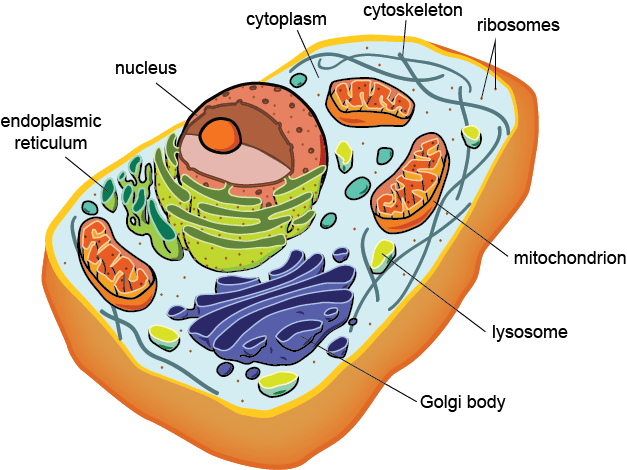
parts of animal and plant cells
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
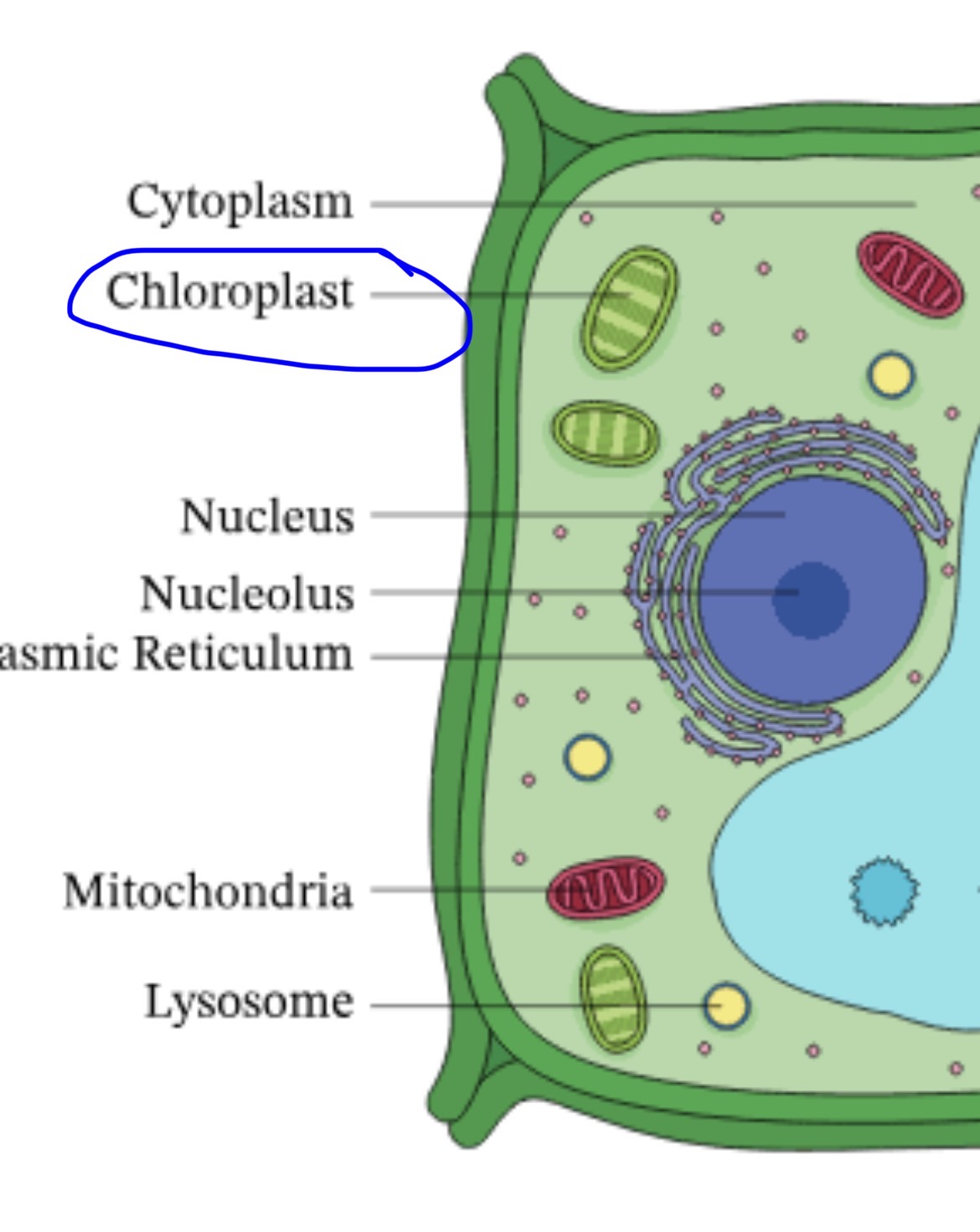
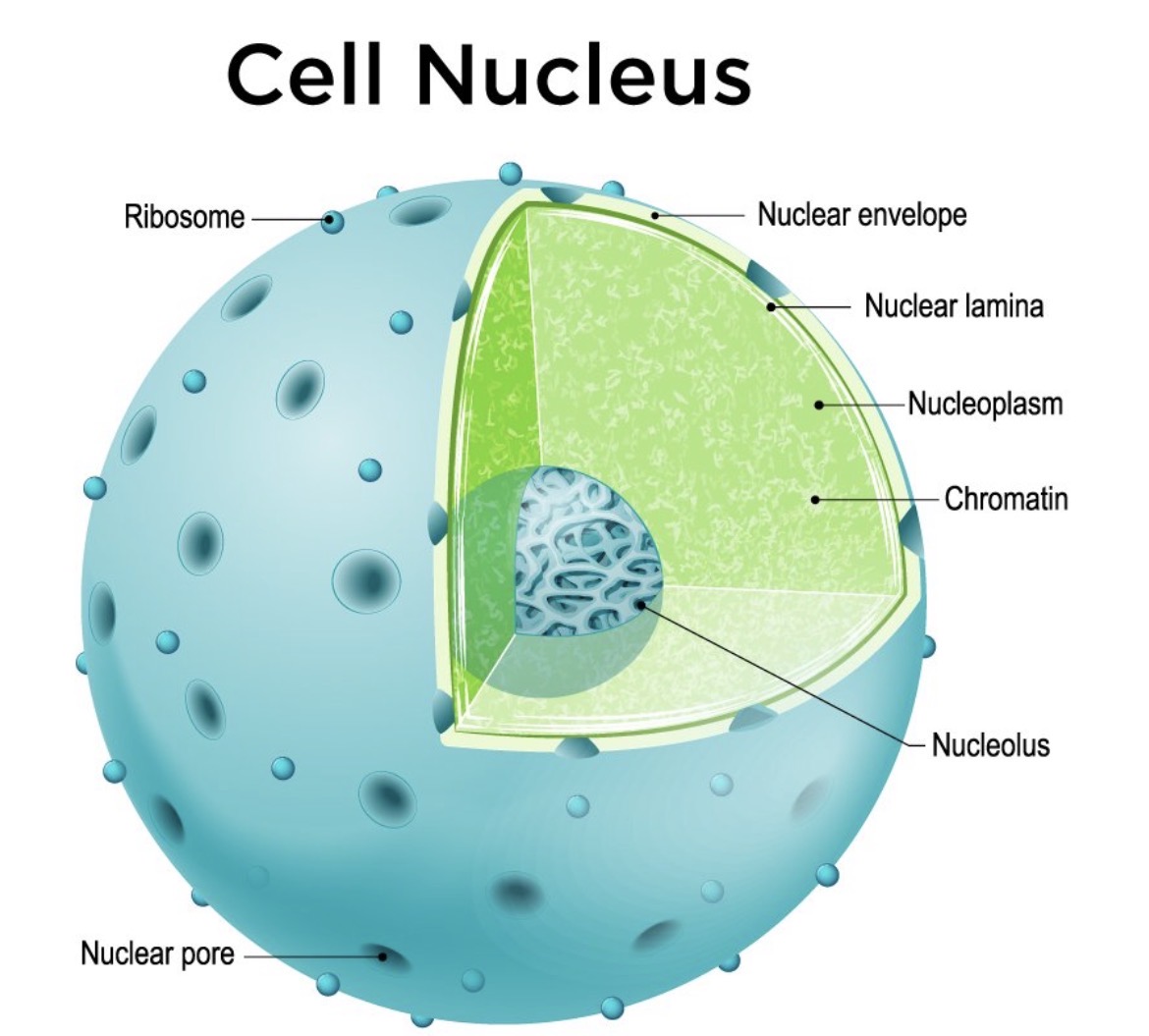
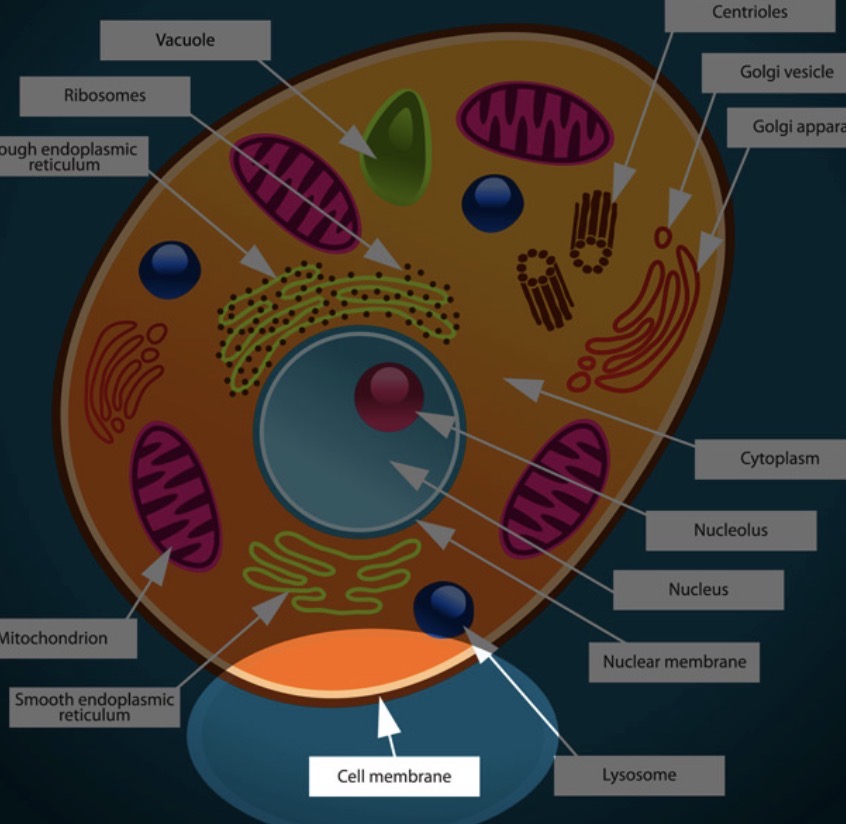
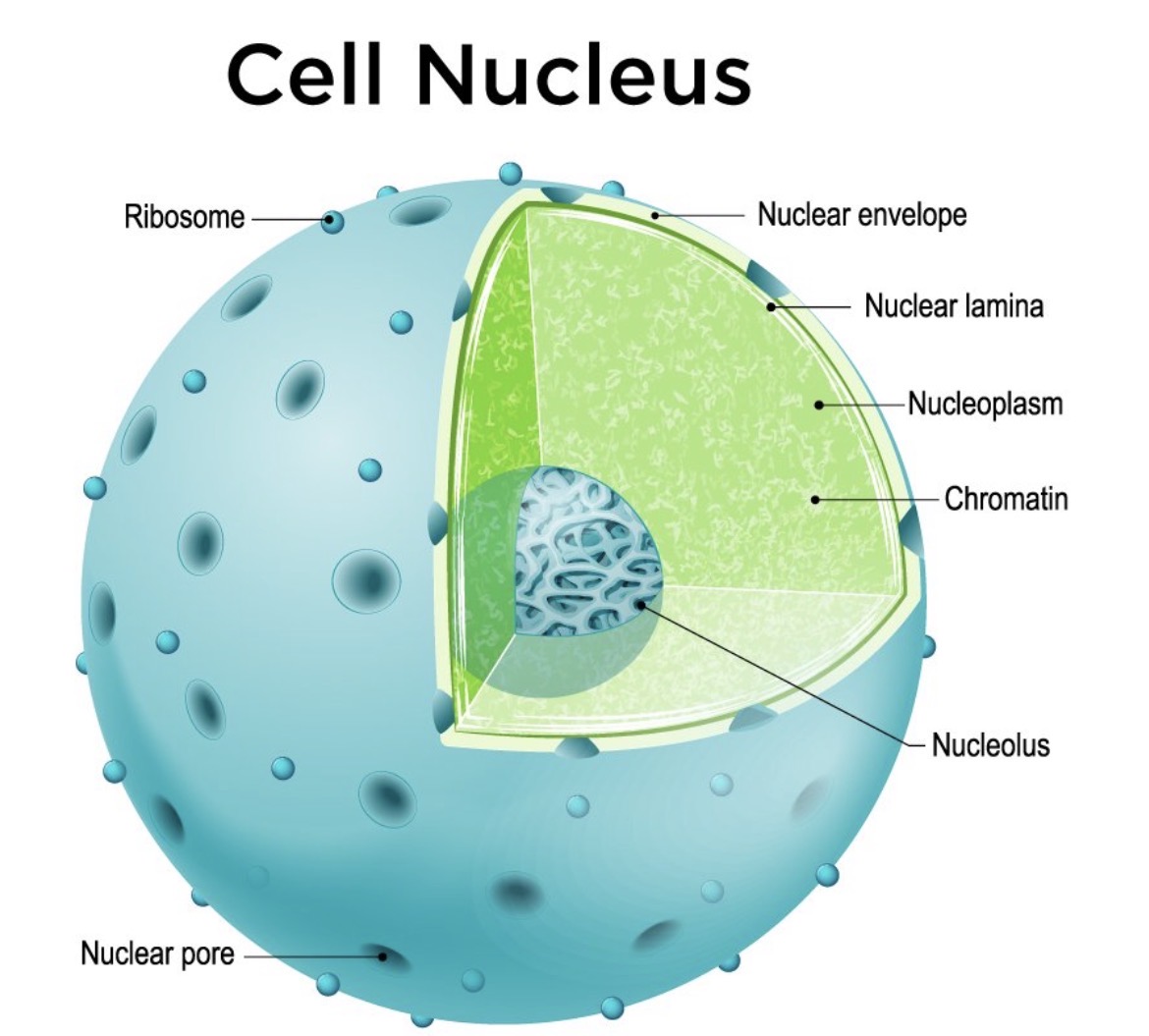
Nucleus
Stores genetic information (DNA) and controls the cell's activities, things move in and out
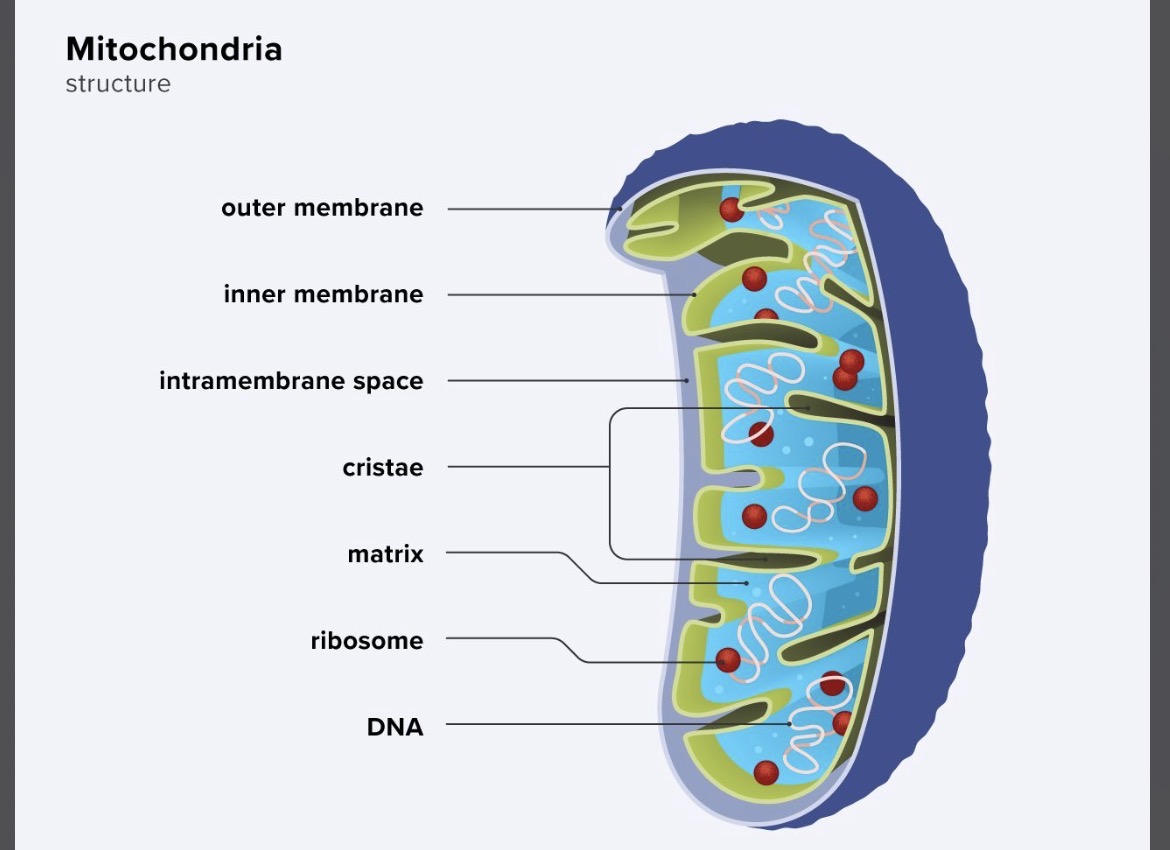
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell that create energy through cellular respiration, have their own DNA
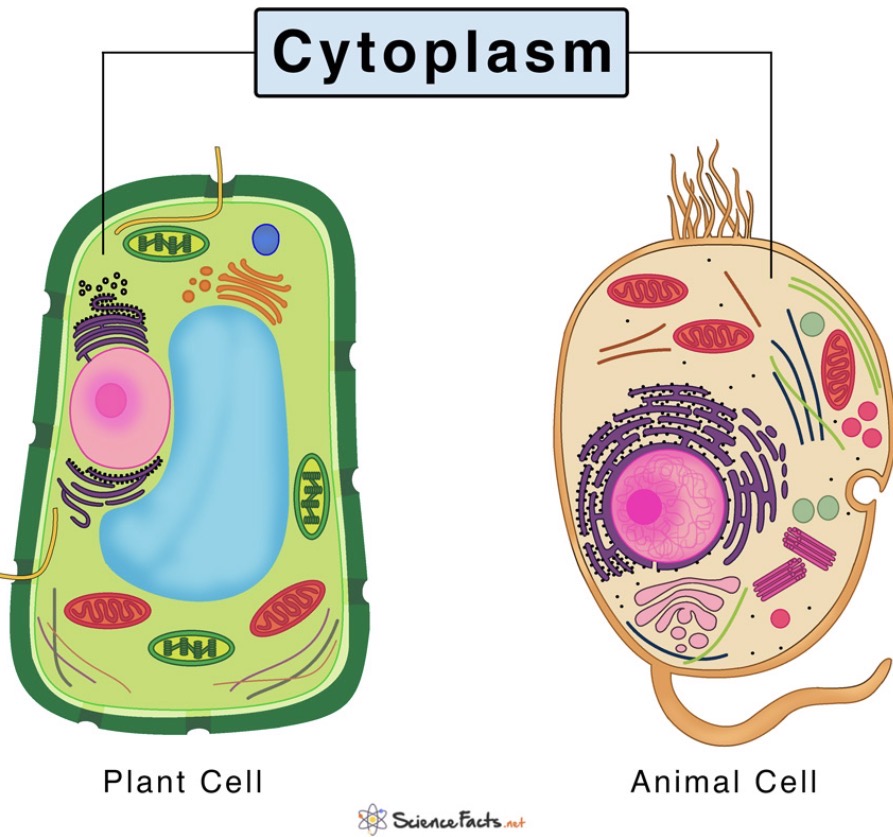
Cytoplasm
The jelly-like substance that fills the cell, where chemical reactions occur
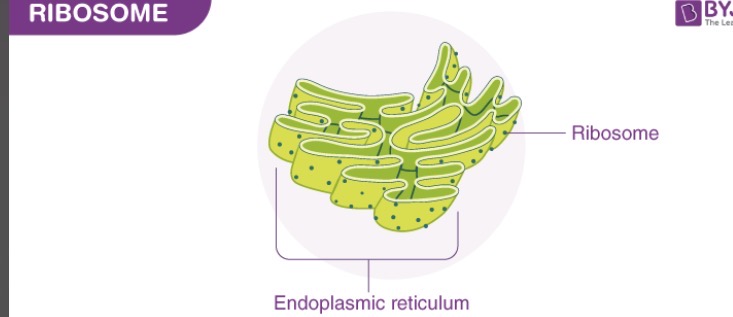
Ribosome
Responsible for making proteins, has two parts called the small and large subunits
Cell membrane
A flexible outer layer that separates the cell from its environment and controls which substances can enter and exit
Nucleolus
Where ribosomes are made, put out the genes in chromosomes
Vesicle
A membrane container, moves material around, are very small
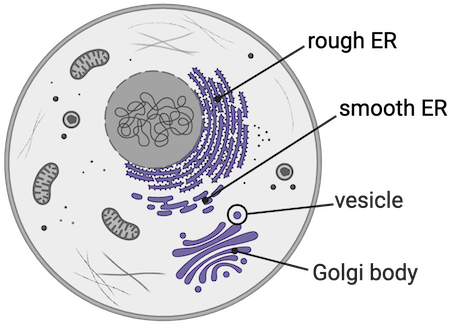
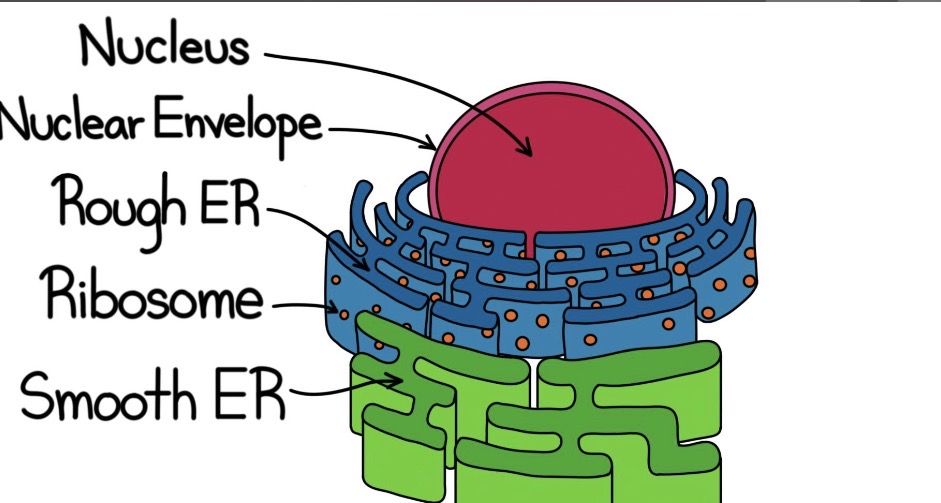
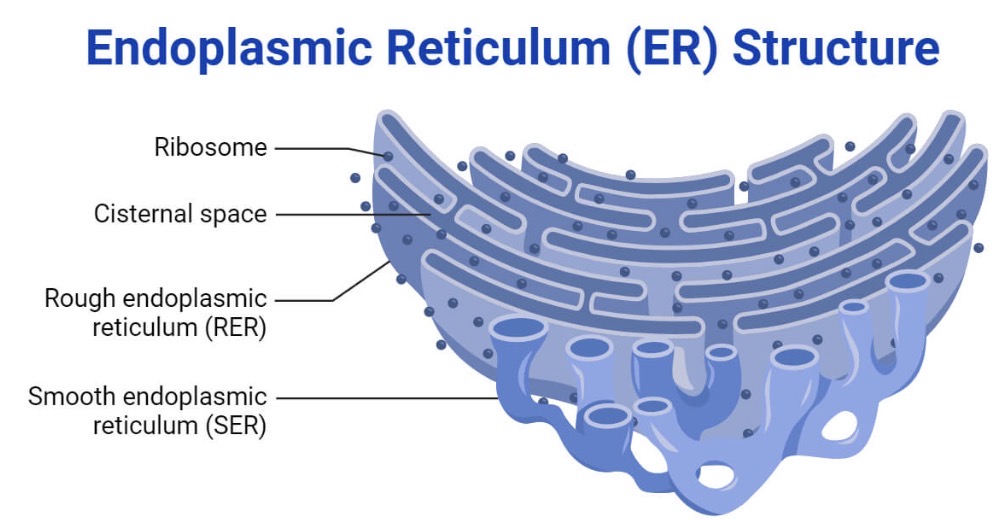
Rough ER
Membrane that is continuous with the nucleus, produces membranes, is like a factory
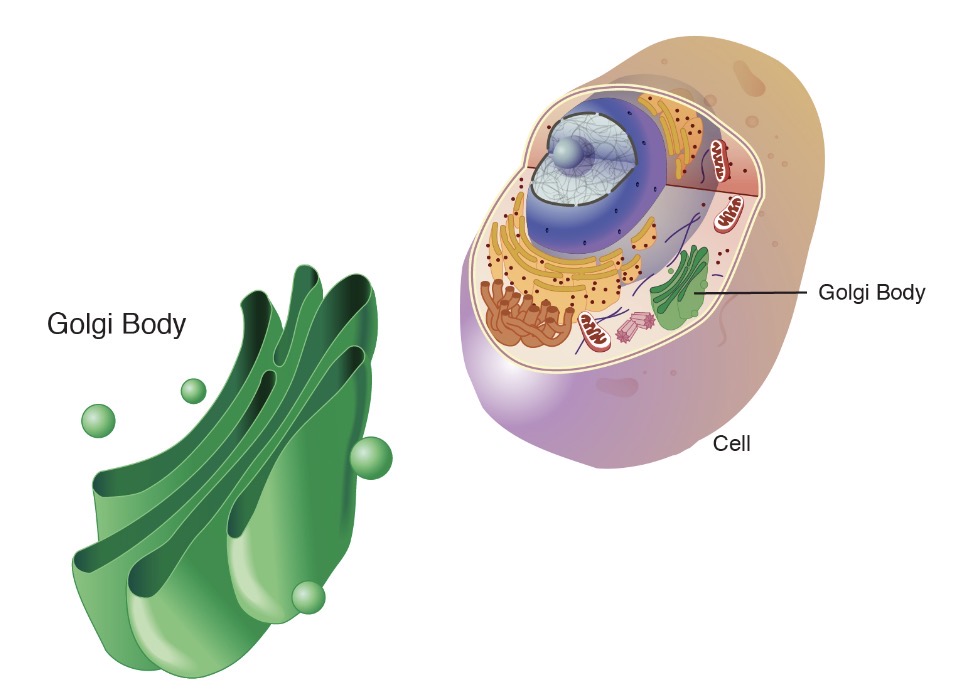
Golgi body
The proteins are transferred to this and they add things to the proteins
Cytoskeleton
Gives the cell structure, is like a bridge
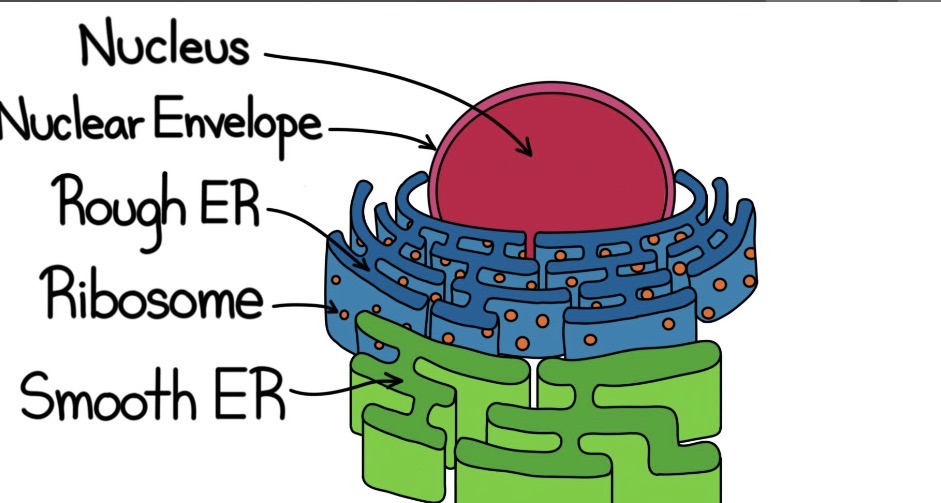
Smooth ER
Produces a lot of lipids, break down toxins
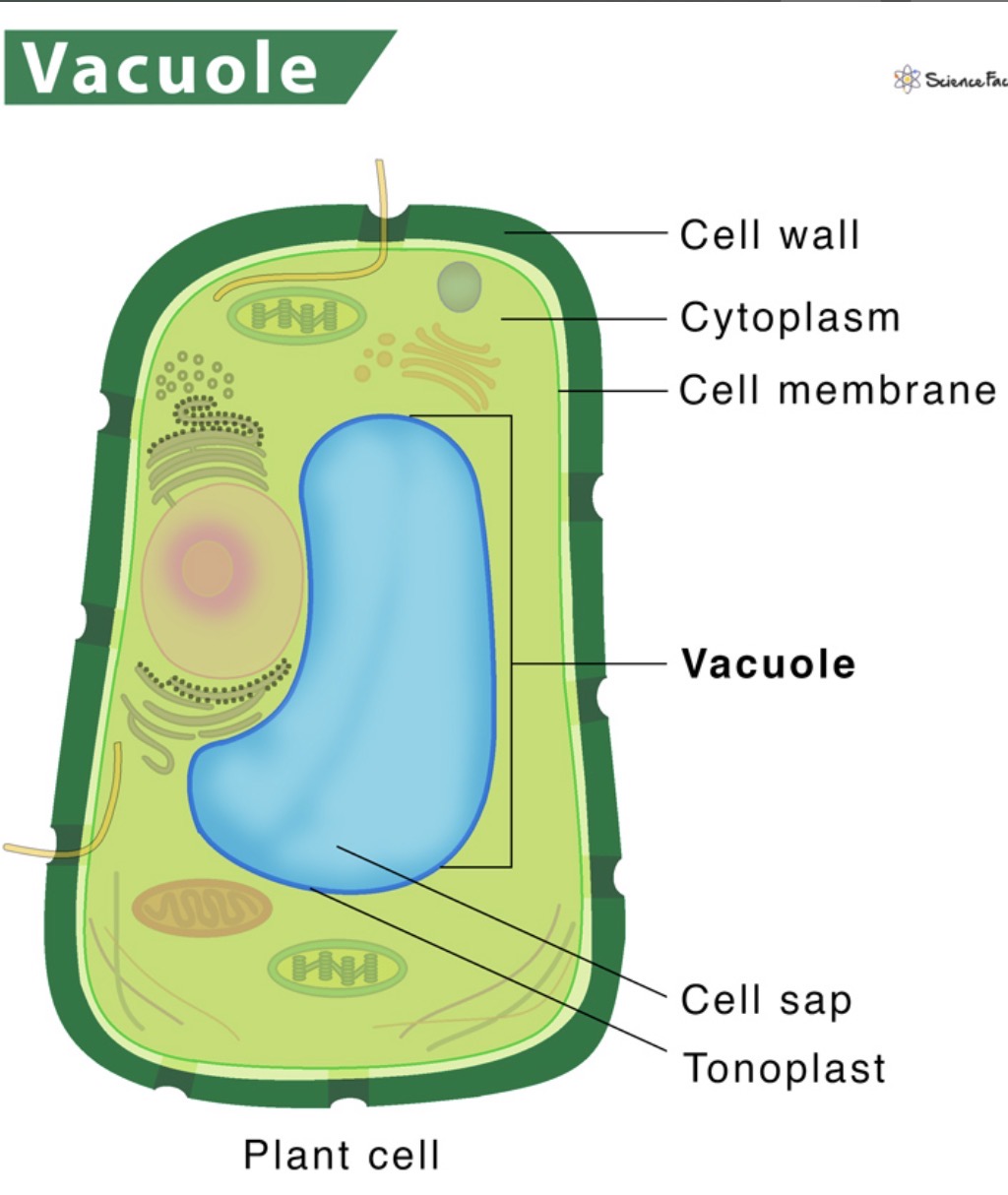
Vacuole
Found in plant cells, stores water, not usually in animal cells, are large
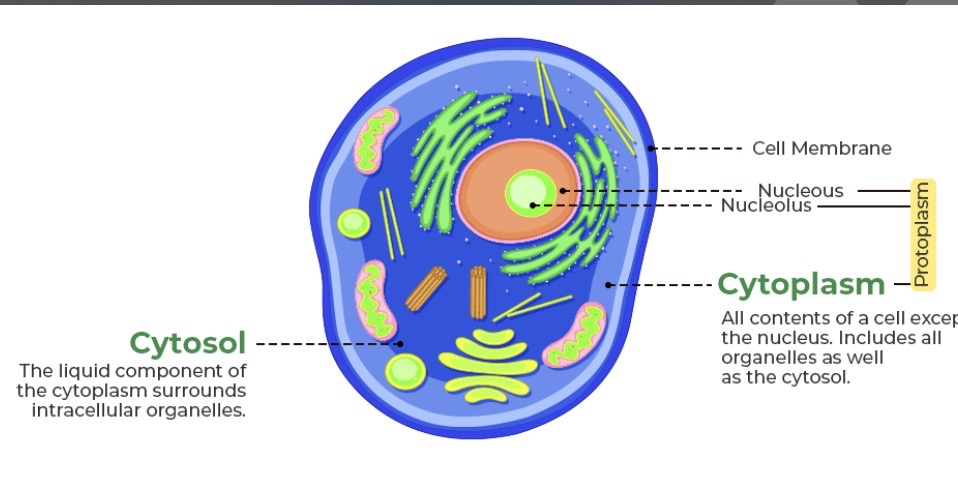
Cytosol
Dissolved material, have concentration gradients in this area
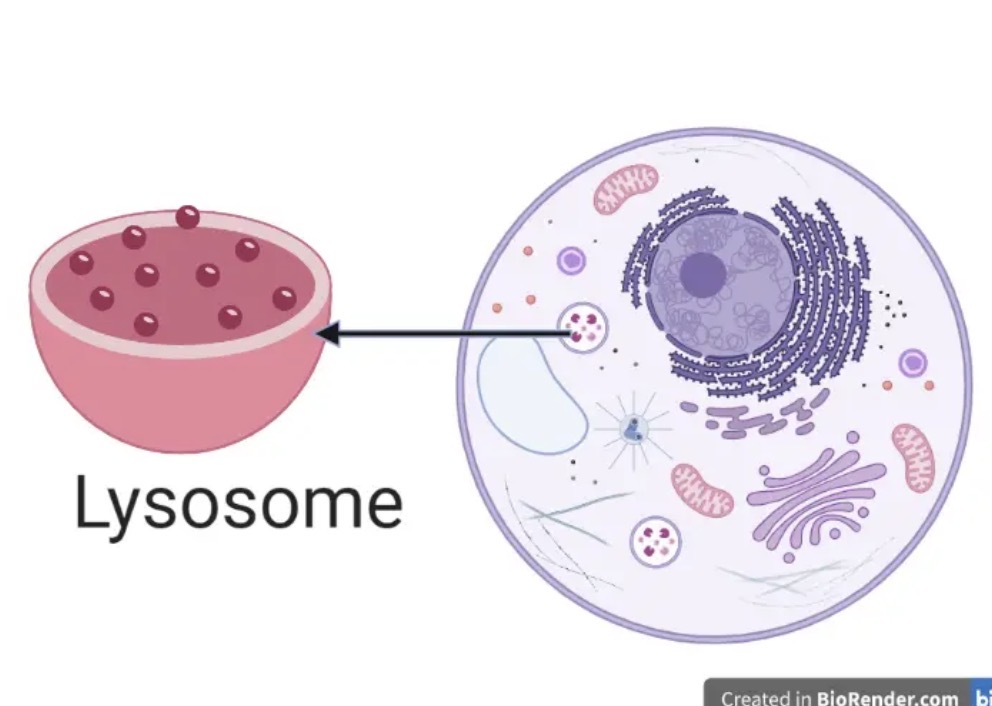
Lysosome
Known as the “suicide sac”, has digestive enzymes that break things down, digestive enzymes come out and kill it
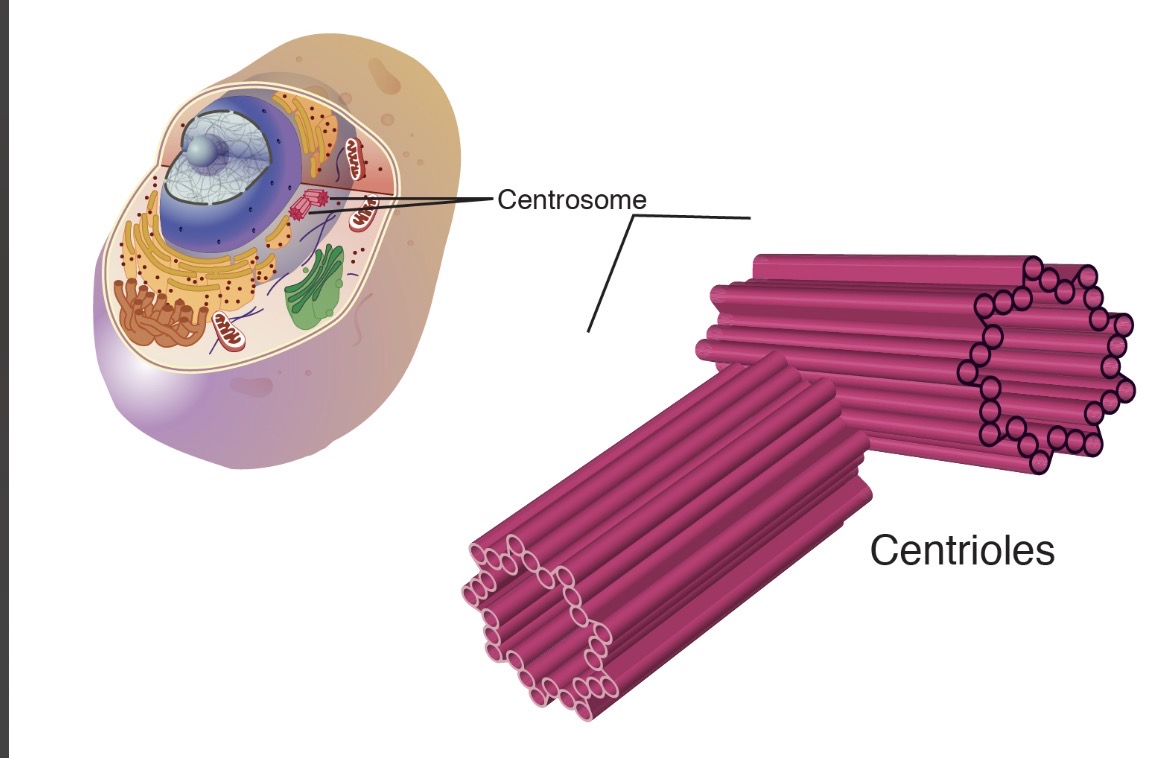
Centriole
Focusing on the positioning around the cell, plant cells don’t have this
Microtubules
Provide support, maintain cell shape, helps with transporting
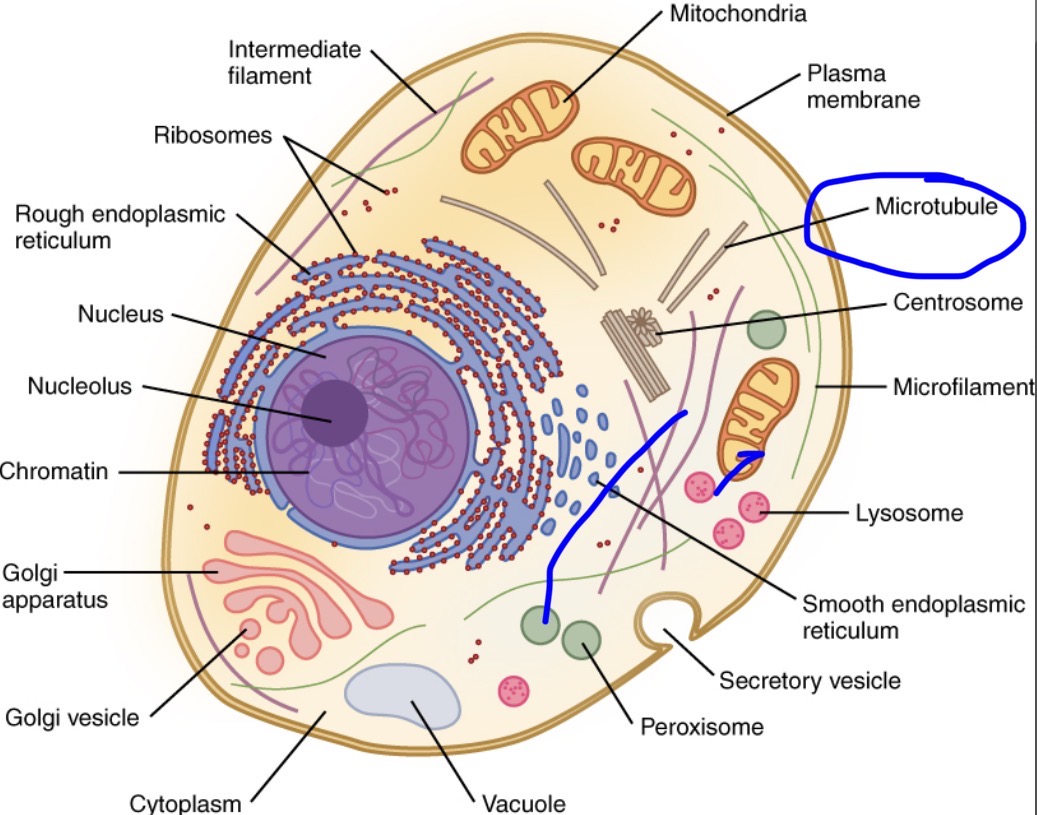
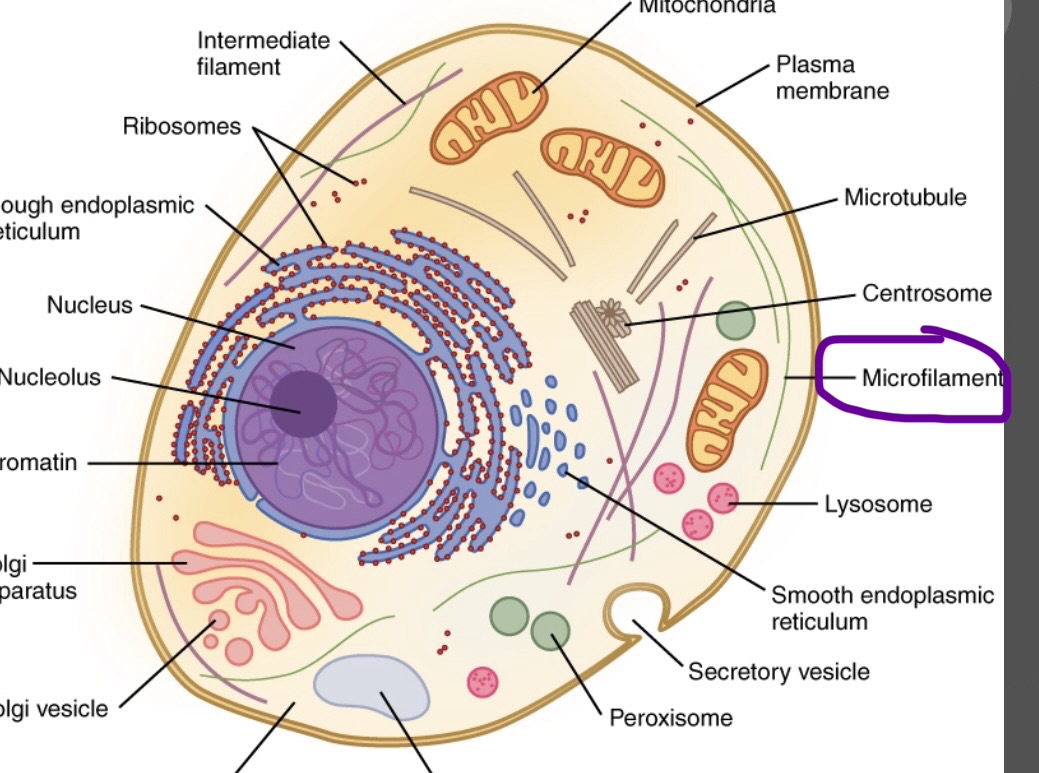
Microfilaments
Also provides support and cell shape, difference is that this enables movement
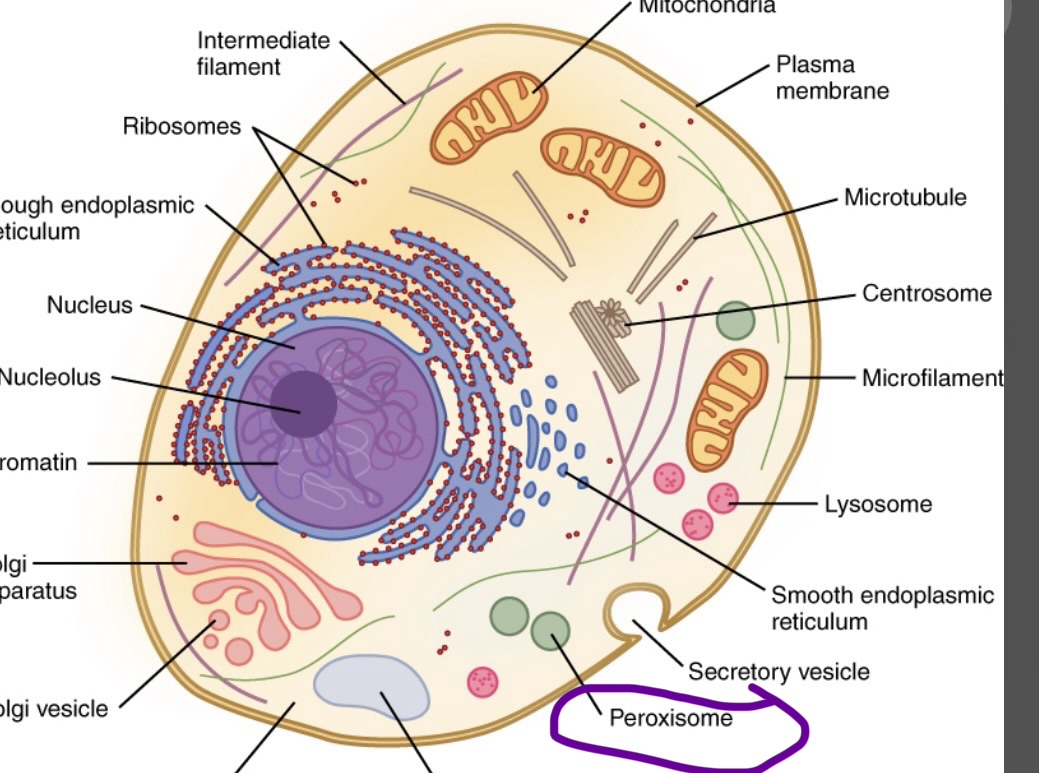
Peroxisome
Fatty acids and amino acids are metabolized to hydrogen peroxide
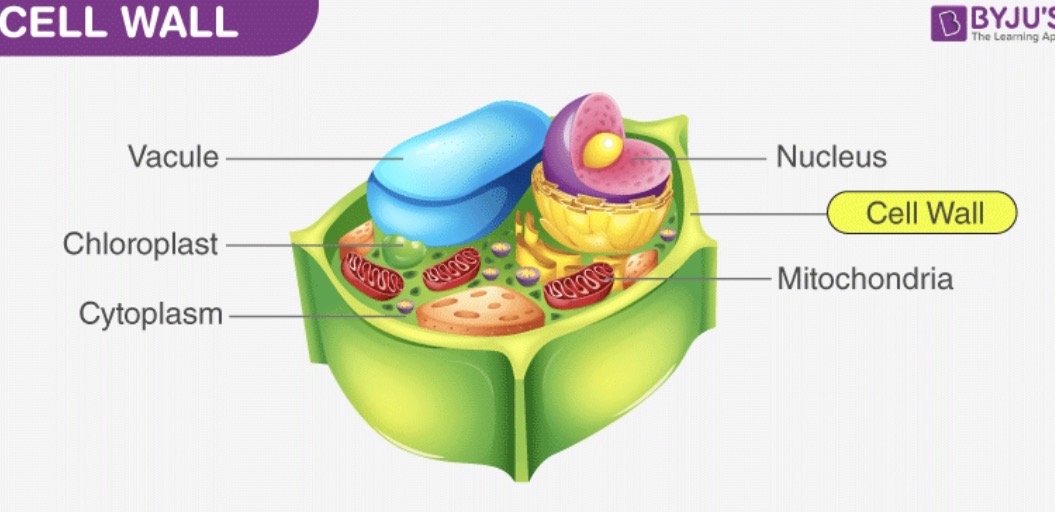
Cell wall
Provides support and protection
Endoplasmic reticulum
transports proteins and lipids
Chloroplast
Responsible for photosynthesis