Hunger and Thirst
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Israel Kamakawiwo’ole
Obese, 757 lbs
Died of heart failure at 38
Homeostatic systems use our behavior to keep things _________
Balanced
Negative feedback systems
Main homeostatic mechanisms
Desired set point deviations triggers compensatory actions
Types of thirst
Hypovolemic:
Stimulated by low extracellular/intravascular volume
Osmotic thirst:
Stimulated by high extracellular solute concetration
Hypovolemic thirst
Baroreceptors in blood vessels and heart detect initial drop → brain activates thirst and salt craving → arteries constrict to raise BP
Hypovolemia → vasopressin release
Constricts blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the bladder
Vasopressin deficiency
Kidneys send more urine to the bladder → chronic thirst
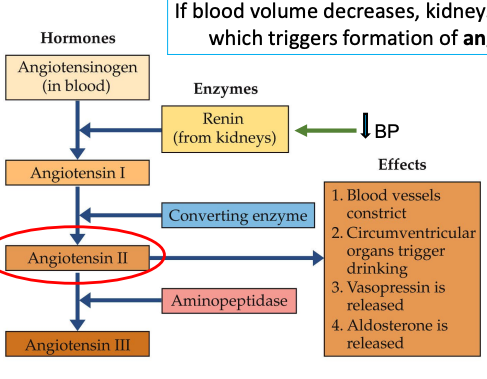
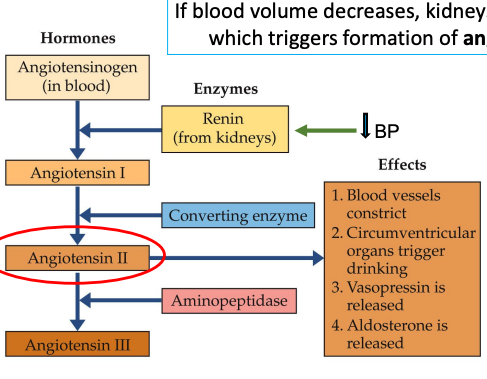
Angiotensin Cascade
Kidneys release renin wen blood volume decreases → formation of angiotensin II
Which constrict blood vessels
Circumventricular organs trigger drinking
Vasopressin is released
Aldosterone is released
Angiotensiogen → Angiotensin I → Angiotensin II → angiotensin III
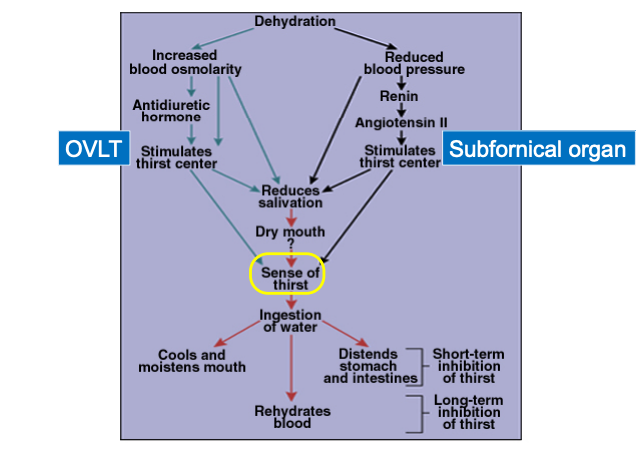
Brain control of drinking
Circulating angiotensin II acts in the subfornical organ to signal other brain sites to initiate drinking.
Osmotic thirst
Osmosensory neurons in hypothalamus (OVLT) respond to rise in blood osmotic pressure (salt)
Respond to increased osmotic pressure by causing pituitary to release antidiuretic hormone.
Cell membranes shrink → opening mechanical-gated Na+ channels
Dehydration and rehydration summary
Why don’t diets work?
Energy expenditure adjusts in response of nutrition
BMR falls at the start of a diet to prevent losing weight
Obesity and reduced metabolism
BMR:
Energy required to fuel brain/body and maintain temperature
75% EE in average sedentary student
Heredity accounts for 40% of BMR
Activity can increase BMR
Energy storage/Utilization
Glucose: the principal fuel for energy.
Glycogen: glucose stored for short term in the liver
Glycogenesis: Converting glucose to glycogen using pancreas hormone insulin
Lipids: Long term storage, fat tissue
Metabolic rate variations
Up until age 1 calorie burning is at its peak
From age 1 to about age 20, metabolism gradually slows
From age 20 to 60, it holds steady
After age 60, it declines about 1 percent a year
Brain ________ insuline and glucose levels with other signals to decide when to start/stop eating.
integrates
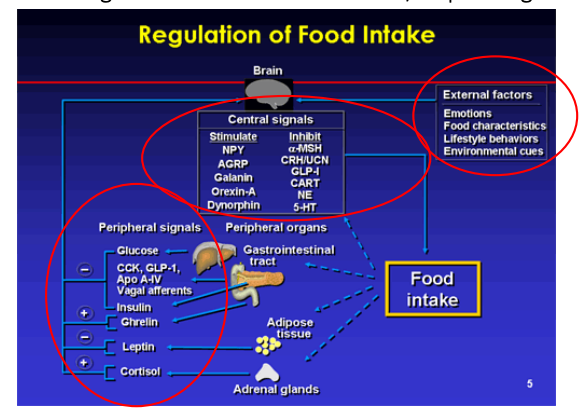
Leptin
Fat cells produce and secrete them into the bloodstream.
Defects in leptin production/sensitivity give a false low report of body fat.
Obese people are leptin-resistant
Overnutrition inflames the hypothalamus → obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Ghrelin
Appetite stimulant
Released by stomach/gut endocrine cells
Rises during fasting
Drops after eating
Prader-Willi syndrome
Causes a sense of hunger.
Genetic disease
Ghrelin levels are elevated
Hypothalamus as the hunger control center
Lateral:
Lesions lead to the refusal to eat, destroy hunger-causing LHA
Resume and stabilize their weight at new, lower level
Ventromedial:
Lesions lead to obesity (eating too much), destroy hunger ending PVN
Increased weight stabilizes
New weight maintained even after food challenges
Neurons groups in hypothalamus
NPY/AgRP → neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide
Stimulate appetite and lower metabolism
Ghrelin stimulates them.
POMC/CART → pro-opiomelanocortin & cocaine and amphetamine-related transccript
Inhibite appetite
Raise metabolism
Stimulates by leptin
Brain damage from overeating
Hypothalamic inflammation → inhibits neurogenesis, resets set point.
Hypothalamic scarring, microglial activation, fewer POMC neurons
Can recover if overeating stops
Newborn hypothalamic cells can become POMC neurons.Anore
Anorexia Nervosa
Restricting or binge eating/purging
Refuse to maintain body weight
Fear of gaining
Body image disturbance
Highest mortality rate
Bulimia
Recurrent binge eating
Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior
2x/wk for 3 months
Women with anorexia/bulimia
40% childhood anxiety disorders
90% depression
246 women with eating disorder
30% attempted suicide
5% died
Teen girls with anorexia
Larger insula → disgust
larger orbitofrontal cortex → you shouldn’t do that
Obesity treatment
Eat less
deficit of 200 calories
Exercise
Strenuous aerobic activity for over 200 minutes per week
Long time
with calorie restriction
Walking doesn’t count
Glucagon-like peptide agonists
Mounjaro
Ozempic