Drug Administration in dialysis and renal insufficiency
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1, Dr. Wai
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
renal insufficiency can interfere with medications
decreasing clearance due to reduced glomerular filtration
altering tubular secretion and reabsorption
changes in renal and on-renal metbaolism
antibiotics, direct oral anticoagulants
common medications that require dose reductions in patients with renal insufficiency.
determining a dosing regimen
reduce the dose and maintain the dosage interval
maintain the dose and extend the dosing interval
anticoagulants
requries special attention in renal insufficiency
renal adjustments may be required depending on agent and indication
enoxaparin
anticoagulant that clearance is reduced in patients with renal insufficiency
ACEI/ARB
require special attnetion in renal insufficiency
most are cleared renally
acute but sustained decrease in GFR
may see a 25-30% decrease in GFR within 307 days after initiation
not a reason to discontinue therapy *****
alpha blockers
require special attention in renal insufficiency
active metabolites that can accumulate in CKF
Doxazosin, Prazosin, Methyldopa
Terazosin kinetics unaltered in CKD
beta blockers
require special attention in renal insufficiency
some may need adjustment (atenolol, nadolol)
hepatically metabolized preffered in advanced CKD → metoprolol, labetalol, and propranolol
digoxin
require special attention in renal insufficiency
Vd is reduced by 30-50% in ESRD
not dialyzable, antidote Digifab
two approached: extend dosing interval, reduce dose
morphine, meperidine
narcotics that require special attention in renal insufficiency
morphine
require special attention in renal insufficiency
metabolized in the liver to 5 metabolites → accumulates in CKD
dose reductions CrCl < 60ml/min
adverse effects: CNS depression, respiratory depression
consider avoiding use in advanced CKD
meperidine
require special attention in renal insufficiency
normeperidine → active metabolite
neurotoxic
½ analgesic effect, 2x convulant effect
accumulates in renal insufficiency
avoid use in advanced CKD
insulin
require special attention in renal insufficiency
dosing reduction may be required
degradation occurs in liver, muscles, and kidneys
sulfonylureas
active metabolites may accumualte in renal insufficiency
glyburide, glipizide
sitagliptin
requires dosing adjustment for renal insufficiency
diabetic medication
metformin
dose recommendations based on eGFR
potential to cause lactic acidosis
eGR <30 contraindicated
aminoglycosides
gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin
clearace reduced in renal dysfunction
increased risk of ADE: Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity
Avoid use in CKD if possible
◦Follow serum levels (peaks and troughs) if used
◦PK equations
cephalosporins
◦Most are cleared renally and require dosing adjustments
◦Concern for neurotoxicity
◦Ceftriaxone is exception – no renal adjustment
penicillins
◦Most are cleared renally and require dosing adjustments
◦Concern for neurotoxicity
◦Exceptions: nafcillin, dicloxacillin
fluoroquinolones
◦Most are cleared renally and require dosing adjustments
◦Exception: Moxifloxacin
◦Adverse effects: tendonopathy, aortopathy, neuropathy, arrhythmia, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia
vancomycin
◦Cleared renally and requires a dosing adjustment
◦Dosed based on serum levels and PK
◦May follow random levels in acute kidney injury and ESRD
◦May extend interval especially in dialysis pts
metoclopramide
◦Clearance reduced by approximately 30% in CKD
◦Dose reduction when CrCl < 50 ml/min
◦Adverse effect: tardive dyskinesia
H2 antagonists
◦Depends on agent
◦Require dosing adjustment at CrCl < 50 mL/min
◦Adverse effect: CNS effects (agitation, confusion, delirium)
metformin, sitagliptin, famotidine, metoclopramide
TR is a 65 yo M with DM2, HTN, HLD, CKD, anemia, GERD, gastroparesis. His medications include: Lisinopril 20 mg daily, metformin 1000 mg BID, sitagliptin 100 mg daily, atorvastatin 40, erythropoietin 10000 units SQ weekly, famotidine 40 BID, metoclopramide 10 mg TID. His CKD has progressed, his SCr now 2.5 (previously 2.0) and his estimated CrCl (Cockroft-Gault) is 30 ml/min.
which medications should be renally dose adjusted?
SCr increase 0.5, which is <30% of baseline
TR is a 65 yo M with DM2, HTN, HLD, CKD, anemia, GERD, gastroparesis. His medications include: Lisinopril 20 mg daily, metformin 1000 mg BID, sitagliptin 100 mg daily, atorvastatin 40, erythropoietin 10000 units SQ weekly, famotidine 40 BID, metoclopramide 10 mg TID. His CKD has progressed, his SCr now 2.5 (previously 2.0) and his estimated CrCl (Cockroft-Gault) is 30 ml/min.
why does lisinopril not need dosage adjustment?
dialysis
lower life expectancy
increased hospitalizations
poor quality of life: limited by 3x weekly HD sessions (3-4 hours), fatigue
indications for maintenance dialysis
Plan for dialysis when progresses to CKD stage 4 (< 30 ml/min/1.73m2)
Decision for hemodialysis vs peritoneal dialysis
Symptoms usually develop when GFR ~5-10 mL/min/1.73m2
Symptomatic uremia (e.g., serositis, acid-base, electrolytes, pruritis)
◦Inability to control volume status or blood pressure
Cognitive impairment
◦Deterioration in nutritional status
hemodialysis pros
intermittent
defined parameters to detect under-dialysis early
low techniwue failure rate
hemostasis parameters better corrected
close monitoring
hemodialysis cons
3x weekly for several hours
disequilibrium, hypotension, muscle cramps
infections
thrombosis
more rapid residual kidney decline
peritoneal dialysis pros
hemodynamic stability
higher clearance of large solutes
convenient route for antibiotics, insulin
independence, freedom from machine
less blood loss and iron deficiency
no systemic heparinization
lower physiologic EPO doses
peritoneal dialysis cons
amino acid loss through peritoneum- malnutrition
peritonitis
cather malfunction
inadequate ultrafiltration and solute clearance
patient burnout, high rate of technique failure
risk of obesity with excessive glucose absorption
hernias, dialysate leaks, hemorrhoids, back pain
abdominal surgery precludes use
hemodialysis
Blood is pumped to the dialyzer at 300 to 600 mL/min.
Heparin prevents clotting.
Dialysate is pumped at a rate of 500 to 1000 mL/min countercurrent against semi-permeable membrane.
Fluid removal is adjusted by pressure in the dialysate compartment.
hemodialysis access
A) Arteriovenous (AV) fistula: Surgical anastomosis of cephalic vein with radial artery. Blood flows from high-pressure artery leading to hypertrophy of vein. 3 months to mature
B) Synthetic AV graft: Connects brachial artery and basilic or cephalic vein. Blood flow may be diminished in radial and ulnar arteries since blood preferentially flows into low-pressure graft.
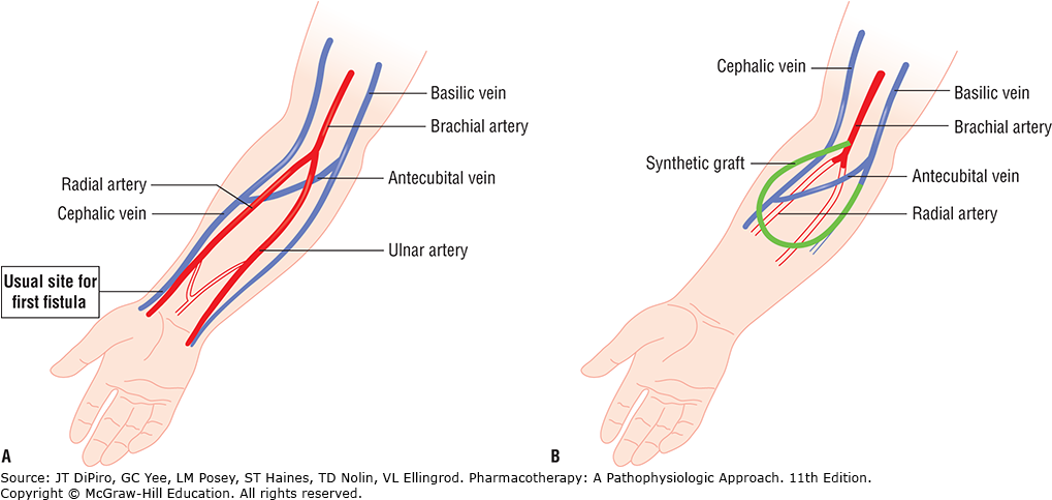
vascular access
central venous catheters
temprary access only
inserted into jugular, femoral, subclavian vein
use for emergent dialysis
or when AV graft or AV fistula are no longer an option
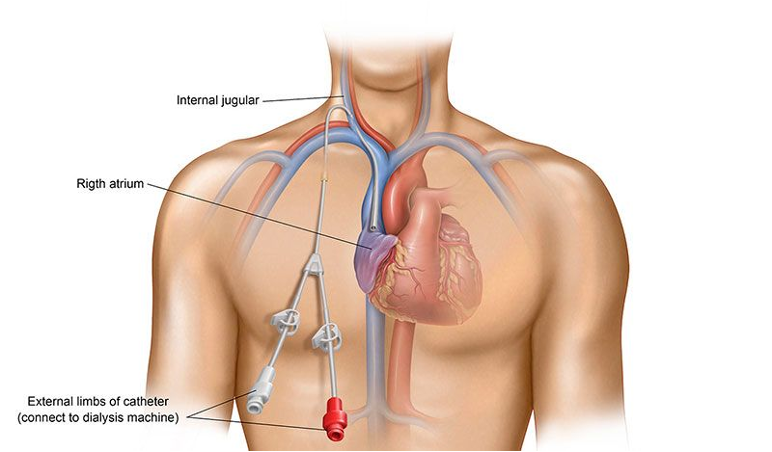
catheter> AV graft > AV fistula
thrombosis rates
thrombosis of vascular access
most common complications: stenosis, thrombosis, infections
rates: catheter> AV graft > AV fistula
early dysfunction (< 5 days after placement)
catheter thrombosis management
locked with anticoagulant
installation of a solution into catheter lumen
low dose unfractionated heparin 5,000 units twice weekly
sodium citrate 4$
alteplase 1mg weekly
catheter thrombosis treatment
nonpharm→ forced saline flush, referral to vascular surgeon
pharm→ alteplase 2mg/2ml for 30 minutes
dose is instilled into lumen for 30 min, then attempt to aspirate. repeat if necessary
vascular access infection
2nd leading cause of mortality in dialysis patients
Accounts for ~20% of access complications
Infection site rates
catheters > AV grafts > AV fistulas
Local infection vs extensive infection
antibiotic therapy vs antibiotics + surgical revision
Can lead to endocarditis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, septic pulmonary emboli, septic syndrome
catheters > AV graft > AV fistulas
vascualr access infection site rates
prevention of catheter related infections
◦Minimize the use, access, and duration of catheters
◦Proper handling minimizing use and duration of catheters
◦Proper disinfection and sterile technique
◦Use of exit-site mupirocin or povidone-iodine ointment
AV graft infection treatment
appropriate antibiotics given IV for 2-4 weeks
gram + (including enterococcus ) and gram -
gentamicin + vancomycin then individualized after culture results available
AV fistulae infections
treat with appropriate antibiotics for at least 6 weeks
always cover gram positive organisms → vancomycin, cefazolin
gram negative coverage is indicated for patients with diabetes, HIV, prosthetic valves, or those receiving immunosuppressive agents- > gentamicin
antibiotic locks
solution that contains a concentrated amount of antibiotic along with heparin
instilled into the infected catheter or port and left to dwell between dialysis session
sodium citrate, alteplase, heparin
what are some strategies that can prevent HD catheter thrombosus?
intradialytic hypotension
10-30% of HD treatments
increase risk of frequent hypotensive episodes→ autonomic insuffiiency, heart disease, advanced age
antihypertensive agents should be given with caution prior to dialysis, but should not be routinely held on dialysis days
acute management of intradialytic hypotension
◦Trendelenburg position (lower head)
◦Decrease ultrafiltration rate
◦100–200 mL 0.9% NaCl bolus
midodrine
for hypotension
oral alpha 1 adrenergic agonist
dosing: 2.5-10mg prior to dialysisto prevent intradialytic hypotension.
side effects: scalp paresthesia, heartburn, flushing, headache, neck pain, and weakness
peritoneal dialysis catheter complications
peritonitis (infection)
exit site tunnel infections
catheter related infections
peritonitis
within 1 year of starting CAPD, 40-60% patients develop their first episode
empiric therapy for both gram positives and gram negatives x 14 days
PD related peritonitis symptoms
◦abdominal tenderness, abdominal pain, fever, nausea and vomiting, and chills
PD related peritonitis signs
◦Cloudy dialysate effluent may be observed
◦Temperature may or may not be elevated
PD related peritonitis lab tests
◦Dialysate white blood cell count >100/mm3, of which at least 50% are polymorphonuclear neutrophils
◦Gram stain of a centrifuged dialysate specimen
PD related peritonitis diagnostic tests
◦Culture and sensitivity of dialysate should be obtained
prevention of peritonitis and catheter exit site infections
Daily application of topical antibiotics
◦Mupirocin cream or ointment
◦Gentamicin ointment
Eradicating nasal S. aureus
◦Intranasal mupirocin 2% ointment, administered twice daily for 5 days of every month
vancomycin + cefepime
NR has been managing nightly PD for 1 year when she developed a fever 103°F, abdominal pain and noticed that dialysate effluent was cloudy. She sees her nephrologist who suspects peritonitis and cultures the dialysate effluent. Which would be an appropriate empiric antibiotic regimen?
renal clearance, therapeutic index
2 main considerations that determine if a drug requires dose reduction in dialysis
drug dosing in dialysis
HD is more effective than PD in removing drugs
Drug dialyzability depends on:
◦Molecular weight (<20 kDa)
◦Protein binding
◦Volume of distribution
Also depends on filter, dialysate, membrane, flow rate
commonly prescribed drugs that are not renally cleared and do not need adjustment
PPIs
statins
corticosteroids
calcium channel blockers
acetaminophen
drug dosing with dialysis
if no dialysis dose is available, assume GFR <15ml/min/1,73m2
generally five the dose after dialysis