DNA Profiling II
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Allele frequencies
To calculate the significance of a match the frequency of an allele must be calculated
Number allele occurs / Total number of possible alleles = frequency of that allele
If 20 of a given allele is observed in a population group of 100, the frequency would be…
20 / 200 = 0.1
Hardy-Weinberg equations
PP (homozygotic) = p2
QQ (homozygotic) = q2
PQ (heterozygotic) = 2pq
Find allele frequency on the allelic frequency table
Multiply all the results of each STR together
Then do 1 / answer
Example of Hardy-Weinberg
Example 2
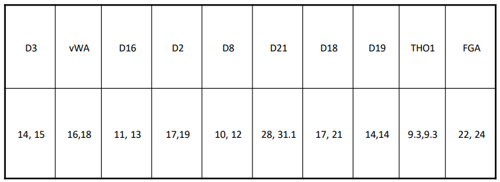
D2 – 17, 19
Heterozygotic, so 2pq
2 x 17 x 19
Example 3
THO1 – 9.3, 9.3
Homozygotic, so p2
9.3 x 9.3
The National DNA Database (NDNAD)
Held by the Home Office
Criminal justice forces feed into the database
Buccal scrape kit (a cheek swab) is how DNA data is collected
Current criteria for sampling is all arrestable offences
Samples are kept in the UK, but in other countries this can differ
Missing Persons DNA Database (MPDD)
2000 profiles held on here from people who have disappeared or family members who have given their profiles for matching
Not held on the NDNAD
Each year these produce ~15 matches
Vulnerable Persons DNA Database (VPDD)
Anyone thought to be at high risk can request their profile is added
Not held on NDNAD
6200 profiles held
1-2 matches per year
Police Elimination Database (PED)
All serving police profiles held for elimination from crime scene samples
Held for 12 months after they leave
Removal of samples
DNA profiles and fingerprints of anyone convicted of a recordable offence will be stored permanently
Those obtained on arrest even with no conviction will be stored for 6 years
Renewable on new arrests
Mass screens
Involves major crime, murder, abduction or rate
Where police believe the offender is local
Where the population of potential offenders can be targeted
SNP analysis advantage
Good if the DNA is heavily degraded and contains short fragment sizes of 40-50 bp
SNP detection is highly suited to high throughput automated methods
SNP analysis disadvantage
Need to do more SNPs to get same information as STR typing
Require 50 – 70 SNPs to match STR analysis
SNP classifications
Transition
Transversions
Synonymous
Non-synonymous
Transition
Same base is retained e.g. purine to purine
Transversions
Base change e.g. pyrimidine to purine
Synonymous
Mutation does not change the amino acid
Non-synonymous
Mutation does change amino acid
Genetic markers
Large numbers
Stable
Spread out uniformly across genome
Genetic markers uses
Complex diseases
Pharmacogenomics
Genetic markers
Forensics
Population, migration genetics
Genetic markers forensic uses
Mitochondrial DNA sequences
Y chromosome genetic markers in paternity cases or sexual assault
Degraded DNA samples
SNPs for physical appearance
Tells you above physical appearance and height
Pigmentation can tell location on body, age and gender
Geographic ancestry
Detecting SNPs
Restriction digests
Molecular beacons
Multiplex PCR
Sequencing
Restriction digests
Make an EcoRI site GAATTC
Can check if they have SNP
If there is an SNP, it works vs if it doesn’t, there is no SNP
Molecular beacons
Hairpin-shaped fluorescent hybridisation probes
The ends of the oligonucleotide are designed to be complementary to each other and can form a stem structure
Intervening loop is complementary to a sequence within the amplified product
In solution, the unhybridised probe adopts a hairpin structure
If the molecular beacon is bound to its complementary target, the fluorophore and quencher are far enough apart that there is no quenching and the molecular become fluoresces
This can be detected in a real-life PCR machine
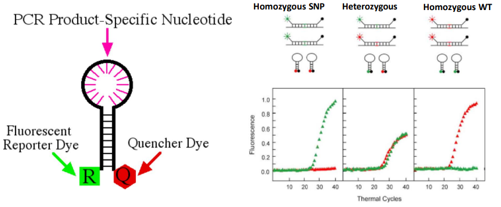
Molecular beacon results
The wild type is red vs SNP is green
Homozygous WT – only red
Homozygous SNP – green
Heterozygous – green + red
Multiplex PCR
Amplify mitochondrial PCR
Design set of forward and reverse primers which will produce different size amplicons covering different SNP sites
Protocol – amplify DNA with multiplex primers (10 SNPs)
Primer extends using SNaPshot – analyse sequencing on capillary gel DNA detection system
Sequencing
Next-generation throughput sequencing
Sanger-based dideoxy sequencing using fluorescent dye labelled terminators
Each nucleotide base has a different coloured dye which allows sequences to be determined from a single lane on a capillary gel by a scanning laser
Analysis on the Beckman CEQ 800
Analysis profiling
Use SNP-based profiling to produce a phenotypic description rather than DNA fingerprint
DNAWitness
This gives percentage of European, East Asian, Native American and Sub-Saharan African from DNA using 176 SNPs
Ratio of each for an individual is called the Bio-Geographical Ancestry (BGA) profile
Can use profile to give general characteristics of a suspect or victim without prior knowledge of the person