IB DT: Topic 5.6: Roger's characteristics of innovation and consumers
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/10IFF6QRCazxVQbHPls2qMWD17EnUIV49i8dH_aF_mkY/present?slide=id.g27ead02df49_0_225
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what are rogers’ four main elements that influence the spread of new ideas and what do they rely on?
innovation
communication channels
time
a social system
heavily reliant on human capital - ideas must be widely accepted in order to be self-sustainable
what are rogers’ five characteristics on consumer adoption of an innovation?
comparative/relative advantage
compatibility
complexity
observability
trialability
what is comparative advantage?
the degree to which the innovation is perceived as better than the idea it supersedes - the extent to which the innovation is more productive, efficient, costs less, or improves in some other manner
what is compatibility?
the degree to which an innovation is perceived as being consistent with existing values, past experiences, and needs of potential adopters. an innovation must be socially acceptable to be implemented.
what is complexity?
the degree to which the innovation is perceived as difficult to understand and use
what is observability?
the degree to which the results of the innovation are visible to others - changes of adoption are greater if people can easily observe relative advantage of new technology
what is trialability?
the degree to which the innovation may be experimented with on a limited basis - easier to adopt if they can be tried out in part/on a temporary basis
what is the influence of social media on the diffusion of innovation?
consumers can influence the diffusion of innovation
boycotting and crowdfunding
raising brand awareness
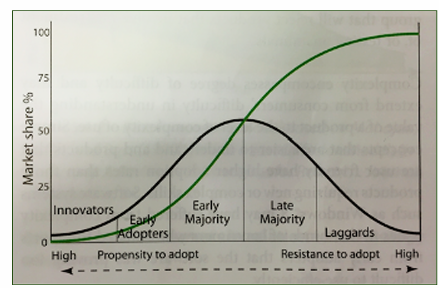
what are the different categories of consumers in relation to speed of adoption of technology?
innovators (risk takers) - the first - willing to take risks
early adopters (hedgers) - second fastest
early majority (waiters) - the third group, take more time to consider adopting new innovations and is inclined to draw from feedback from early adopters
late majority (skeptics) - adopts the innovation after it has been adapted in the market, seldom willing to take risks
laggards (slow pokes) - the last to adopt an innovation - prefer tradition