1st Trimester abnormalities
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Subchorionic hemorrhage
Bleeding between the UT wall and chorion
Can lead to spontaneous abortion
Usually diagnosed after 9 weeks
Subchorionic hemorrhage usually causes:
Bright red spotting due to fresh bleeding in affected area
Subchorionic hemorrhage USA
Hypoechoic structure between chorion and UT wall
Usually crescent shaped
May see debris with thrombus formation within
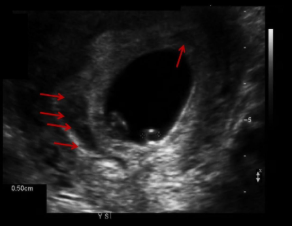
Subchorionic hemorrhage
Risk factors of ectopic
Hx of PID, fertility treatment, tubal surgery, previous ectopic, DES exposure
IUD device
#1 risk for ectopic
Tubal surgery/trauma
Most common location for ectopic
Ampulla
Locations for ectopic
Throughout fallopian tube
C-section scar
Cervix (hourglass shaped UT)
Ovary
Abdomen
Retroperitoneal
Angular pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy that implants at the upper lateral corner of the endo cavity near the opening of the fallopian tube
Ectopic usually occurs on the ____ side as corpus luteum
Same
Highest risk for complications occur if ectopic is located in the _______ portion of the fallopian tube
Interstitial
Classic triad of ectopic symptoms
Missed period, pain, irregular vaginal bleeding
Symptoms of ectopic rupture
They vary
Shoulder pain
Vertigo
Syncope
Shock
Methotrexate used to treat early unruptured ectopic causes:
Involution of ectopic and preserves fertility of pt
Indirect signs of ectopic pregnancy
FF in cul-de-sac or Morrisons pouch
Empty GS in uterus with no yolk sac
Pseudosac with one decidual layer (IUP has 2)
USA ectopic pregnancy
Complex adnexal mass located between ovary and UT
Fetal heart motion may be seen
Adnexal tubal ring (bagel or donut sign)
RING OF FIRE (increased vascularity surrounding decidual reaction)
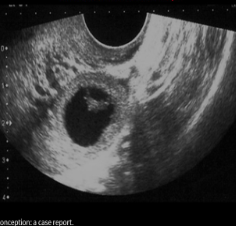
Ectopic
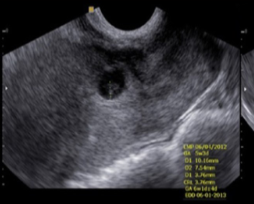
C-section ectopic
Hydatidiform Mole
GTD
Hyperplasia and overgrowth of trophoblastic material
Fertilization occurs without chromosomes present
80% are benign
HIGH levels of hCG → nausea and hyperemesis
String indicator of molar pregnancy
Acute onset of maternal systemic HTN in first trimester
Moles are caused by
Excessive paternal genetic material = two sperm fettilize a single egg
Moles are associated with
Theca lutein cyst and enlarged UT for gestational age
Complete mole
MOST COMMON
No fetus
Severely increased hCG
May be seen with theca lutein cyst
Enlarged uterus with heterogeneous endo cavity, SNOWSTORM appearance
Hydropic villi appear as multiple cystic structures within the uterine cavity
Partial mole
Fetus and molar pregnancy; can occur with an abnormal or normal fetus
If abnormal, most fetuses are triploid (2 sperm, 1 egg = 3 copies of all)
Area of heterogeneous molar tissue Adjacent to fetus
Placenta >4cm AP at 18-22 weeks
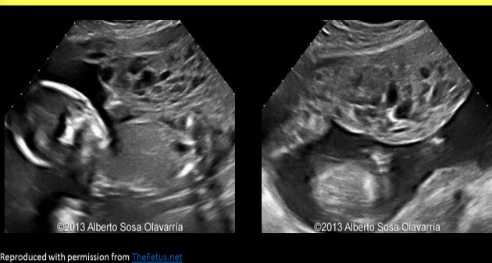
Partial molar pregnancy
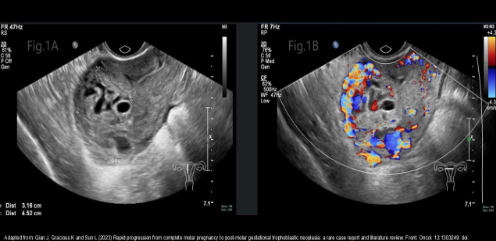
Complete molar pregnancy
Chorioadenoma Destruens
Persistent trophoblastic neoplasm
Invasive malignant molar pregnancy that moves into myometrium, uterine wall and PERITONEUM
Very invasive but specific to uterus
Pelvic nodes are normal and liver is clear
Heterogeneous with vascularity
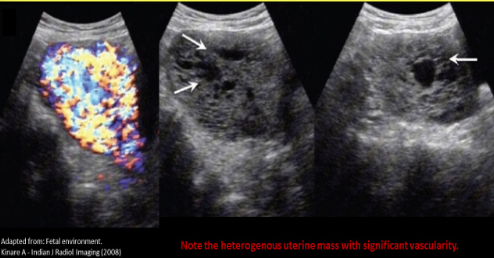
Chorioadenoma destruens
Choriocarcinoma
Persistent trophoblastic neoplasm
Malignant molar pregnancy that mets to liver
Abnormal pelvic lymph nodes
Elevated hCG levels in a non pregnant female
May see masses in cervix and vaginA
Highly vascular complex mass
Most common solid mass found with pregnancy
Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids have highest risk for …
Early pregnancy complications
Cervical fibroids have highest risk for…
Delivery complications
Major anomalies easily identified in 1st tri
Acrania, anencephaly, alobar holoprosencephaly, body stalk anomaly, ectopia cordis, megacystitis, omphalocele, gastroschisis
NT
11-14wks
Midsagittal plane
Neck in neutral position
3 echogenic lines should be demonstrated (inner and outer borders of skin and amnion)
>3mm = abnormal
Abnormal NT/NSF = Trisomy 21 (80%)
Use largest measurement
Nuchal skin fold >__mm is abnormal, measured in 15-21 weeks
6
Alobar holoprosencephaly
SINGLE ventricle, fused thalami, absent CC
Cephalocele
Bony defect with intracranial contents protruding
Ventriculomegaly
Dilated lateral ventricles with dangling choroid plexus
Dandy walker malformation
Enlarged IT space, compressed brainstem, large posterior fossa
Omphalocele
Midline wall defect with viscera covered by membrane, can contain intestines, liver and stomach
Gastroschisis
Wall defect adjacent to cord insertion, herniated bowel NOT covered by membrane
Increased AFP
Pentalogy of Cantrell
Midline supraumbilical wall defect
Diaphragmatic hernia
Defect of distal sternum
Defect in pericardium
Intracardiac defect/ectopia cordis
Ectopia cordis
Sternal defect with heart protruding out of chest
Limb body wall complex
Large wall defect, short/no umbilical cord with fetus fixed to placenta
Bladder exstrophy
Wall defect below cord insertion, bladder protrudes outside body
Malposition of heart
Heart in mid or right chest
Abnormal cardiac axis
Normal axis is 45 degrees from midline, rotation from this axis is abnormal
Diaphragmatic hernia
Stomach and/or liver in chest cavity
Lung agenesis or hypoplasia
Absence of echogenic lung tissue surrounding the heart, smaller thoracic circumference, cardiac malposition
Anencephaly
1 of most common NTD (spina bifida is other)
Failure of neurulation defect
Cephalic end of neural tube fails to close
Absence of upper cranial vault and cerebral tissue
Seen as early as 12 weeks
Increased AFP
Fetal demise
FROGGY EYES
Acrania
Or exencephaly
Lack of cranial bone formation
Cerebral tissues form but in abnormal fashion
Brain tissues droop to sides - MICKEY MOUSE SIGN
Seen as early as 12 weeks
Increased AFP
Spina bifida that can be identified in first trimester
Open spina bifida
Spina bifida first trimester diagnosis relies on …
Documentation of compression of choroid, intracranial translucency, and CM with enlarged brainstem
Spina bifida
Changes occur due to posterior shift of cranial contents
Typical banana and lemon sign not well demonstrated first tri b/c cerebellum is not formed and cranium is not fully ossified
Eval of skin line can demonstrate defect
Frontomaxillary angle is narrow in first trimester cases of open defects
Bladder exstrophy
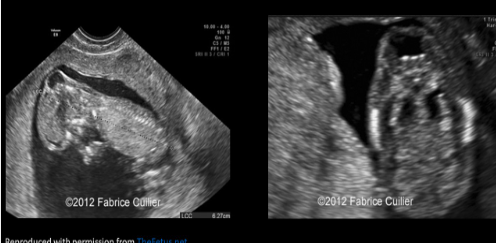
Encephalocele
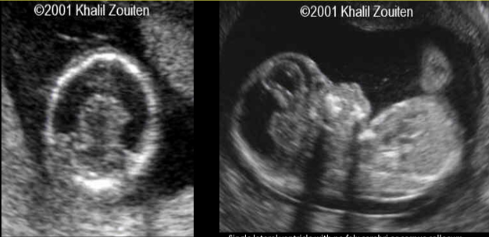
Alobar holoprosencephaly
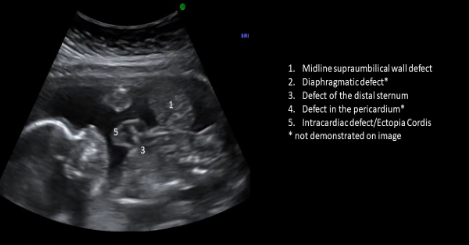
Pentalogy of Cantrell
Aneuploidy
Increased NT thickness
Abnormal bhCG and PAPP-A
Eval nasal bone, face, mandible, post fossa, NT, lungs, heart, stomach, kidneys
CVS is recommended with abnormal US
Trisomy 21
Increased NT thickness
Serum bhCG levels are elevated
Serum PAPP-A levels are decreased
Other Markers:
Hypoplasia/absence of nasal bone
AVSD
Tricuspid regurgitation
Echogenic cardiac focus
Retrograde A-wave of ductus venosus
Trisomy 13
Increased NT
Decreased bhCG and PAPP-A
Alobar holoprosencephaly
Midline facial anomalies
Megacyctitis
Severe hydrops
Tricuspid regurgitation
Retrograde A wave on ductus venosus
Trisomy 18
Largest NT thickness of T21, 13 and 18
Decreased bhCH and PAPP-A
Hypoplasia/absence of nasal bone
Dilated 4th ventricle and post fossa
CP cysts
Spina bifida
Omphalocele
Diaphragmatic hernia
Severe hydrops
Tricuspid regurgitation
Retrograde A wave on ductus venosus
Turner syndrome (monosomy X)
Sex gene syndrome 45X0
Markedly thickened NT → Cystic hygroma
Serum bhCG are normal, PAPP-A are decreased
Normal nasal bone
Tachycardia
Hypoplastic left heart
Hydrops
Renal anomalies
Tricuspid regurgitation
Retrograde A wave on ductus venosus
Triploidy
Complete extra set of chromosomes
Extra paternal chromosome - Diandric triploidy
Increased NT thickness
Serum bhCG are normal and decreased PAPP-A
Normal CRL or short
Molar placenta
Extra maternal chromosomes
Large head, small abdomen
Small placenta
Echogenic bowel
Spina bifida
Most common method for assessing bhCG
Urinalysis
Most common cause of fetal demise in first trimester
Chromosomal abnormalities
__________ is most commonly associated with molar pregnancy
Preeclampsia
A triploidy fetus is commonly associated with ______ molar pregnancy
Partial
An ectopic that implants at the upper lateral corner of the endo cavity near the opening to the fallopian tube is called:
Angular
In a partial molar pregnancy the accompanying fetus typically has what chromosomal anomaly?
3 copies of all chromosomes
Optimal vies for NT measurement
Midsagittal plane that demonstrates echogenic tip of nose, rectangular palate, translucent diencephalon and NT
First trimester diagnosis of spina bifida relies on documentation of:
Compression of choroid, intracranial translucency, CM with enlarged brainstem
What doppler finding in the first trimester pregnancy is suggestive of aneuploidy
Retrograde A-wave of ductus venosus