N209 - Eyes
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Pupillary Light Reflex
What is occurring when the pupil of the eye constricts when bright light shines on the retina?
There is no conscious control of the reaction
What does it mean for the pupillary light reflex to be a subcortical reflex arc?
CN II (Optic)
What cranial nerve is the sensory afferent link for the eyes?
CN III (Oculomotor)
What cranial nerve is the motor efferent link for the eyes?
the client’s right eye
the eye that is opposite of the light source is constricted
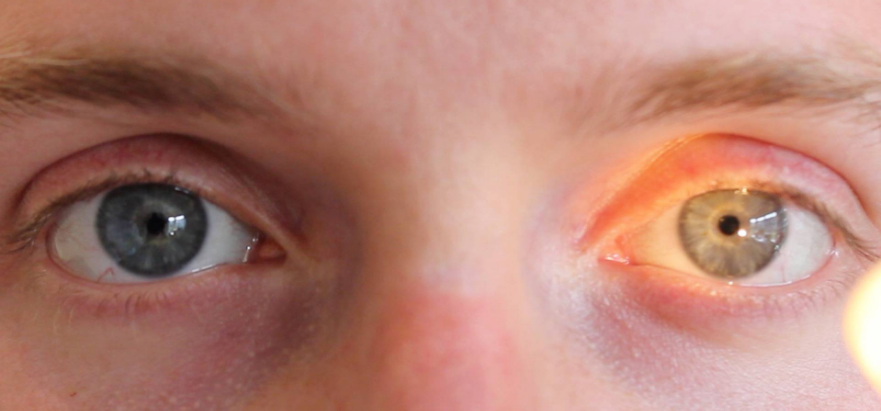
Which eye is exhibiting a consensual light reflex? Why?
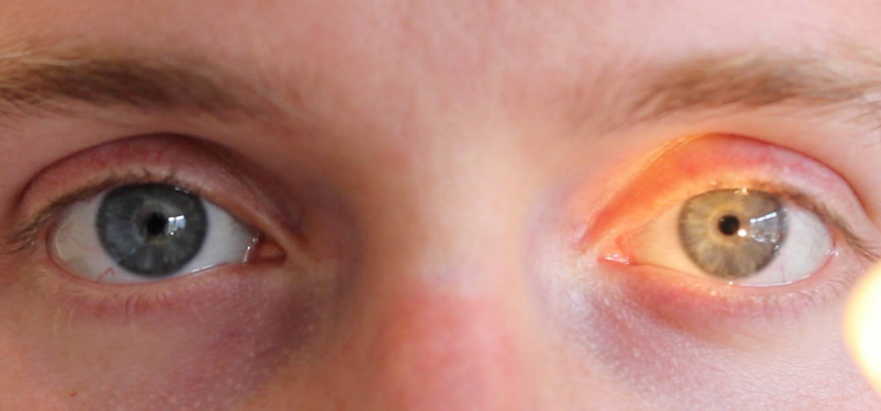
The client’s left eye
the same eye as the light source is constricted
Which eye is exhibiting a direct light reflex? Why?
Accommodation
What reflex does the lens changing shape to focus on objects that are closer/farther demonstrate?
Fixation
drugs, alcohol, fatigue and inattention
What is the reflex of the eye following things that attract our attention called and what is it impaired by?
Is there any difficulty with vision?
Any pain in the eye?
Do they experience Strabismus?
Any watering or excessive lacrimation (tearing)?
Do they have a history of ocular problems (including head injury, surgery and trauma)?
Is Glaucoma present?
Do they use any vision aids (i.e., glasses & contacts)?
What subjective data (health history) should the nurse ask pt.’s in relation to the eyes?
Glaucoma
A pt. experiencing vision loss, narrowed vision, redness in the eye, nausea and vomiting may have what?
Glaucoma
What condition of the eyes is characterized by increased ocular pressure or damage to the optic nerve?
Acuity
What is the measure of the sharpness of vision?
The Snellen Chart
Have the pt 20 ft away from the chart
pt. w glasses/contacts should use them
shield one eye at a time
ask the pt to read the smallest line
What test is used to measure central visual acuity of far vision? How is this test done?
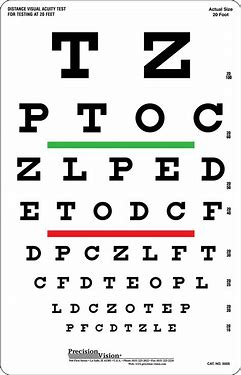
Pt. reads the 20/20 line without hesitation, squinting, or tilting of the head
What is a normal finding with a Snellen Chart?
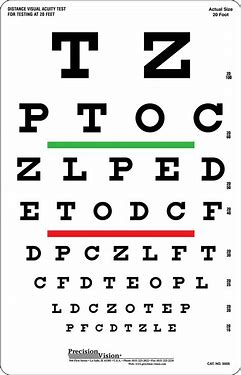
“The pt. can read at 20 ft what the normal eye can see from 30 ft away.”
What does 20/30 vision mean?
Rosenbaum Chart
have the pt. hold the card 14 inches from eyes
shield one eye at a time
What test is used to measure central visual acuity of near vision? How is this test done?
pt. reads 14/14 line without hesitation, squinting, or moving the card closer or farther away
What is a normal finding with a Rosenbaum Chart?

Presbyopia
suggested when a pt. reading a Rosenbaum chart has to move the card farther from the eyes to read it.
What is a decrease in power of accommodation with aging called? When is this suggested?
Confrontational Test
What test screens for loss of peripheral vision by comparing it with your own (assuming yours is normal)?

Stand 2 ft away from pt, and have them look straight @ you
Pt. covers one eye & you cover the opposite (e.g. your left & their right)
Advance a finger in from the periphery in several directions
Have the pt. verbalize when they see the object
Patient and examiner should see the object or movement at the same time.
How should a confrontational test be done? What are the normal findings?
Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg Test)
= test that assesses the parallel alignment of the eye axes
have the pt. focus on a faraway object, shine a light from 12 in. away at the bridge of the nose.
should see light reflected symmetrically on the cornea in both eyes
Deviation in alignment from eye muscle weakness or paralysis, and neurological problems
What does asymmetry in a Hirschberg test indicate?
Diagnostic Position Test
=leading the eyes through the 6 cardinal positions of gaze
Have the pt. follow an object/finger held 12 inches from their face w their eyes only
Should exhibit symmetrical, smooth, coordinated and parallel movement.
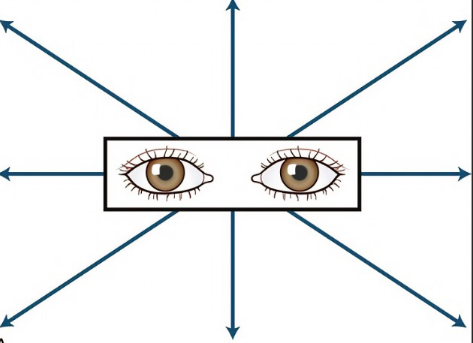
Nystagmus
= a fine, oscillating movement of the eyeball that is normal in the extreme lateral gaze and abnormal anywhere else
Lid Lag
= when the white rim of the sclera is seen between the iris and upper eyelid
occurs with hyperthyroidism.
CN III (oculomotor)
CN IV (trochlear)
CN VI (abducens)
What 3 cranial nerves innervate the extraocular muscles?
4. while the lower lid is at the iris, the upper lid should go over the iris
Which of the following is NOT a general normal finding of the external ocular structures? Why is it incorrect?
moist & pink
pupils 2-6 mm
involuntary blink w complete closure
the upper and lower lid is at the iris
the eyes are bilateral & symmetrical
Palpebral Fissures
= the space b/t your eyelids when they are open
should be aligned w helix of the ear
hypothyroidism
A person with the absence of the lateral third of the eyebrow likely has:
Bell’s Palsy (unequal) or Stroke (absent)
A person with unequal or absent movements of their eyebrows likely has experienced what?
Exophthalmos (Protruding Eyes)
= forward displacement of the eyeballs & widened palpebral fissures
presents “lid lag”
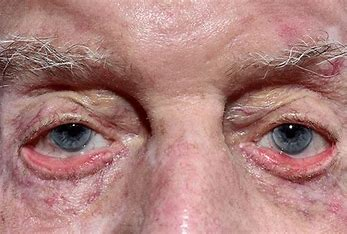
Ectropian
= lower lid is loose and rolling out (eversion)
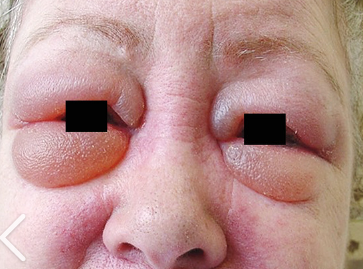
Periorbital Edema
= lids are swollen and puffy; excess fluid is easily apparent
Entropion
= lower lid rolls in (inversion) bc of spasm of lids or scar tissue contracting
china white
What color do you expect the sclera to be?
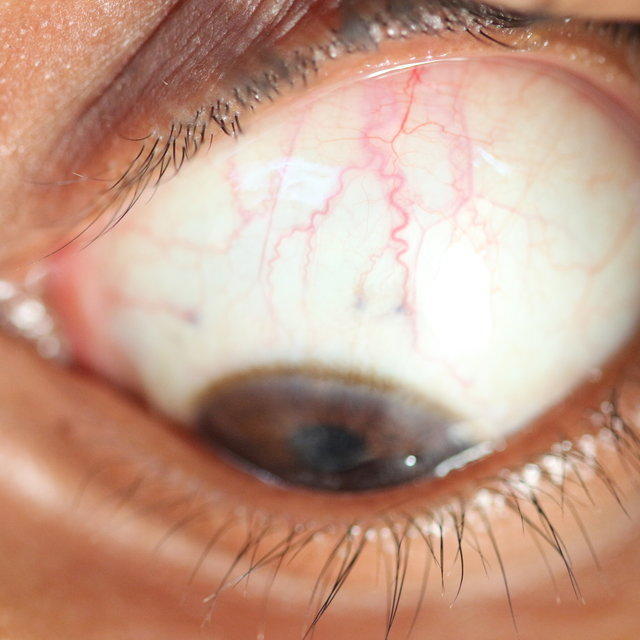
Bulbar
Which conjunctiva is this?
Palpebral
Which conjunctiva is this?
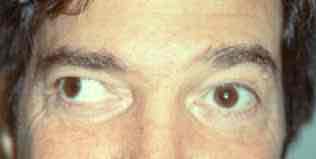
Esotropia
Inward turn of the eyes

Exotropia
Outward turning of the eye
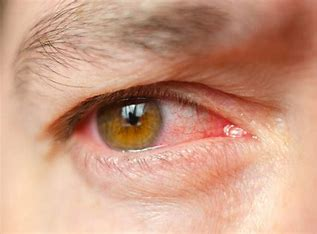
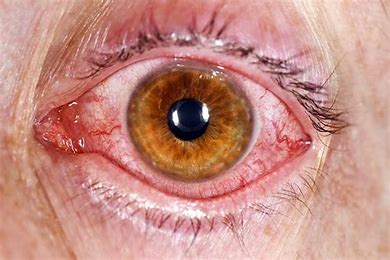
conjunctivitis
= infection of the conjunctiva (“pink eye”)
red beefy looking vessels @ periphery
common from viral or bacterial infections, allergy, or chemical irritant
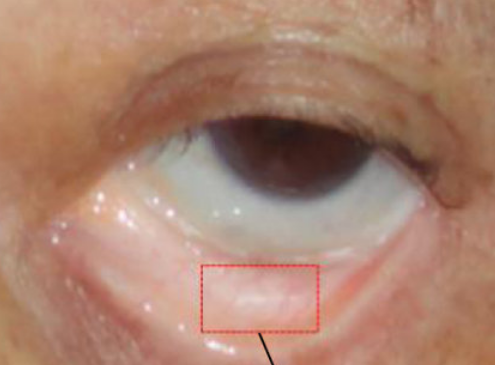
scleral edema
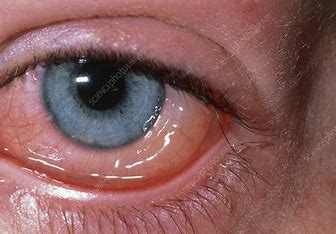
Lesion/Foreign Body
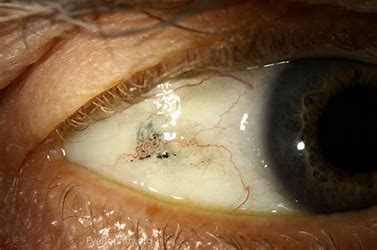
Scleral Icterus
an even yellowing of the sclera extending up to the cornea
indicates jaundice
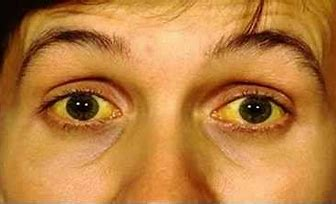
Anemia
What does pallor near the outer canthus of the lower lid indicate?
Lacrimal Gland
What structure, located in the upper outer corner of the eye, secretes tears?
Puncta
Where do tears drain into?
Abnormal
A nurse is inspecting the lacrimal apparatus and finds the following:
redness, tenderness, edema, inc. tears, exudate, discharge or regurgitant
Is this a normal or abnormal finding?
duct obstruction or infection
What does regurgitation of fluid out of the puncta suggest?
should appear smooth and clear
no opacities
A nurse shines a light across the cornea (tangential lighting), what should she normally see?
Pterygium
= bulbar conjunctiva overgrows towards the center of the cornea
may obstruct vision if it covers the pupil
occurs from chronic exposure to hot, dry, sandy climates
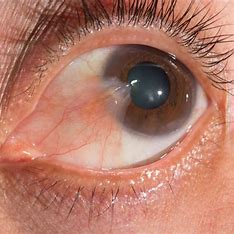
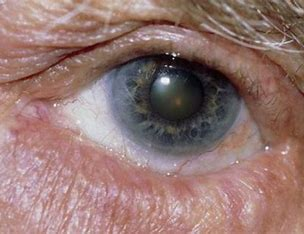
arcus senilis
= a grey-white circle around the cornea from lipids deposited in the sclera
normal variation in OA
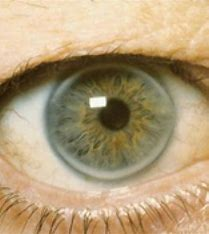
hyphema
= blood in the anterior chamber
result of herpes zoster, trauma, or spontaneous hemorrhage
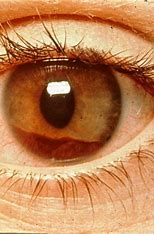
The iris is flat and creates no shadow (this is normal)
When a light is shown from the side and the entire eye lights up, what does this tell us about the iris?
The anterior chamber is shallow bc the iris is pushed anteriorly
When a light is shown from the side and the shadow forms on the side not under direct light, what does this tell us about the iris?
Pupils Equal, Round, Reactive to Light and Accommodating
What does PERRLA stand for?
2-6 mm
deep black
What is the normal size and color of the pupils?
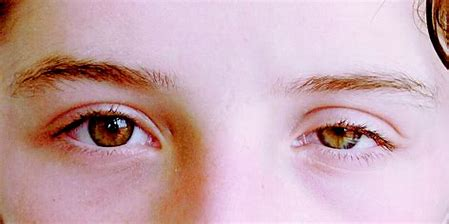
Anisocoria
= pupils of 2 different sizes (normal in a small % of the population)
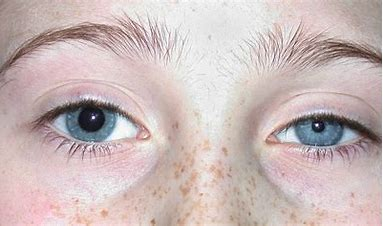
Horner syndrome
= damage to the sympathetic nerves of face & eyes
Symptoms
Ptosis & elevated lower lid
Dec. pupil size in affected eye
dec. sweat on one side of the face (anhidrosis)
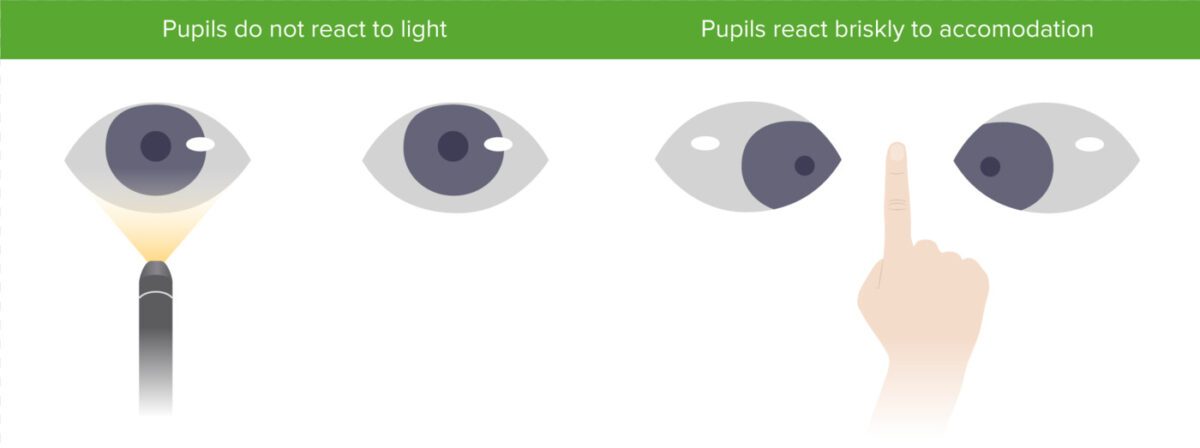
Argyll-Robertson’s
= occurs w CNS syphilis, brain tumors, meningitis, alcoholism, drugs, DM
small & mishappen pupils that do not react to light but can accommodate
Miosis
= constricted & fixed pupils
from opiates, brain damage & iritis

Mydriases
= dilated & fixed pupils
from sever head trauma & cardiac arrest
“pupils blown”
glaucoma
What does an ovoid shaped pupil suggest?
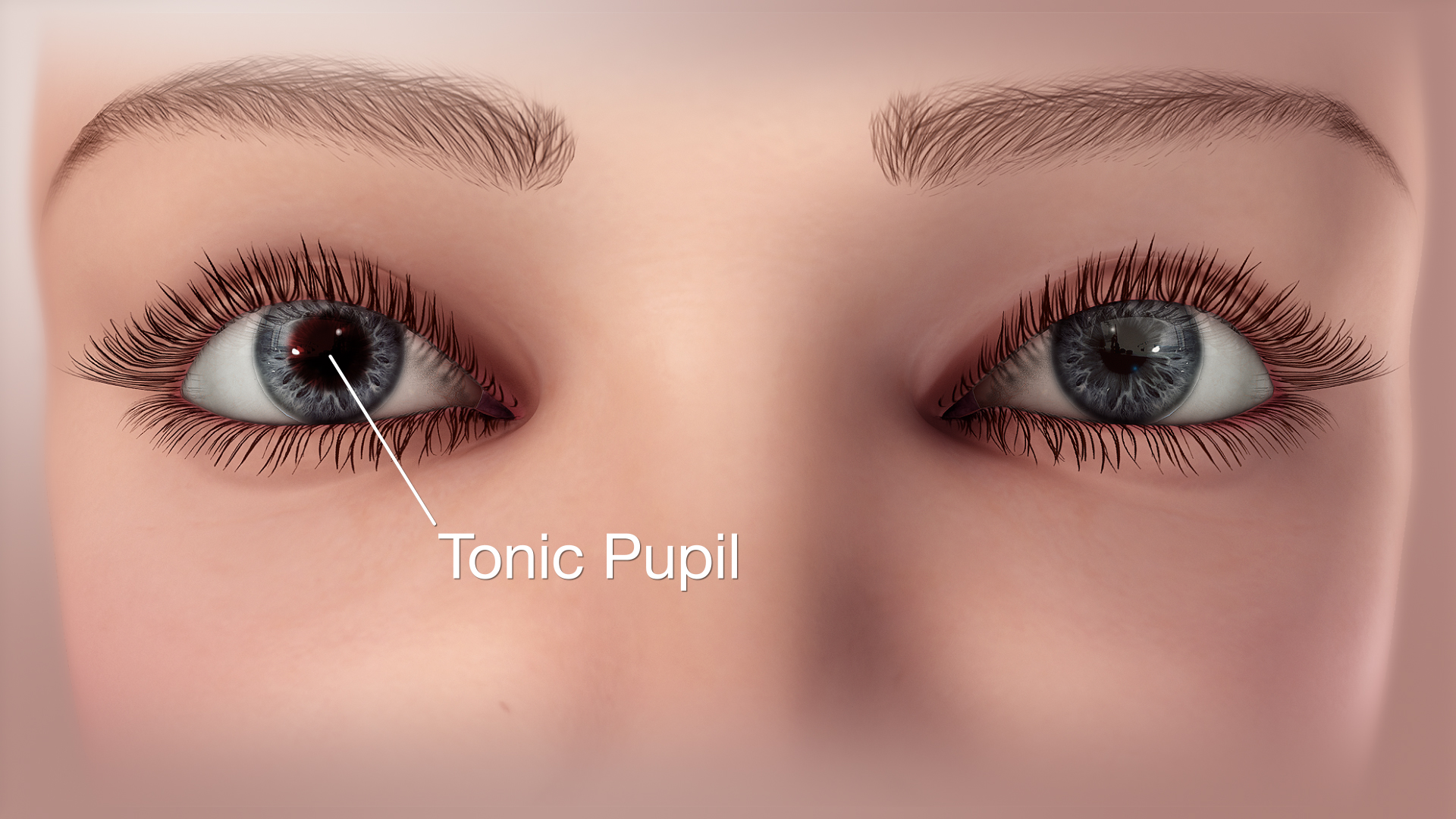
Adie’s Pupil (Tonic Pupil)
Sluggish reaction to light & accommodation
Unilateral large pupil
No pathological significance
monocular blindness
Light on the blind eye gives no response in either eye
Light on the normal eye gives a direct and consensual response
What do these reactions demonstrate?
0
What diopter would you use on the ophthalmoscope if yourself & the pt. have normal vision?
a positive (or black) diopter
What diopter would you use on the ophthalmoscope if yourself & the pt. have hyperopia (farsightedness)?
negative (or red) diopter
What diopter would you use on the ophthalmoscope if yourself & the pt. have myopia (nearsightedness)?
15 degrees
12 inches
At what angle and distance should the nurse stand from the pt. during an internal eye exam?
red light reflex
bright reddish-orange glow
round in shape
What reflex tests the reflection of light off of the inner retina? What are normal findings?
retinoblastoma (CA of retina)
What does white pupils in a red light reflex suggest?
cataracts
What does opaque pupils in a red light reflex suggest?
Fetal Alcohol syndrome
What does wide set eyes in pediatrics indicate?
3-5 yrs old
When should pediatrics start eye screenings?
Strabismus (“lazy eye”)
if untreated, it can lead to permanent visual damage
cover test
Focuses on an object, cover 1 eye while watching for movement in the other
What is it important to test for in young children’s eyes? Why? How do you test for it?
OA variations
Arcus senilis; Cataracts
Dry eyes
Drooping eyelids (senile ptosis)
Presbyopia – decrease ability to accommodate from loss of elasticity in the lens
Overall decrease in near vision, accommodation and peripheral vision
Decrease in color perception, esp. green-blue-violet
Vessels in retina pale/narrowed
Senile macular degeneration common – a loss of central vision
The uncovered eye is weaker, and tries to fixate when the stronger eye is covered
While performing a cover test, the uncovered eye jumps to fixate on the designated point. What does this mean/which eye is weaker?
The covered eye is weaker, and has to fixate once it is uncovered again
While performing a cover test, the covered eye drifts to a relaxed position. What does this mean/which eye is weaker?