Introduction- Lecture 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
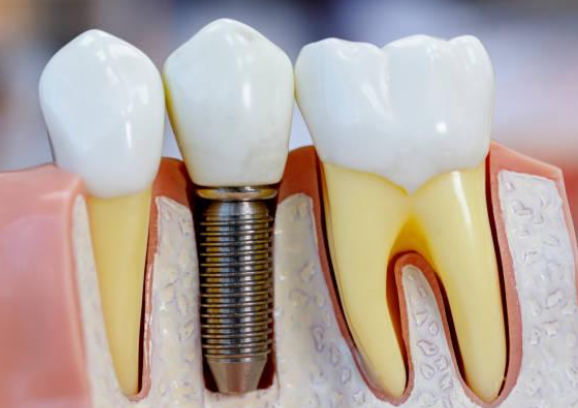
Define dental implant
Artificial device inserted in the edentulous area in the jaw to provide anchorage for a fixed or a removable prosthesis
What are the components/steps of implant dentistry?
Patient selection
Treatment planning phase
Surgical phase
Restorative phase
Follow-up/maintenance phase
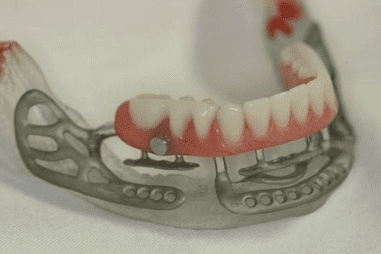
What are subperiosteal implants (eposteal)?
Beneath the periosteum (Placed above rather than within the jaw bone. They are placed below the gums)
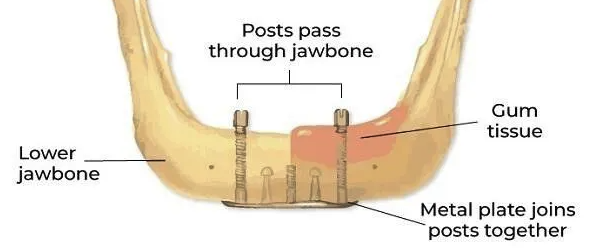
What are transosseous implants (transosteal, staple, transmandibular)?
Through the bone
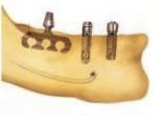
What are endosseous implants (endosteal)?
Inside living bone
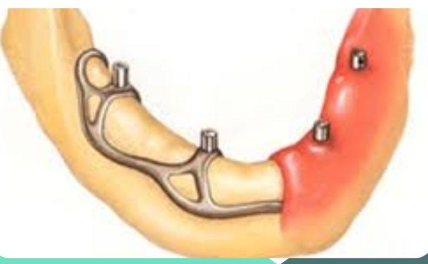
What are subperiosteal implants made of?
Cast metal framework in Chrome Cobalt or Titanium
What is the main surgical challenge of subperiosteal implants?
It is a complicated and painful surgical technique requiring a major flap and impression of the alveolar bone
Why is the impression technique for subperiosteal implants considered difficult?
It requires an impression of the exposed alveolar bone —> increasing technical difficulty and patient infection + paraesthesia
What are the major risks associated with subperiosteal implant surgery?
High risk of infection and paresthesia
How many surgical stages are involved in placing subperiosteal implants?
Two stages:
Initial flap reflection for impression
Second flap reflection 7–10 days later for framework delivery
When is the framework placed for subperiosteal implants?
7–10 days after the initial surgery, requiring re-reflection of the flap
How is the subperiosteal implant framework supported?
It rests directly on the alveolar bone without any mechanical anchoring components

Titanium framework with HA coating
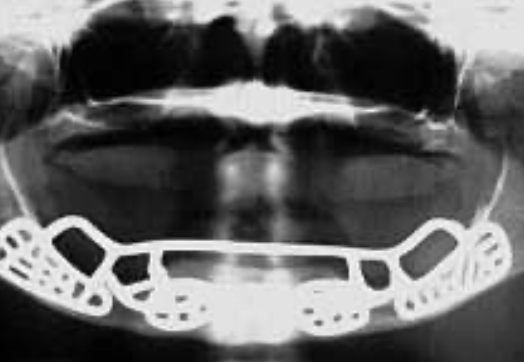
Panoramic view after placement

What is a Ramus Frame Implant?
Titanium metal bar is customized to fit the specific patient and secured in the ramus area and the anterior mandible
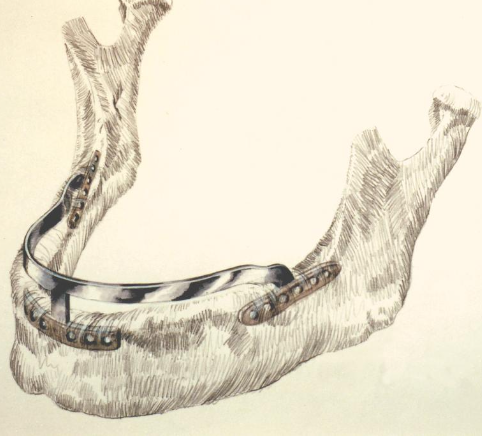
In which cases are ramus frame implants used?
On narrow ridges with proper vertical height. Narrow osteotomies are prepared in the AP mandible to fit the metal substructure. No screws used to stabilize. Denture is seated onto the framework

What is the primary purpose of the screw in transosseous implants?
To secure the metal plate to the mandible

What component of transosseous implants allows customization during placement?
Adjustable threaded rods

What type of surgical approach is required for transosseous implants?
Extra-oral incision under general anesthesia

Where are sites prepared for stabilization of transosseous implants?
On the base of the mandible to stabilize the metal plate

What surgical preparation is done to retain the denture in transosseous implants?
Osteotomies are prepared through the mandible for posts that retain the denture

What materials are used to fabricate the screws and plates in transosseous implants?
Gold alloy or semi-precious metal alloys

What distinguishes transosseous implants from other implant types in terms of bone engagement?
They pass completely through the mandible with posts emerging to retain a denture

What type of design is this endosseous implant?
Cylindrical: solid or hollow
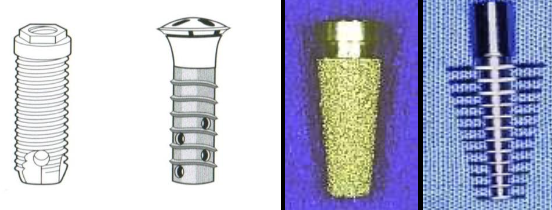
What type of design is this endosseous implant?
Screw type: parallel sided or tapered
Flat plates- blade
What are some implant body material?
Commercially pure titanium
Titanium alloy (alumina and vanadium)
Titanium/zirconia alloy (roxolid)
Tantalum
Ceramics (Zirconia)
Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium
Implant bodies are ______/______ using a strictly controlled process
Milled/turned
Rods of _____/ ______ are used
Commercially pure titanium/titanium alloys
What has moderately rough surface characteristics shown?
Improved healing ability and stability (1-5micrometers)
What are some methods you can use for surface modification?
Sand/titanium blasting
Acid etching
Electrochemical treatment by anodic oxidation
Crystalline deposition (CaP)
What are some other materials being introduced for fabrication of dental implants
Zirconia
Tantalum
Titanium- Zirconia alloy
What are some factors that are important for successful results?
Surface cleaning and sterilization
High quality- precision
Monitored process- strict quality control
What are some differences between first generation implants and implants today?
First gen —> machine turned smooth surface
Implants today —> modified/ moderately rough surface
What are the implant systems used at UW?
Nobel Biocare
Straumann
What are the two different types of implant body (fixtures)?
“Tissue level” design
“Bone level” design
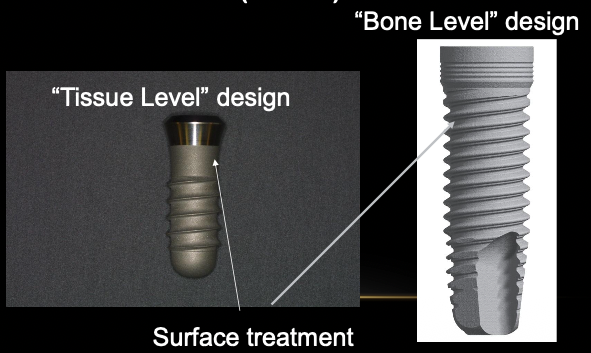
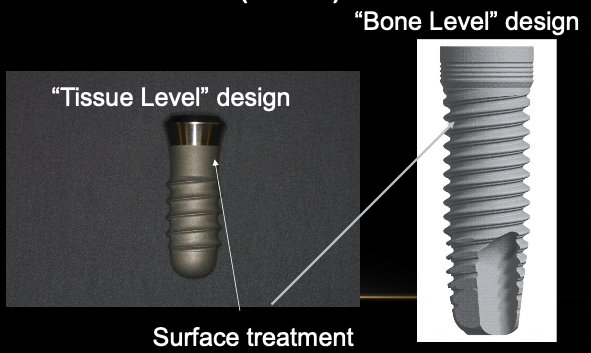
What is the difference between an internal and external connection?
Internal threads used to secure a restoration / component (abutment) to the implant body
What are some types of prostheses?
Single tooth restorations
Multi-unit fixed prostheses (bridge)
Removable prostheses
Maxillofacial prosthetics
What circumstances would you use maxillofacial prosthetics in?
Reconstruction after cancer
Reconstruction after trauma
Anomalies
Bone anchored hearing aid
How long is the healing phase after insertion of implant?
8-12 weeks
What does the restorative phase entail?
Impression making
Fabrication of Master Cast
Abutment selection
Fabrication of Final Restoration (Single tooth, FPD, or removable prosthesis)
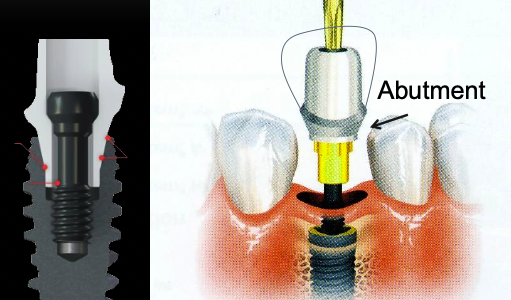
What is responsible for the connection between the implant and restoration?
Abutment
What are the two different types of restorative options?
Cemented Crown
Screw-Retained Crown
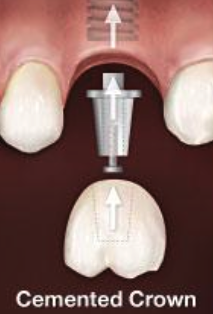
What kind of crown is abutment supported?
Cemented crown
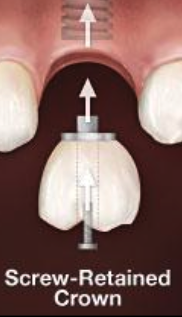
What kind of crown is implant supported?
Screw Retained Crown

What is an abutment?
Device which serves to support and attach the prosthesis to the implant
How is an abutment secured to the implant?
By a screw (there are many types of abutments available)