Biosci 221 Exam 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Viruses, The Prokaryotic Cell, Microbial Growth, & Genetic Recombination
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
General information about viruses
* Acellular and NOT living
* They’re ultramicroscopic (most are
* They’re ultramicroscopic (most are
2
New cards
Structure of basic virus (genome, capsid, +/- envelope)
* A viral genome is composed of either **DNA or RNA** and it can be **double- or single-stranded**
* The **capsid** (or protein coat) keeps the viral genome intact outside the host. It comes in many shapes and is made up of capsomers
* Icosahedral (which has the min. # of capsomers)
* Helical
* Amorphous or complex viruses (no symmetrical form)
* Some species have their capsid encased by an **envelope**, often forming out of host membranes with embedded viral envelope proteins
* Mostly associated with animal viruses
* Some have spike proteins that help them attach to particular cells
* +envelope?
* -envelope?
* The **capsid** (or protein coat) keeps the viral genome intact outside the host. It comes in many shapes and is made up of capsomers
* Icosahedral (which has the min. # of capsomers)
* Helical
* Amorphous or complex viruses (no symmetrical form)
* Some species have their capsid encased by an **envelope**, often forming out of host membranes with embedded viral envelope proteins
* Mostly associated with animal viruses
* Some have spike proteins that help them attach to particular cells
* +envelope?
* -envelope?
3
New cards
Lytic cycle of bacteriophage
* During the lytic cycle of virulent phage, the bacteriophage attaches, penetrates, and takes over the cell; it then reproduces new viral components, assembles new phages, and lyses the cell

4
New cards
The lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage (prophage, lysogenic conversion)
* In a lysogenic cycle, the phage genome also enters the cell through attachment and penetration. The phage genome integrates into the bacterial chromosome and becomes part of the host. The integrated phage genome is called a **prophage**. As the bacterium replicates its chromosome, it also replicates the phage’s DNA and passes it on to new daughter cells during reproduction.
* Temperate phages tend to be inactive within the cell
* Other viruses will not be able to infect a cell that’s already prophaged
* When stressed, the prophage DNA is excised from the bacterial chromosome and enters the lytic cycle
* Lysogenic conversion: phage genes in the bacterial chromosome can cause the production of toxins or enzymes that cause pathology
* May carry the ability to make a bacterium more virulent
* Temperate phages tend to be inactive within the cell
* Other viruses will not be able to infect a cell that’s already prophaged
* When stressed, the prophage DNA is excised from the bacterial chromosome and enters the lytic cycle
* Lysogenic conversion: phage genes in the bacterial chromosome can cause the production of toxins or enzymes that cause pathology
* May carry the ability to make a bacterium more virulent
5
New cards
The difference in cycles of animal viruses versus bacteriophage (entering and exiting the cell)
(photo)

6
New cards
Acellular agents in addition to viruses
* **Viroids**
* A piece of RNA
* No capsid
* most/all infect __plants__
* __27 identified__
* Is a **satellite virus** = dependent on other viruses for replication
* **Prions** (Kuru, Varient Crutzfeld Jakob Disease, Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy)
* No nucleic acid
* Abnormal form of a protein
* Extremely resistant to normal sterilization
* Cooking and autoclaving cannot destroy it
* **Creutzfeldt-Jakob**: deterioration of abilities (neurological); holes in the brain; 100% fatal
* **Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob (VarCJD)**: also from organ transplants
* **Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) (mad cow disease)**: meat that came from cow(s) that have Jakob
* **Scrapie**: in sheep and transmissible in sheep
* **Kuru**: obtained through cannabilism; funeral ritual
* A piece of RNA
* No capsid
* most/all infect __plants__
* __27 identified__
* Is a **satellite virus** = dependent on other viruses for replication
* **Prions** (Kuru, Varient Crutzfeld Jakob Disease, Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy)
* No nucleic acid
* Abnormal form of a protein
* Extremely resistant to normal sterilization
* Cooking and autoclaving cannot destroy it
* **Creutzfeldt-Jakob**: deterioration of abilities (neurological); holes in the brain; 100% fatal
* **Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob (VarCJD)**: also from organ transplants
* **Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) (mad cow disease)**: meat that came from cow(s) that have Jakob
* **Scrapie**: in sheep and transmissible in sheep
* **Kuru**: obtained through cannabilism; funeral ritual
7
New cards
Viral Disease Wiki
* Norovirus
* Single-stranded RNA non-envelope
* Capsid is about 23-40nm
* Highly contagious and mainly infecting children due to lack of handwashing
* It is transmitted by human-to-human contact, through contaminated food or water, as well as touching contaminated surfaces.
* Often misdiagnose this virus to a stomach bug or food poisoning because they all have similar symptoms
* 900 people die yearly
* Ebola
* Nucleocapsid which has helical single-stranded RNA enclosed in a spiked outer envelope
* A rare disease that causes affects the immune system and often results in death
* The virus spreads among humans through human-to-human contact and is spread to people by wild animals
* Single-stranded RNA non-envelope
* Capsid is about 23-40nm
* Highly contagious and mainly infecting children due to lack of handwashing
* It is transmitted by human-to-human contact, through contaminated food or water, as well as touching contaminated surfaces.
* Often misdiagnose this virus to a stomach bug or food poisoning because they all have similar symptoms
* 900 people die yearly
* Ebola
* Nucleocapsid which has helical single-stranded RNA enclosed in a spiked outer envelope
* A rare disease that causes affects the immune system and often results in death
* The virus spreads among humans through human-to-human contact and is spread to people by wild animals
8
New cards
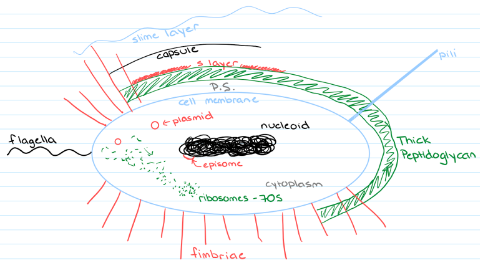
ALL the structures associated with the prokaryotic cell:
* **Cell membrane** = semi-permeable barrier that regulates the passage of substances
* **Cell wall** = single, interlinked molecule that encloses the entire cell and is made up of peptidoglycan (provides structure to the cell) and 2 sugars: N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) and N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG)
* Some have no cell wall
* Some are **pleomorphic** (have different shapes) and thus can pass through filters
* Some lose their cells walls making them more susceptible to changes and lyse
* **L-forms** = survive and reproduce despite lack of cell wall
* **Protoplast** = could mean a cell lost some or all of its cell walls but it can also refer to the cell membrane and the contents inside the cell
* **Spheroplasts** = specifically refer to a rod-shaped organism that loses peptidoglycan and starts to form a sphere
* **S-layer** = a self-assembling highly structured layer of proteins that are found in some bacteria, both gram + and -; it gives structure, protects the organism, and allows attachment
* **Glycocalyx** = coating of glycoproteins outside cell wall that help to protect the cell and also help with attachment
* Two types:
* **Capsule** - highly organized, tightly attached
* Not all bacteria have a capsule
* If it’s small or happy, bacteria would not want to make a capsule b/c it wants to conserve energy
* **Slime layer** - loosely organized and attached
* On most bacteria
* **Cytoplasm** = fluid inside the cell, acts as a solvent
* **Nucleoid** = DNA containing region of the bacterial cell
* Has **chromosomes** which are single, circular, double-stranded, and tightly coiled DNA that contains all the genetic info required by a cell
* **Plasmids** may become part of the chromosome → episome
* **Ribosomes** = 70s size and site of protein synthesis
* Specialized structures
* **Fimbriae** attach cells to surfaces; shorter and more numerous
* F (fertility) pili, or **sex pili**, facilitates the transfer of DNA between cells (conjugation)
* Some specialized cells have **stalks**
* Types of flagella
* **Monotrichous** = one end
* **Amphitrichous** = both ends
* **Peritrichous** = all around
* **Lophotrichous** = tuft at one end
* **Periplasmic flagella** = exist in a spirochetes’ periplasmic space
* **Cell wall** = single, interlinked molecule that encloses the entire cell and is made up of peptidoglycan (provides structure to the cell) and 2 sugars: N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) and N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG)
* Some have no cell wall
* Some are **pleomorphic** (have different shapes) and thus can pass through filters
* Some lose their cells walls making them more susceptible to changes and lyse
* **L-forms** = survive and reproduce despite lack of cell wall
* **Protoplast** = could mean a cell lost some or all of its cell walls but it can also refer to the cell membrane and the contents inside the cell
* **Spheroplasts** = specifically refer to a rod-shaped organism that loses peptidoglycan and starts to form a sphere
* **S-layer** = a self-assembling highly structured layer of proteins that are found in some bacteria, both gram + and -; it gives structure, protects the organism, and allows attachment
* **Glycocalyx** = coating of glycoproteins outside cell wall that help to protect the cell and also help with attachment
* Two types:
* **Capsule** - highly organized, tightly attached
* Not all bacteria have a capsule
* If it’s small or happy, bacteria would not want to make a capsule b/c it wants to conserve energy
* **Slime layer** - loosely organized and attached
* On most bacteria
* **Cytoplasm** = fluid inside the cell, acts as a solvent
* **Nucleoid** = DNA containing region of the bacterial cell
* Has **chromosomes** which are single, circular, double-stranded, and tightly coiled DNA that contains all the genetic info required by a cell
* **Plasmids** may become part of the chromosome → episome
* **Ribosomes** = 70s size and site of protein synthesis
* Specialized structures
* **Fimbriae** attach cells to surfaces; shorter and more numerous
* F (fertility) pili, or **sex pili**, facilitates the transfer of DNA between cells (conjugation)
* Some specialized cells have **stalks**
* Types of flagella
* **Monotrichous** = one end
* **Amphitrichous** = both ends
* **Peritrichous** = all around
* **Lophotrichous** = tuft at one end
* **Periplasmic flagella** = exist in a spirochetes’ periplasmic space
9
New cards
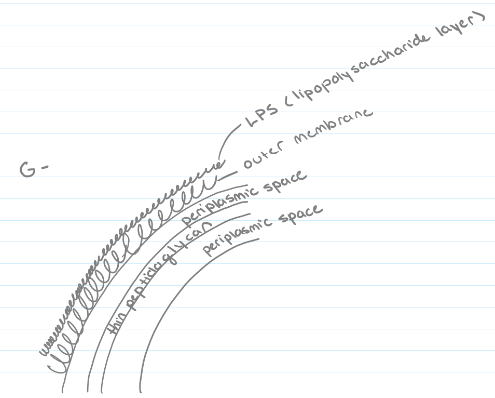
Gram-negative cell wall
**Gram-negative** = multilayered cell wall, more complex than a gram-positive, single layer of peptidoglycan, enclosed by an outer membrane with a lipopolysaccharide layer (LPS)
* LPS layer contains lipid A, an endotoxin that is released when the cell dies and causes endotoxic shock in patients
* LPS layer contains lipid A, an endotoxin that is released when the cell dies and causes endotoxic shock in patients
10
New cards
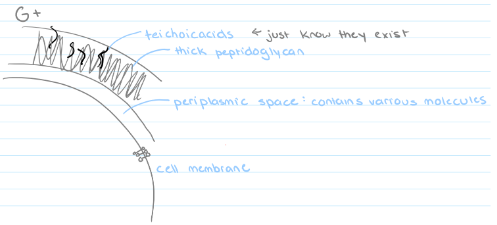
Gram-positive cell wall
**Gram-positive** = thick cell wall, multiple layers of peptidoglycan, teichoic acids
* Some cells have a periplasmic space between the cell membrane and the cell wall
* Some cells have a periplasmic space between the cell membrane and the cell wall
11
New cards
Drawing of a monotrichous gram positive bacterial cell
(photo)
12
New cards
Gram staining
Separates bacteria into two groups based on differences in their cell wall structure
13
New cards
**Plasmids** and types of plasmids
* Plasmids are free small circular, double-stranded DNA
* Nonessential to bacterial growth and metabolism
* But can provide significant advantages to the survival of bacteria in adverse environments
* Types of plasmids?
* Nonessential to bacterial growth and metabolism
* But can provide significant advantages to the survival of bacteria in adverse environments
* Types of plasmids?
14
New cards
**5 differences** between the bacterial cell and the archaeal cell
* Bacterial cell has a lipid bilayer, archaea cell has a monolayer
* Bacterial cell walls have peptidoglycan, archaea cell walls do not have peptidoglycan
* Capsules and slime layers are rare in archaea
* Many archaea (only) have S layers as the structural component
* Some archaea have no cell walls
* Bacterial cell walls have peptidoglycan, archaea cell walls do not have peptidoglycan
* Capsules and slime layers are rare in archaea
* Many archaea (only) have S layers as the structural component
* Some archaea have no cell walls

15
New cards
Reasons endospores are particularly resistant
* Being dehydrated and metabolically inactive gives it stability
* Production of high amounts of dipocolinic acid (DPA) gives protection from the heat
* Increase in SASPs (small acid-soluble proteins) helps to condense and protect the DNA
* A thick spore coat gives resistance against enzymes and chemicals
* Production of high amounts of dipocolinic acid (DPA) gives protection from the heat
* Increase in SASPs (small acid-soluble proteins) helps to condense and protect the DNA
* A thick spore coat gives resistance against enzymes and chemicals
16
New cards
The 4 main layers of the endospore (outer to inner)
* **Exosporium** = lipids, carbs, and proteins
* **Spore coat** = thin protein layers
* **Cortex** = peptidoglycan
* **Core** = DNA, RNA, ribosomes, essential enzymes
* **Spore coat** = thin protein layers
* **Cortex** = peptidoglycan
* **Core** = DNA, RNA, ribosomes, essential enzymes
17
New cards
**Biofilms**
* A mass of bacteria that stick to and multiply on a solid surface
* Produces EPS (extracellular polymeric substance)
* Protects the cell
* Produces EPS (extracellular polymeric substance)
* Protects the cell
18
New cards
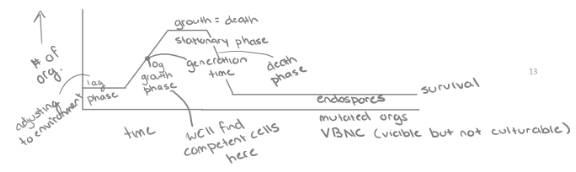
**The Growth Curve**
Represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time
* **Lag phase** = bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing
* The bacteria are adjusting to their new conditions
* **Log phase** = time of exponential growth
* Once cells have accumulated all that they need for growth, they proceed into cell division. Ideal conditions → rapid growth
* **Stationary phase** = growth reaches a plateau as the number of dying cells equals the number of dividing cells
* Nutrients become less available and waste products increase
* **Death phase** = exponential decrease in the number of living cells
* Conditions have deteriorated to a point where the cells are irreparably harmed
* **Lag phase** = bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing
* The bacteria are adjusting to their new conditions
* **Log phase** = time of exponential growth
* Once cells have accumulated all that they need for growth, they proceed into cell division. Ideal conditions → rapid growth
* **Stationary phase** = growth reaches a plateau as the number of dying cells equals the number of dividing cells
* Nutrients become less available and waste products increase
* **Death phase** = exponential decrease in the number of living cells
* Conditions have deteriorated to a point where the cells are irreparably harmed
19
New cards
Carbon source/Energy source terms (chemoheterotroph, photoheterotroph, chemoautotroph, photoheterotroph)
* Phototroph = sunlight
* Chemotroph = chemical breakdown of carbon source
* Heterotroph = organic carbon source
* Autotroph = inorganic carbon source
* Chemotroph = chemical breakdown of carbon source
* Heterotroph = organic carbon source
* Autotroph = inorganic carbon source
20
New cards
Capneic bacteria - **capnophiles**
Need carbon dioxide; most pathogens grow better in the presence of CO2
21
New cards
**Barophiles**
pressure-loving
22
New cards
Temperature terms
* Psychrophile = 0°C-20°C
* Psychrotroph = 0°C-35°C
* Mesophile = 15°C-45°C
* Thermophile = 45°C-80°C (high temps)
* Hyperthermophile = 65°C-113°C
* Cardinal Temperatures = the range that a particular bacterium grows in
* Psychrotroph = 0°C-35°C
* Mesophile = 15°C-45°C
* Thermophile = 45°C-80°C (high temps)
* Hyperthermophile = 65°C-113°C
* Cardinal Temperatures = the range that a particular bacterium grows in
23
New cards
Osmotic pressure terms
* Osmosis = the net movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, from an area of low solute (high water activity) concentration to higher solute concentration (lower water activity)
* Isotonic = equal amount of solute inside and outside the cell
* Hypertonic = more solutes outside of the cell, higher osmotic pressure; there will be a net movement of water out of the cell
* Plasmolysis = cell shrinkage
* Hypotonic = more solutes inside of the cell relative to the solution and the net movement of water will be into the cell, which may result in **lysis** of the cell.
* Halophiles = need a high concentration of salt
* Extreme Halophiles = Growth is even more dependent on large amounts of salt
* Osmophiles = Adapted to environments with high osmotic pressures (high salt concentrations)
* Osmotolerant = The ability to grow in an environment with a high osmotic pressure
* Isotonic = equal amount of solute inside and outside the cell
* Hypertonic = more solutes outside of the cell, higher osmotic pressure; there will be a net movement of water out of the cell
* Plasmolysis = cell shrinkage
* Hypotonic = more solutes inside of the cell relative to the solution and the net movement of water will be into the cell, which may result in **lysis** of the cell.
* Halophiles = need a high concentration of salt
* Extreme Halophiles = Growth is even more dependent on large amounts of salt
* Osmophiles = Adapted to environments with high osmotic pressures (high salt concentrations)
* Osmotolerant = The ability to grow in an environment with a high osmotic pressure
24
New cards
pH terms
* Acidophile = acidic conditions (pH 0-5.5)
* Neutrophile = neutral conditions (pH 5.5-8.0)
* Alkaliphile = basic conditions (pH 8.0-11.5)
* Neutrophile = neutral conditions (pH 5.5-8.0)
* Alkaliphile = basic conditions (pH 8.0-11.5)
25
New cards
Oxygen terms
* Aerobe = requires oxygen
* Anaerobes = cannot survive in the presence of oxygen because they do not have the enzymes to break down toxic by-products and will quickly die in the presence of oxygen
* Microaerophiles = prefer a reduced oxygen atmosphere
* Facultative Anaerobe = have the necessary enzymes and can grow with or without oxygen
* Aerotolerant Anaerobe = can grow in the presence of oxygen but do not use oxygen for growth
* Strict/Obligate Anaerobe = tolerate the presence of oxygen and can only grow in the absence of oxygen.
* Anaerobes = cannot survive in the presence of oxygen because they do not have the enzymes to break down toxic by-products and will quickly die in the presence of oxygen
* Microaerophiles = prefer a reduced oxygen atmosphere
* Facultative Anaerobe = have the necessary enzymes and can grow with or without oxygen
* Aerotolerant Anaerobe = can grow in the presence of oxygen but do not use oxygen for growth
* Strict/Obligate Anaerobe = tolerate the presence of oxygen and can only grow in the absence of oxygen.
26
New cards
**Mutation**
* A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence and a main source of diversity in bacteria
* Random chance
* Might produce a good, neutral, or bad effect
* If mutation allows for better survival of the mutated bacterium then that mutation may be selected for and increase in the population
* Random chance
* Might produce a good, neutral, or bad effect
* If mutation allows for better survival of the mutated bacterium then that mutation may be selected for and increase in the population
27
New cards
**Ames Test**
* The Ames test is a simple, important test to determine the mutagenic activity of chemicals by observing whether they cause mutations in sample bacteria.
* You expose bacteria to said chemical and see if the bacterium changes or undergoes a reverse mutation
* If they are mutagenic, they may be carcinogenic
* The mutagenicity of chemicals is proportional to the number of colonies observed.
* If there is a large number of colonies on the test plate in comparison to the control, then such chemical is said to be mutagens.
* it can also be used to detect the mutagenicity of environmental samples such as drugs, dyes, reagents, cosmetics, wastewater, pesticides, and other substances
* You expose bacteria to said chemical and see if the bacterium changes or undergoes a reverse mutation
* If they are mutagenic, they may be carcinogenic
* The mutagenicity of chemicals is proportional to the number of colonies observed.
* If there is a large number of colonies on the test plate in comparison to the control, then such chemical is said to be mutagens.
* it can also be used to detect the mutagenicity of environmental samples such as drugs, dyes, reagents, cosmetics, wastewater, pesticides, and other substances
28
New cards
**Conjugation**
* The DNA donor cell produces an F (sex) pilus to bring cells in contact with each other so they can replicate and pass genetic material to another bacteria
* Can take a few hours
* Usually doesn't happen all the way
* Cells that carry the F-factor plasmid are called F1 cells. The conjugation process begins when a specialized pilus on an F1 donor cell contacts a plasmidless recipient cell called the F2 cell. Once attached, the pilus contracts to draw the two cells together. Their membranes fuse, and the F+ cell forms a protein bridge to connect to the F– cell. The F– recipient cell will be converted to a new F+ donor cell.
* Cells carrying integrated F factors are called Hfr cells because of the high likelihood (compared with F+cells) that genes from the Hfr cell’s chromosome will be transferred into the recipient and replace homologous (similar) genes in the recipient’s chromosome (Hfr = high-frequency recombination of chromosomal genes).
* An F plasmid that contains host DNA is called an F-prime (F9) plasmid or F-prime (F′) factor
* Can take a few hours
* Usually doesn't happen all the way
* Cells that carry the F-factor plasmid are called F1 cells. The conjugation process begins when a specialized pilus on an F1 donor cell contacts a plasmidless recipient cell called the F2 cell. Once attached, the pilus contracts to draw the two cells together. Their membranes fuse, and the F+ cell forms a protein bridge to connect to the F– cell. The F– recipient cell will be converted to a new F+ donor cell.
* Cells carrying integrated F factors are called Hfr cells because of the high likelihood (compared with F+cells) that genes from the Hfr cell’s chromosome will be transferred into the recipient and replace homologous (similar) genes in the recipient’s chromosome (Hfr = high-frequency recombination of chromosomal genes).
* An F plasmid that contains host DNA is called an F-prime (F9) plasmid or F-prime (F′) factor
29
New cards
**Transduction**
* Improper de-integration can lead to transduction, the transfer of bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another by a virus
* **Specialized** = takes a piece of the cell DNA they were attached to
* **Generalized** = takes a fragment of bacterial DNA
* **Specialized** = takes a piece of the cell DNA they were attached to
* **Generalized** = takes a fragment of bacterial DNA
30
New cards
**Transformation**
* Some bacteria may pick up genes from the surrounding environment (from dead bacteria), via “transformation.”
* These genes, often on a plasmid, may code for antibiotic resistance mechanisms.
* These genes, often on a plasmid, may code for antibiotic resistance mechanisms.
31
New cards
**Transposons**
* Genes that can undergo transposition, where they can jump from one place in a genome to another (or to a plasmid residing in the same cell)
* Contributes to antibiotic resistance when genes move from the chromosome onto a plasmid which can then be transferred to other bacteria
* Contributes to antibiotic resistance when genes move from the chromosome onto a plasmid which can then be transferred to other bacteria