Psyc 6 Action Potential
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Cations have a _ charge
positive
anions have a _ charge
negative
ions important to the nervous system
Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-
what is the tertiary structure of a protein
a subunit composed of multiple a-helixes
characteristics of ion channels
no energy required (passive transport), can be gated or not
types of ion channels
always open, ligand gated, voltage gates, mechanically gated
characteristics of ion pumps
require energy, moves ions against their conc. gradient
neuron intracellular charge at rest
negative (-65mV)
K+ conc. at rest
more K+ inside cell, so it wants to get out
Na+ conc. at rest
more Na+ outside cell, so it wants to get in
at rest, there’s a higher concentration of Ca2+ _ the cell
outside
at rest, there’s a higher conc. of Cl- _ the cell
outside
sodium potassium pump function
uses energy to pump 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in
calcium pump function
uses energy to pump Ca2+ out
depolarization
getting less polarized (neurons get more positive)
pore loop function on voltage gated Na+ channel
attracts extracellular Na+
what causes the Na+ channel to open
when the neuron become more positively charged
describe the inactivated state of the Na+ channel
even if the channel is open, Na+ can not go through, occurs after depolarization
describe the neuron at rest
negative charge, Na+ and K+ channels are closed
membrane threshold voltage
-55mV
what happens immediately after threshold is reached
Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes in, causing rapid depolarization, K+ still closed
what happens after depolarization
repolarization, Na+ channels inactivate, K+ channels open allowing K+ to flow out, neuron becomes negative
what happens after repolarization
hyperpolarization, Na+ channels return to closed state, K+ channels still open leading to a very negative neuron (-100mV)
absolutely refactory periods
no chance of firing another action potential (depolarization and repolarization)
relatively refactory periods
small chance of another action potential because the neuron is already more negative than normal
tetrodotoxin
targets Na+ channels
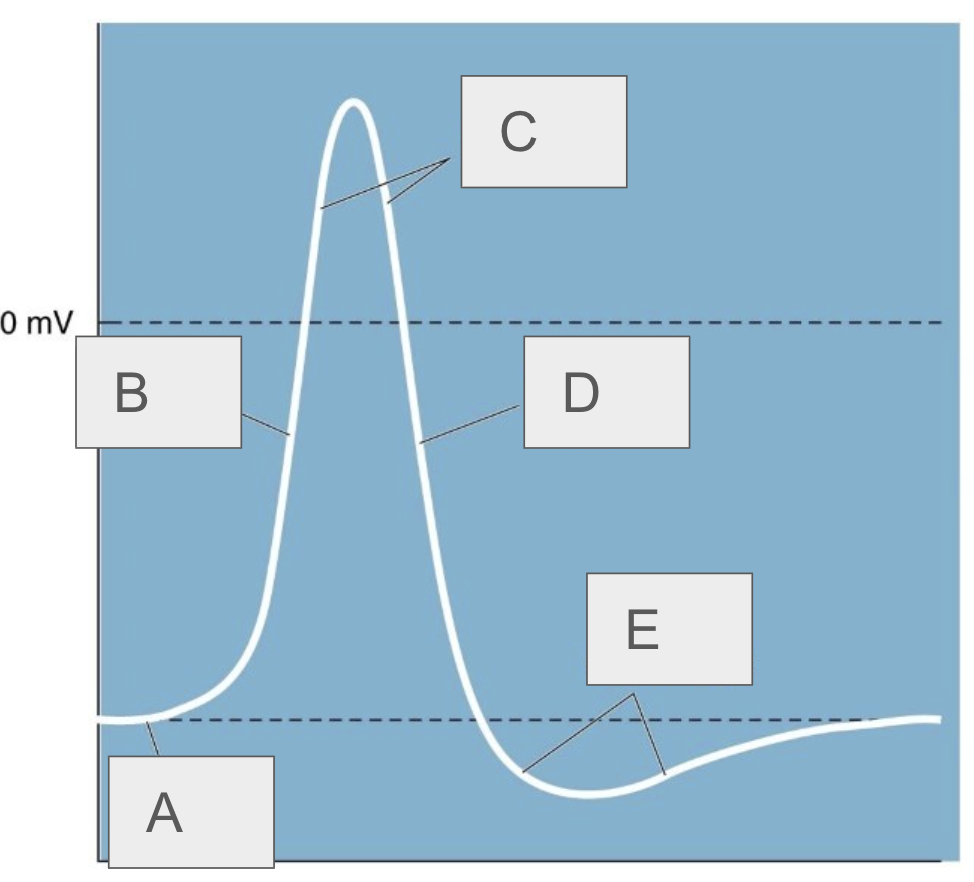
A
resting potential
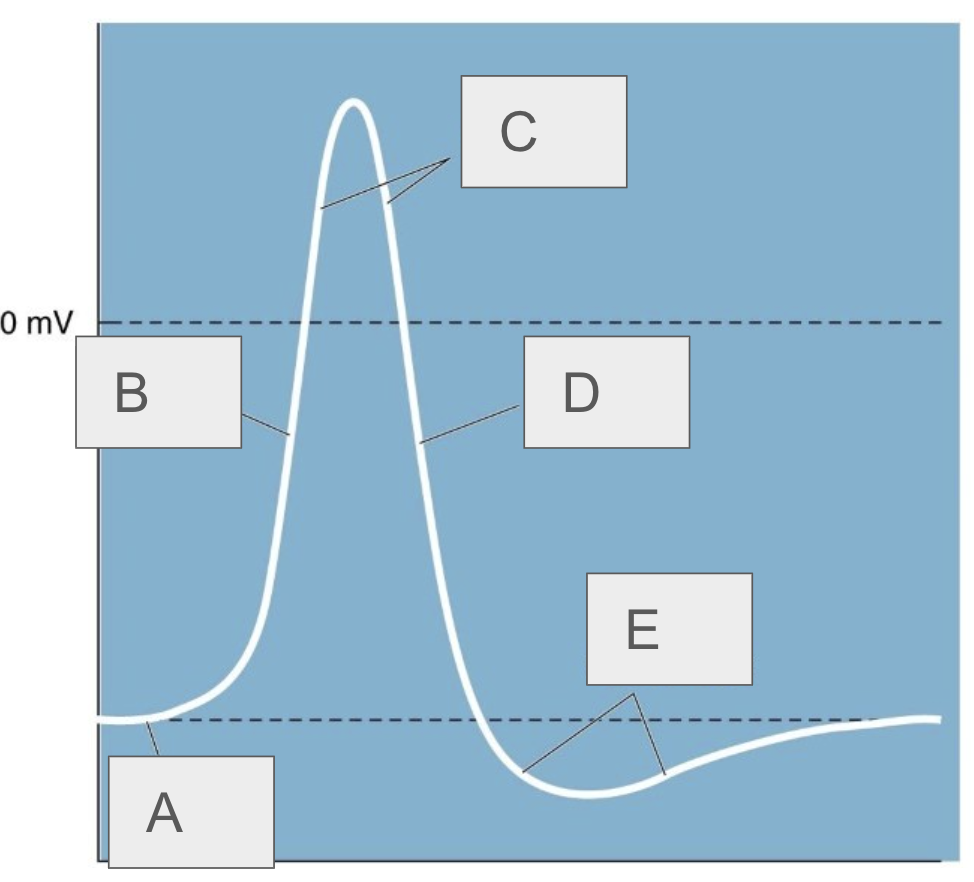
B
rising phase
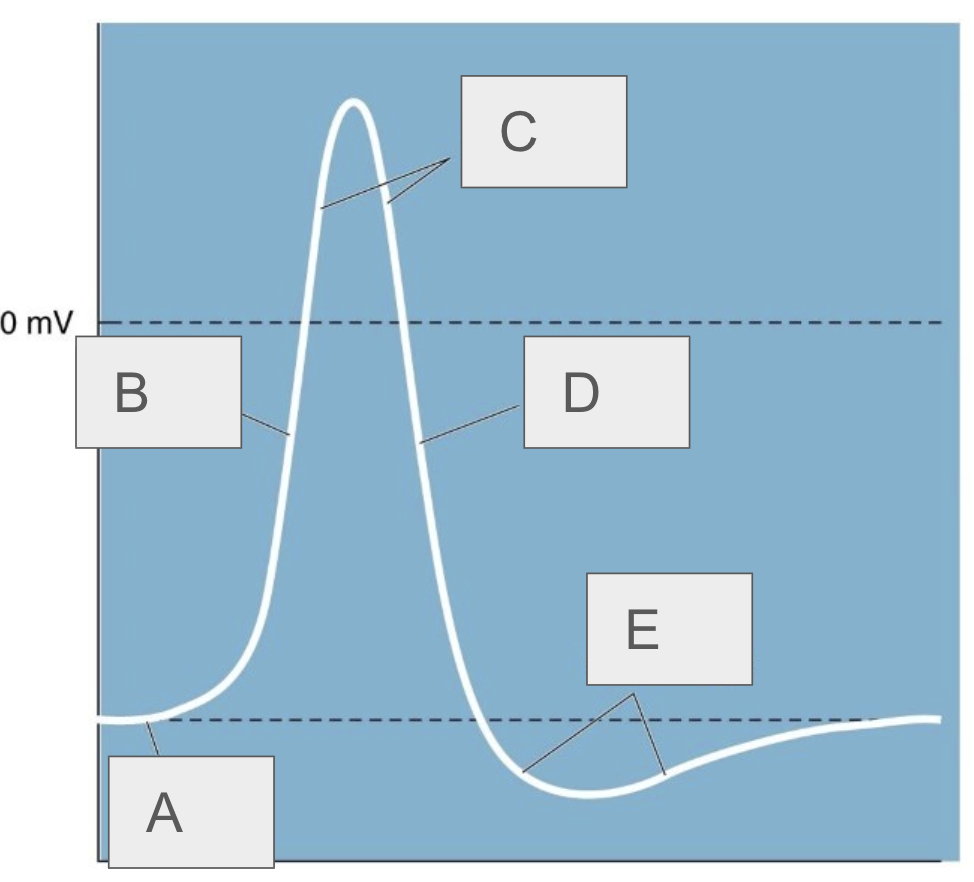
C
overshoot
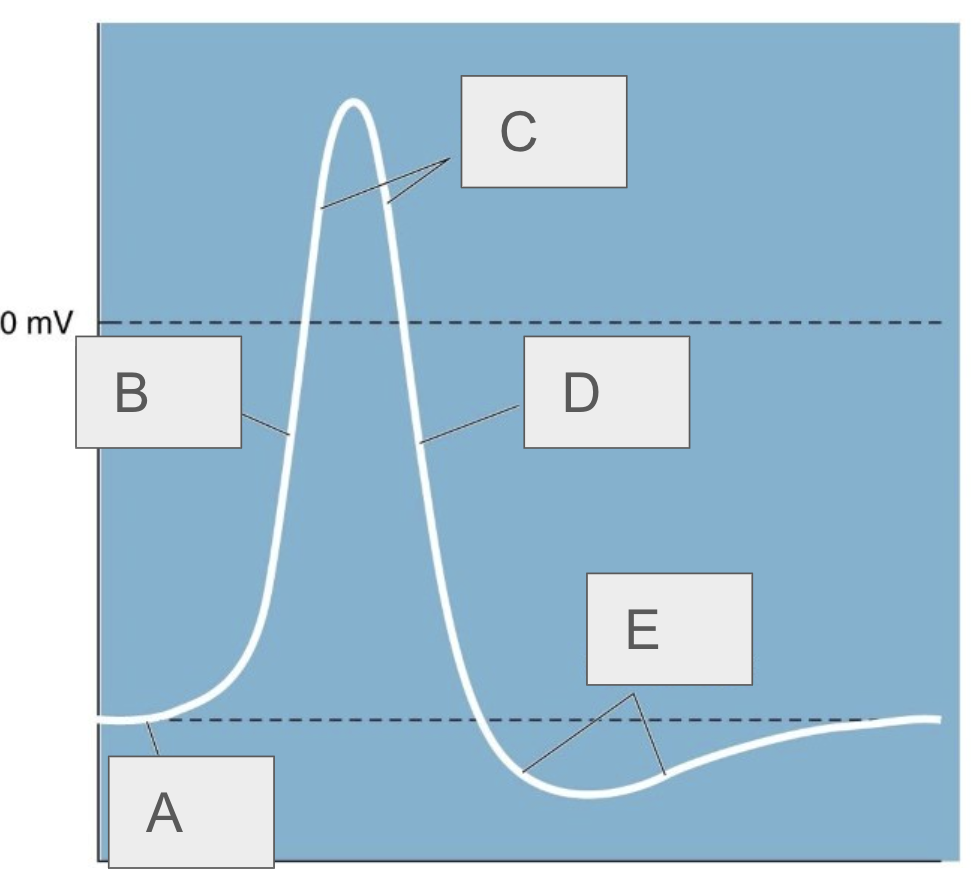
D
falling phase
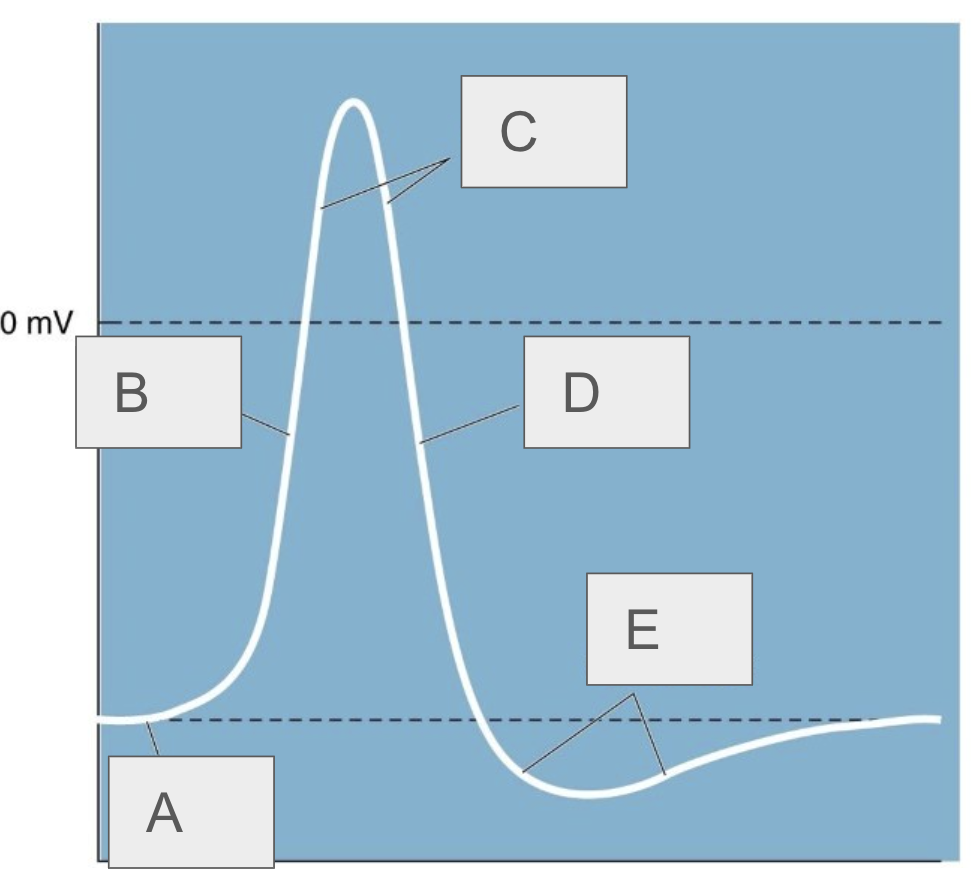
E
undershoot
how do neurons communicate stronger signals through action potentials
higher frequency of action potentials (NOT higher voltage spikes)
why is conduction unidirectional in neurons
Na+ wants to diffuse forwards because it is more negative in that region, previously used Na+ channels are inactive
conduction occurs at a faster velocity in _ axons
wider
saltatory conduction
the action potential leaps from one node of Ranvier to another
EPSP
excitatory post synaptic potential - ligand gated Na+ channels open to make neuron more positive (easier to cause an action potential)
IPSP
inhibitory post synaptic potential - K+ and Cl- channels open, neuron become more negative (hyperpolarized) so its harder to cause an action potential
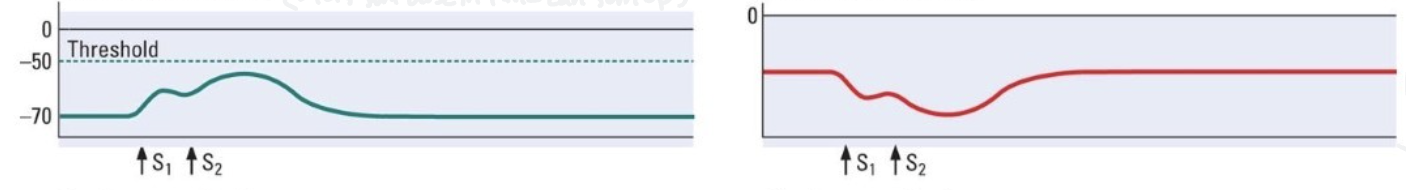
What does the picture show
close temporal spacing - two signals sent in close succession
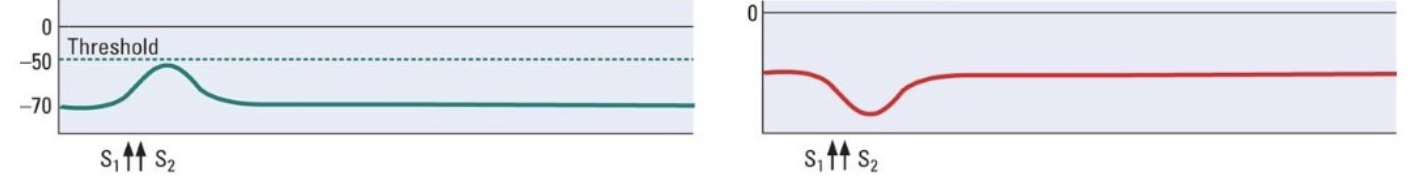
What does the image show
simultaneous stimuli - two signals received at the same time
spatial summation
signals are received by dendrites that are close together and are summed
what determines if an action potential is fired
if the sum of all the incoming signals is enough to depolarize the membrane at the axon hillock past the threshold
vagus nerve stimulation showed that
messages can be sent through chemicals
how do ions travel between neurons in electrical synapses
gap junction channels
characteristics of electrical synapses
faster, weaker, usually large networks
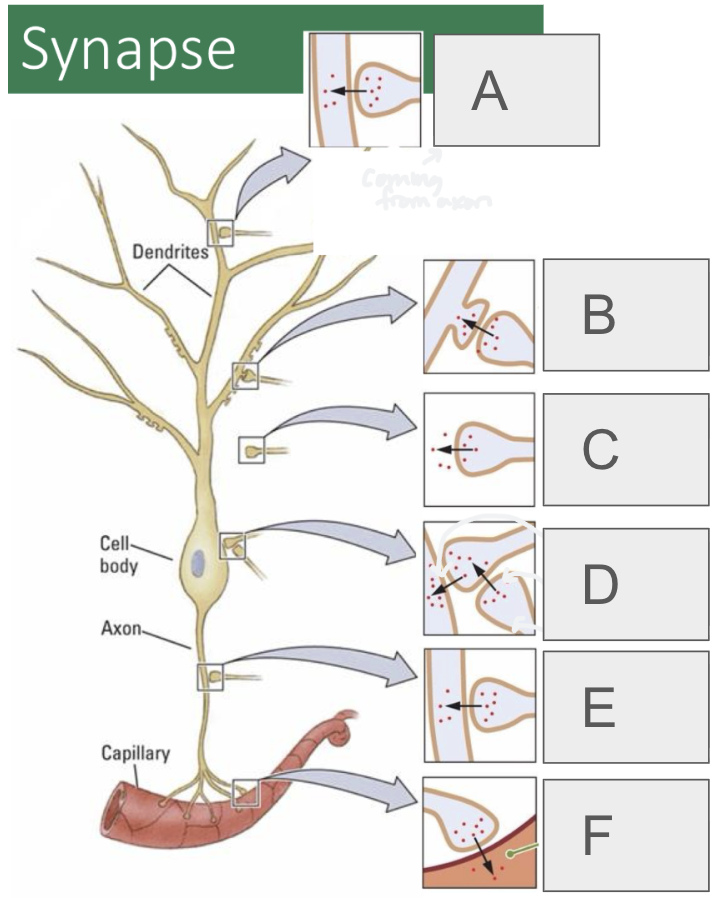
A
axodendritic
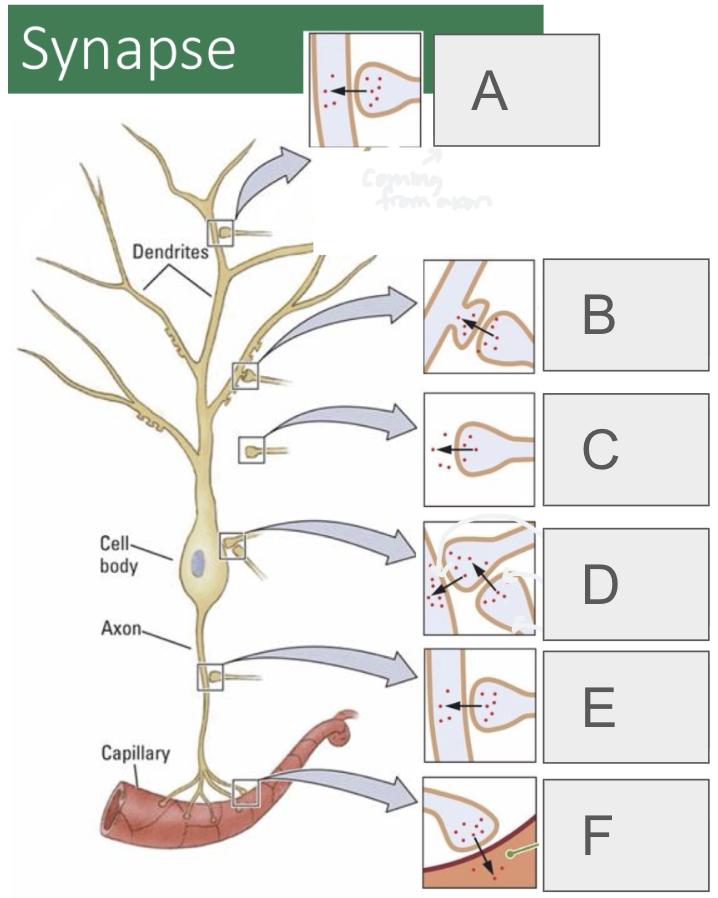
B
axospinous
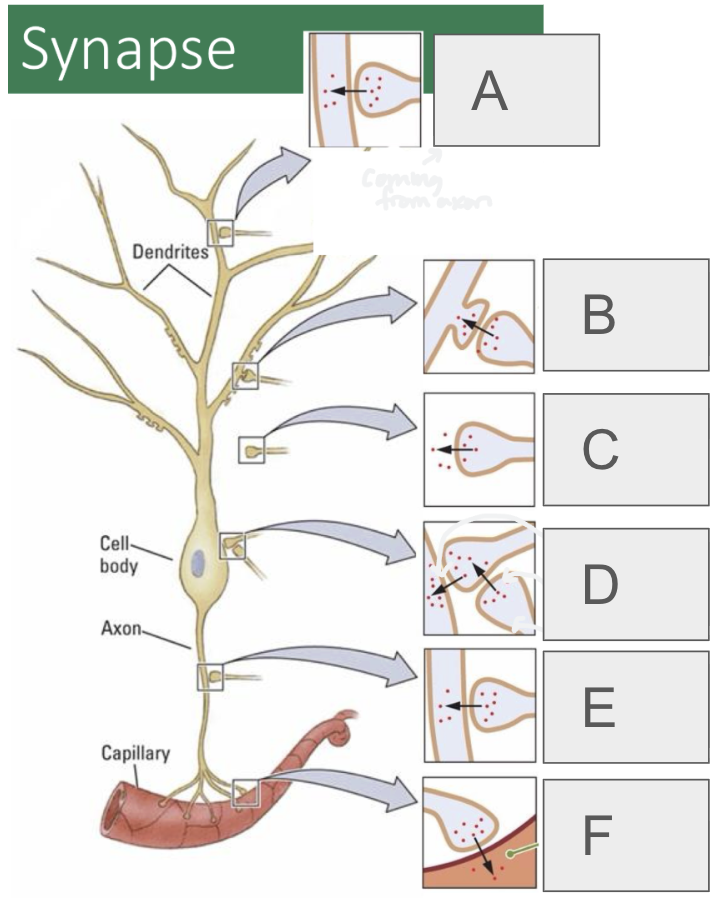
C
axoextracellular
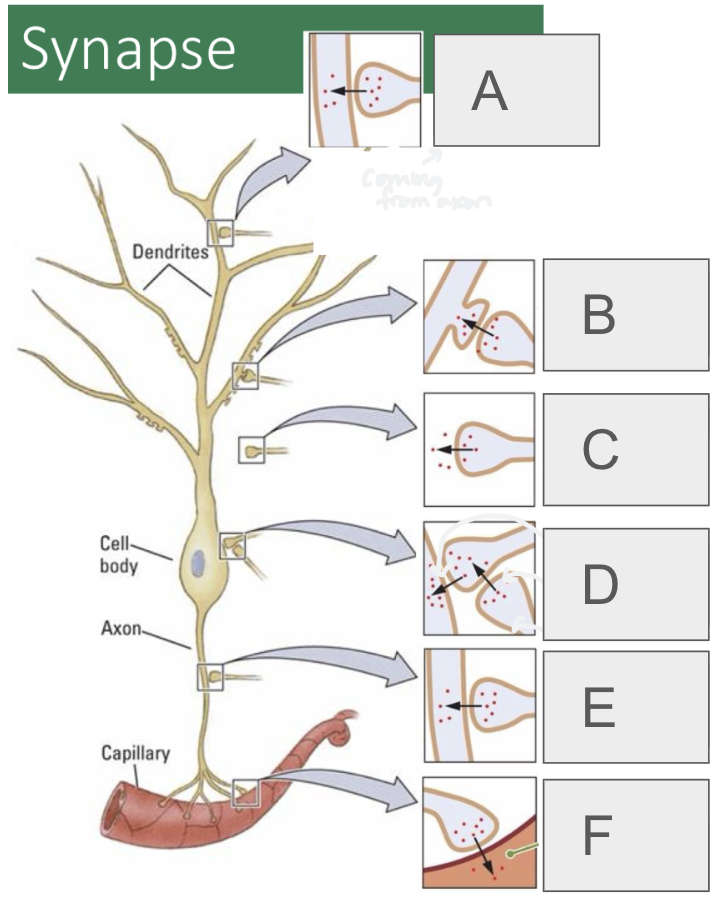
D (2 types)
axosomatic, axosynaptic
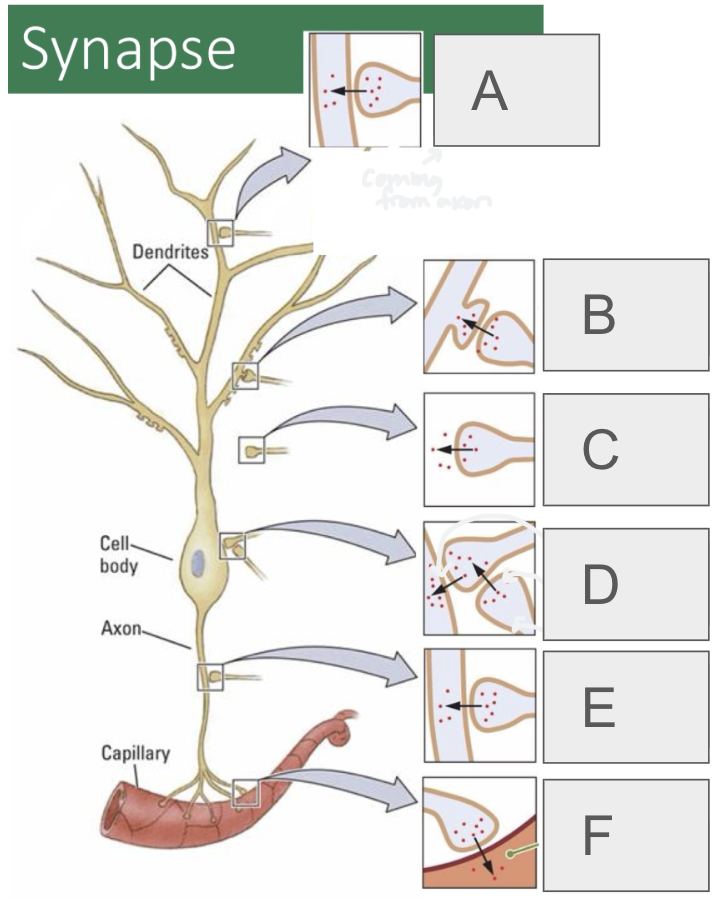
E
axoaxonic
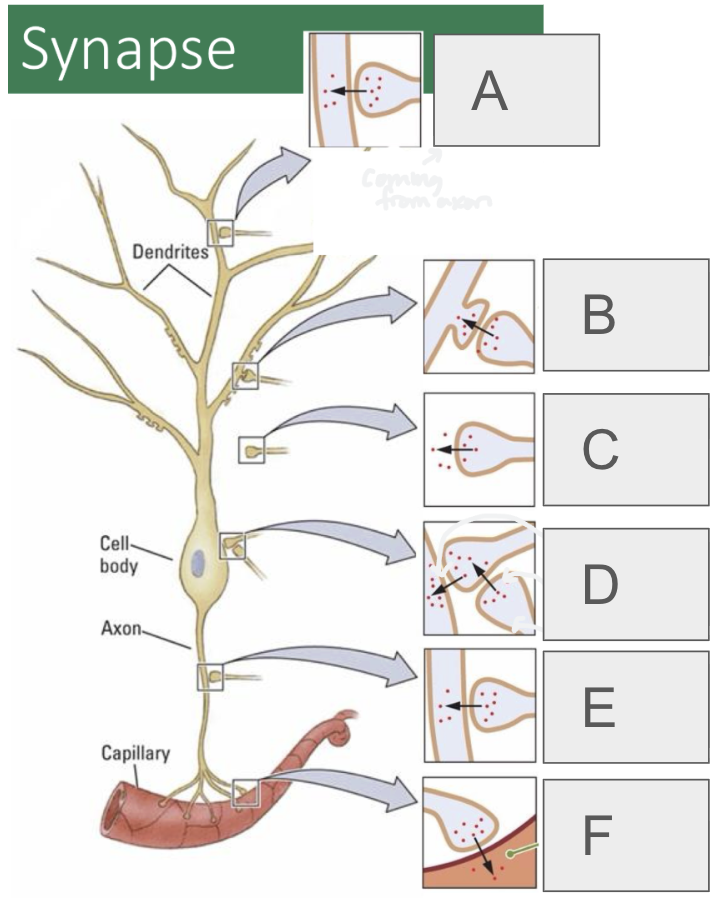
F
axosecretory (from axon to bloodstream or muscle)
neuromuscular junction characteristics
axon branches apart, junctional folds to trap neurotransmitters
4 types of neurotransmitters
amino acids, amines, peptides, gasotransmitters
3 main amino acid neurotransmitters
GABA, glutamate, glycine
4 stages of neurotransmission
neurotransmitter synthesis and storage, neurotransmitter release, receptor activation, neurotransmitter deactivation
synaptic vesicles hold
amino acids, amines
peptide synthesis process
made in cell body and packaged into secretory vesicles (rough ER and golgi)
snare protein function
tie vesicles to the cell membrane
process of neurotransmitter release
action potential depolarizes axon terminal, Ca2+ channels open, Ca2+ rushes in causing vesicles to fuse to membrane, vesicles dump out neurotransmitters (exocytosis)
receptor activation process
neurotransmitter binds to ligand gated channel which opens and lets ions in/out
receptor on presynaptic neuron that binds to its own neurotransmitters for regulation purposes
autoreceptor
neurotransmitter deactivation methods
glia uptake, enzyme degradation, diffusion, reuptake (endocytosis)
receptor where an ion actually passes through
ionotropic
receptor where nothing passes through but a conformational change occurs
metabotropic receptor/G-protein coupled receptor
what happens when a receptor binds to a metabotropic receptor
alpha subunit is kicked off and can bind to an ion channel or second messenger
how can the same neurotransmitter have different effects
different receptors, how fast the receptors open/close
agonist drug
binds to the receptor and mimics the natural chemical (increases effect of the natural chemical)
antagonist drug
binds to the receptor and prevents the natural chemical from binding (decreases effect of natural chemical)
cholinergic system neurotransmitter
acetylcholine (ACh)
cholinergic system RLF
choline (must come from diet)
cholinergic system synthesis process
ChAT synthesizes ACh from Choline and Acetyl CoA, ACh packaged by ACh transporter into vesicles
cholinergic system neurotransmitter deactivation process
ACh broken down by extracellular enzyme (AChE) and choline reuptake through choline transporter protein (uses Na+ to pull choline into cell)
where are the soma of cholinergic neurons found
basal forebrain complex (medial septum, basal nucleus of Meynert), PMT
where do the axons of cholinergic neurons go
spread across entire brain
ACh is important in
motor/muscle function, autonomic functions (heartbeat), learning, memory
catecholaminergic system neurotransmitters
dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), epinephrine
catecholaminergic system precursor molecule
tyrosine
catecholaminergic system RLF
tyrosine hydroxylase (enzyme)
dopamine synthesis
enzyme makes DA from tyrosine, DA packaged into vesicles by transporter protein
catecholaminergic system neurotransmitter deactivation process
reuptake, some of the reuptaken neurotransmitters are broken down by monoamine oxidase (MAO) found on the mitochondria
where are dopaminergic soma found
substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area (both in brainstem)
where do dopaminergic axons go
frontal lobe, striatum
dopamine is important for
reward learning, addiction
how do cocaine and amphetamine work
cocaine blocks reuptake protein so dopamine is not deactivated (prolonged effect), amph sneaks into neurons and releases DA from vesicles so they freely diffuse out of cell through transporter proteins
how is norepinephrine synthesized
dopamine beta hydroxylase (DBH) enzyme within vesicles convert DA to NE
where are noradrenergic soma found
locus coeruleus (in brainstem)
where do noradrenergic axons go
spread over CNS and PNS
norepinephrine is important for
attention, sleep/wake, PNS response to stress
how is epinephrine synthesized
norepinephrine leaves vesicles, PNMT converts NE to E in cytosol, E packaged back into vesicles
serotonergic system precursor and RLF
tryptophan (must come from diet)
how is serotonin synthesized
tryptophan is converted by enzymes into serotonin, serotonin packaged into vesicles
serotonin deactivation method
reuptake
this neurotransmitter has MANY effects depending on the receptor
serotonin
where are serotonergic soma found
raphe nuclei (in brainstem)
where do serotonergic axons go
spread over CNS and PNS
serotonin is important for
sleep/wake cycle, mood and emotions
where are amino acidergic soma found
grey matter
glutamate and GABA precursor molecule
glutamine
method of amino acid deactivation
reuptake and glial uptake by astrocytes
inhibitory amino acids
GABA, glycine