Anatomy Exam 1 DPT
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Functions of the skin
1. Protection
2. Containment
3. Heat regulation
4. Sensation
5. Synthesis of Vit. D
Epidermis
basal layer: stack up until apoptosis
avascular (nursihed by dermis)
afferent nerve endings
Dermis
Includes: hair follicles, arrestor pili, sebaceous & sweat glands. Deep layers: collagen & elastic fibers (also have blood vessels)
Superficial Fascia (SubQ tissue)
loose fatty connective tissues. Regulates heat and protects skin from body prominences. Has: sweat glands, blood vessel, lymph & cutaneous nerves.
Skin Ligaments (in SubQ)
fibrous bands --> Sub Q to dermis to attach dermis to deep fascia (ie. holds skin to deep fascia)
Deep Fascia
dense CT, covers muscles to increase efficiency from unneeded bulging when contracting. Has facial compartments
Two types of bones
Spongy & Compact
Spongy Bone
has medullary cavity where bone marrow resides. Red & Yellow- only adults have red in sternum and iliac crest
Compact Bone
Crystalline structure; hard
Organic bone
osteoblasts/clasts & other cells
Inorganic bone
made of 'salts' - Ca & Ph
Rickets
Low inorganic compound causing knock knee/bow legs in children--> weak
Osteoporosis
low organic and inorganic components
Green-stick Fx
Occur in youth due to soft bones bending and then breaking (green stick like a fresh twig bends then snaps)
6 Classifications of bones (shape)
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular, Sesamoid, Accessory
Short bones
[tarsals & carpals] have a 1st degree ossification center ONLY, except the calcaneus
Arterial Supply to Bones (3)
1. periosteal arteries - supply periosteum
2. nutrient artery- into foramen
3. metaphyseal & epiphyseal arteries- supply each part
Venous and Lymph vessels in bones
take blood/fluid away and to heart
Nerve Supply of Bones
periosteal nerves : sensory
vasomotor nerves
Vasomotor Nerves of the bone
cause vaso-constriction/dilation to regulate flow to bone marrow
5 Functions of the Bones
Protection
Support
Movement (levers)
Blood Cells
Storage (salts)
3 types of Joints
Fiborous (Synarthrosis)
Cartilaginous
Synovial
3 types of Fiborous Joints
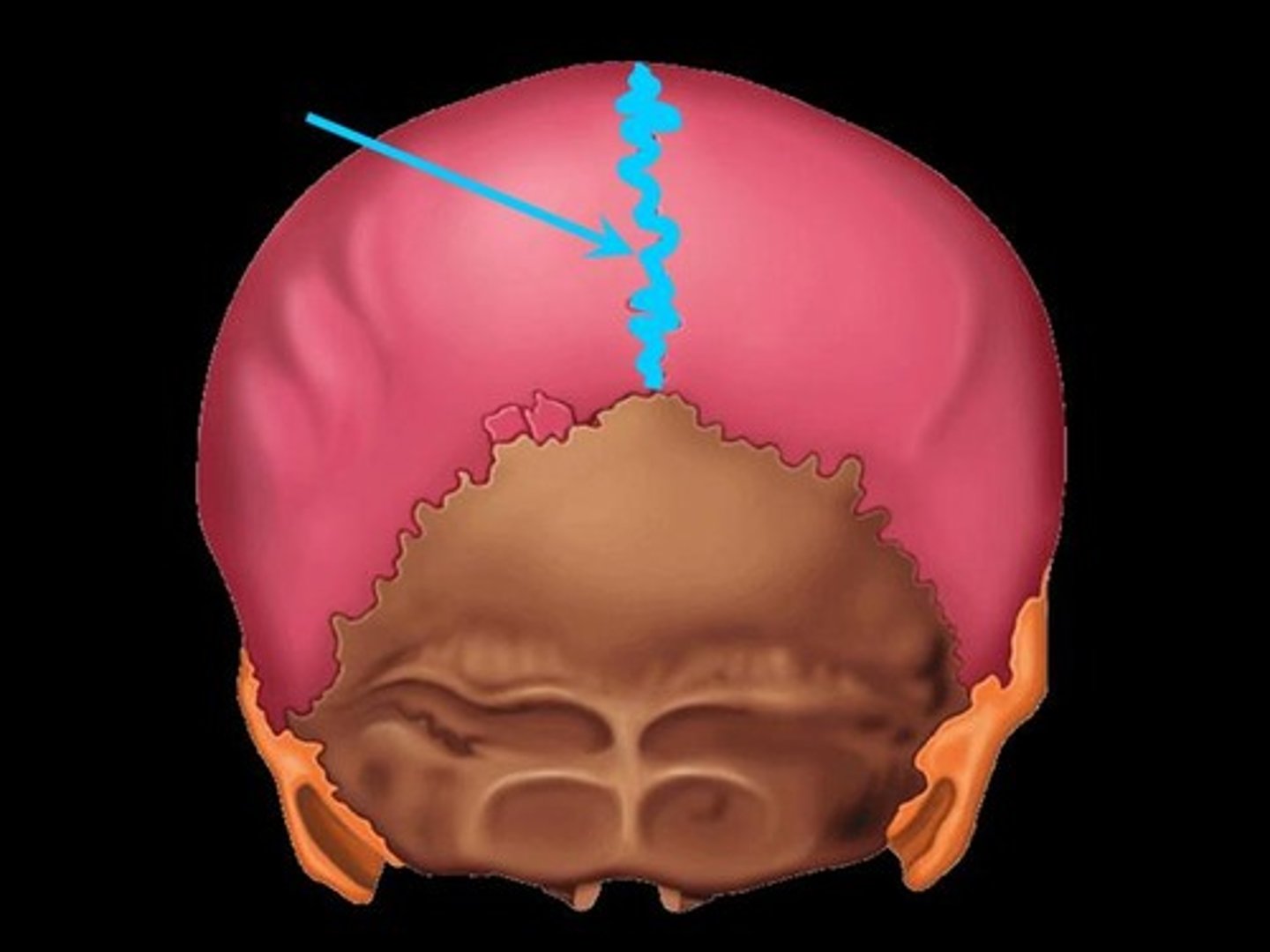
Sutures
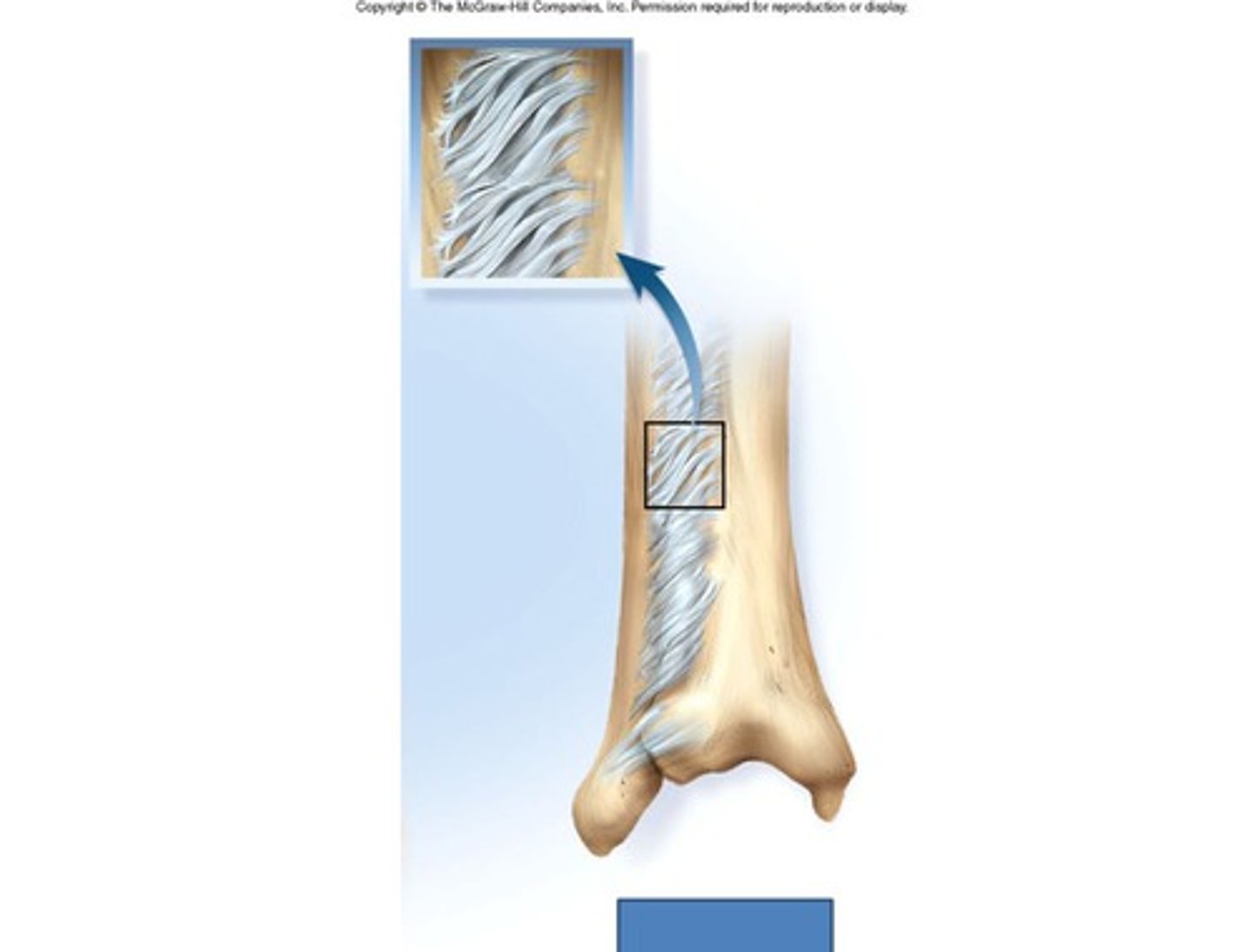
Syndesmosis
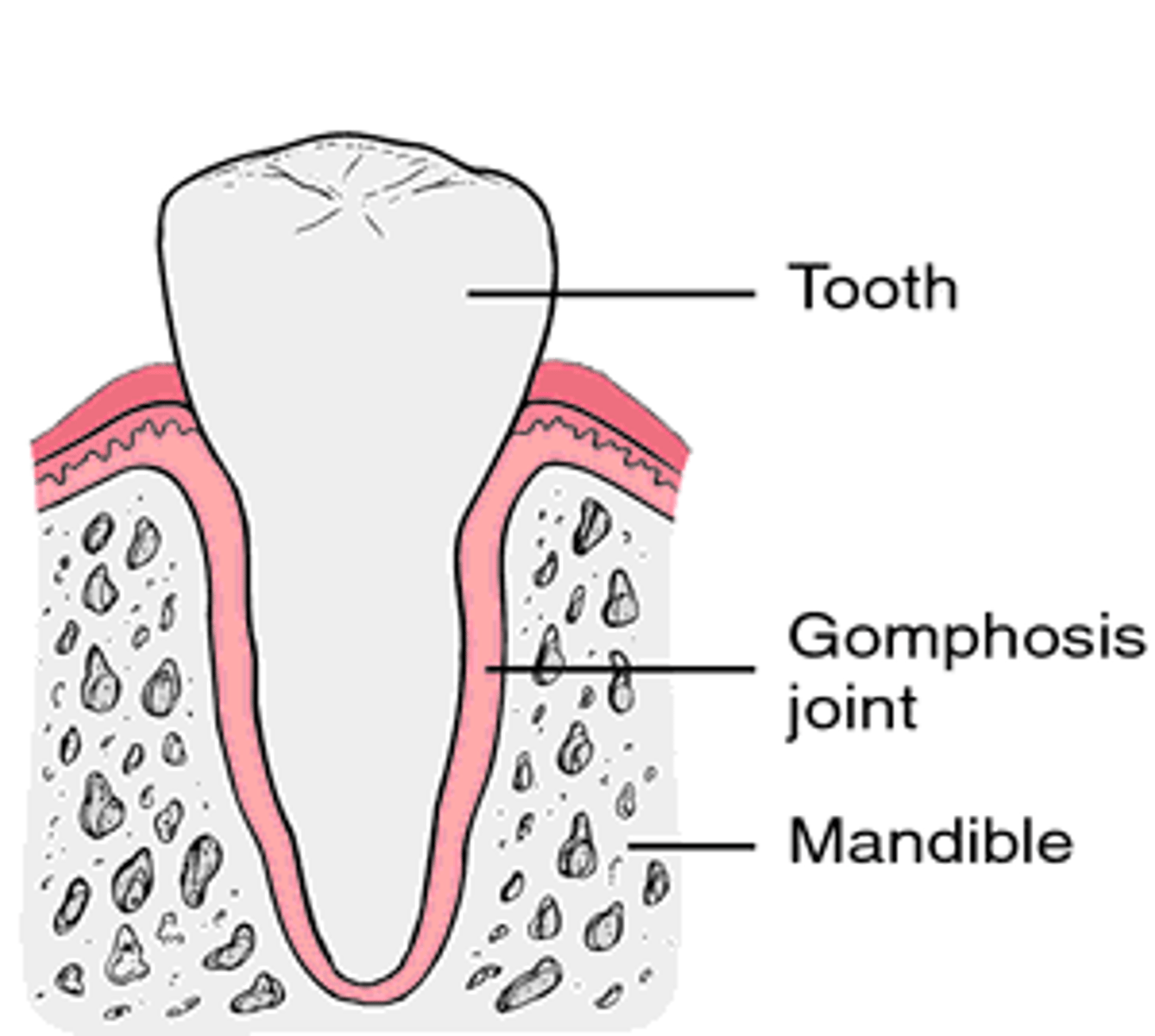
Gomphosis
Suture Joints
multiple layers of FT
Syndesmosis
single layer of FT
Gomphosis
"bolt-like", hold teeth to jaw bone
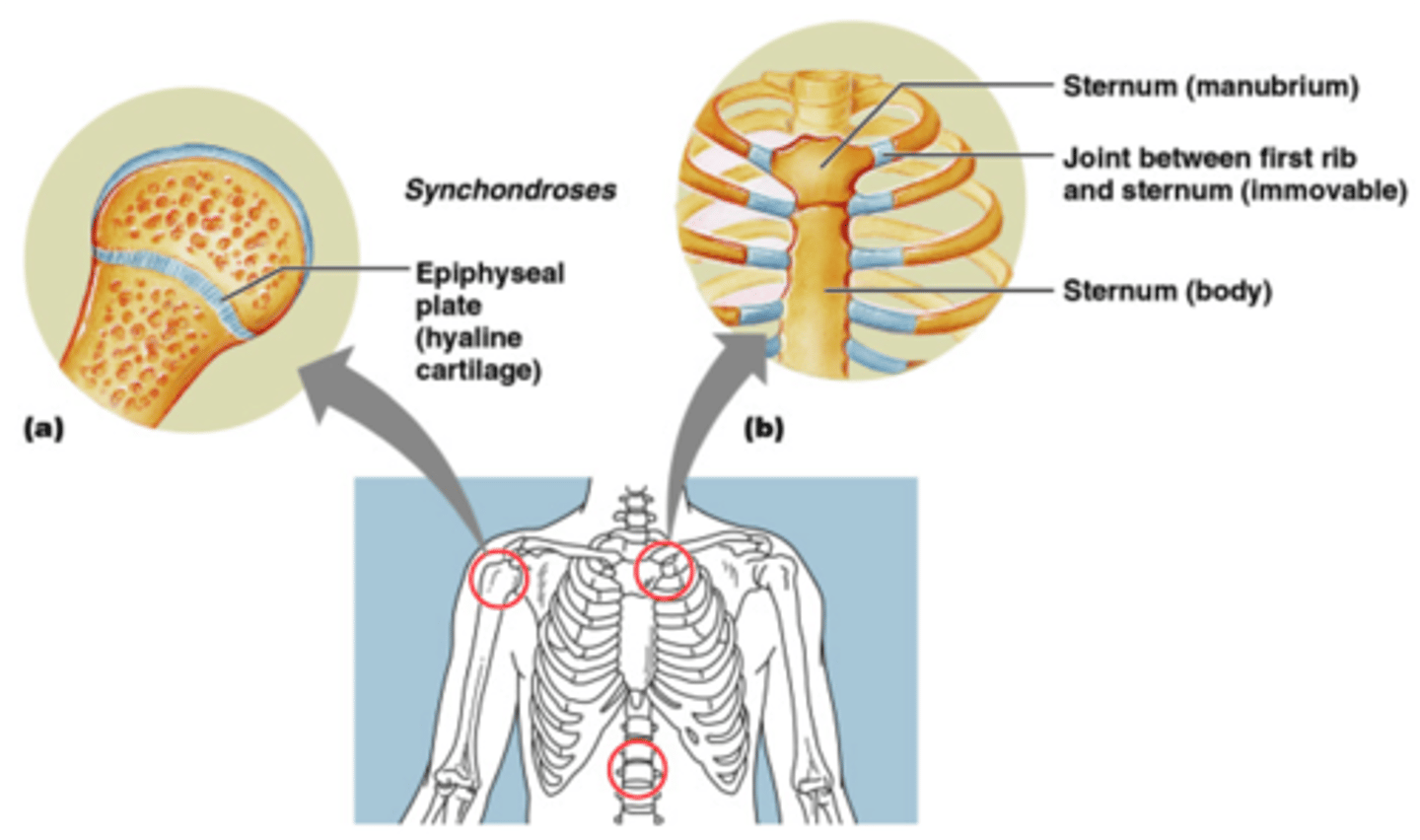
Cartilaginous Joints
Hyaline (primary)
Fibrocartilage (secondary)
Synchondroses
hyaline (primary) cartilaginous joints. R1 to sternum
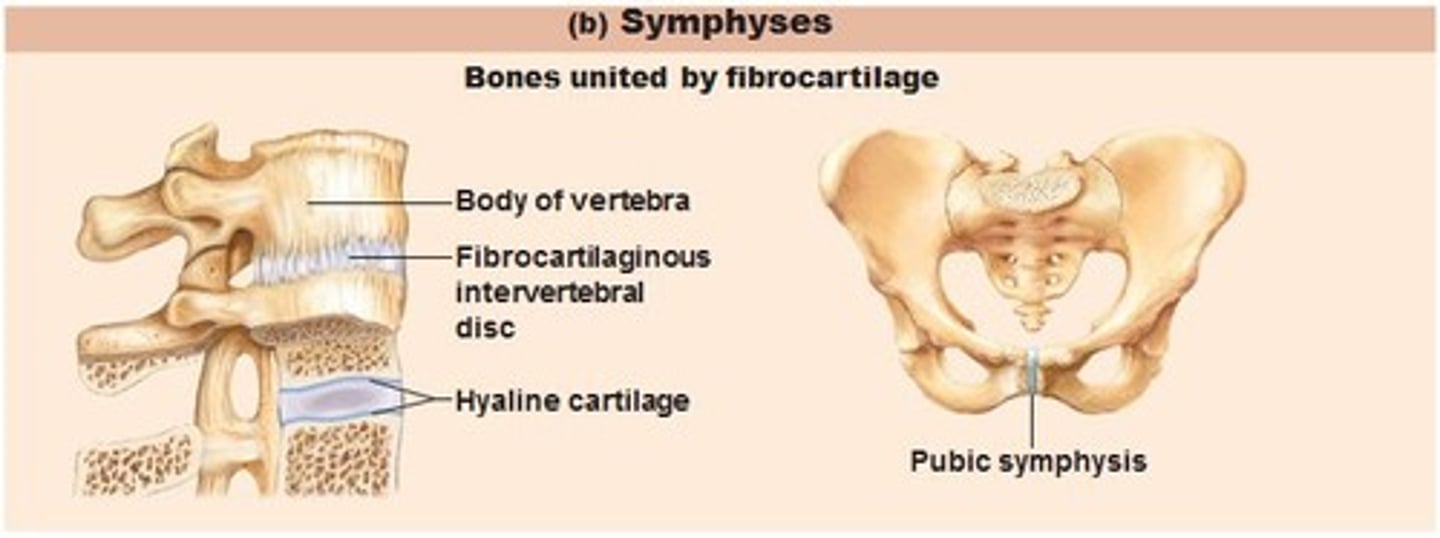
Symphyses
fibrocartilaginous (secondary)
vertebral disc, mentee (chin), pubic symphysis
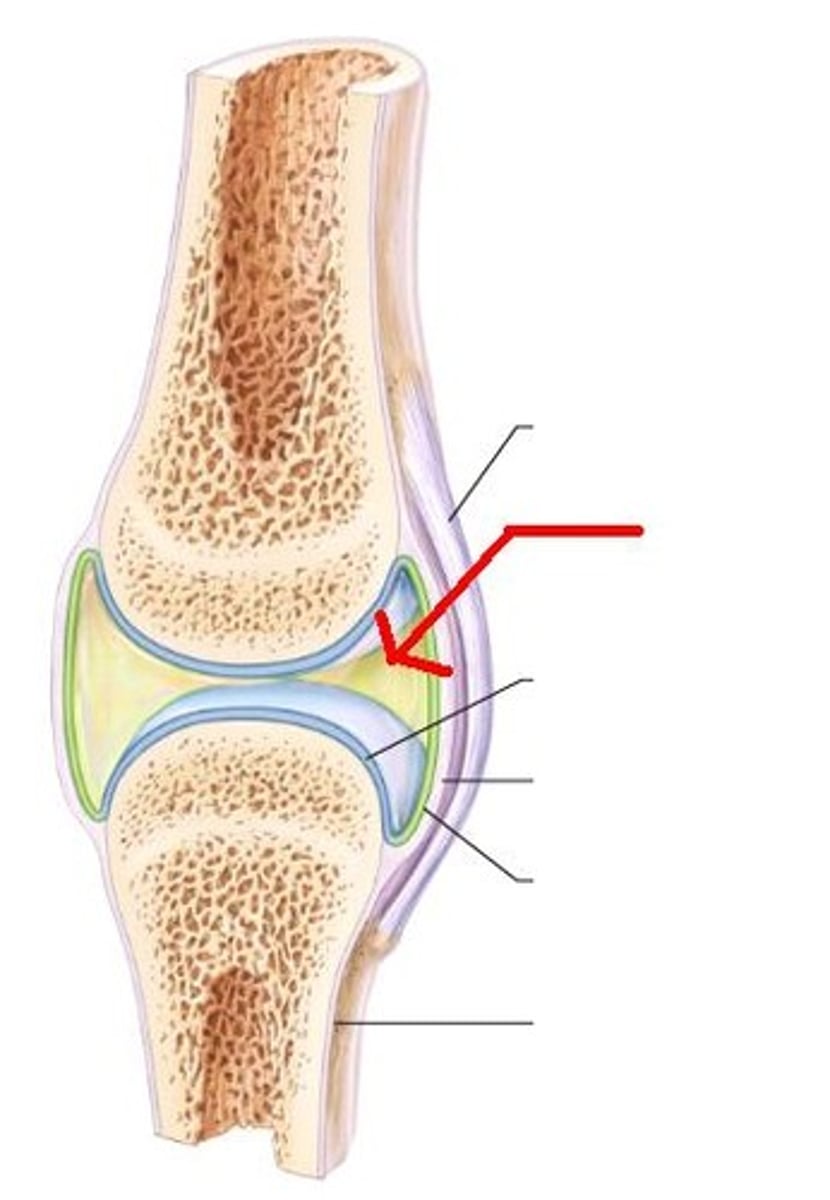
Synovial Joint features
Most Common *
1. Joint Cavity with fluid
2. Articular Cartilage
3. Articular Capsule
Articular Cartilage
hyaline, avascular, contains synovial fluid
Articular Capsule
fiborous capsule with intrinsic & extrinsic ligaments. synovial membrane, articular discs.
Types of Synovial Joints (6)
Condyloid
Pivot
Hinge
Saddle
Ball & Socket
Plane
Plane Joint
Synovial. Uniaxial
[ AC joint, wrist, ankles ]
Hinge Joint
Synovial. Uniaxial.
[ ulnar humeral]
![<p>Synovial. Uniaxial.</p><p>[ ulnar humeral]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2be1b595-9260-4135-84e5-17fa9a55f7fe.jpg)
Condyloid Joint
Synovial. Biaxial.
[ knuckles, occipital & C1 ]
![<p>Synovial. Biaxial.</p><p>[ knuckles, occipital & C1 ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c4c726c6-c759-49b0-bcdb-b54aefbe446b.jpg)
Saddle Joint
Synovial, Biaxial.
[ thumb ]
![<p>Synovial, Biaxial.</p><p>[ thumb ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/02252213-1b27-4aee-b230-a36eff868270.jpg)
Ball & Socket Joint
Synovial. Multiaxial.
[ shoulder, hip ]
![<p>Synovial. Multiaxial.</p><p>[ shoulder, hip ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e75b6378-f6d1-4cc9-8d19-37e25cf4027c.jpg)
Pivot Joint
Synovial. Uniaxial.
[ C1 C2 ]
![<p>Synovial. Uniaxial.</p><p>[ C1 C2 ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0d0f40f8-7b57-4b77-8c6e-818a4f7991c3.jpg)
Hilton's Law
"a nerve that supplies the joint also supplies the muscles that move the joint & the skin covering that muscle"
Joint Proprioception & Pain
joint nerves have proprioception
pain is sensed by the fibrous layer of the joint capsule & the accessory ligaments
Articular Arteries
supply joints with blood, accompanied by viens
Anastomoses around joints
2 different blood vessels branch from one source to surround joint. For backup if one gets pinched off
Types of Skeletal Muscles (7)
Longitudinal
Uni/Bi pennate
Multipennate
Flat
Fusiform
Quadrate
Circular/Sphincteral
Longitudinal Muscles
fibers are parallel to F generated
suited for long distance of mov't
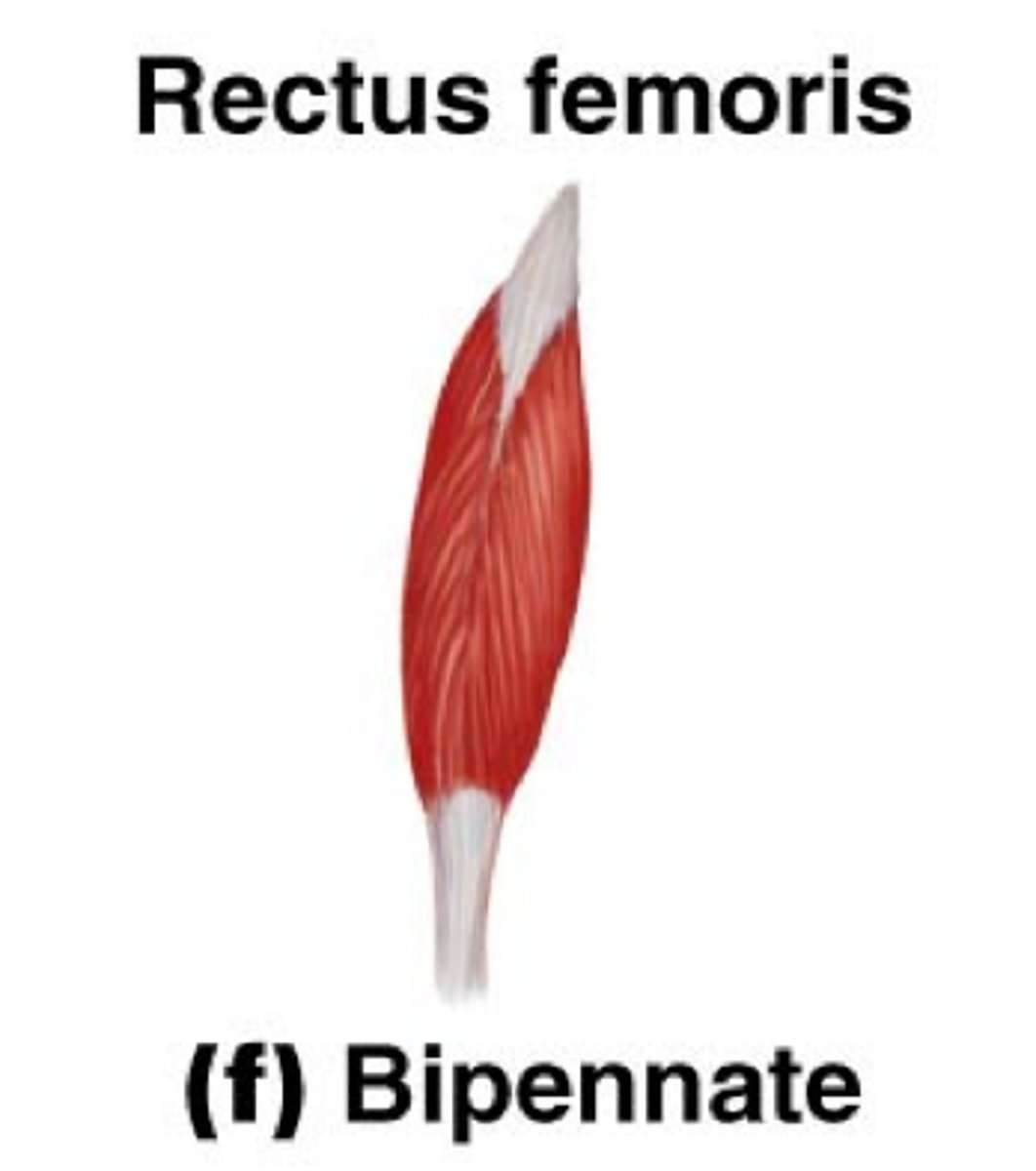
Uni/Bipennate Muscles
arranged at an angle (usually 0-30 degrees)
pennation allows for compact/space saving & a greater force production
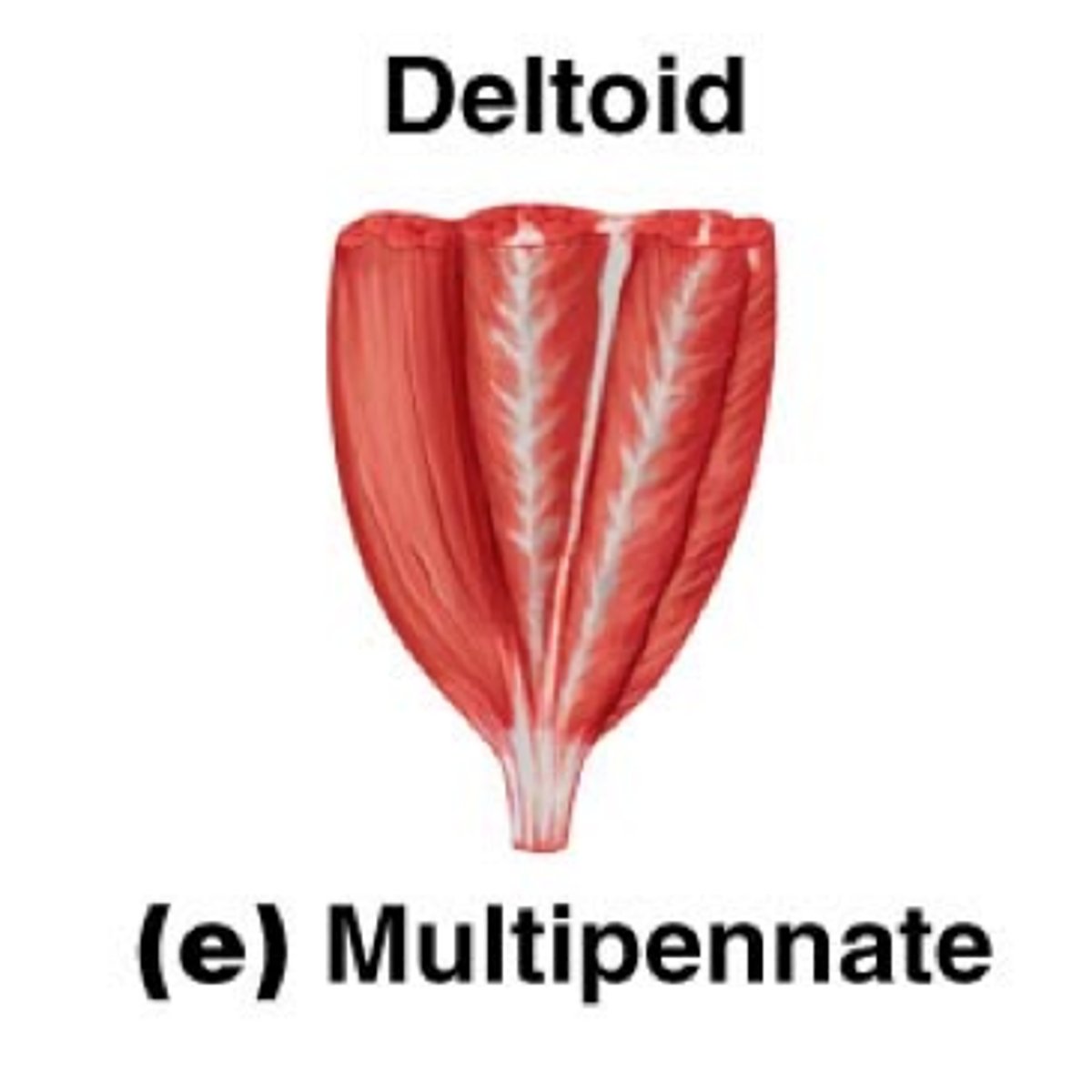
Multipennate
several angles
Flat Muscles
parallel fibers with often aponeurosis (takes place of tendon in sheet like muscles)
Quadrate Muscles
4 = sides
Circular/Sphincteral Muscle
surround body opening
Muscle Attachment Sites (6)
tendon
aponeurosis
fascia
skin (facial expression)
mucous membranes (swallowing)
insertion & distal attachments
Cardiac Muscle
myocardium
involuntary
autonomic control
Smooth Muscle
walls of blood vessels & GI tract
involuntary
autonomic control
partial contractions
peristaltic waves
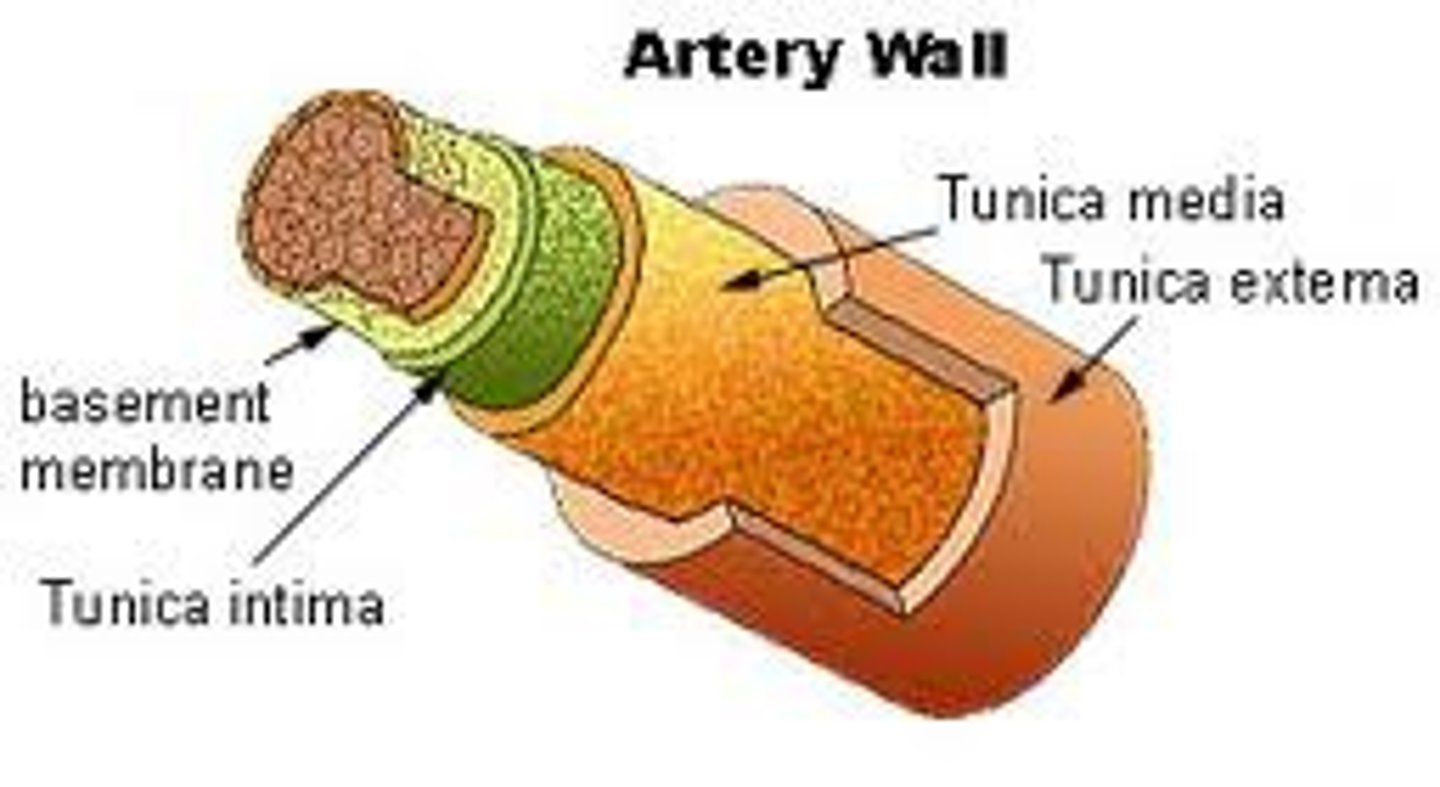
Artery Walls
Superficial to deep:
Tunica Adventitia
Media
Intima
Types of Arteries
Arterioles
Muscular Arteries
Elastic Arteries
Arterioles
smallest type
thick walls, narrow lumen
regulate pressure
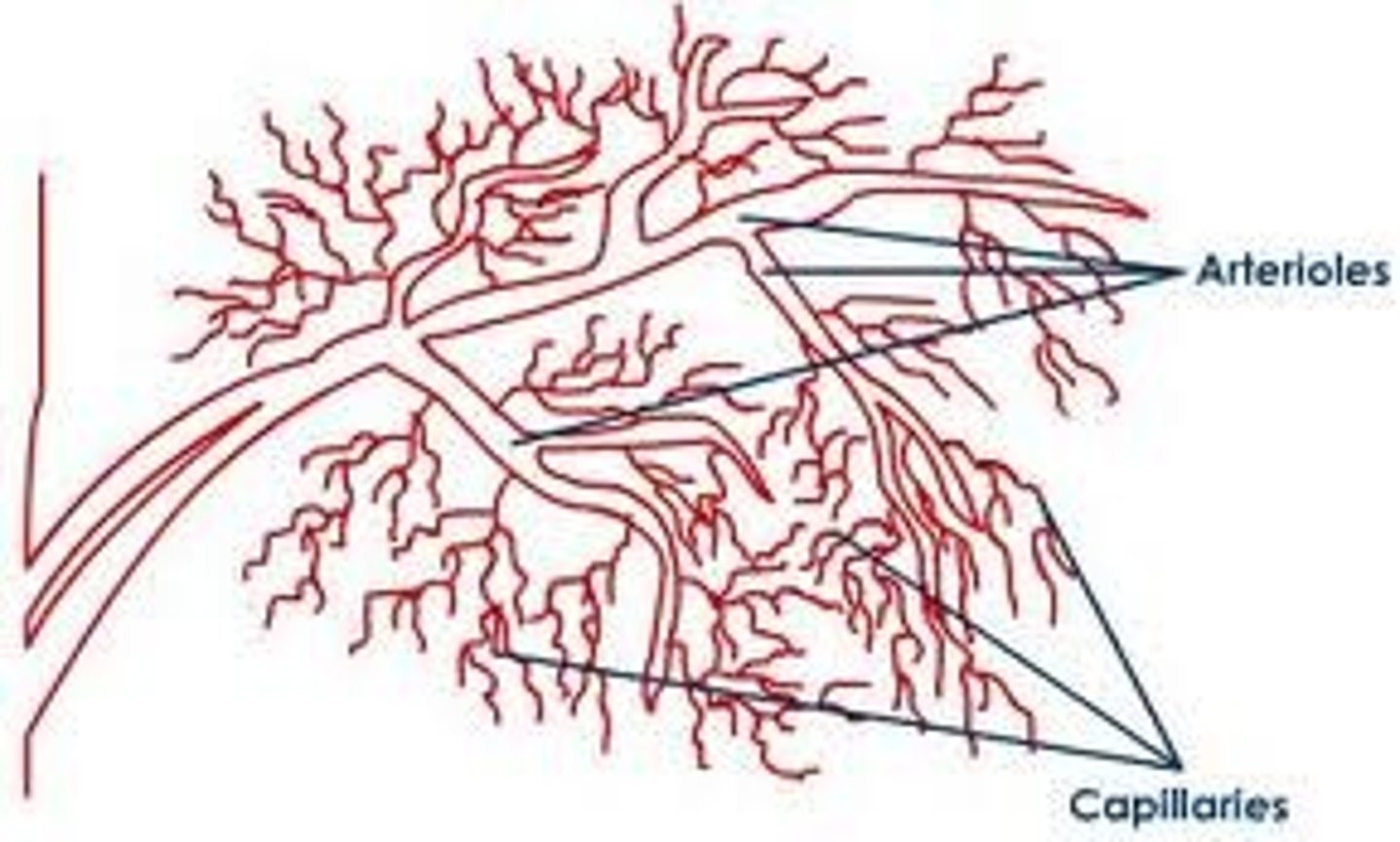
Muscular Arteries
distribute blood
regulate flow to certain body parts
Elastic Arteries
largest
elastin walls
maintain BP in cardiac contractions [aorta]
Vasa Vasorum
blood vessel for (large) blood vessels
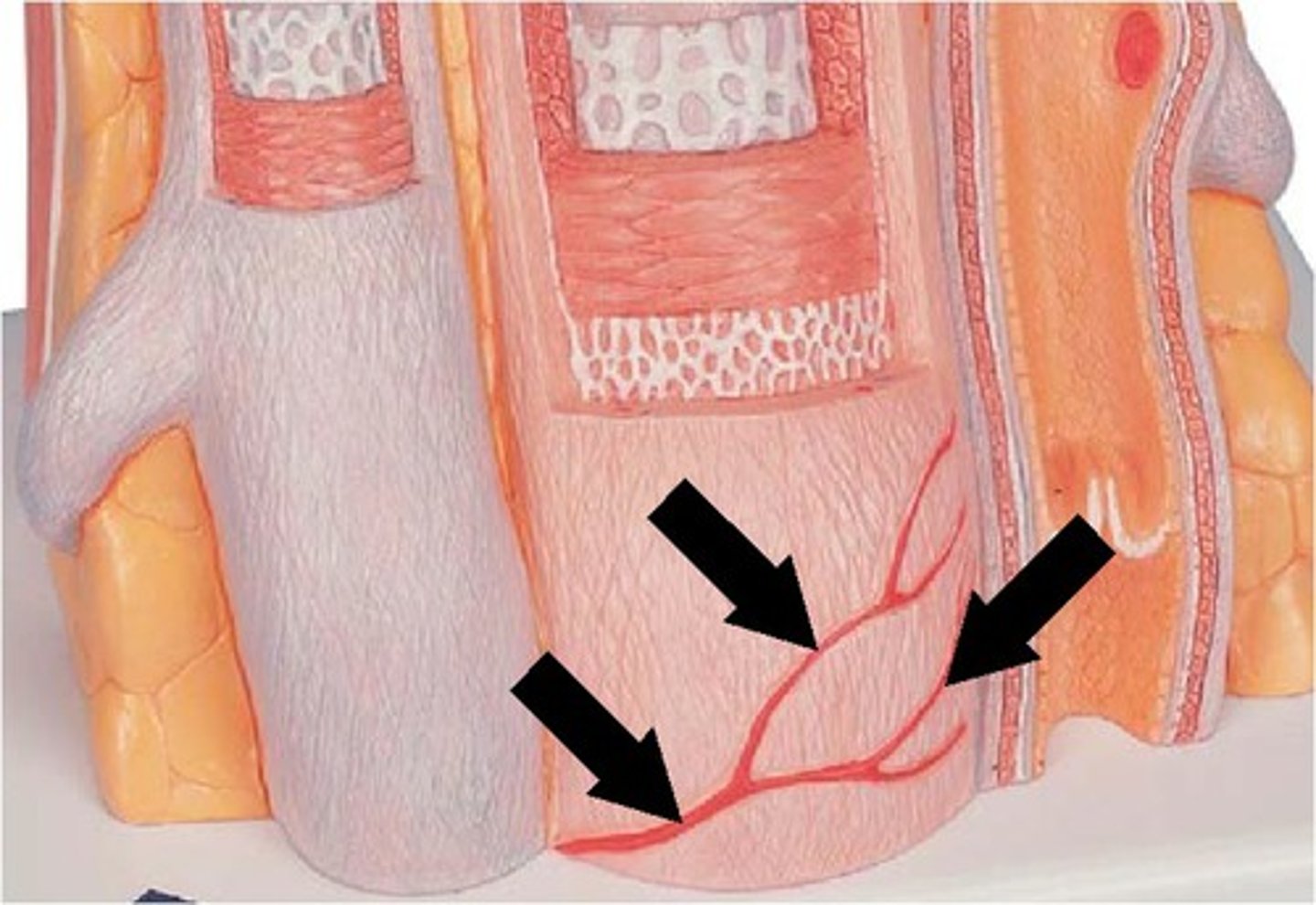
Veins...
blood return
thin walls
skeletal muscles "pump"
valves (unidirectional)
venules (to capillaries)
plexuses (bunch of small veins)
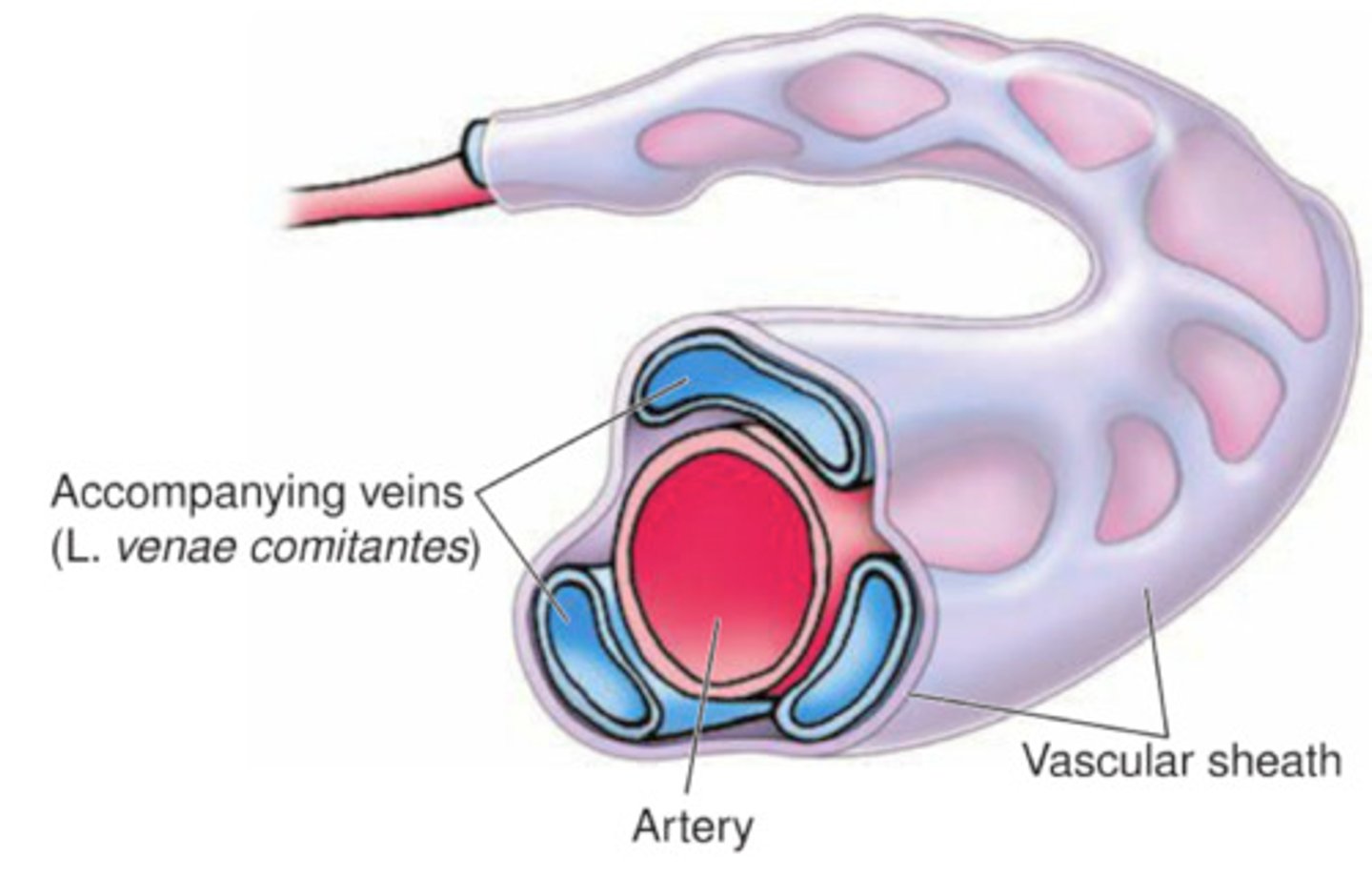
venae comitantes
vasa vasorum
Venae Comitantes
paired viens on sides of artery to aid blood return
Capillaries are:
endothelial tubes connecting artery to vein
under autonomic control
AV shunts- conserve body heat
AV Shunts
control body heat by regulating superficial and distal blood flow
Lymphatic System
tissue fluid -> lymph -> lymph capillaries -> afferent lymphatics -> lymph node -> efferent lymphatics
The lymph trunk drains into thoracic and right lymphatic ducts
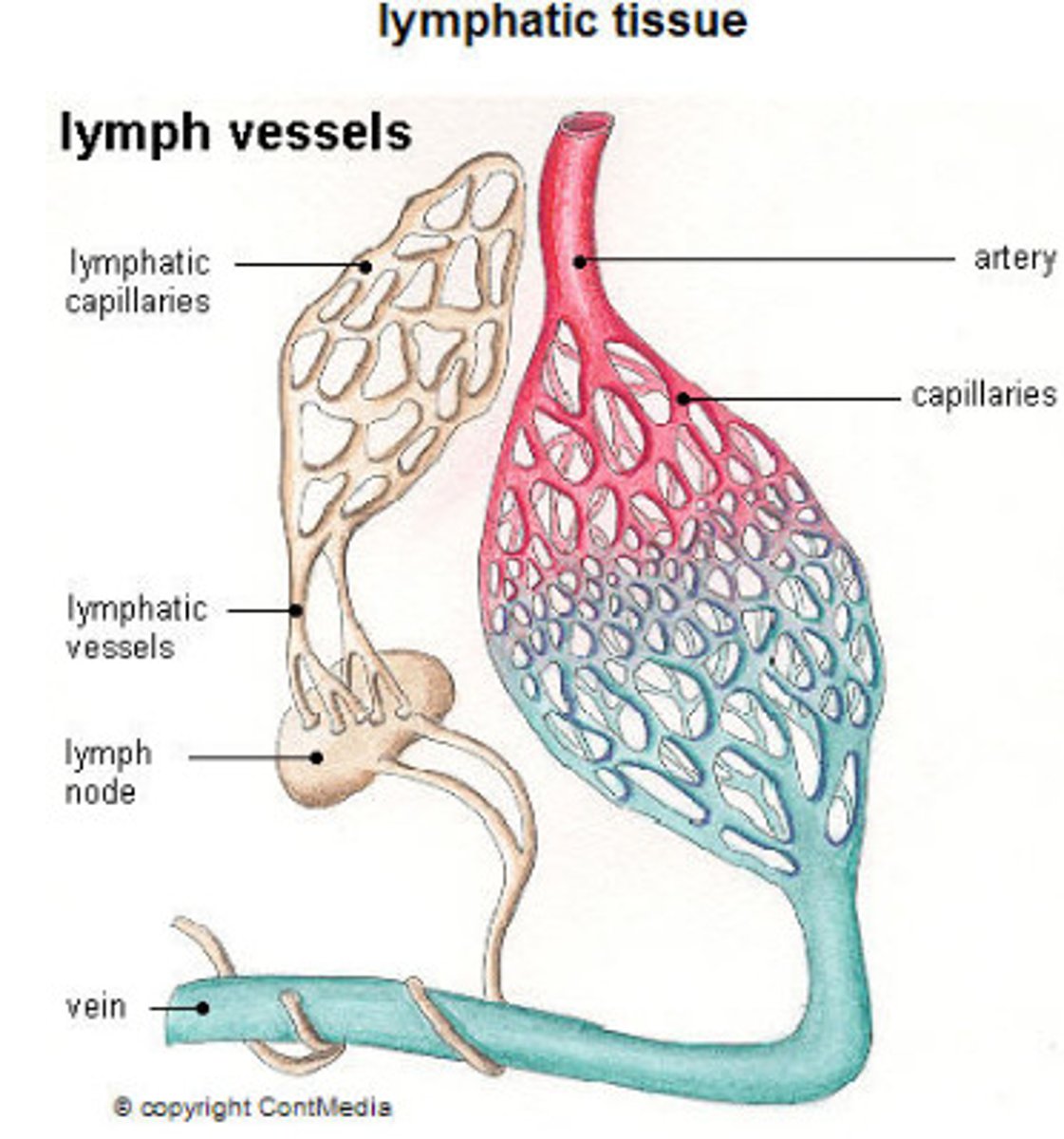
Lymphatic Functions (3)
1. drain & filter tissue fluid
2. absorb & drain fat
3. defense mechanism