Chapter 21: Confidence Intervals for Population Means
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the purpose of a confidence interval for a mean?
To estimate a population mean (\mu) using a sample mean (x) and a margin of error.
What is the general form of a confidence interval for \mu?
Where t* is the critical value from the t-distribution.
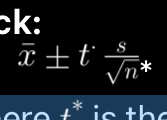
When do you use the t-distribution instead of the Normal distribution?
When the population standard deviation \sigma is unknown and the sample size is small.
What are the conditions for using a t-interval for \mu?
Random sample
10% Condition (if sampling without replacement)
Nearly Normal condition: sample data should be roughly symmetric with no strong skew or outliers
How does sample size affect the t-distribution?
As sample size increases, the t-distribution becomes more like the standard Normal distribution.
What is the margin of error for a mean?
It depends on the confidence level, sample standard deviation, and sample size.

What is a critical value t*?
A value from the t-distribution corresponding to a specific confidence level and degrees of freedom.
How do you find degrees of freedom (df) for a one-sample t-interval?
df = n - 1
What does the confidence level represent?
The percentage of intervals (in repeated samples) that would contain the true mean.
What happens to the margin of error if you increase sample size?
The margin of error decreases — larger samples give more precise estimates.
What happens to the margin of error if you increase confidence level?
The margin of error increases — higher confidence requires a wider interval.