Chemistry Unit 2 🔬- The Atoms
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms

Which number is the atomic number? (rounded if needed)
28

Which Number is the Number of Protons? (rounded if needed)
28

Which Number is the Mass Number? (rounded if needed)
59

What is the Average Atomic Mass in this element?
.6934

Which Number is the number of Electrons? (round if needed)
28
Mass Number - Atomic Number= _____
Neutrons

If the ion is Co2+ then what is the number of protons?
27

If the ion is Co2+ then what is the number of electrons?
25

If the ion is Co3+ then what is the number of electrons?
24

If the ion is Co3+ then what is the number of protons?
27

if the ion is S2- then what is the number of protons?
16

if the ion is S2- then what is the number of electrons?
18
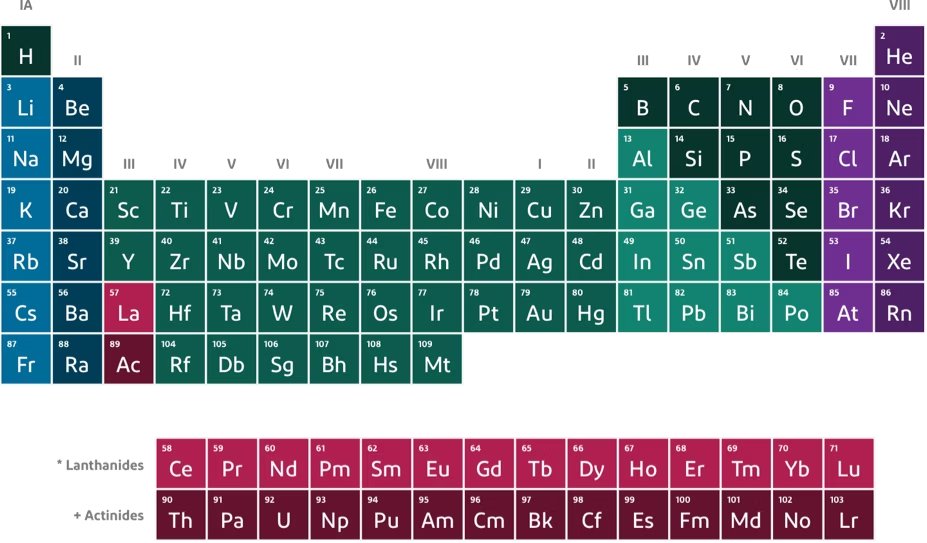
How many valence electrons are in Nitrogen?
5
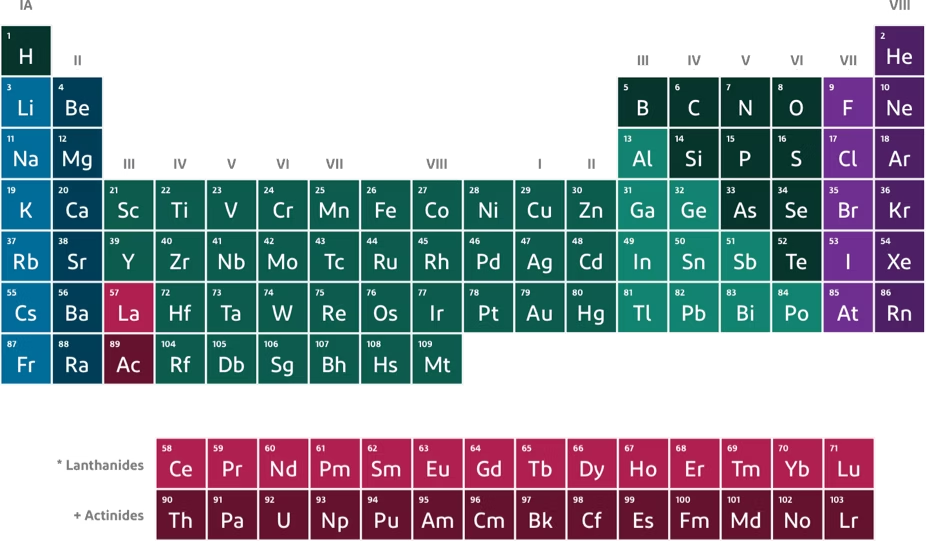
How many valence electrons are in argon?
8
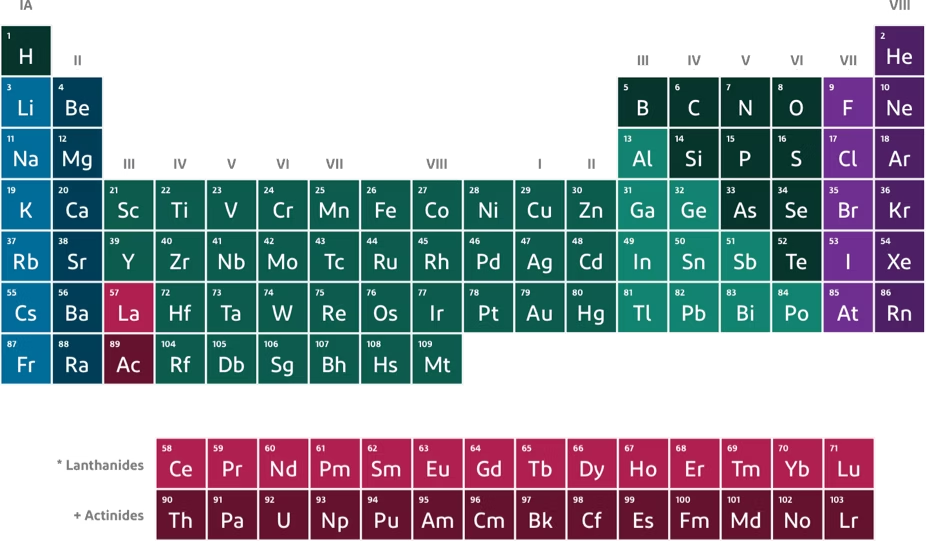
How many valence electrons are in magnesium?
2
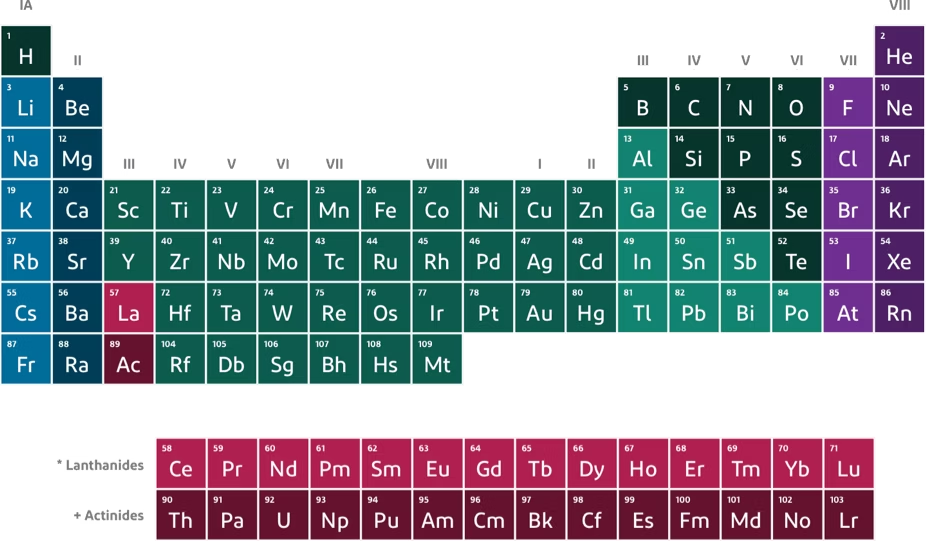
How many valence electrons are in lithium?
1

How many neutrons are in Nickel?
31

How many neutrons are in Cobalt?
32

How many neutrons are in Sulfur?
16
Orbital Notation Filling Diagrams and Electron Configurations
a visual way to represent the arrangements of all electrons in an atom.
Aufbau Rule
lowest energy level fills first (always go in the right order)
Pauli Rule
2 electrons in the same orbital can’t spin in the same direction (opposites attract)
Hund Rule
every sub orbital gets 1 electron before getting any seconds (pizza rule)
Sublevel/Orbital Capacities: each hold ___ electrons
2
S sublevel holds
2
S sublevel has ___ orbitals
1
P sublevel holds ____
6
P sublevel has ____ orbitals
3
D sublevel holds ___
10
D sublevel has ____ orbitals
5
F sublevel holds ____
14
F sublevel has ____ orbitals
7
2P → ___
3s
4s→___
3d
1s → ___
2s
Roentgen (1895)
study fluorescent materials that glow bright when they’re hit with electrons “X-Rays”
Becquerel (1896)
discovered that uranium emits its own energy (radiation)
Pierre & Marie Curie (1898)
coined the term “radioactivity” (atoms gives off rays/particles)
Rutherford (1908)
discover that elements “decay” into other elements. 3 Types: Alpha Decay, Beta Decay, Gamma Decay.
Elements 1-20 Stability
Very stable (1:1 ratio of protons to neutrons)
Elements 21-80 Stability
Marginally (kinda) stable (1:15 ratio of protons to neutrons)
Elements bigger than 83
Unstable (1:12 ratio of protons to neutrons) spontaneously decay

Alpha

Beta

Gamma