Module 1 - LHC Hemodynamics
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
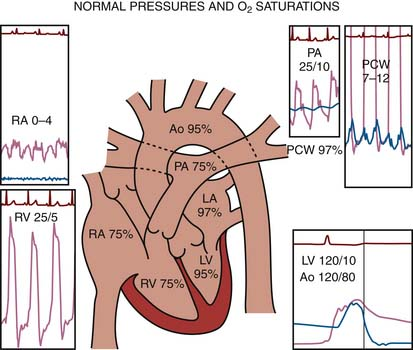
The normal mean pressure for the pulmonary artery is ____
10-20 mm Hg.
PA mean pressure is
10-20 mmHg


average RV pressure
25/5
normal RA O2 sat
75%
average aortic mean pressure is what
70-90 mmhg
In PA pressure what does the dicrotic notch signify
the closure of the pulmonicvalve.
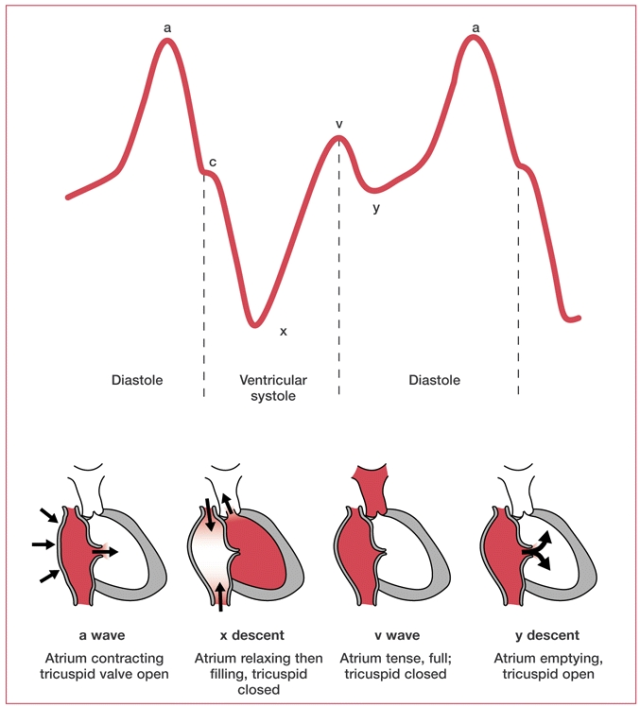
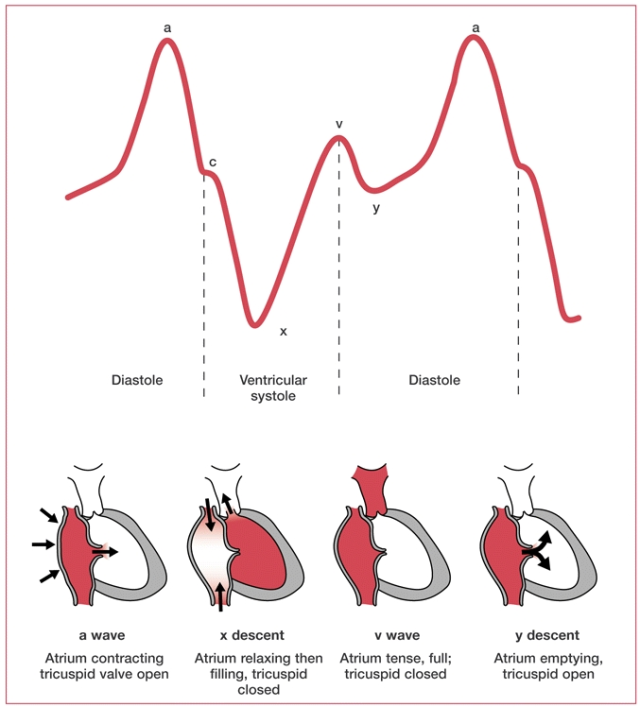
The a wave in atrial pressure tracings represents
atrial contraction

The c wave in atrial pressure tracings represents bulging of the _____ during early ventricular systole
TV/MV
positive pressure spike that occurs during the early phase of ventricular contraction, caused by the closed tricuspid valve bulging into the atrium as the right ventricle begins to contract
TEMP BACK PRESSURE

The x descent in atrial pressure tracings represents ____ of the atrium as the AV valve moves downward
atrial relaxation
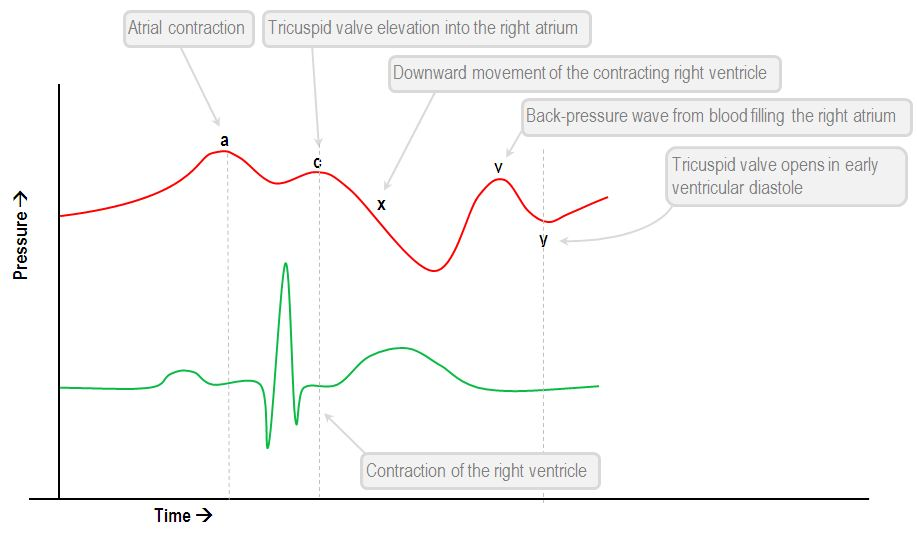
The v wave in atrial pressure tracings represents passive ____ of the atrium while the AV valve is closed
FILLING
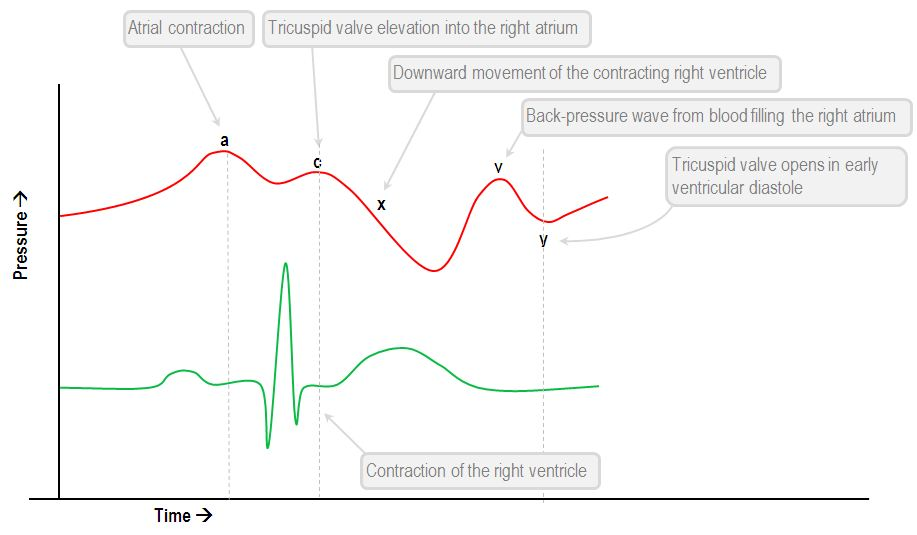
The y descent in atrial pressure tracings represents _____ of the atrium as blood flows into the ventricle.
and opening of the ______ valve
represents emptying of the atrium
opening of the tricuspid valve
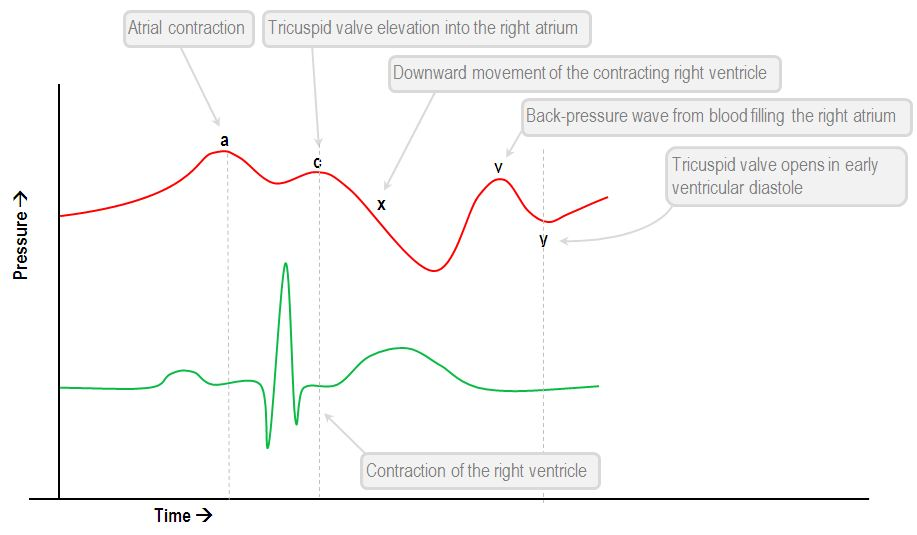
In a fib the absence of coordinated atrial contraction leads to loss of the ___ wave
In the ECG the **** wave is absent due to fibrillation
A wave for pressure waveform
p wave for ECG
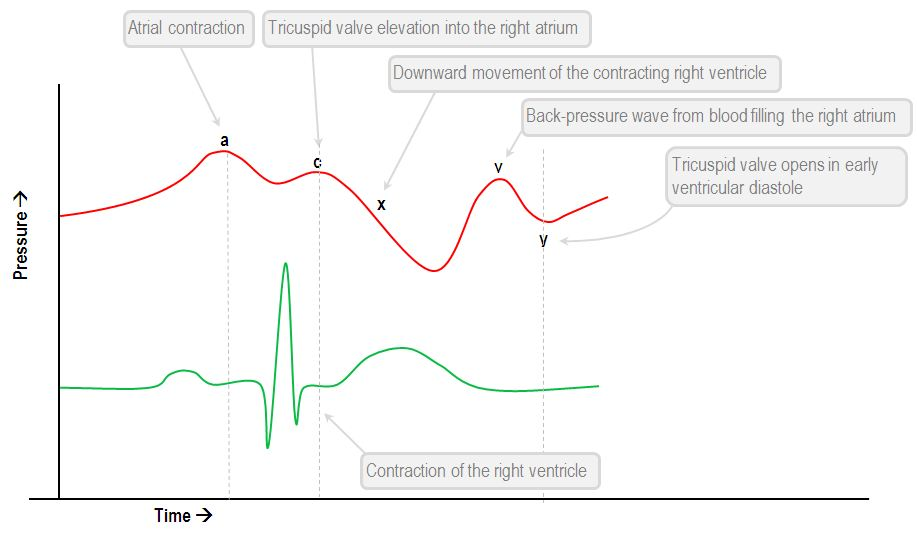
Tricuspind regurg causes an exaggerated ____ wave due to backflow of blood into the RA
V wave
In the PA waveform the dicrotic notch reflects closure of what valve
pulmonary valve
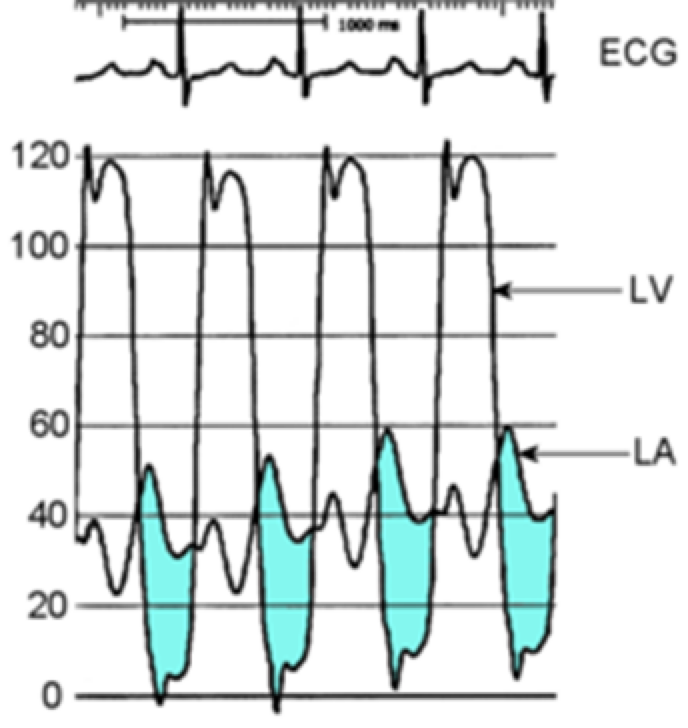
What is going on here
Mitral stenosis.
Blues represent the diastolic pressure gradient due to stenotic valve
elevated LA pressure due to backup in LA
Good representation for increased preload
- The most common cause of mitral stenosis is prior ____ ______ (50%- 70% of patients with symptoms)
rheumatic fever
left atrial (LA) waveform, the A wave typically occurs just ____ the ____
Before the QRS
in the right atrial (RA) waveform, the ***** (first wave) typically follows the *** on the electrocardiogram (ECG)
A wave typically folllows the p wave
Cardiac tamponade leads to blunted ____ and _____ due to impaired atrial filling and emptying
X & Y
What is normal LVEDP
Normal left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is typically between 4 and 12 mmHg, indicating proper filling pressure in the left ventricle.
The A wave represents __
The A wave represents (1) atrial contraction;
LVEDP greater than 12 mmHg usually suggests_______________, often seen in______ or ____ dysfunction.
LVEDP greater than 12 mmHg usually suggests increased left ventricular filling pressure, often seen in heart failure or LV dysfunction.
The dicrotic notch reflects the ___ during the cardiac cycle, marking the end of ventricular systole.
The dicrotic notch reflects the (1) closure of the pulmonic valve.
EDP stands for ___ , which is caused by the ___________ after filling, influencing the stroke volume.
EDP stands for (1) End Diastolic Pressure, which is caused by (2) blood volume in the ventricle after filling.
Ficks principle measures how an organ takes in or releases oxygen based on the differences in __________
oxygen concentration levels
A Stroke Volume (SV) represents the volume of blood ___ from the heart with each ___ , contributing to overall cardiac performance.
A Stroke Volume (SV) represents the volume of blood (1) ejected from the heart with each (2) contraction.
The normal percentage of ejection fraction is ___, indicating healthy left ventricular function and overall cardiac health.
The normal percentage of ejection fraction is (1) 50% - 70%.
Factors that increase preload include ___ circulating volume & _(valve problem)__ and ___ , leading to enhanced cardiac filling.
Factors that increase preload include (1) increased circulating volume, (2) mitral regurgitation (build up in the retro side), and (3) heart failure. (reduced CO so body activates compensation mechanisms like RAAS that lead to fluid overload)
Increased afterload on the heart would be indicated by ___ (1) and increased ___ ), making it harder for the heart to pump efficiently.
Increased afterload on the heart would be indicated by (1) hypertension and increased (2) systemic vascular resistance (SVR).
The normal systolic pressure range for the aorta is ___ (1) between 100 and 140 mm Hg, which is critical for ensuring adequate systemic perfusion.
The normal systolic pressure range for the aorta is (1) 100 - 140 mm Hg.
The 'V' wave corresponds to _____ to the __ while the ___valves is________ during the cardiac cycle.
The 'V' wave corresponds to (1) venous return to the atrium while the (2) AV valve is closed.
Isovolumetric contraction is characterized by a significant rise in ___ without a change in __ ___ until the ___ valves opens for ejection.
Isovolumetric contraction is characterized by (1) a rise in ventricular pressure without a change in volume until the (2) semilunar valve opens.
Normal pulmonary artery pressures are characterized by a systolic range of ___ and an end-diastolic range of ___ , reflecting healthy right heart function.
Normal pulmonary artery pressures are characterized by a systolic range of (1) 20-40 mmHg and an end-diastolic range of (2) 8-12 mmHg.
25/10
The formula for mean arterial pressure (MAP) consists of the components: ___ (1) MAP = DBP + (SBP - DBP) / 3, providing insight into overall arterial pressure during the cardiac cycle.
The formula for mean arterial pressure (MAP) consists of the components: (1) MAP = DBP + (SBP - DBP) / 3.
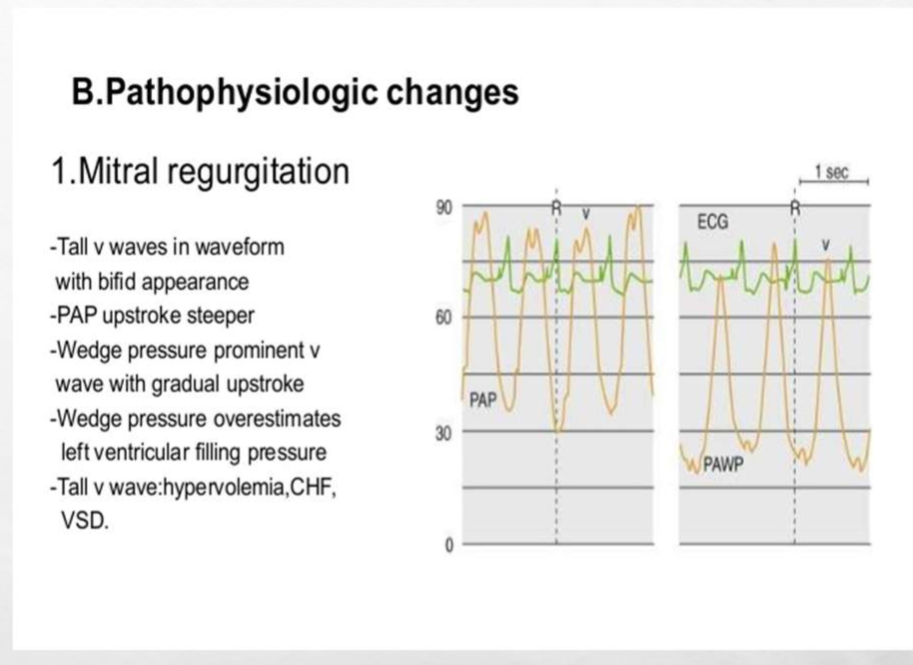
A tall 'V' wave in mitral regurgitation suggests ___ which can indicate worsening heart function or volume overload states.
A tall 'V' wave in mitral regurgitation suggests (1) hypervolemia and congestion.
Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) may indicate ___ or ___ serving as a marker for elevated left atrial pressure.
Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) may indicate (1) left ventricular failure or (2) mitral stenosis.
The relationship between stroke volume and ejection fraction is that ejection fraction represents the percentage of **** **** in relation to *** **** volume.
The relationship between stroke volume and ejection fraction is that ejection fraction represents the percentage of (1) stroke volume in relation to (2) end-diastolic volume.
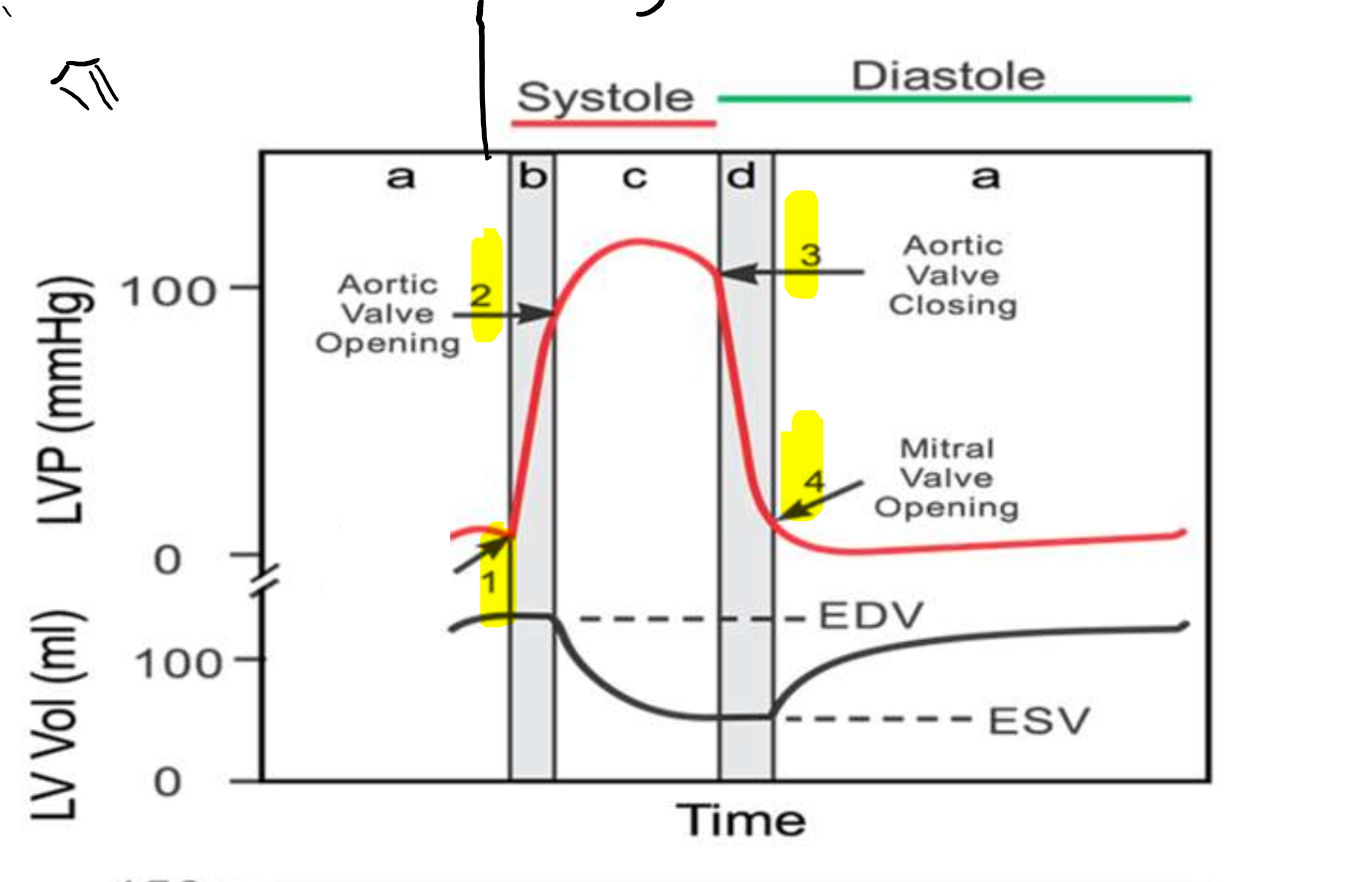
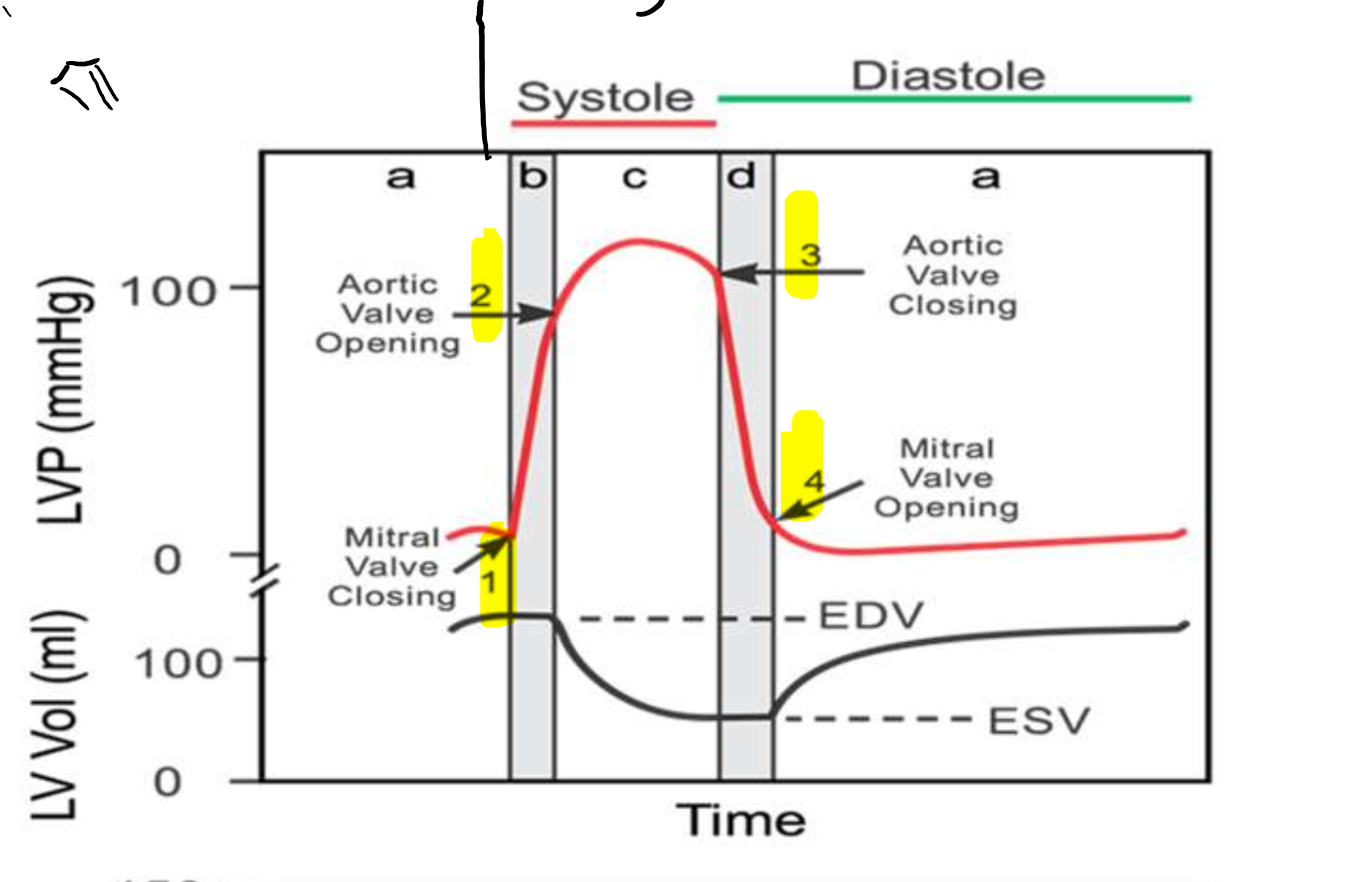
What is occurring at step 1?
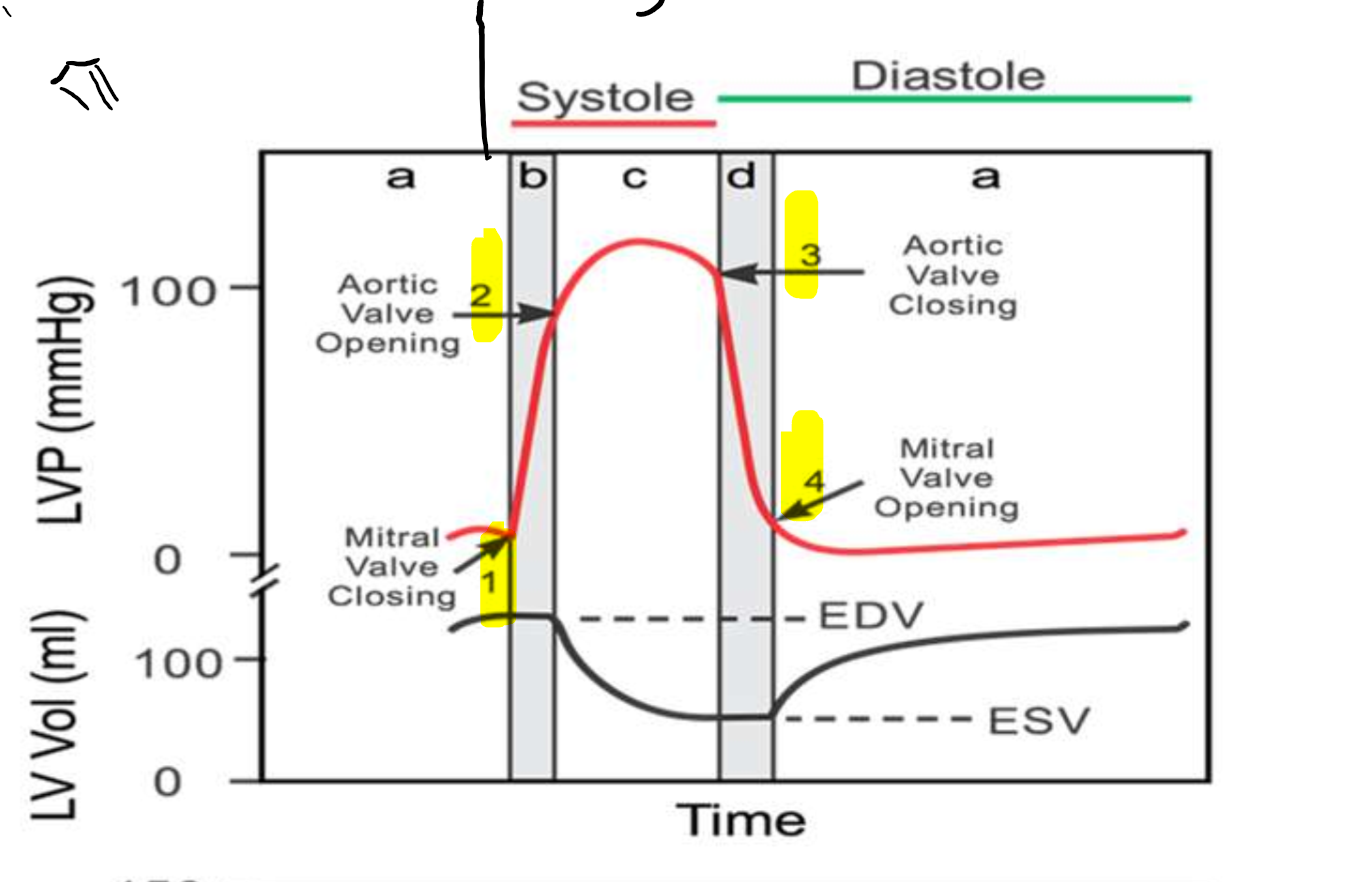
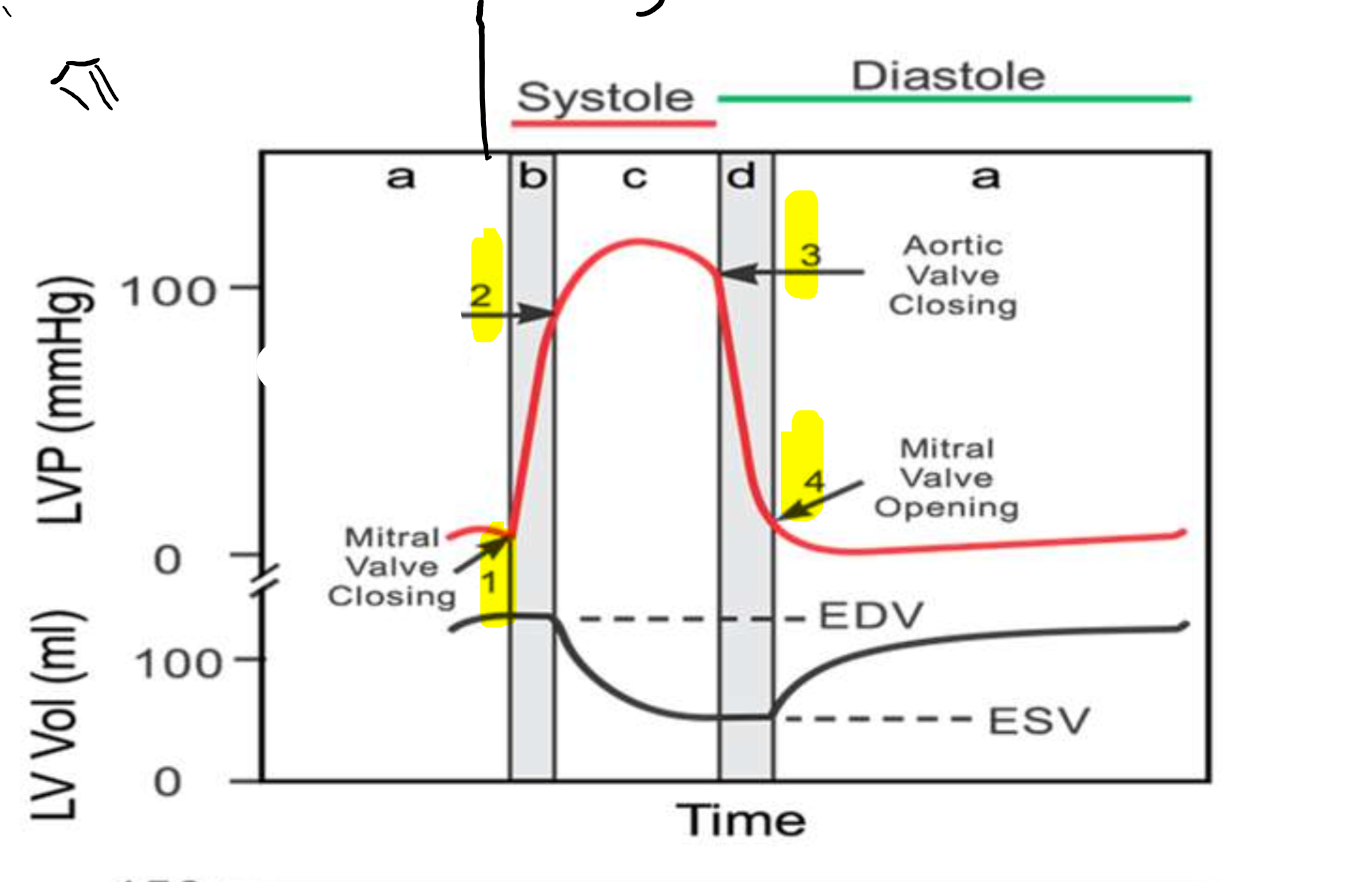
What is occurring at step 2?
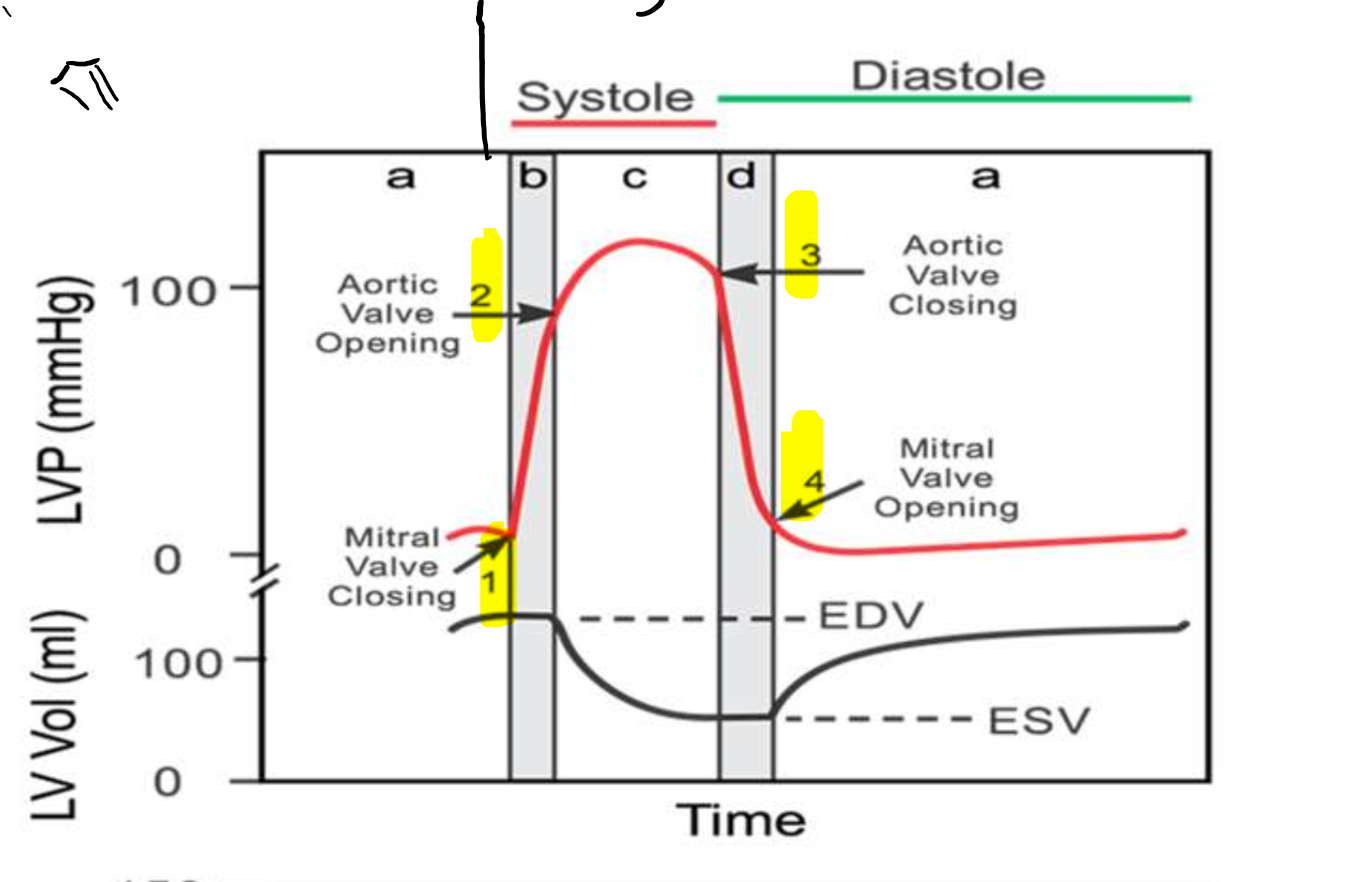

What is occurring at step 3?
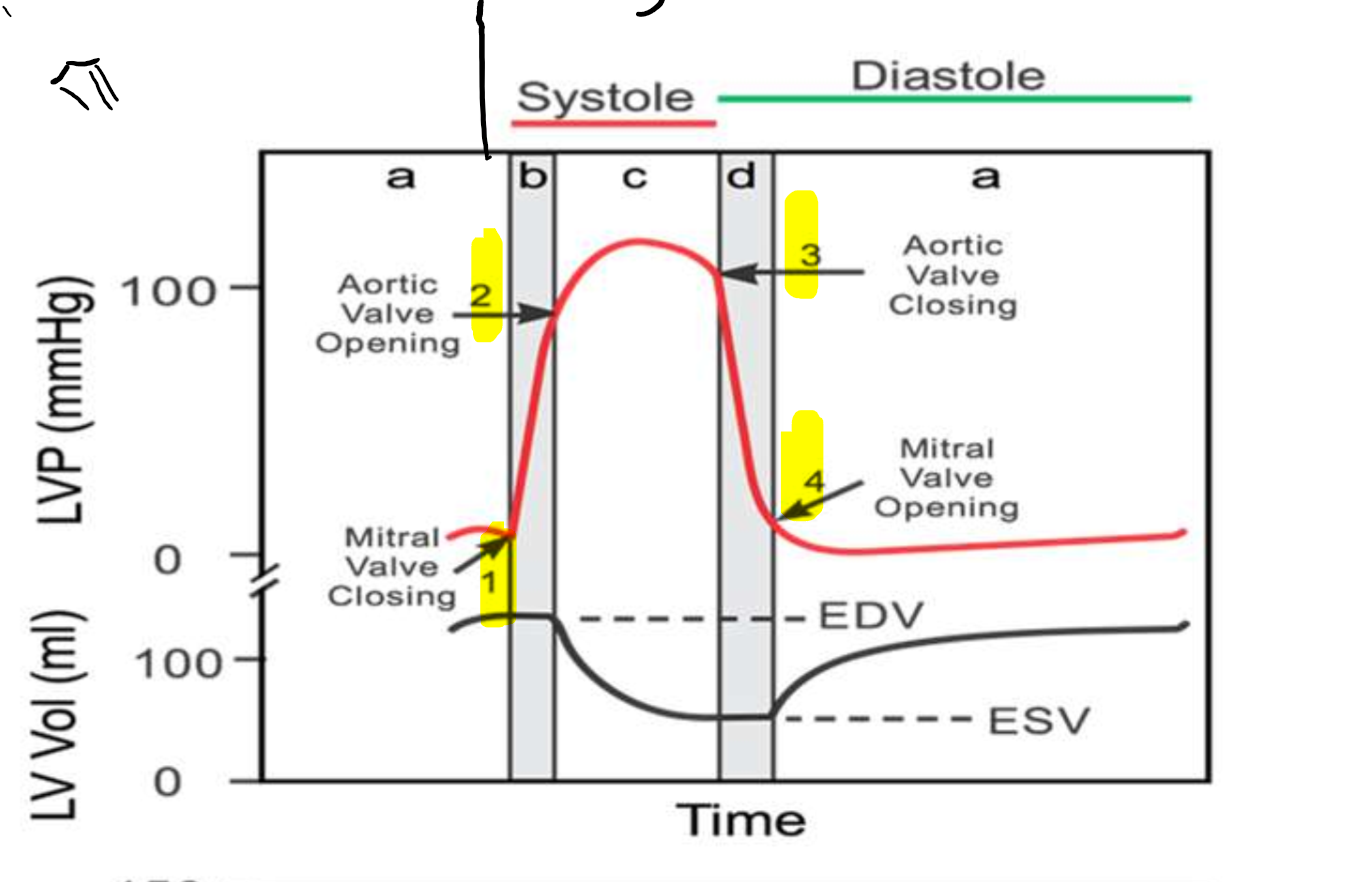
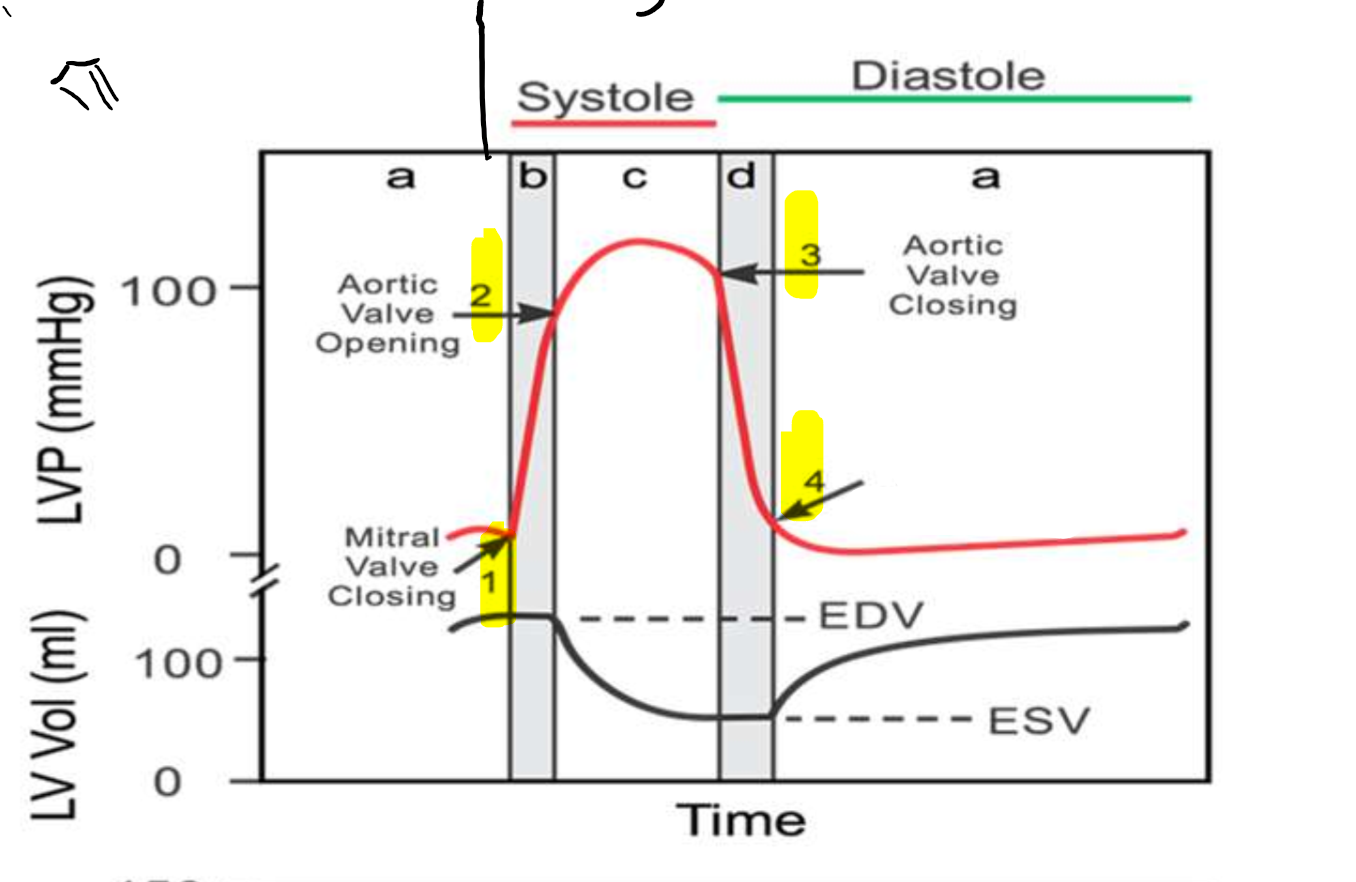
What is occurring at step 4?
dicrotic notch on an arterial pressure waveform represents the ****** of the **** valve
closure of the aortic valve
average RV EDP is
5 mmHg
at what point is EDP taken in the LV
during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle, specifically when the left ventricle is at its fullest. Just about when wave reflects up.
average RV pressures
25/5
average LV EDP
8 or 5-12 mmHg
Normal LV pressures
128/10
The difference between diastolic pressure and EDP is diastolic is taken at the ***** ****** in the LV during diastole
Lowest pressure
The difference between diastolic pressure and EDP is EDP is at the end of diastole taken just before the *** *** *****
ventricle: lv and rv whats the answer
just before the outflow valve opens; primarily ventricles;
LV just before ao valve opens
RV b4 PV opens
just before isovolumetric contraction begins
Pulse pressure is found by the **** between *** and ***** pressure
difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure.
PP = *** - ****
PP = SYSTOLIC - DIASTOLIC PRESSURE
map = *** + 2*** / *
SBP + 2DBP / 3
MAP for PA is typically
10-20 mmHg
the PA peak systolic range is
20-40 mmHg
the PA diastolic range is *** mmHg
8-12 mmHg
PA sys/diast pressure is typically
20-40/8-12 mmHg
2 potential causes for ^ PCW pressure
LV failure
MS
LVEDP is a good indicator for ***** heart *****
overall heart funciton
5 causes for ^ RA press
PHTN
TR
RVMI
PE
L>R SHUNT
^ RV pressure
PHTN
PVALVESTENOSIS
PE
L>R SHUNT
^ PA PRESS
PHTN
COPD
MS
PE
L>R SHUNT
Range for Ao systole pressure
100-140 mmHg
Range for Ao diastolic pressure
60-80 mmHgThe normal range for aortic diastolic pressure is typically between 60 and 80 mmHg, indicating the pressure in the aorta during the heart's relaxation phase.
MAP for Ao
70 - 90 mmHg
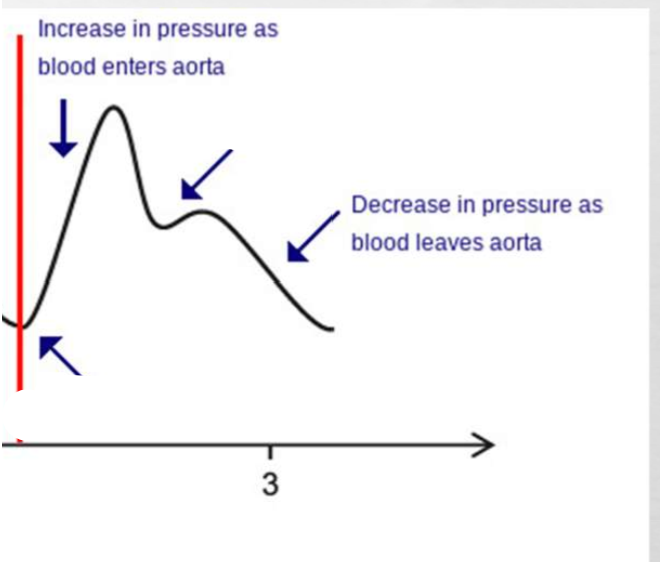
what is occurring at these blanks and what do they signify
signify.. start of what cycle
and the end of what
indicate the closure of valve signifying the end of systole and the beginning of diastole
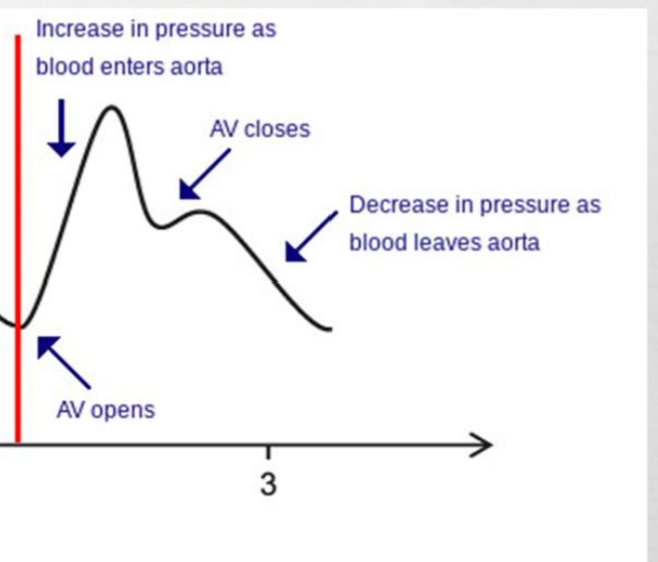
the dicrotic notch displays the closure of the aortic valve and indicates the beginning of the **** ****
diastolic phase
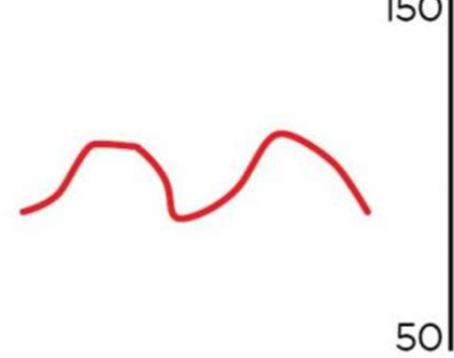
what is occurring in this arterial waveform
overdamped
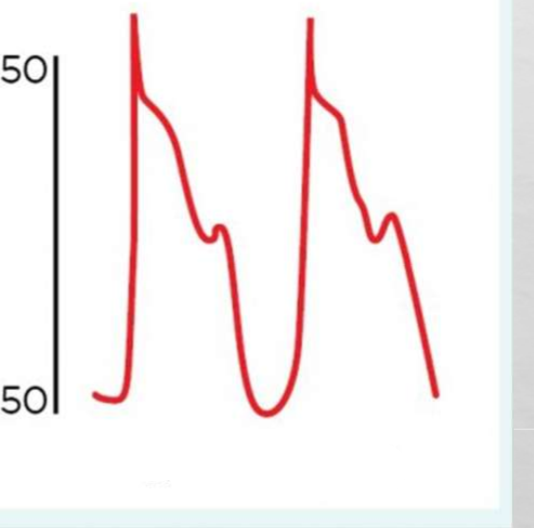
Whats occurring in this
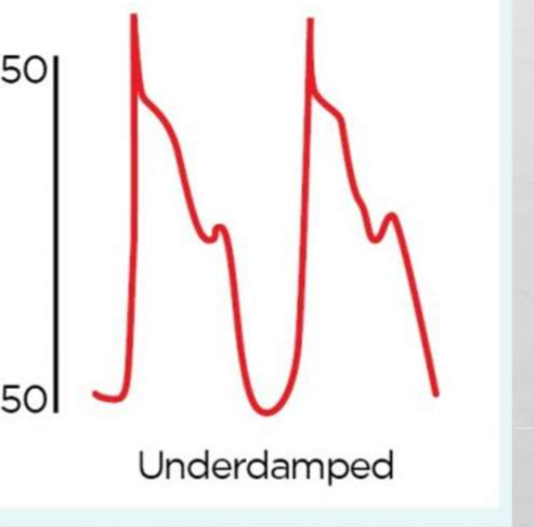
What is occurring in this waveform
Ventricularization from cto of CA and the ventricle muscle sucks the catheter
50-70% EF signify what
normal function
what percentage is considered high EF
70%
EF is calculated by what equation
SV/EDV
SV is calculated by what equation
EDV - ESV
these 3 issues decrease preload
decreased circulating volume (dehydration, hypovolemia)
MS (narrow valve limits blood flow into LV)
asynchorny of a/v (torsads or pulse alternans) (decreased ventricular filling time, weak beats weat stroke volume, chaotic electrical activity leads to ineffecive ventricular contractions)
4 problems that increase preload
increased circulating volume
MR
HF
AR
Vasodilators do what to preload
decrease
vasoconstrictors do what to preload
increase preload
vasopressors do what to afterload
increases
vasopressors do what to BP
INCREASE by constrictive vessels
its in the name
vasodilators do what to afterlaod
decreases afterload
easiest way to assess afterload is measuring **
BP
Fick principle states that An organ absorbs or releases a substance depending on how much the substance changes in the blood as it passes through and how much blood is flowing through the organ
Fick principle states that An organ absorbs or releases a substance depending on how much the substance changes in the blood as it passes through and how much blood is flowing through the organ
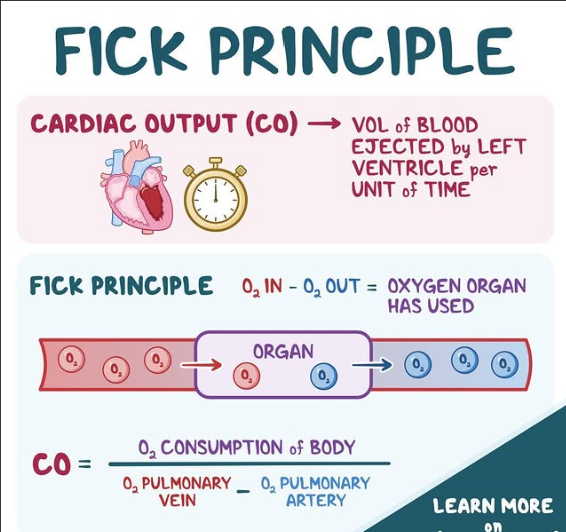
CO(f) is calculated by
O2 CONSUMPTION / AVO2 DIFFERENCE
The principle states that the amount of oxygen consumed by the body is equal to the amount of oxygen delivered to the tissues, which can be used to estimate cardiac output.
by using oxygen consumption and the arteriovenous oxygen difference, providing an indirect measure of how efficiently the heart is pumping blood to deliver oxygen to tissues.
O2 consumptions / AVO2 difference solves for what
CO(f)
thermodilution injection require syringes fill with what amount
10ml for adults
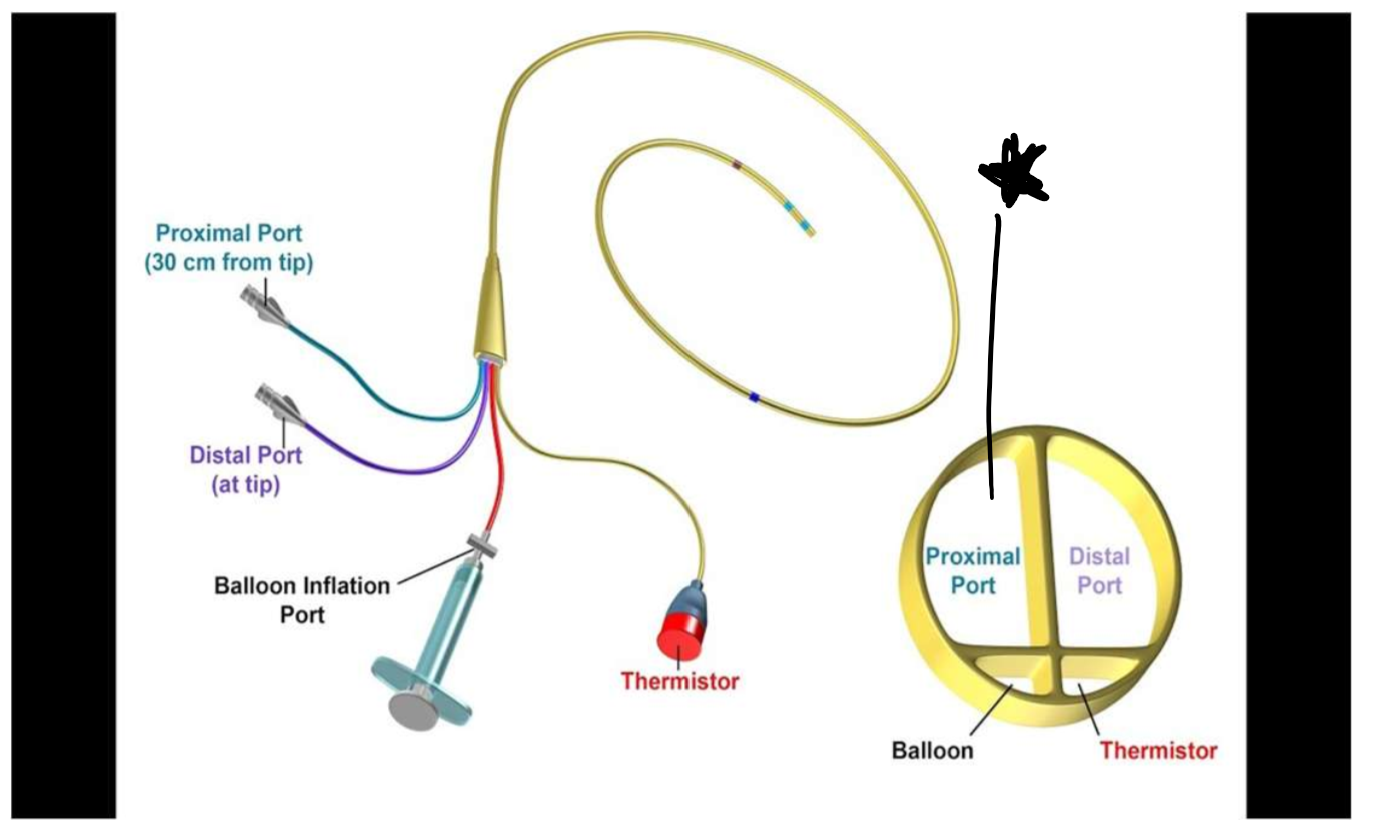
Label this lumen
CO (angiographic) easy calculation
sv x hr
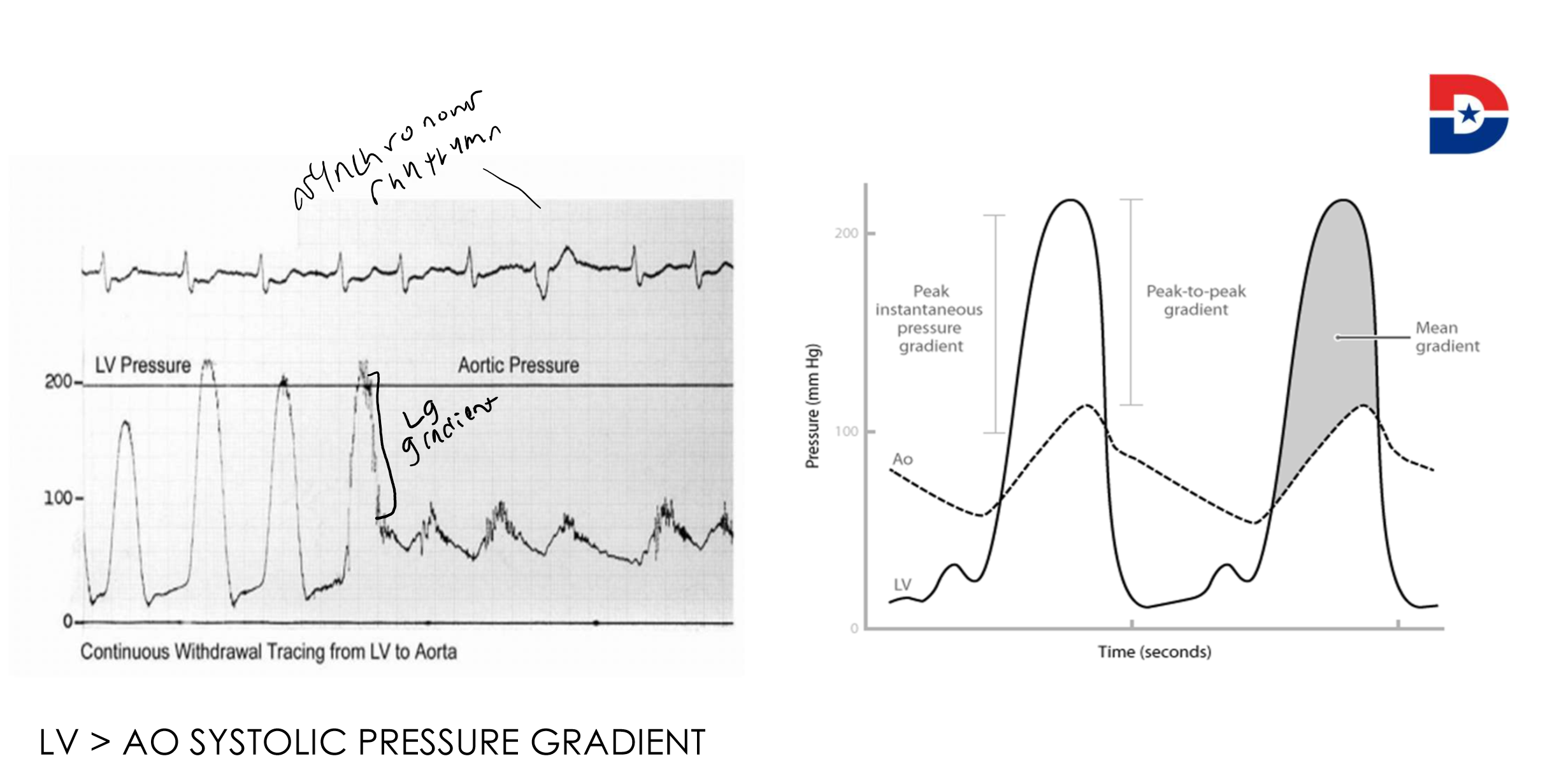
What does this indicate
Aortic stenosis
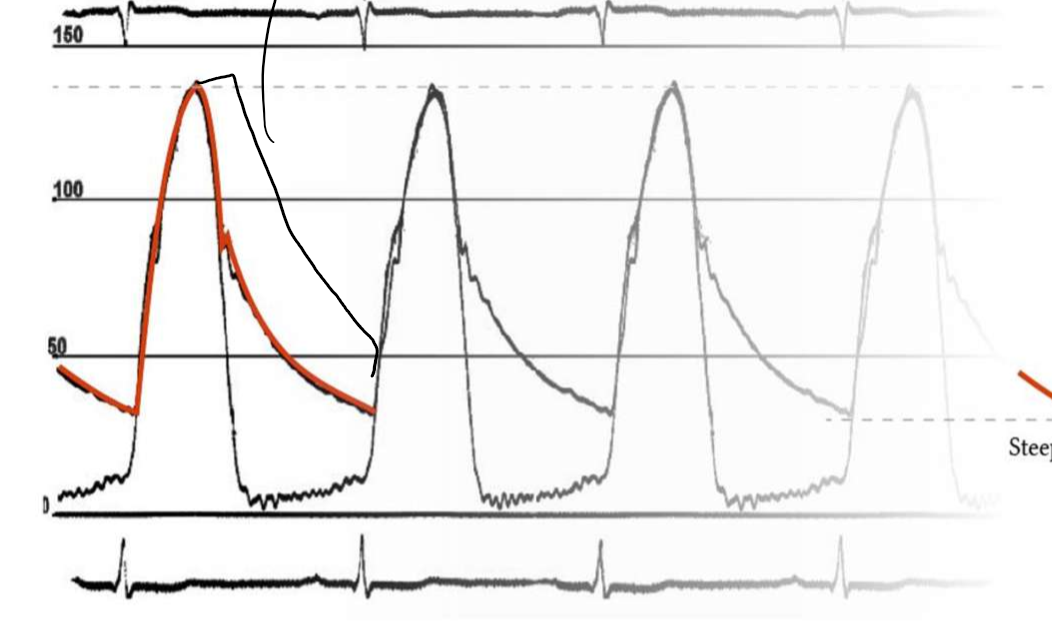
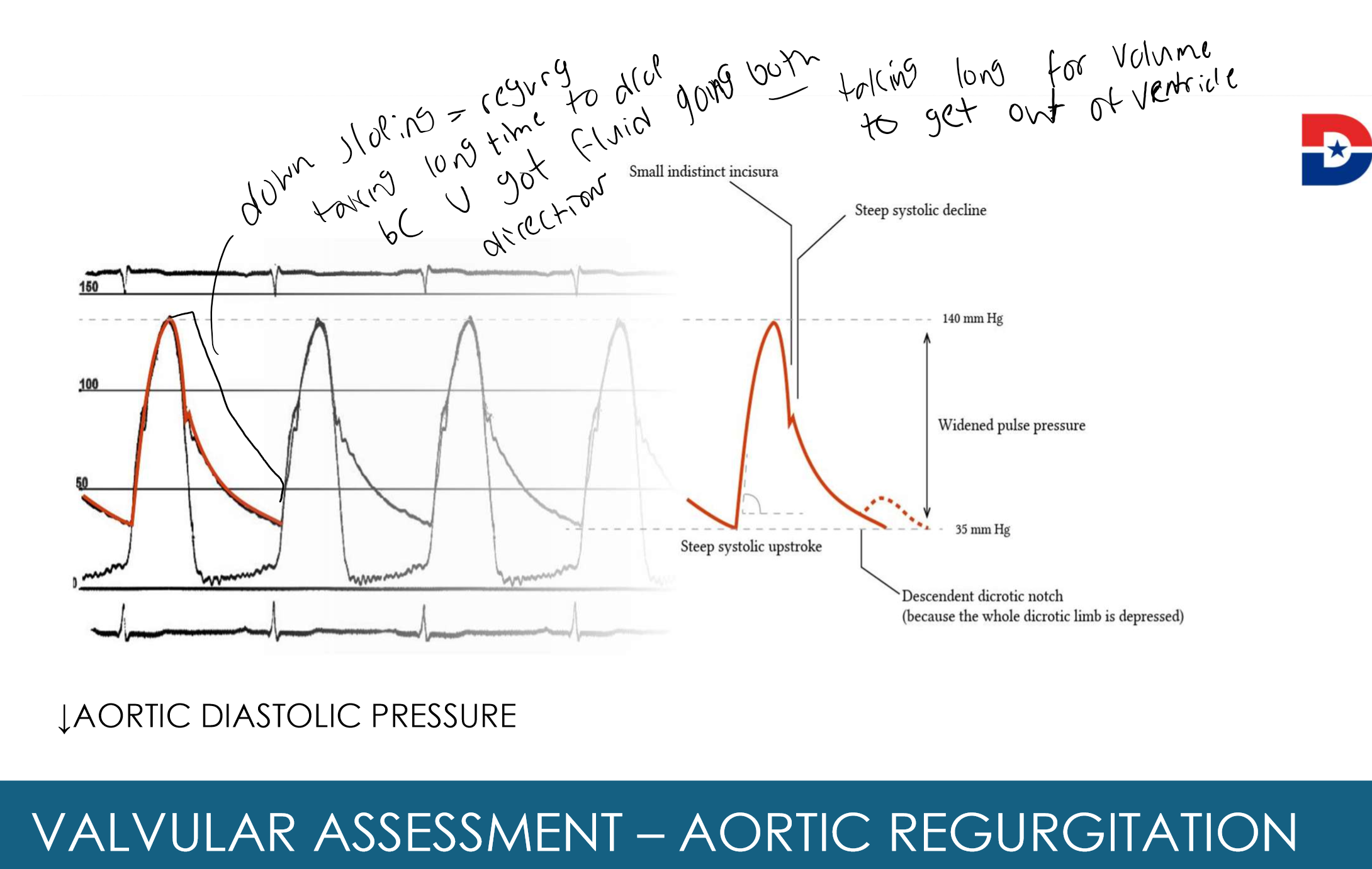
What does this indicate
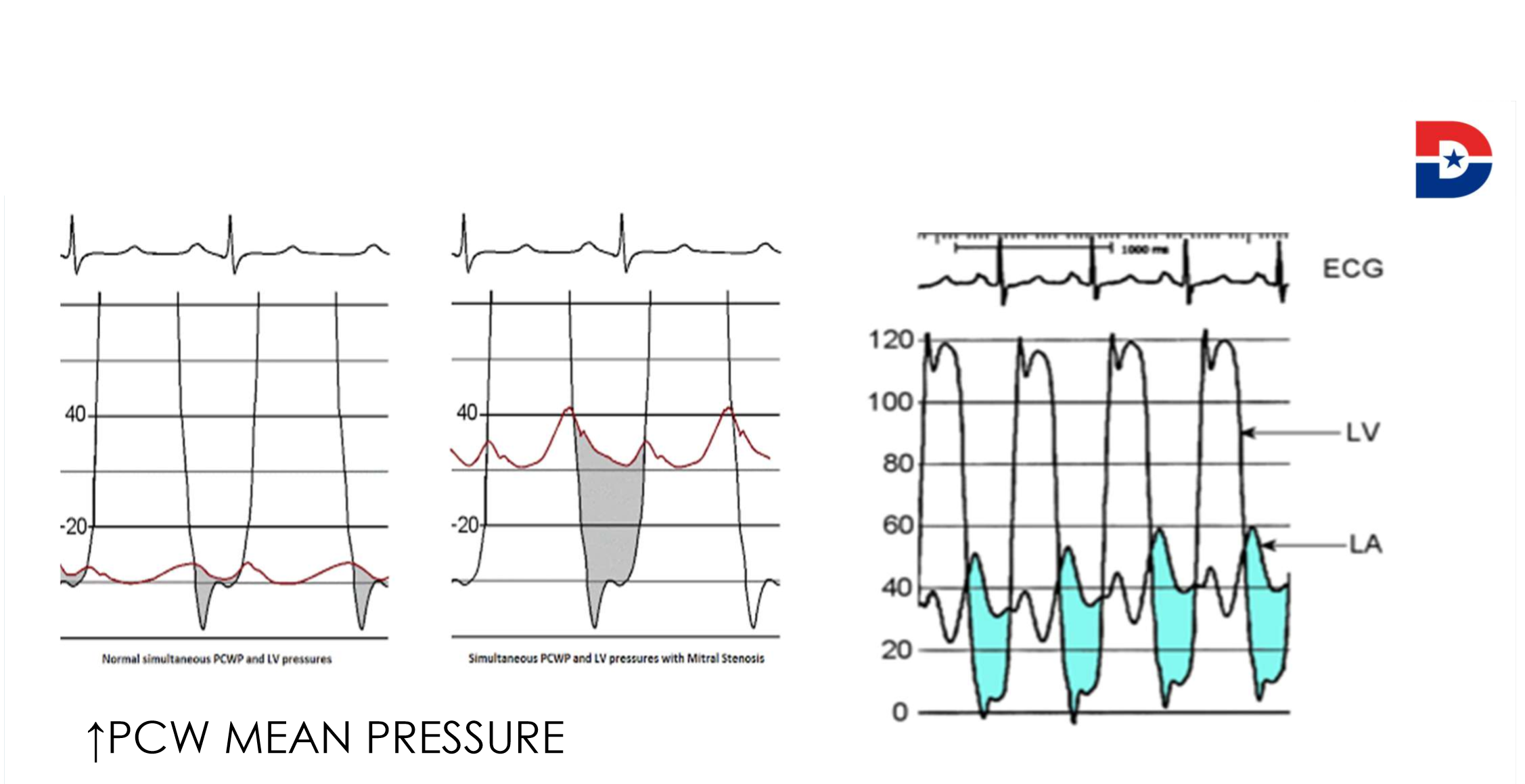
What is occurring here
mitral stenosis
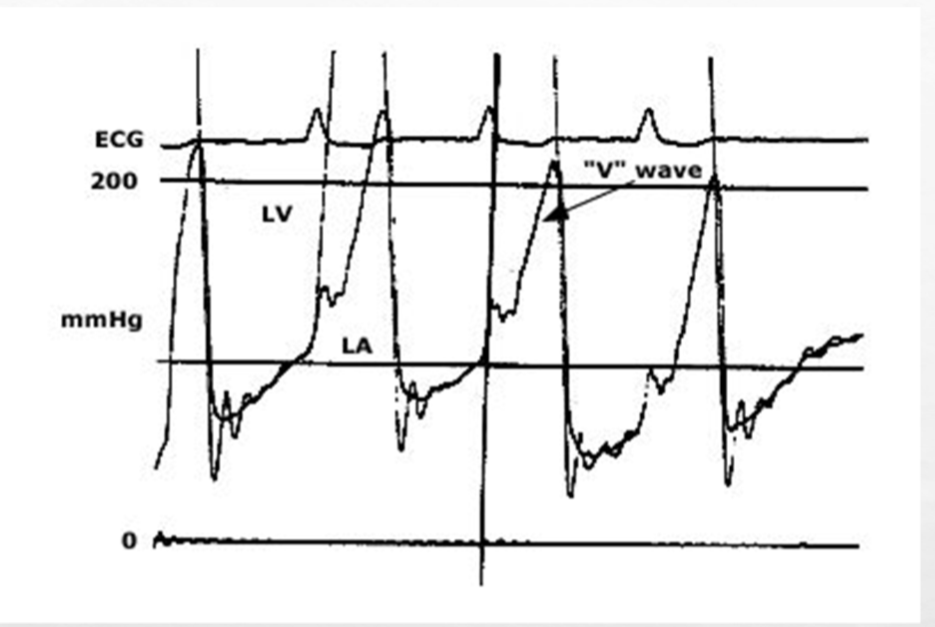
increased V wave in PCW signifies what valvular assessment
MR
normal RV sat
75%
normal RA pressure
2-6 mmHg
normal PA saturation
approximately 75%
normal PA pressure
20/8
normal lv sat
95%
normal la sat
95%
normal mean LA pressure
<8
normal RA mean
<5pressure in mmHg