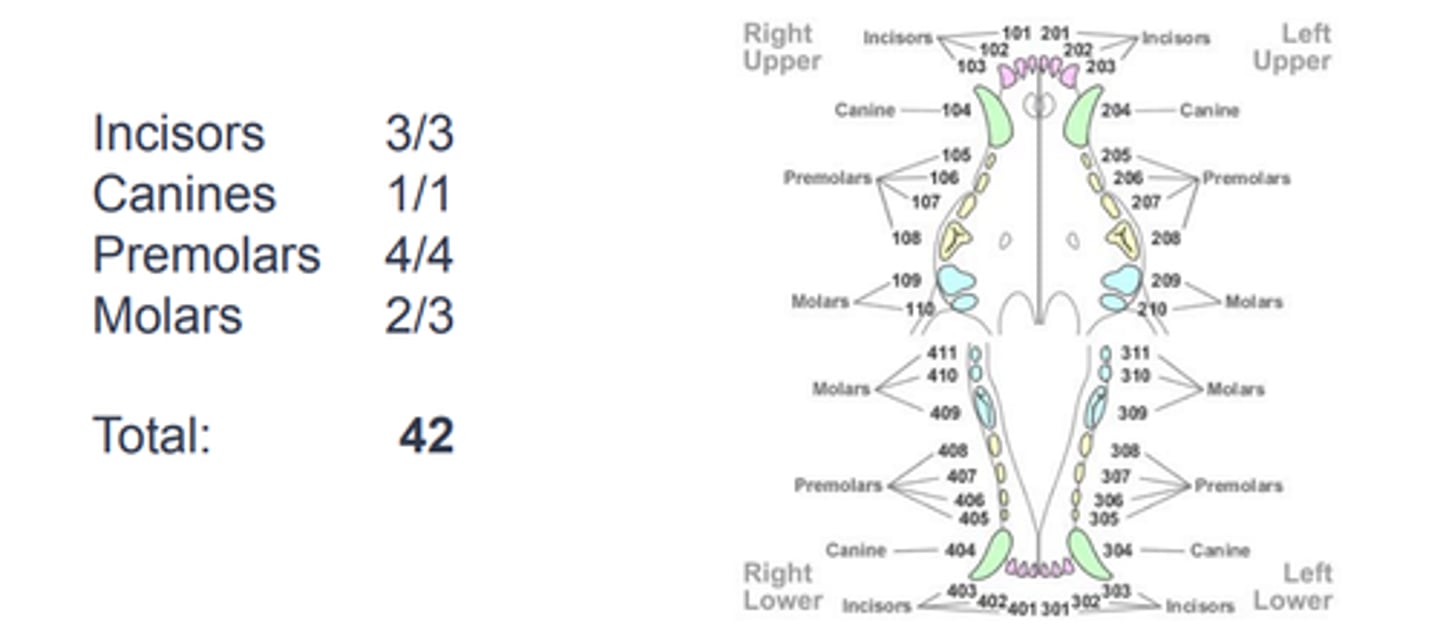
Canine dental formula: Adult
Roots?
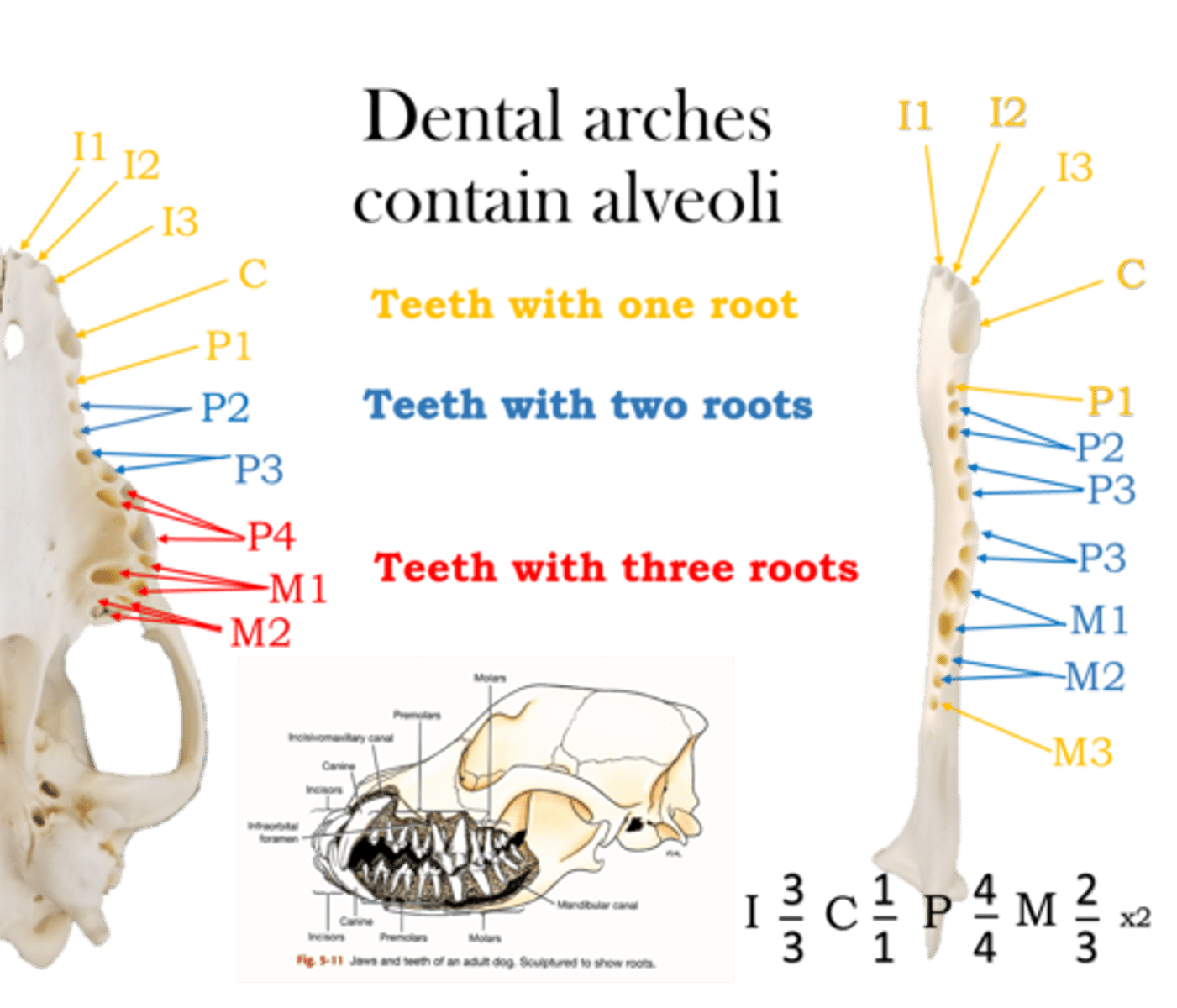
Number of three rooted teeth in a canine?
6
Only present in the maxilla P4, M1, M2
Feline dental formula: Adult
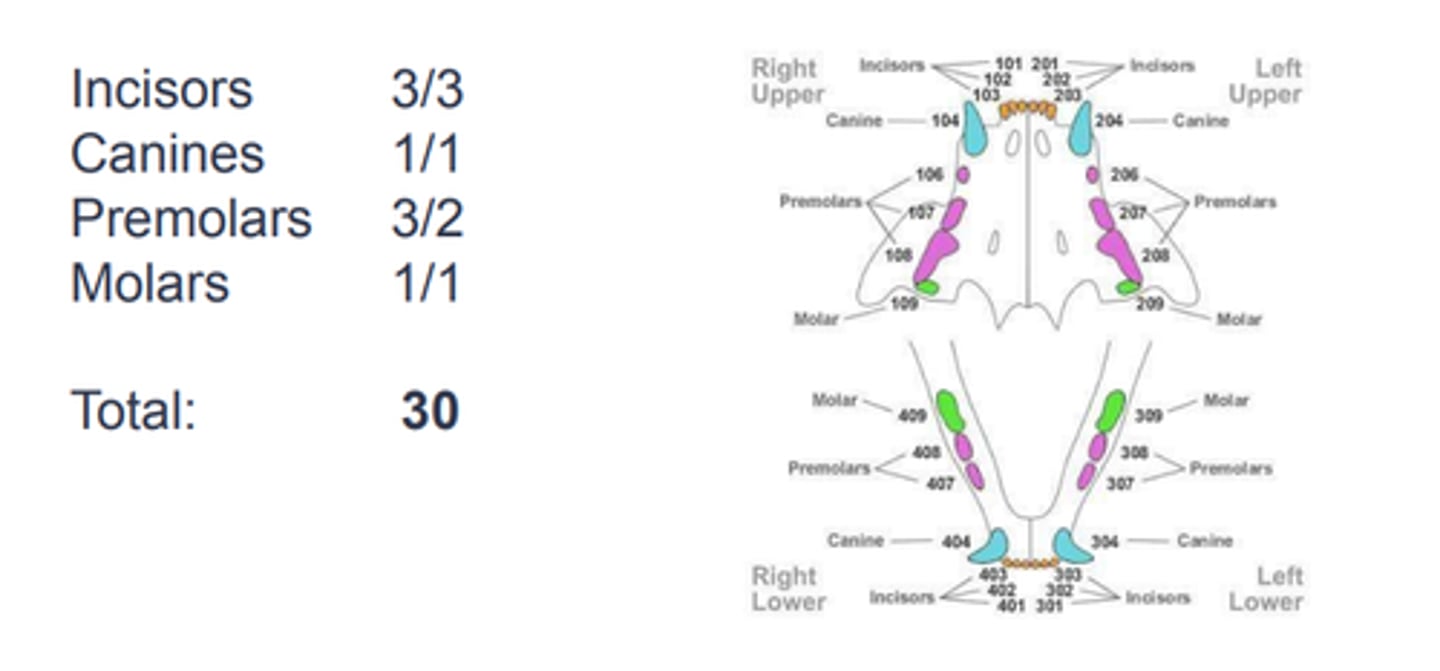
Feline dental formula: Adult
Roots?
Teeth -01 through -06 have one root: incisors, canines, and P2 in maxilla
Teeth -08 have three roots
All other teeth have two roots
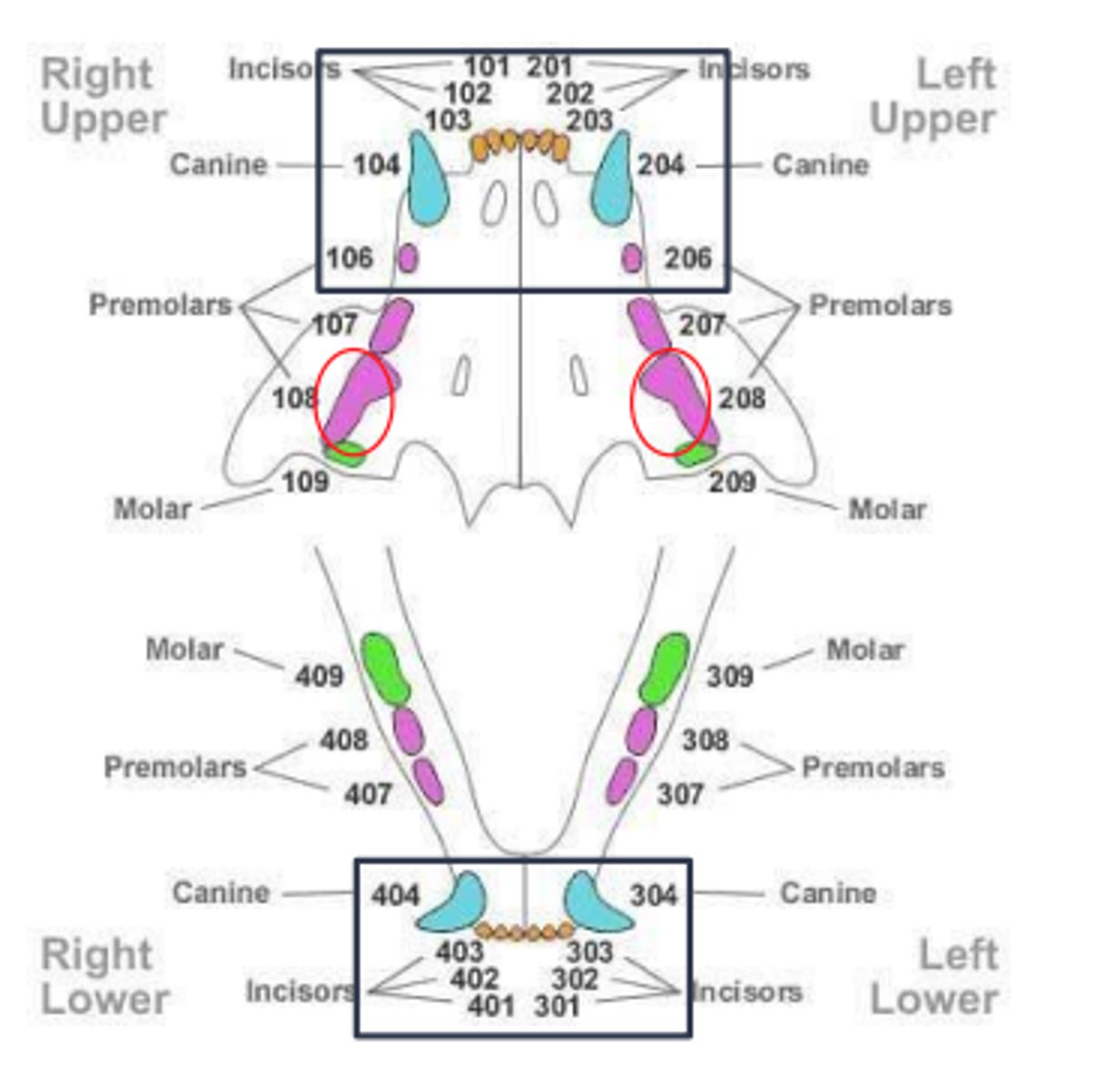
Number of three rooted teeth in felines?
2
Only present in the maxilla P4
Felines are missing which teeth?
Upper P1 an M2
Lower P1, P2, M2, and M3
Conscious oral examination includes?
1. Temporomandibular joint
2. Facial Examination
3. Salivary glands and Lymph nodes
4. Dental occlusion - Mouth closed, then mouth open
5. Teeth, especially enamel
6. Gingiva and Oral mucosa
7. Tongue and sublingual
8. Palate
Facial examination assesses? Look for?
Assess: Facial bones, including zygomatic arch and orbit, and mandible.
Look for: Symmetry, Muscle wasting, Palpate for pain, Swelling (firm or fluctuant?), and Bulging of the eyes
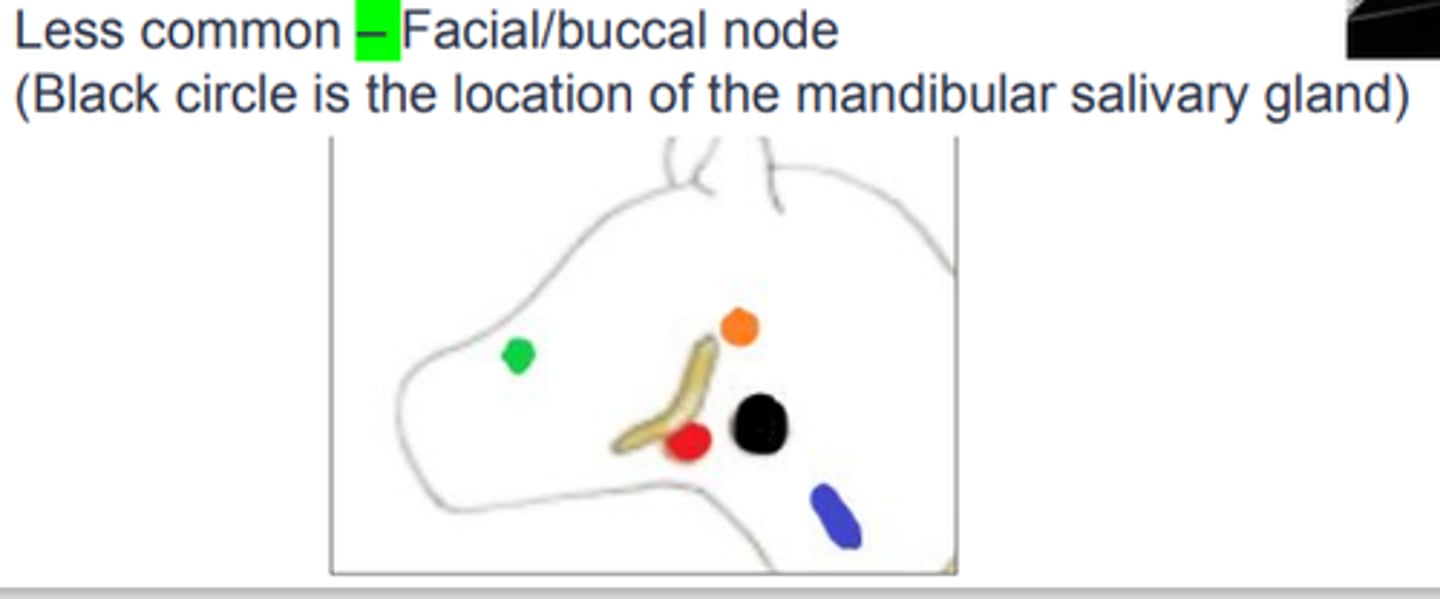
Three most common cranial lymphocentrums?
1. Mandibular lymphocentrum
2. Retropharyngeal node
3. Parotid node
Least common cranial lymphocentrums?
Facial/buccal node
What are the four characteristics of normal dental occlusion?
1. Mandibular incisors just lingual to maxillary incisors – scissor bite.
2. Mandibular canine centered between maxillary 3rd incisor and canine.
3. Interdigitation of premolars – “pinking shear”
4. Mandibular carnassial tooth (M1) lingual to maxillary carnassial tooth (P4)
Treatment should be considered on ALL teeth negatively affecting oral ________ or ________.
Comfort or Function
What is the hardest structure in the body?
Enamel - covers and protects the crown. CANNOT self-repair
__________ _________: Thin, knife-like edge with no redness or swelling.
______________: Any redness or swelling.
Normal Gingiva
Gingivitis
End of Dental Lecture
:)