The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Why are rates of reaction so important in industry?
The faster you make chemical, the faster you make money.
Give two examples of slow rates of reactions.
1) Rusting of Iron
2) Chemical weathering (like acid rain to limestone buildings).
Give an example of a moderate reaction speed.
Metal magnesium reacting with an acid to produce a gentle stream of bubbles.
Give an example of a fast rate of reaction?
Burning, explosions.
How do you calculate the speed if a reaction?
Recording the amount of product formed or the amounts of reactant used up over TIME.
The steeper the line on a graph… (finish the sentence in terms of rate of reaction).
The faster the rate of reaction.
Why does the line on a rate of reaction graph become less steep over time?
The reactants are used up.
How can you tell a reaction is quick based on a graph?
Steepest line and becomes flat in the least time.
Define collision theory.
The rate of reaction depends on:
1) The collision frequency of reacting particles (how often they collide). The MORE collisions there are, the faster the reaction.
2) The energy transferred during a collision. Particles have to collide with ENOUGH ENERGY for the collision to be successful.
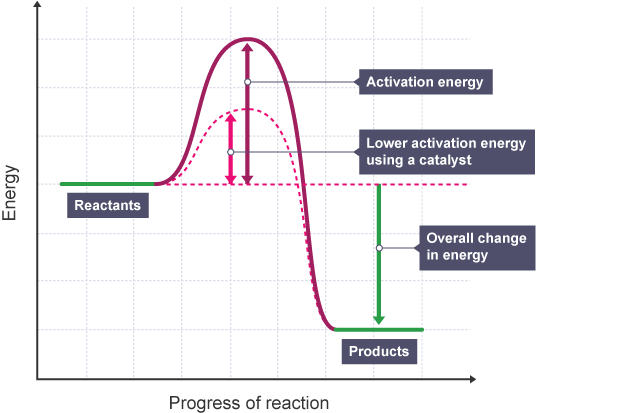
Define activation energy.
The minimum amount of energy that particles need to react. Particles need this much energy to break the bonds in the reactants and start the reaction.
Factors that increase the number of collisions, or the amount of energy particles collide with will… (finish the sentence).
Increase the rate of reaction.
Define “successful” collision.
A collision that ends in the particles reacting to form products.
What 4 factors determine the rate of reaction?
1) Temperature
2) The concentration of a solution or the pressure of gas.
3) The surface area
4) The presence of a catalyst.
What is the VERY IMPORTANT phrase you need to know that describes what the four methods of increasing rate of reaction do?
Increases the number of successful collisions between reacting particles.
How do you increase the rate of reaction in terms of temperature?
Increase the temperature.
Why does increasing temperature increase the rate of reaction?
1) The particles move faster and therefore are going to collide more frequently.
2) The faster they move, the more energy they have (kinetic), so more of the collisions will have enough energy to make the reaction happen.
How do you increase the rate of reaction in terms of concentration and pressure?
Increasing
How does increasing concentration and pressure increase the rate of reaction?
1) If a SOLUTION is made more concentrated, it means there are more particles knocking about in the same volume of water (or other solvent).
2) If the pressure of a GAS increases, it means that the same number of particles occupy a smaller spaces
BOTH OF THESE make the collisions between reactants particles more frequent, therefore increasing the number of successful collisions.
How does increasing surface area increase the rate of reaction?
It means for the same volume of the solid, the particles around it will have more area to work on, so there will be collisions more frequently.
How do you increase the surface area of a solid?
Break it down into smaller pieces.
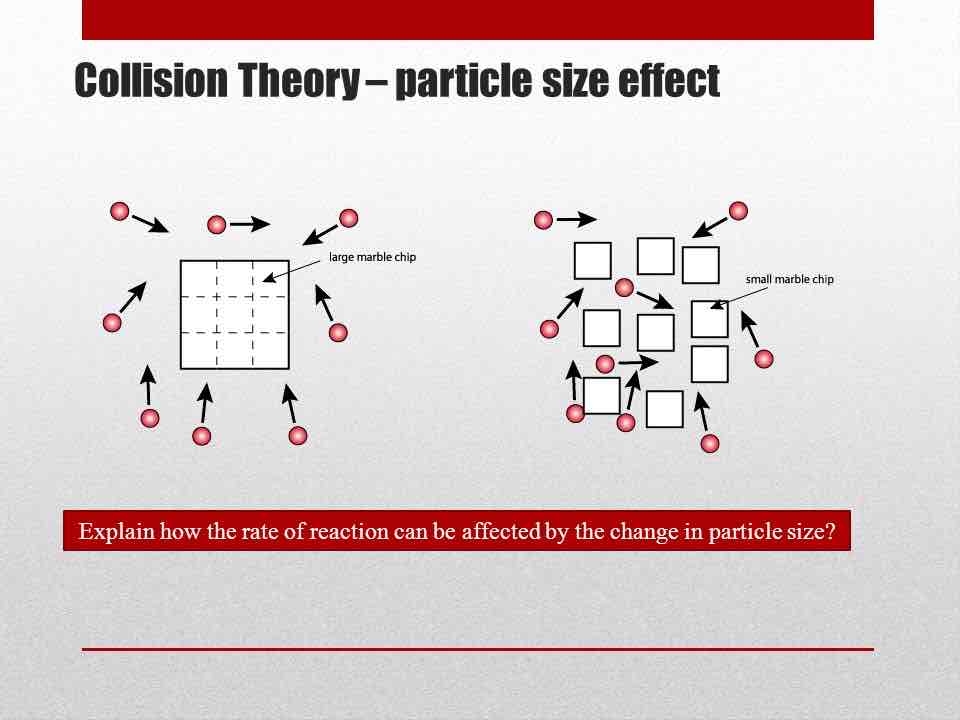
Define catalyst.
A substance that speeds up a reaction.
Why is a catalyst not part of the overall reaction equation?
It isn’t used up in the reaction.
How do catalysts work?
They decrease the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur. They do this by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
Describe the reaction profile for a reaction with a catalyst.
Lower peak.
Equation for calculating rate of reaction.
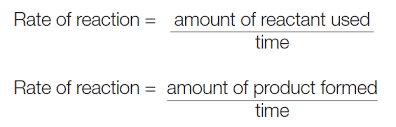
If the product is a gas what unit of measurement do you use?
Cm³
If the product is a solid what unit of measurement do you use?
Grams (g)
What is time measured in in the rate of reaction equation?
Seconds (s).
What’s one drawback to the rate of reaction equation?
It calculates the MEAN rate of reaction, not specific.
How would you calculate the mean rate of reaction at a particular time?
Plot a graph and find the gradient at that time.
What are the 3 ways of measuring rate of reaction?
1) Precipitation and colour change
2) Change in mass (usually gas given off)
3) The volume of gas given off.
How do you calculate rate of reaction using precipitation and colour change?
Observe a mark through a flask of solution and measure how long it takes for it to disappear.
Transparent - Opaque
Coloured - Colourless (or vice versa)
What are the drawbacks of using a mark to determine the rate of reaction?
1) Results are very subjective, different people might not agree over the exact point when the mark no longer is visible.
2) You can’t plot a rate of reaction graph from the results.
How can you record a change in mass to determine rate of reaction?
Place a flash of solution on a mass balance, read the balance as the reaction is happening (the faster the reading on the balance drops, the faster the rate of reaction).
Disadvantages of mass balance method.
Releases gas straight into the room (gas could be toxic).
How do you measure the rate of reaction in terms of volume of gas?
Use a gas syringe and measure the gas given off.
What conclusion can you come too ab out the volume of gas in proportion to the rate of reaction?
The more gas given off during a set time interval, the faster the rate of reaction.
Why are gas syringes an effective way of calculating rate of reaction?
1) Gas syringes are given to the nearest cm³ (usually), so it is quite accurate
2) You can plot a reaction graph with the results if you take measurements at regular intervals.
Drawbacks of gas syringe method when calculating the rate of reaction.
If the reaction is too vigorous, you could easily blow the plunger out of the end of the syringe.
Describe the practical concerning magnesium and HCL when investigating the effect of CONCENTRATION on the rate of reaction.
1) Add a set volume of dilute hydrochloric acid to a conical flask and carefully place on a mass balance.
2) Add some magnesium ribbon to the acid and quickly plug the flask with cotton wool.
3) Start the stopwatch and record the mass on the balance. Take readings of the mass at regular intervals.
4) Plot the results in a table and out the mask lost for each reading.
5) Repeat with more concentrated acid solutions.
Why is cotton wool used to plug up a flask?
Allows gas to escape but stops acid from spitting out.
What goes on the x-axis and the y-axis for the magnesium ribbon and hcl practical?
X = time
Y = loss of mass
How do you ensure the magnesium ribbon and HCL practical is a fair test?
Since your investigating concentration, ONLY increase the concentration of the acid, NOT the amount of magnesium ribbon or the volume of acid used.
What conclusion will you come to about the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction?
Higher concentration = faster rate of reaction.
Describe the practical concerning sodium thiosulfate and HCl when investigating the effect of CONCENTRATION on the rate of reaction.
1) Start by adding a set volume of dilute sodium thissulphate to a conical flask.
2) Place the flask on a piece of paper with a black cross drawn on it. Add some dilute HCl to the flask and start the stopwatch.
3) Now watch the black cross disappear through this cloudy sulfur and time how long it takes to go.
4) Reaction can be repeated with solutions of either reactant at different concentrations.
What is a tangent.
A straight line that touches the curve at ONE point and doesn’t cross it.
What properties of sodium thiosulfate and HCl have that make it suitable to investigate concentration on the rate of reaction?
Both are clear solutions that turn form a YELLOW PRECIPITATE of sulfur.
How do you keep the sodium thiosulfate and HCl thing a fair test?
Only change the concentration of one reactant at a time, and keep the depth of the liquid the same.
Safety measure you would need to take when conducting sodium thiosulfate and HCl experiment.
The reaction releases sulfur dioxide, so the experiment should be carried out in a well-ventilated room.
Describe how you would use a graph to calculate the mean rate of reaction.
Work out the overall change in the y-value and divide this by the total time taken for the reaction.
Describe how you would use a graph if you wanted to find the reaction rate at a particular point.
Draw a tangent, then work out the gradient of the tangent.
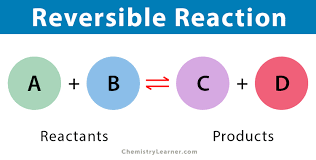
Define reversible reactions.
A reaction where the products of the reaction can themselves react to produce the original reactants.
How do you represent a reversible reaction?
Define FORWARD reaction.
When reactants turn into products.
Define BACKWARDS reaction.
When products turn into reactants.
What makes reversible reactions reversible?
As the reactants react, their concentrations fall, so the forward reaction will slow down. But as more and more products are made and their concentrations rise, the backwards reaction will speed up.
What happens when the system is “at equilibrium”?
The forward reaction will be going at exactly the same rate as the backwards one.
Define dynamic equilibrium.
When both forwards and backwards reactions are still happening, but there is no overall effect on reactants or products.
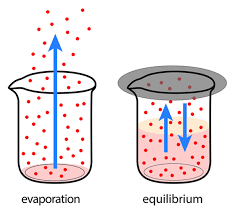
What is meant by “no overall effect” when referring to dynamic equilibrium?
The concentration of reactants and products have reached a balance and WONT change.
What condition must be met for equilibrium to be reached?
If the reversible reaction takes place in a closed system.
Define closed system.
A system in which none of the reactants or products can escape and nothing else can get in.
What is a common misconception about equilibrium?
That it means that the amount of products and reactants are equal.
If the equilibrium lies to the left…
The concentration of reactants is GREATER than that of the products.
If a reversible reaction is exothermic in one direction, what is it in the other?
Endothermic
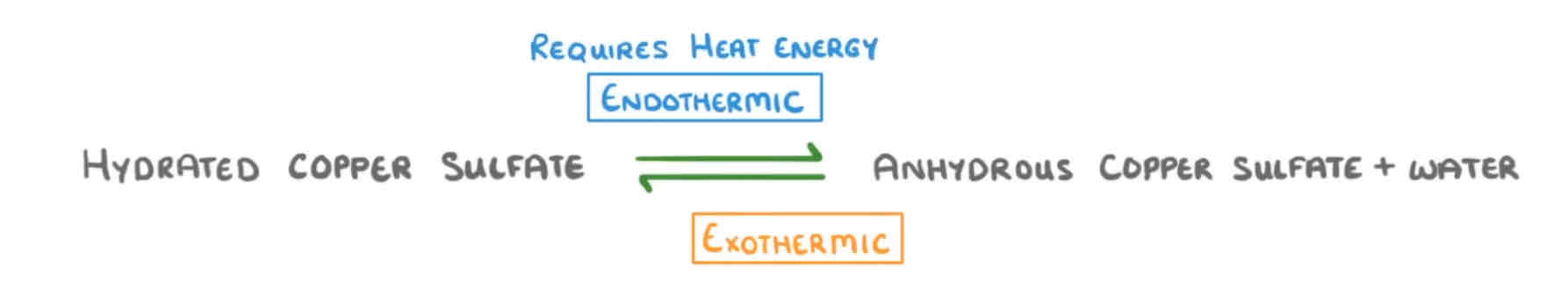
Explain this.
If you heat HYDRATED copper sulfate crystals, it drives the water off and leaves white ANYHYDROUS (without water) copper sulfate powder. This is ENDOTHERMIC as you need take IN heat from the surroundings.
If you then add a couple of drops of water to the white powder, you get blue crystals back again. This is EXOTHERMIC as it releases heat TO the surroundings.
The energy transferred FROM the surroundings by the endothermic reaction is EQUAL TO…
The energy transferred TO the surroundings during the exothermic reaction.
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
The idea that if you try to change the conditions of a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try and counteract that change.
What can Le Chatelier’s principle be used to predict?
The effects of any changes you make to a reaction system.
What 3 factors can affect the position of equilibrium?
1) Temperature
2) Pressure (only in gases)
3) Concentration of reactants and products.
What happens to the position of equilibrium if you DECREASE the temperature?
Move in the exothermic direction to produce more heat (and counteract the DECREASE in temperature), this means you’ll get more products for the exothermic reaction and fewer products for the endothermic reaction.
What happens to the position of equilibrium if you RAISE the temperature?
The equilibrium will move in the endothermic direction (where it takes in heat from its surroundings) to try and counteract the increase in temperature. You’ll now get more products for the endothermic reaction and fewer products for the exothermic reaction..
What state of matter do changes in pressure apply to?
Gases.
What happens if your increase the pressure of a reversible reaction at equilibrium?
The equilibrium tries to reduce itself - it moves in the direction where there are fewer molecules of gas.
What happens if your decrease the pressure of a reversible reaction at equilibrium?
The equilibrium tries to increase itself it moves in the direction where there are more molecules of gas.
How do you calculate the molecules of gas in a reaction?
Make a balanced symbol equation.
How does changing the concentration of either the reactants or products affect the system?
The system will no longer be at equilibrium.
What happens if you increase the concentration of the reactants in a reversible reaction in equilibrium?
Tries to decrease it by making more products.
What happens if you decrease the concentration of the products in a reversible reaction in equilibrium?
Decreases number of reactants.
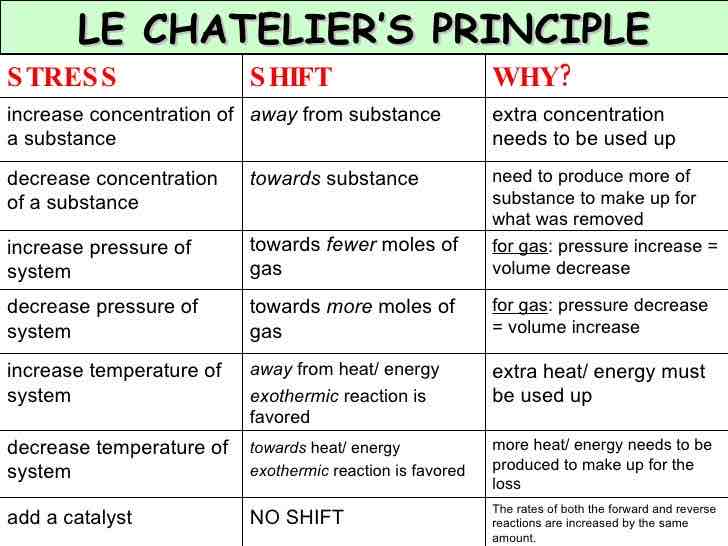
Memorise this entire chart by heart (cover with hand and read it)
Done?