EQ3- How are the carbon + water cycles linked to the global climate system?
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Reason for land conversion
Growing demand for fuel, food + other resources.
-biosphere sequesters ¼ of fossil fuel carbon emissions per year, slowing rate of global warming
Impact of deforestation
-soil health, water+carbon cycle
On soil health
rapid soil erosion leads to loss of nutrients- 400 tonnes per hectare per year
biomass loss due to reduced photosynthesis
On water cycle
↓ interception by vegetation so ↑ infiltration to soil
↑ erosion+soil runoff, increasing sediment eroded + transport to rivers
On water cycle
↑ carbon flux to atmosphere by burning+decomposing vegetation
↓ CO2 intake during photosynthesis
Impact of afforestation
Planting trees on land that has never had forest or has been without forest for a long time.
+block strong winds to prevent soil erosion
+intercept rainfall to prevent flooding+ ↑ infiltration
+act as large carbon store+ ↑ carbon sequestration
-commercial trees e.g. palm oil store less carbon, use more water and are prone to disease
-growing same species: less diverse insects for seed dispersal, disease can spread more easily
-space can be used to grow crops instead
Impact of conversion of grasslands to farming
-on soil health, carbon+water cycle
Soil health
fertilisers, chemicals pollute soil- soil degradation
Water cycle
biofuel crops need lots of water, so need irrigation which has significant impact on aquifers
cultivated soils are liable to erosion by runoff
Carbon cycle
initial removal of grassland releases CO2 from soils into atmosphere
annual ploughing enables soil bacteria to release CO2
Ocean acidification
Ocean becomes more acidic due to ↑ levels of CO2 dissolving into ocean water.
-exacerbated by warming temp, pollution, tropical storms
-acidity is 25% greater than pre-industrial times
Impact of ocean acidification
Risks crossing the critical threshold (point beyond which damages become irreversible) for health of coral reefs.
-fewer carbonate ions→ thinner, weaker shells/ skeletons→ more attacks from worms, sponges→ reef building collapses + dissolves
-corals shelter 25% marine species- these shelters disappear so risk of extinction
-loss on income from tourism+fishing industries
How does climate change ↑ frequency of drought?
Shifting climate belts- 2 degrees ↑ in temp may lead to 5% of Earth’s land area shifting to a new climate zone- ↑ of droughts
GHG emissions cause temp to ↑ so more moisture evaporates
warmer temps also ↑ evaporation from soil, which affects plants + reduce rainfall even more
drier soils are less able to absorb rainwater, ↑ likelihood of flooding
Amazon droughts
Amazon pumps 20bn tonnes of water into atmosphere each day
rainfall has ↓ downwind of deforested areas leading to Sao Paulo water crisis 2013-15: water reservoirs dropped to single digit %
has had droughts in 2005, 2010 + 2015
feedback loop: more trees die→ less transpiration + enhanced greenhouse effect→ more likely for droughts to occur
Forest ecosystem services
Cultural services: spiritual (flower bathing), educational, aesthetic (waterfalls), recreational (tourism)
Provision of goods: food production, water, wood+fiber
Supporting services: nutrient cycling (trees drop leaves, minerals enrich soil..), soil formation (dead organic material drop from trees), primary production (convert sunlight to energy)
Regulating services: water purification (water passes via plants + remove of toxins), flood regulation, climate regulation (evapotranspiration causes more moisture- rainfall, removes CO2)
How does protection of forest stores change as a country develops?
Kuznets curve suggest that communities reach a tipping point where exploitation of forests changes to more protection.
Factors affecting change in attitude:
wealth of a country
increased knowledge of the role that the environment plays in our well-being
power+influence of TNCs
aid given to developing countries to reduce exploitation
political systems + enforcement of environmental laws
UK- moving industry to other countries to reduce environmental degradation e.g. China
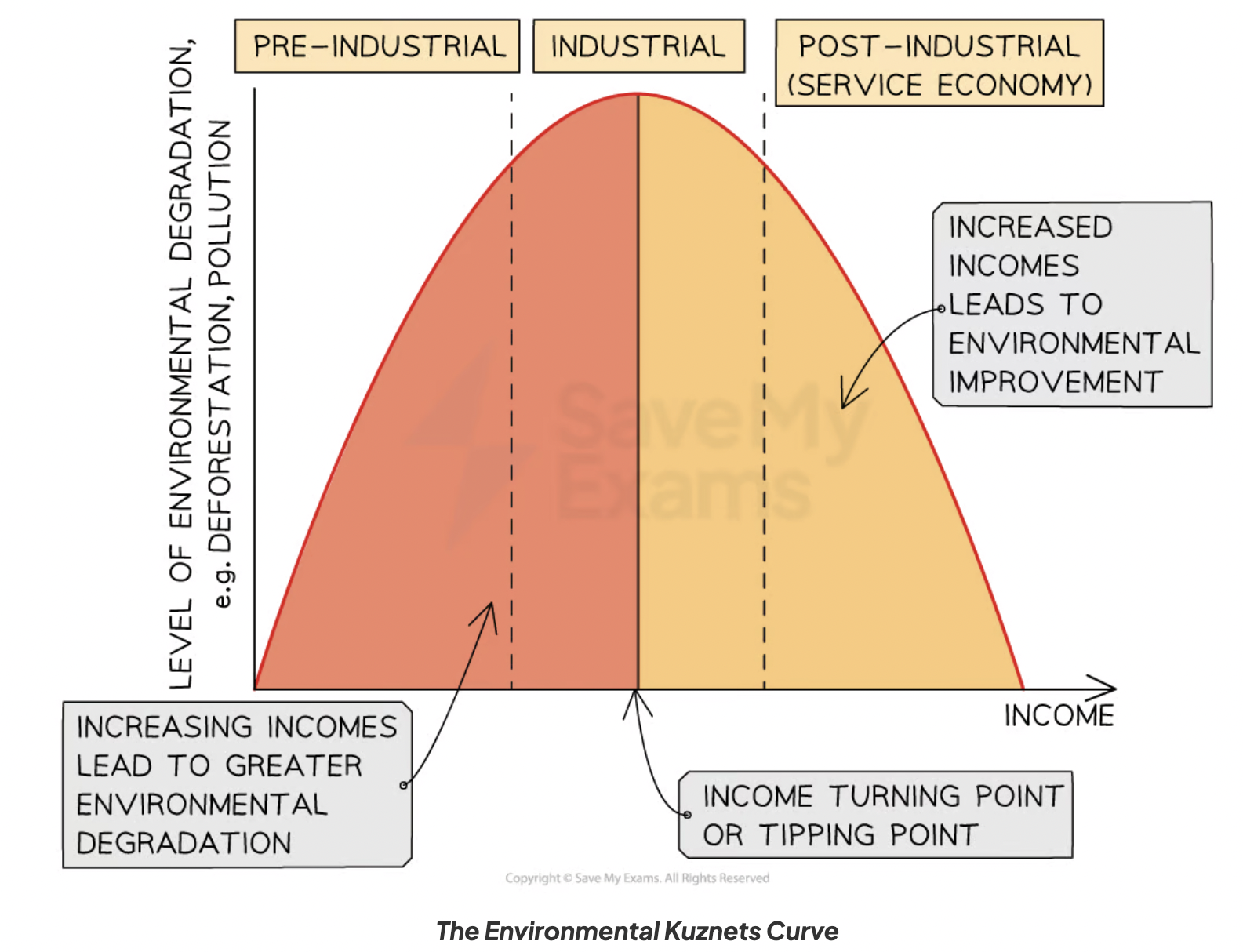
Kuznet’s curve example- Palm oil Indonesia
PRE-INDUSTRIAL: growing demand for palm oil led to increasing production for it-66M tonnes per year.
INDUSTRIAL: 2015-Indonesia is the world’s largest producer of palm oil with GHG emissions overtaking USA due to burning forest.
-Orangutan endangered due to loss of biodiversity + habitats, Sumatran tiger
POST-INDUSTRIAL: forest moratorium (ban/ suspension on an activity) declared aimed at reducing deforestation with $1bn of funding from Norway + UN- emissions fell by 2.5% in 2yrs.
-further reduce by 26% by 2020
What does forest protection in the long term require?
Requires:
protective legislation
18% forests are currently classed as conserved
Brazil + USA have the largest National Parks + Forest Reserves
community involvement in planning + developing policies
EXAMPLE: Players attitudes: Consumers join environmental pressure groups e.g. WWF + Greenpeace, and support their campaigns- money raised is used to fund.
-Greenpeace activists blockaded a palm oil refinery in Rotterdam
Impact of increased temp
impacts evaporation rates + ↑ water in atmosphere
impacts hydrological cycle: precipitation patterns, river regimes, water stores (cryosphere + drainage basin)
Impact of increased temp- Arctic case study
plays vital role as sea ice regulates evaporation + precipitation
Cryosphere impact
Antarctica+Greenland ice sheets have lost mass + glaciers are shrinking
Arctic sea ice + spring snow cover in N. hemisphere continue to ↓ in thickness+extent
Acts as a early warning system
Arctic temp has risen 2x as fast as global avg
loss of ice e.g. NW passage can be navigated in summer
loss of albedo- being replaced by tundra
Implications of ocean threats for humans
Threats to ocean: bleaching, acidification, rising sea levels, loss of sea ice.
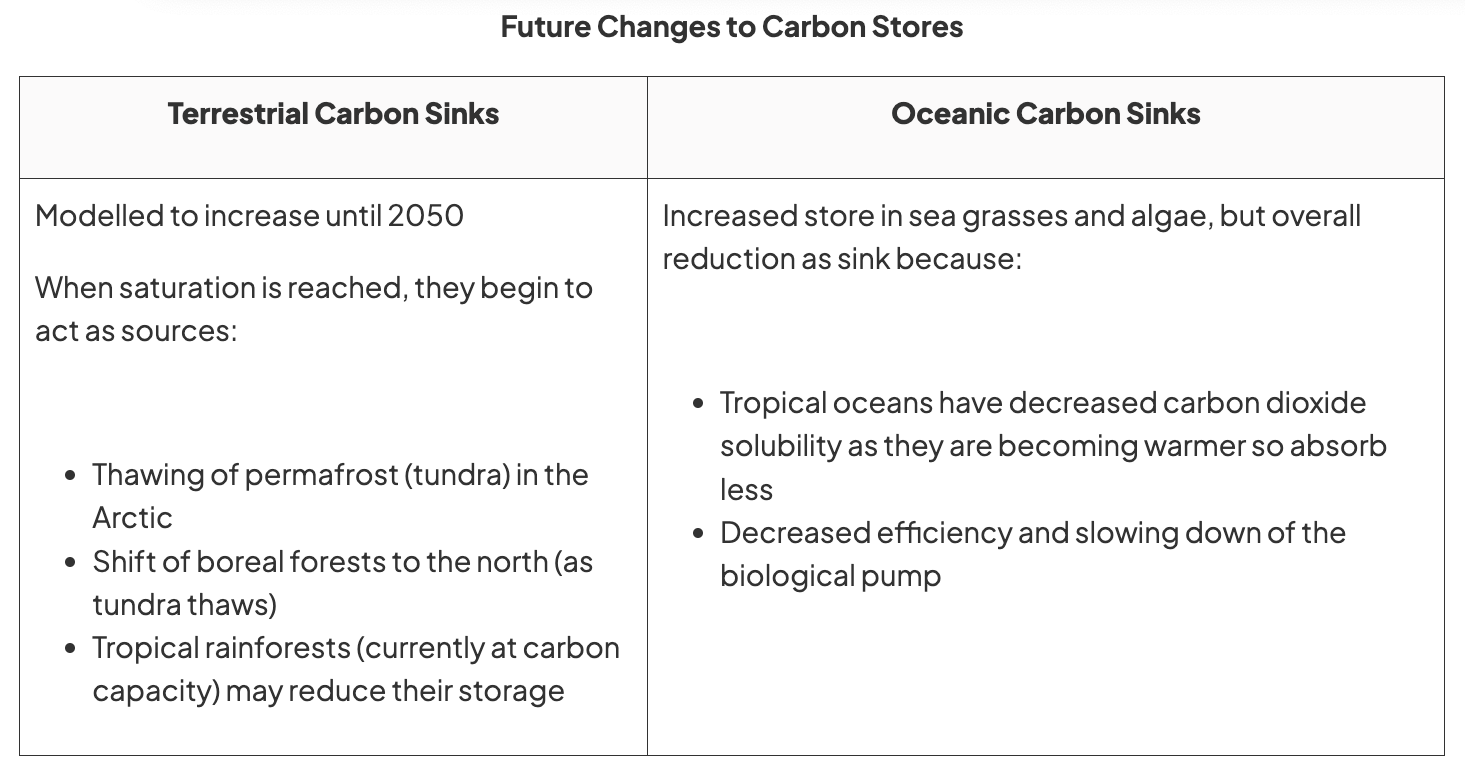
Uncertainty about natural factors (terrestrial + oceanic carbon stores)
role of carbon sinks + their capacity to cope with changes
possible feedback mechanisms e.g. carbon released from peatlands + permafrost
tipping points associated with forest dieback + reversal of thermohaline circulation
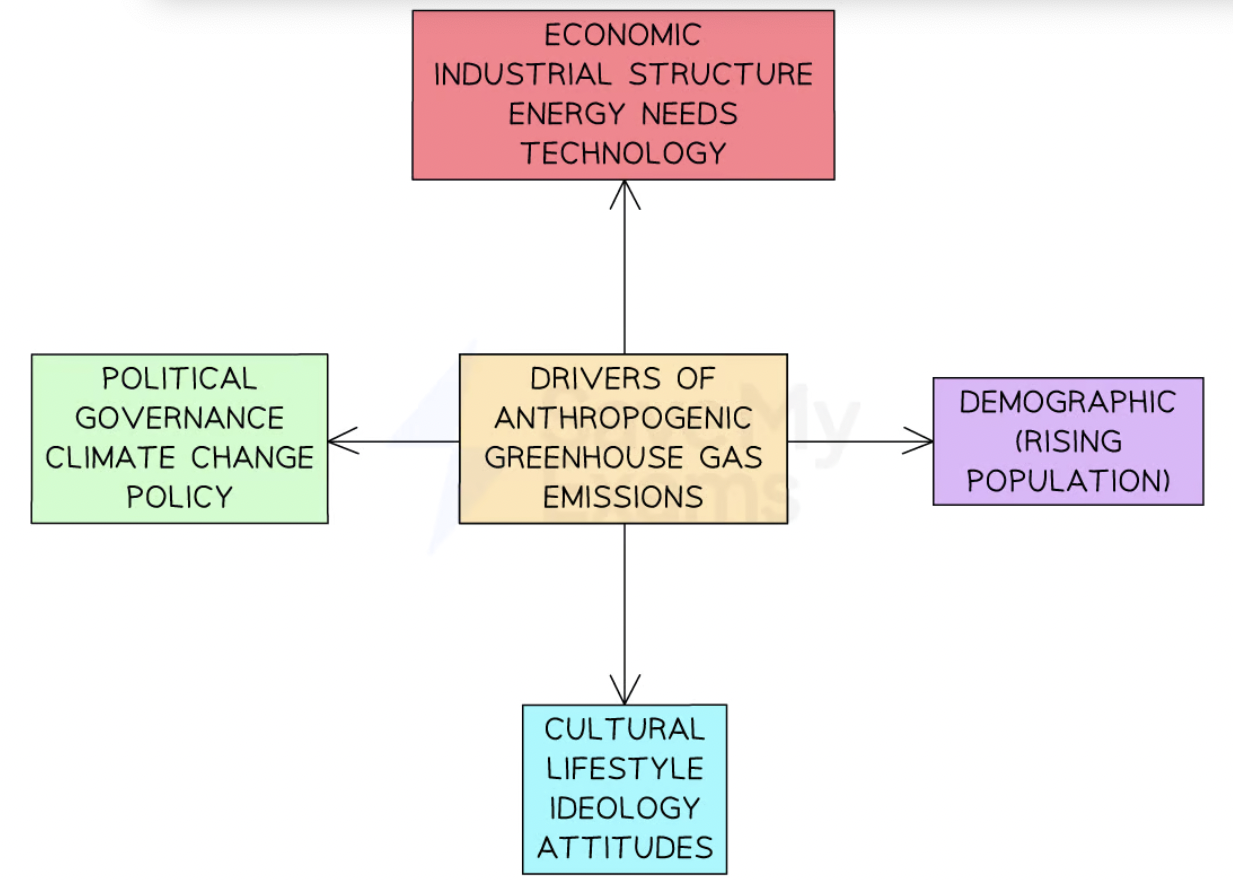
Uncertainty about human factors
future rates of global economic + pop. growth
planned reduction in global carbon emissions
exploitation of renewable energy sources
What is an adaptation strategy?
Strategies which include any passive, reactive or anticipatory action to adjust to a changing climate.
4 adaptation strategies to changed climate
Water conservation
Resilient agricultural systems
Land use planning + flood-risk management
Solar radiation management
Pros + cons of Water conservation
+Reduces soil erosion+floods
+Reduces pesticides + fertilisers runoff, resulting in cleaner lakes e.g. Israel drip irrigation saves up to 70% more than traditional irrigation
-High cost of storage (collecting rainwater)
-May not be able to catch+hold, leading to some entering drains+rivers
Pros + cons of Resilient agricultural systems
+Generate healthier soils- help CO2 sequestration + water storage- reduce ploughing, etc e.g. conservation ariculture in brazil- increases yield, soil structure, water retention
Agroforestry- plant variety of species on same land→improve carbon sequestration e.g. Bali Aga farmers in Indonesia with rice + veg
-more expensive tech
-Seeds+breeds unavailable to subsistence farmers without aid
Pros + cons of Land use planning + flood-risk management
+Ensure efficient use of limited land resources, reducing urban sprawl
+Encourages maintenance of natural landscapes that can absorb floodwater- forests, wetlands
-Land use restrictions limit economic development
-Hard defences against floods are expensive+ruin landscapes
e.g. Thames barrier reduces flood risk, land zoning to prevent building on flood prone land
Pros + cons of Solar radiation management
+Globally cause cooler temps, helping mitigate heat stress on crops+improving agricultural yields
-lead to variations in precipitation + temp, potentially harming vulnerable ecosystems while benefitting others
What is a mitigation strategy?
Involve the reduction or prevention of GHG emissions by using new technologies, renewable or low-carbon energy sources + becoming more energy efficient through changing attitudes + behaviours.
5 mitigation strategies to a changed climate
Carbon taxation
Renewable switching
Energy efficiency
Afforestation
Carbon capture + storage
Pros+cons of Carbon taxation
+Economic incentive for businesses to reduce carbon footprint, lowering emissions.
e.g. lower road taxes for low-carbon cars scrapped in 2015
-Harms low income households who spend larger portion of income on energy costs, which increases due to the tax.
Pros+cons of Renewable switching
+Reduces GHG emissions
e.g. Climate Change Levy to encourage investment in renewable energy was cut in 2015
-Don’t provide consistent power
Pros+cons of Energy efficiency
+Reduces energy consumption, leading to cost saving + cutting emissions.
-Initial investment in infrastructure, can be expensive, acting as a barrier.
e.g. South London housing development uses more insulation to reduce use of energy for heating, energy efficient lamps+appliances
Pros+cons of Afforestation
+Help regulate water flow + water resources (storm flow, erosion control)
e.g. The big Tree Plant campaign encourages communities to plant 1M trees
-monoculture that lacks plant diversity + reduces the no. of available habitat types for forest inhabitants
Pros+cons of Carbon capture + storage
+captures CO2 from industrial processes, preventing it from entering atmosphere. e.g. Canada’s boundary dam
-tech is costly to implement + deploy at wider scale, leaving uncertainty on impact on global emissions.