Bio-50A Exam 2 Study Guide
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What are the functions of Epithelium (ET)?
Barrier of cells that protect, secretes, absorbs, and filters
How do we classify ET (i.e., identify and name)?
Number of layers + cell shape + epithelium + any surface mod
Names for types of layers of ET?
Single: One layer
Stratified: Two or more
What are the different shapes of ET cells?
Squamous = Flat
Cuboidal = Cube Shaped
Columnar = Height taller than Width
What is Basal and Apical?
Basal = Base
Apical = Apex or Peak
What are some surface modifications for ET?
Cilia, Microvilli, Stereocilia, Keratinization, Goblet Cells
How is cilia different than microvilli?
Cilia is to move things like Mucus
Microvilli is for absorption
What is the function of goblet cells?
Goblet cells are special cells that make mucus
What is Keratinization?
a tough protective protein that helps prevent desiccation (Drying Out)
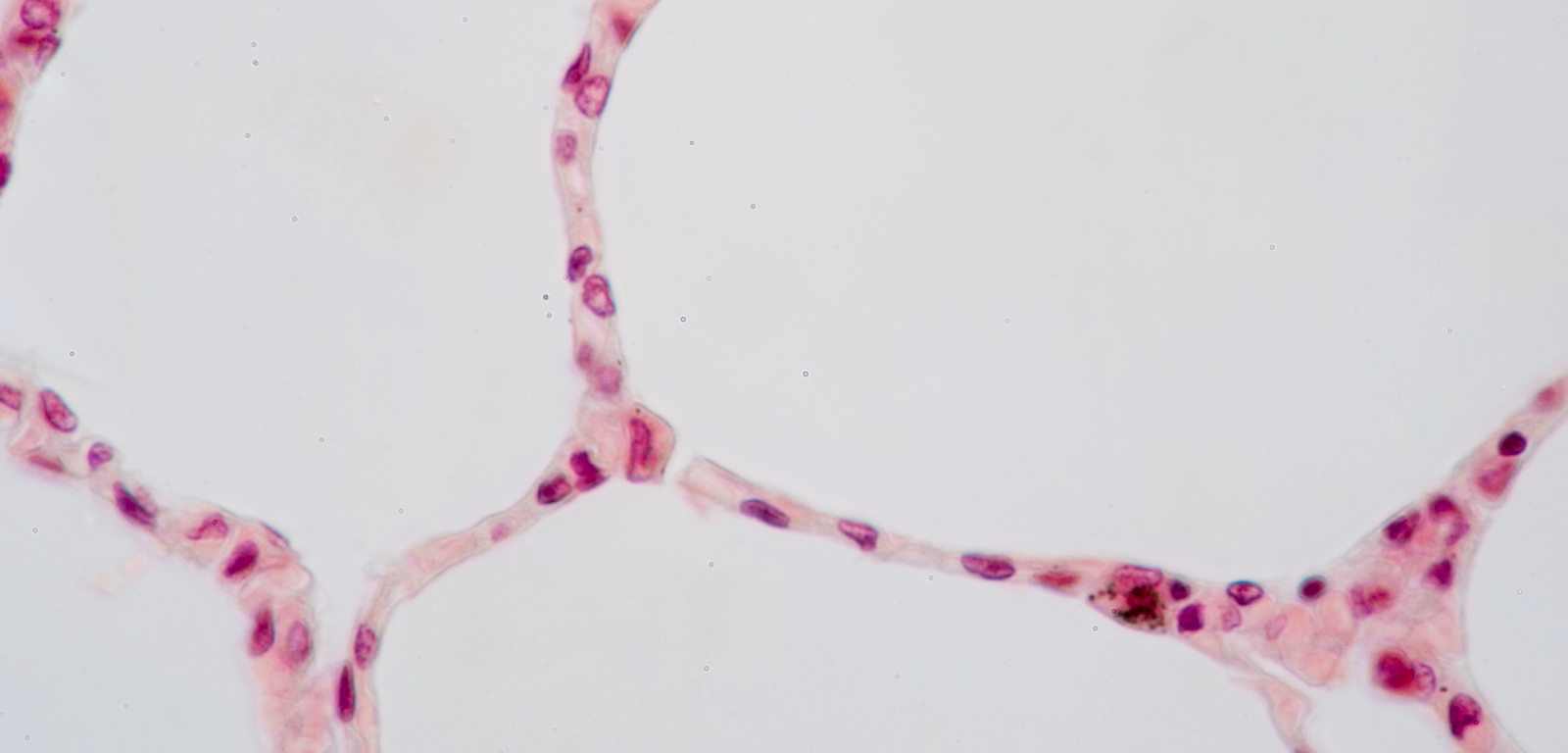
What kind of Epithelia is this?
Simple Squamous Epithelium
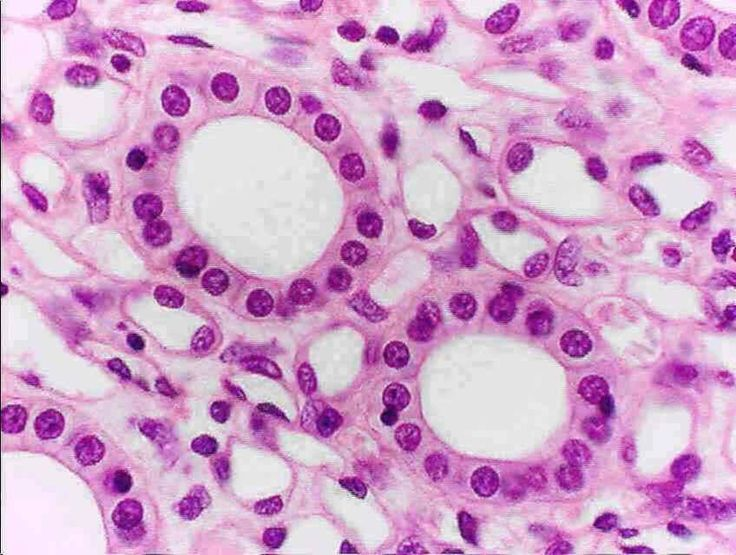
What kind of Epithelia is this?
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
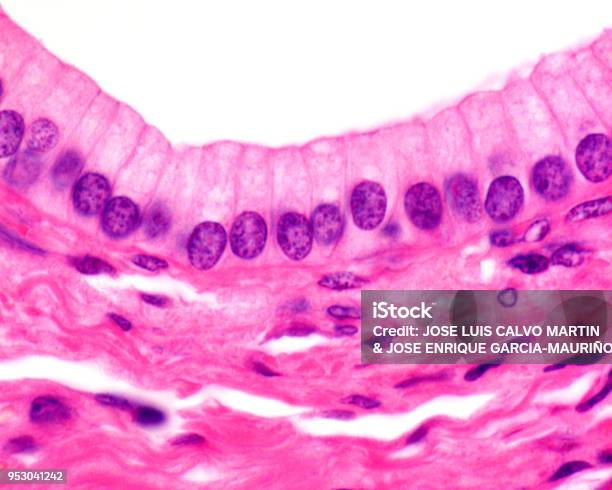
What kind of Epithelia is this?
Simple Columnar Epithelium
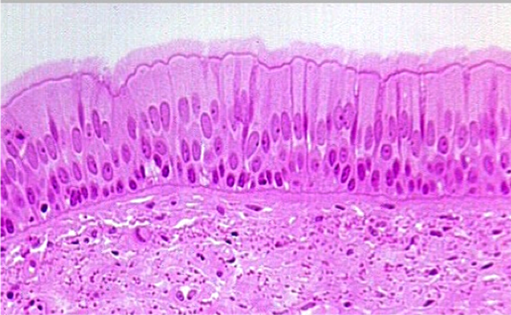
What kind of Epithelia is this?
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
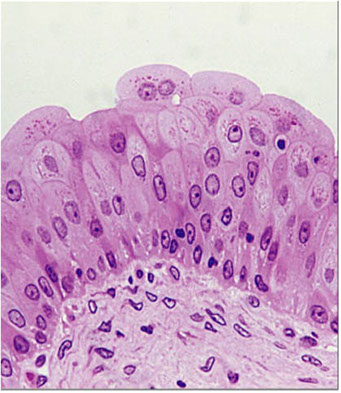
What kind of Epithelia is this?
Transitional Epithelium
How might a single layer of thin cells perform differently than a thick, multi-layered stack of cells?
A thin layer is for rapid diffusion and filtration
A thick layer is for protection and can perform specialized functions
Where in the body is it helpful to have an ET that can stretch (distend)?
Bladder
How might surface modifications assist ET in their functions?
Cilia helps with moving things
Microvilli helps with absorption
Goblet Cells make mucus to collect any dust and bacteria
Keratinization helps with making thicker skin like palms and feet for abrasion and protection
What are the different types of Connective Tissue (CT)?
Bone, Cartilage, Blood, Connective Tissue Proper
What functions does CT perform in the body?
Protect, Support, Binds tissues together, Fuel Reserve, Transport substances
How are the types of CT similar to each other?
They’re all well-vascularized, composed of cells and extracellular matrix
What 3 types of protein fibers are present in CT? What roles are they each specialized for?
Collagen = Form thick fibers that are tough and strong (resist pulling) Most abundant
Reticular = has reticulin and has delicate networks that surround blood vessels and support soft tissue organs
Elastic = Contain Elastin which is stretchy and can be recoiled
What are the components of “ground substance”?
water, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), proteoglycans, and glycoproteins
What are the specific cells for each type of CT?
Bone = Osteoblasts, Osteocytes
Cartilage = Chondroblasts, Chondrocytes
Blood = Hematopoietic Stem Cells
What other cells are found within CT and what do they do?
Adipocytes: (Fat Cells)
WBC: Immune/injury response
Mast Cells: Inflammatory Cells
Macrophages: eat dead tissue and foreign bodies
What are the three types of loose connective tissue?
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
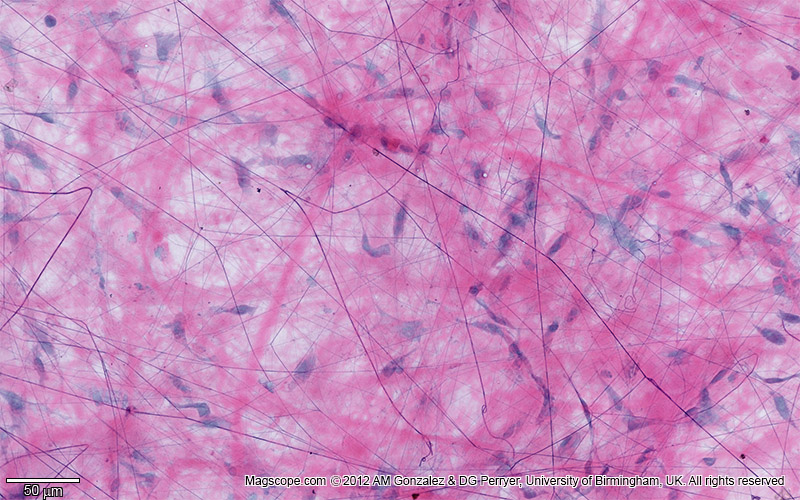
What kind of Loose Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Areolar Connective Tissue
Under Epithelium
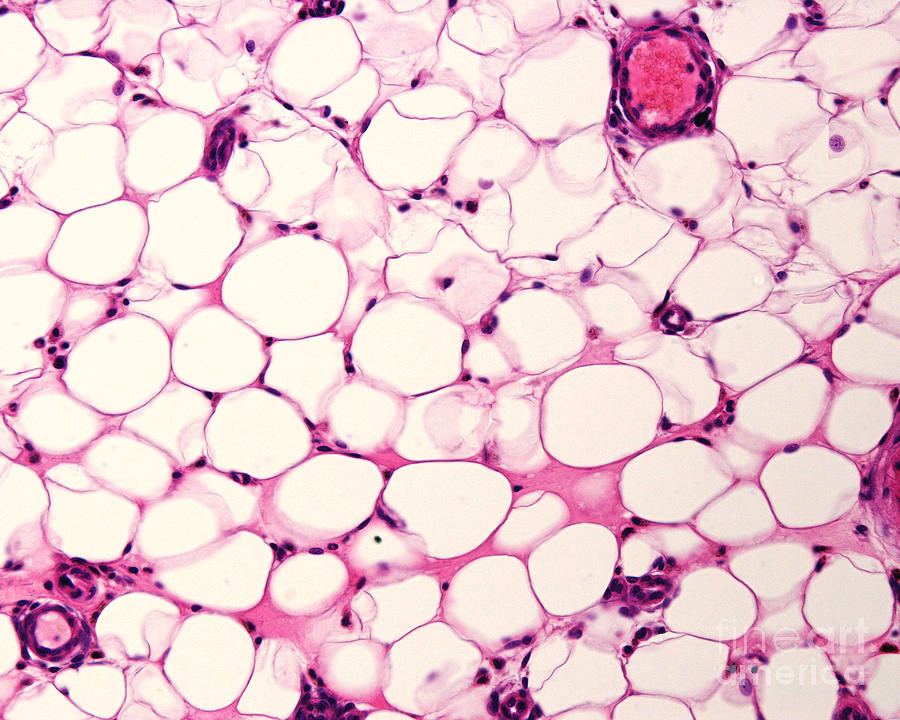
What kind of Loose Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Adipose Connective Tissue
Under skin in subcutaneous tissue

What kind of Loose Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Reticular Connective Tissue
Spleen
What are the three types of dense connective tissue?
Dense Regular CT
Dense Irregular CT
Elastic CT
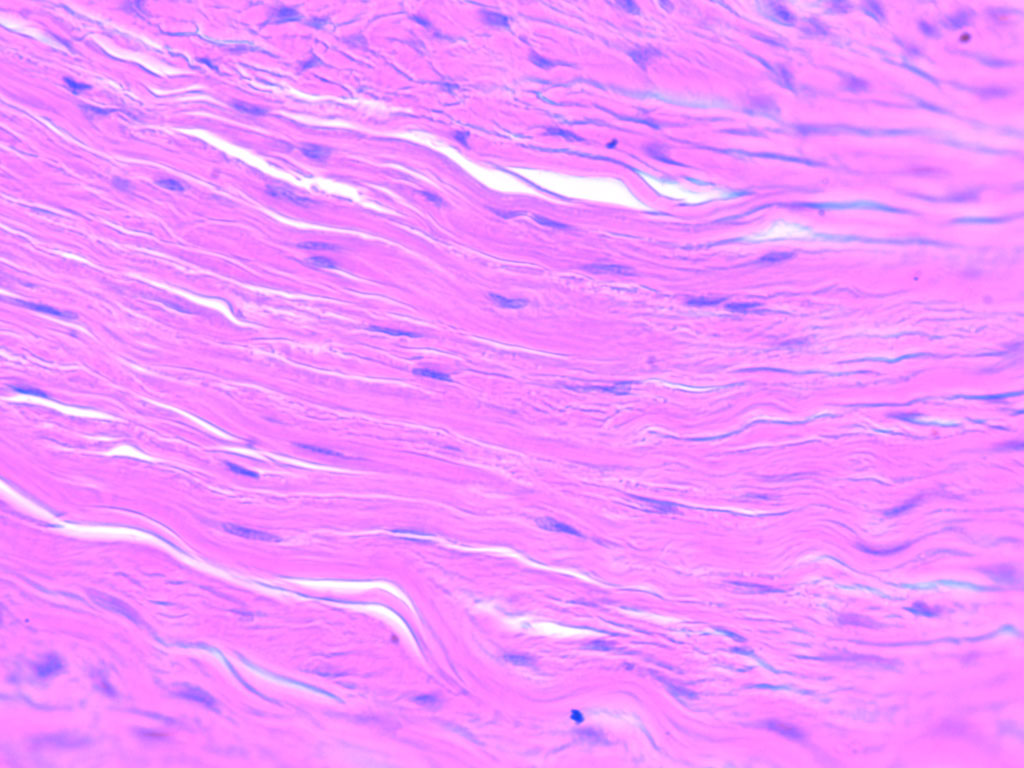
What kind of Dense Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Most ligaments, tendons
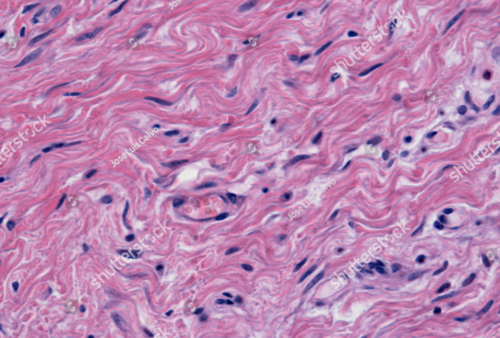
What kind of Dense Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Fibrous Capsule of Joints, Dermis of Skin
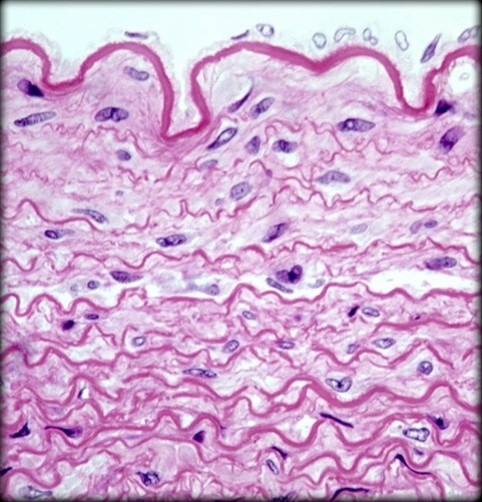
What kind of Dense Connective Tissue is this? Where do you find it?
Elastic Connective Tissue
Walls of large Arteries
How is dense regular CT suited for stress differently than dense irregular CT?
Dense Regular is for stress in one specific direction while Irregular is stress from all directions
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
In cartilage how is their construction different? How does that construction relate to each of their functions?
Hyaline has a moderate amount of fibers and is involved in bone formation
Fibrocartilage has lots of collagen fibers, vertebral discs (space between sections of the spine)
Elastic Cartilage has a mix of collagen and elastic fibers, found in the ear
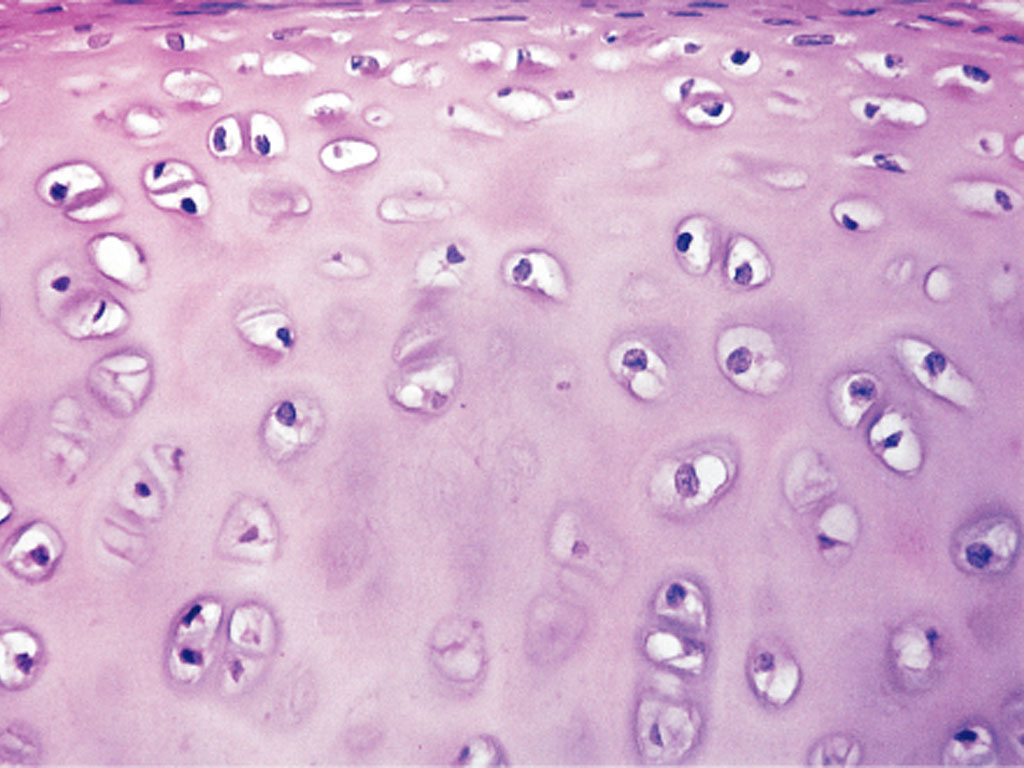
What kind of Cartilage is this?
Hyaline Cartilage
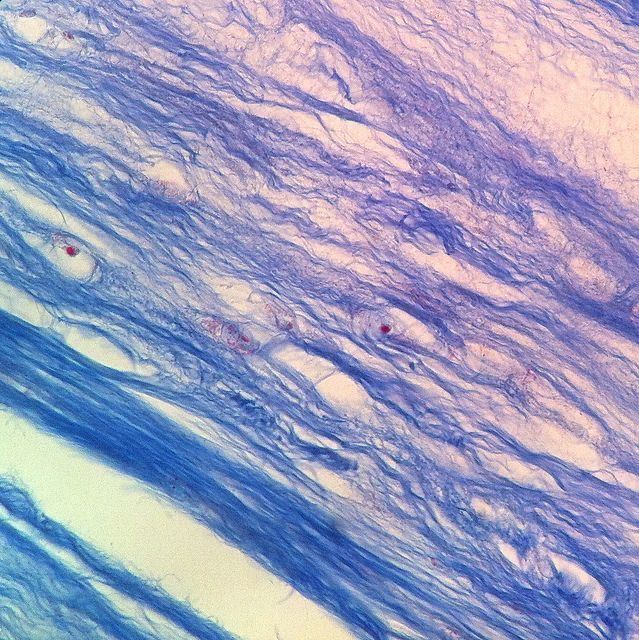
What kind of Cartilage is this?
Fibrocartilage
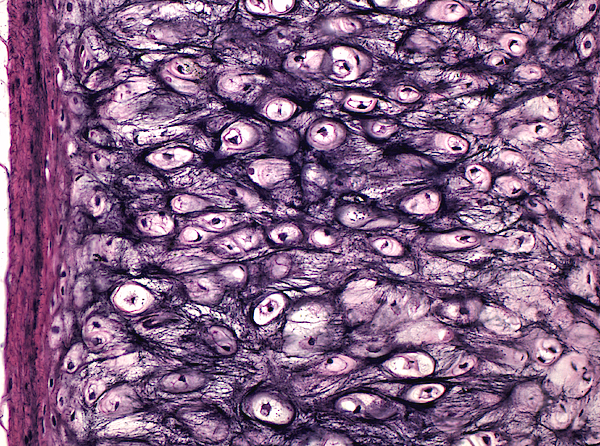
What kind of Cartilage is this?
Elastic Cartilage
What are lacunae?
Unfilled space
What is perichondrium made of and where do you find it?
It is made of Dense Irregular CT and surrounds Cartilage providing nutrients since Cartilage is avascular
How does the blood supply in bone differ from what’s seen in cartilage?
Cartilage is avascular and bone has blood vessels running through it
How does Bones having blood vessels in it make nutrient delivery different compared to Cartilage?
Since Bones have Blood Vessels in them it helps with rapid recovery and delivery of nutrients
What is bone made of?
Bone is made of collagen and calcium phosphate
What is periosteum made of and where do you find it?
It is made of Dense Irregular CT and it surrounds the bone
What are osteons?
The cylindrical, functional units of bone
What is a lacunae in bone?
Spaces in the matrix from Osteoblasts
What are the different canals in bone?
Haversian Canal = Canal that goes up
Volkmann’s Canal = Connects Canals
How is blood different than the other types of CT?
It’s a liquid while the others are solids
What are erythrocytes?
RBC (Red Blood Cells)
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue (MT)?
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
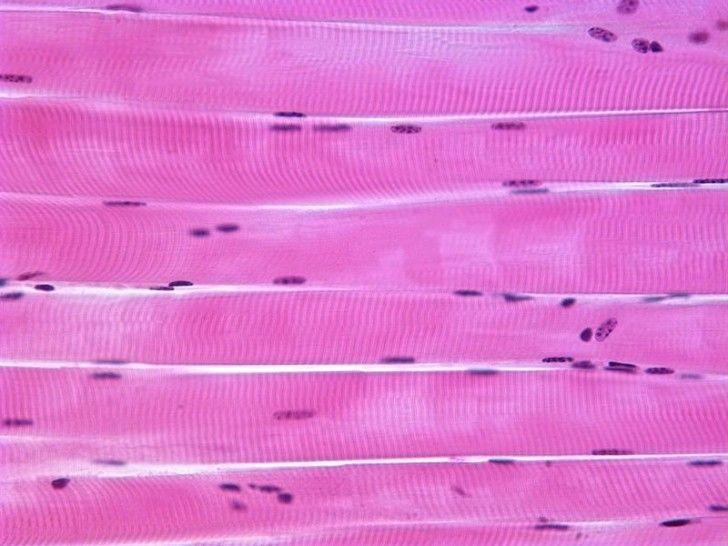
What type of MT is this? How is it controlled? Location?
Skeletal Muscle
Controlled Consciously
Attached to Bones
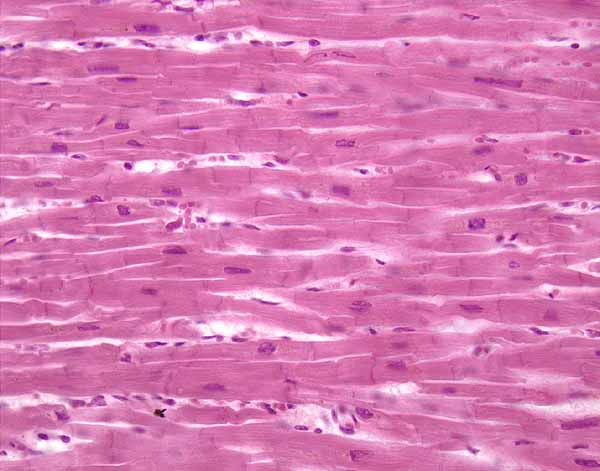
What type of MT is this? How is it controlled? Location?
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary Controlled
Only found in walls of the heart
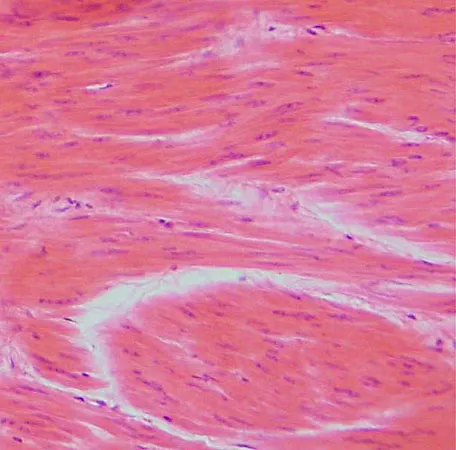
What type of MT is this? How is it controlled? Location?
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary Controlled
Mainly in walls of Hollow Organs
What are the 2 (broad) types of cells of nervous tissue (NT)?
Neurons and Glial Cells
Where do you find Nervous Tissue?
Brain, Spinal Cords, and Nerves
What does the integumentary system consist of?
Skin, Hair, Nails, Sweat Glands, Sebaceous Glands(oil)
What are the layers of skin? What lies deep to skin?
Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
Subcutaneous Fatty Tissue
What tissue types are found in the layers of skin?
Epidermis: Epithelial Tissue
Dermis: Connective Tissue
Hypodermis: Loose connective tissue
How vascularized are the layers of skin?
Epidermis: Avascular
Dermis: Vascular
Hypodermis: Highly Vascular
How does skin protect the body from physical trauma? What sorts of chemicals does it produce (for defense)?
Keratinized cells are made and have multiple layers of dead cells with keratin to help protect
What cells are specialized to combat “biological invaders” (foreign bodies, like bacteria or parasites)?
Dendritic Cells and Macrophages engulf foreign bodies
How does skin help us regulate our body temperatures (hot or cold)?
When hot blood vessels dilate(open) and increase sweat
When cold blood vessels constrict to help keep body heat in
What types of sensations (through receptors) can skin detect?
Gentle Touch
Deep Pressure
Temperatures
Pain
What are the layers of epidermis? (Do you have a mnemonic to help you remember them?)
Come, Lets Get Sun Burned
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
In which epidermis layer(s) are the cells anucleate?
Stratum Corneum
and in thick Stratum Corneum and Lucidum
In which epidermis layer(s) does keratinization begin?
Stratum Granulosum
In which epidermis layer(s) does mitosis occur?
Stratum Basale
What types of cells are found in epidermis?
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes
Dendritic
Tactile
What are the layers of Dermis and what tissues can be found in them?
Papillary: Areolar CT
Reticular: Dense Irregular CT
How are Meissner’s (tactile) and Pacinian (lamellar) corpuscles different from each other?
Tactile Corpuscle = Light Touch
Lamellar Corpuscle = Deep Pressure
What tissues are found in the hypodermis?
Loose(Areolar) and Adipose CT
What functions do friction ridges serve?
Enhance grip ability, contribute to sense of touch, fingerprints is sweat left behind
What three pigments help to determine skin color?
Melanin, Carotene, Hemoglobin
What cells produce melanin and how is it packaged? What does melanin do?
Melanocytes produce melanin, melanin is packaged into melanosomes that protect keratinocytes from UV radiation
What aspect of sun exposure (or over-exposure) is bad for skin? How is some sun exposure good for us?
Can cause cancer but some sun exposure is good for Vitamin D
What three types of skin cancer did we cover in class?
Basal Cell Carcinoma = In Stratum Basale
Squamous Cell Carcinoma = In Stratum Spinosum
Melanoma = Cancer of melanocytes
Which Cancer are benign vs metastatic?
Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma are benign
Melanoma is metastatic
What is a hair follicle made of? How does hair get nutrients to grow? Where does hair growth occur?
Hair is made of dead keratinized cells, it gets nutrients from hair papillae, and hair growth occurs in dermis sometimes hypodermis
What functions does hair serve?
Guards against physical trauma and insects, protects from heat loss, shields skin from sunlight, and filtration
What is/are arrector pili and what does it/they do?
Muscles that attach to hair follicles that when contracts causes hair to stand giving you “goosebumps”
Where does nail growth occur?
at the Nail Matrix
What epidermal layers compare to the nail bed and nail body?
Stratum Corneum
In what layer of integument are sebaceous, eccrine, and apocrine found?
Sebaceous = Dermis
Eccrine = Dermis
Apocrine = Dermis and hypodermis
What do sebaceous, eccrine, and apocrine produce?
Sebaceous = Sebum (oil)
Eccrine = Sweat
Apocrine = Viscous (Oily sweat)
Where do sebaceous, eccrine, and apocrine deposit their products onto the body?
Sebaceous = Hair Follicle
Eccrine = Skin Surface
Apocrine = Hair Follicle
Why do apocrine glands get smelly?
Its odorless until decomposed by bacteria