APES Unit 1 The Living World: Ecosystems
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Primary productivity
rate at which organic matter is created by producers in an ecosystem
GPP (gross primary productivity)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
NPP
(Net Primary Productivity): the energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
Trophic levels
The hierarchical levels of the food chain through which energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, secondary consumers and so on.
Conservation of matter
the principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
Omnivore
A consumer that eats both plants and animals
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded into lower quality energy (usually heat)
Energy pyramid
Shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
Food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
producers (autotrophs)
Organisms that make their own food
Primary consumers
animals that feed on producers; ex. herbivores
secondary consumers
carnivores that eat herbivores
tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat secondary consumers
heterotrophs
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products.
Organic
of, relating to, or derived from living matter, contains carbon
Carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
Carbon sinks
places such as forests, ocean sediments, and soil, where accumulated carbon does not readily reenter the carbon cycle
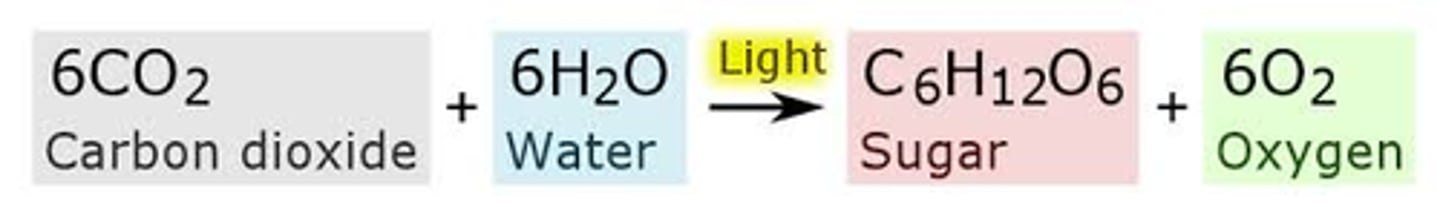
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen
Phytoplankton
Microscopic, free-floating, autotrophic organisms that function as producers in aquatic ecosystems
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen, releases CO2
Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
Detritivore
organism that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter
Nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
Nitrification
Conversion of ammonia (NH4+) into nitrite (NO2-) and then into nitrate (NO3-)
Nitrogen fixation
process of converting nitrogen gas (N2) in the atmosphere into nitrogen compounds that plants can be absorbed and used
Ammonification
fungal and bacterial decomposers use nitrogen-containing wastes and dead bodies as a food source and excrete ammonium (NH4+)
Denitrification
process by which bacteria convert nitrates (NO3-) into nitrogen gas (N2)
Impervious surfaces
surfaces that don't absorb water ex. roads, sidewalks, houses / buildings
Leaching
removal of dissolved materials from soil by water moving downwards
Assimilation
The process by which producers incorporate elements of nitrogen into their tissues.
Phosphorous cycle
The movement of phosphorous atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks.
Phosphorus sinks
- Rocks and minerals
- Long-lived vegetation
Hydrologic cycle
The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff
Groundwater
water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock.
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid (forms clouds)
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
Runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
Evaporation
The change of a substance from a liquid to a gas
Infiltration
the process by which water on the surface enters the soil
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
Percolation
The downward movement of water through soil and rock due to gravity.
Symbiosis
A relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
Interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
Intraspecific competition
Competition among members of the same species
Competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites. It may be intraspecific or interspecific.
Resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species
Limiting factors
Conditions in the environment that put limits on where an organism can live
Ecological niches
the role an organism plays in its environment
Fundamental niche
The niche species could potentially occupy.
Realized niche
The niche species actually occupies.
Competitive exclusion
Strong competition can lead to local elimination of one of the species.
biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
Weather
The condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place.
Climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
Taiga (boreal forest, northern coniferous forest)
biome with long cold winters and a few months of warm weather; dominated by coniferous evergreens; also called boreal forest
Tundra
a vast, flat, treeless Arctic region of Europe, Asia, and North America in which the subsoil is permanently frozen.
Temperate rainforest
The cool, dense, rainy forests of the northern Pacific coast; enshrouded in fog much of the time; dominated by large conifers
Tropical rainforests
Near the equator. Warm with lots of precipitation. Little seasonal temperature variation. Most diverse biome.
Shrubland (chaparral)
Found along the California coast and the coast of the Mediterranean sea. Characterized by hot summers and mild, rainy winters. Dominated by fire-tolerant shrubs.
Temperate grasslands
dominated by grasses, trees and large shrubs are absent. Temperatures vary more from summer to winter, and the amount of rainfall is less than in savannas. Temperate grasslands have hot summers and cold winters. Occur in South Africa, Hungary, Argentina, the steppes of the former Soviet Union, and the plains and prairies of central North America.
Savanna/ Tropical Seasonal Forest
a grassy plain in tropical and subtropical regions, with few trees.
temperate seasonal forest
A biome with warmer summers and colder winters than temperate rainforests and dominated by deciduous trees.
Desert
An extremely dry (arid) area with little water and few plants
Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
Altitude
Elevation (height) above sea level
Permafrost
permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground
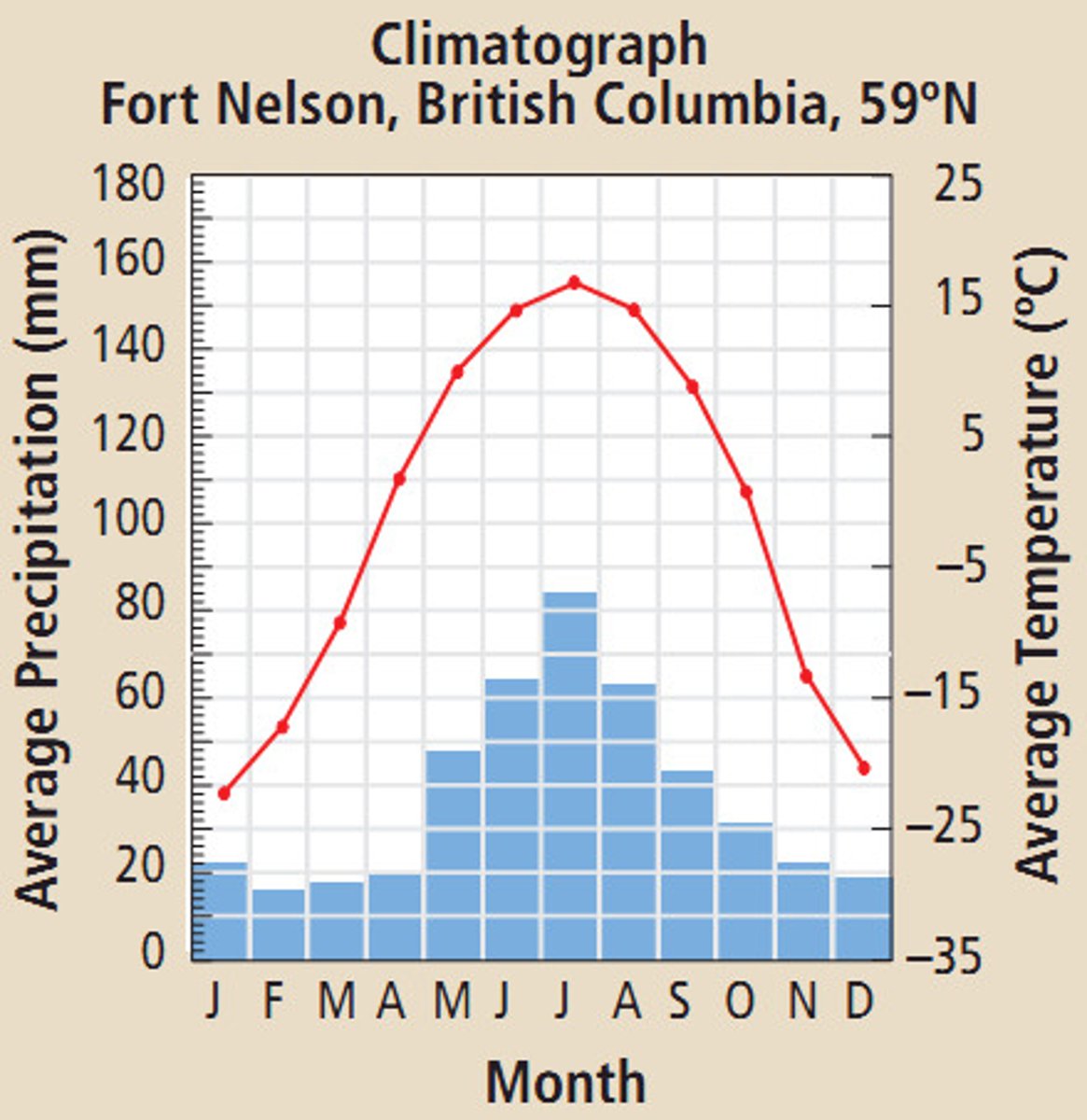
Climatographs
Chart that is used to better understand climate by looking at the average temperature and precipitation
Biotic
Describes living factors in the environment.
Abiotic
Describes non-living factors in the environment
streams
a small, narrow river.
rivers
a large natural stream of water flowing in a channel to the sea, a lake, or another such stream.
ponds
Bodies of fresh water (shallow, allows sunlight to go all the way through the water and makes plants grow)
lakes
A body of water that is surrounded by land it can be fresh water or salt water.
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
oceans
the largest of all the ecosystems. The ocean regions are separated into separate zones: intertidal, pelagic, abyssal, and benthic. All four zones have a great diversity of species.
coral reefs
Prominent oceanic features composed of hard, limy skeletons produced by coral animals; usually formed along edges of shallow, submerged ocean banks or along shelves in warm, shallow, tropical seas
marshlands
Consisting of low lying wetlands ; areas that typically stay flooded/waterlogged. Swamp or bog.
estuaries
the tidal mouth of a large river, where the tide meets the stream.
Algae
a very simple plant without stems or leaves that grows in or near water.
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid
mangrove swamps
A swamp that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water.
Littoral zone
the shallow zone of soil and water in lakes and ponds where most algae and emergent plants grow
Limnetic zone
a zone of open water in lakes and ponds
profundal zone
zone in a freshwater habitat that is below the limits of effective light penetration
intertidal zone
Portion of the shoreline that lies between the high and low tide lines
photic zone (ocean)
the zone that receives enough light to allow photosynthesis to occur
aphotic zone (ocean)
where little or no light reaches in the ocean