BIOL 1020 Lesson 6 Practice Questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
The human X and Y chromosomes
1. include only genes that govern sex determination.
2. are almost entirely homologous, despite their different names.
3. are both present in every somatic cell of males and females alike.
4. are of approximately equal size and number of genes.
5. include genes that determine an individual's sex.
1. include only genes that govern sex determination.
2. are almost entirely homologous, despite their different names.
3. are both present in every somatic cell of males and females alike.
4. are of approximately equal size and number of genes.
5. include genes that determine an individual's sex.
5. include genes that determine an individual’s sex
2
New cards
During which stage(s) of meiosis do centromeres of sister chromatids disjoin and chromatids separate? \n \n I. Prophase I
II. Metaphase I
III. Anaphase I
IV. Telophase I
V. Prophase II
VI. Metaphase II
VII. Anaphase II
VIII. Telophase II
Centromeres of sister chromatids disjoin and chromatids separate.
1. Anaphase I
2. Anaphase II
3. Anaphase I and Anaphase II
4. Metaphase I and Metaphase II
5. Prophase I and Prophase II
II. Metaphase I
III. Anaphase I
IV. Telophase I
V. Prophase II
VI. Metaphase II
VII. Anaphase II
VIII. Telophase II
Centromeres of sister chromatids disjoin and chromatids separate.
1. Anaphase I
2. Anaphase II
3. Anaphase I and Anaphase II
4. Metaphase I and Metaphase II
5. Prophase I and Prophase II
2. Anaphase II
3
New cards
When we see chiasmata under a microscope, that lets us know which of the following has occurred?
1. asexual reproduction
2. separation of homologues
3. anaphase II
4. prophase I
5. meiosis II
1. asexual reproduction
2. separation of homologues
3. anaphase II
4. prophase I
5. meiosis II
4. prophase I
4
New cards
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of
1. the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm.
2. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II, and the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes.
3. the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes.
4. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
5. the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II.
1. the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm.
2. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I, the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm, the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II, and the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes.
3. the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes.
4. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
5. the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II.
4. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I
5
New cards
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
2. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
3. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
4. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
5. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
2. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
3. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
4. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
5. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids
6
New cards
The following question refers to the essential steps in meiosis described below.
1\. Formation of four new nuclei, each with half the chromosomes present in the parental nucleus
2\. Alignment of tetrads at the metaphase plate
3\. Separation of sister chromatids
4\. Separation of the homologs; no uncoupling of the centromere 5. Synapsis; chromosomes moving to the middle of the cell in pairs
Which of the steps takes place in both mitosis and meiosis?
1. 2, 3, and 5
2. 5
3. 2 and 3 only
4. 2
5. 3
1\. Formation of four new nuclei, each with half the chromosomes present in the parental nucleus
2\. Alignment of tetrads at the metaphase plate
3\. Separation of sister chromatids
4\. Separation of the homologs; no uncoupling of the centromere 5. Synapsis; chromosomes moving to the middle of the cell in pairs
Which of the steps takes place in both mitosis and meiosis?
1. 2, 3, and 5
2. 5
3. 2 and 3 only
4. 2
5. 3
5. 3
7
New cards
Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
1. Sister chromatids are separated.
2. The chromosome number per cell is conserved.
3. The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end.
4. Four daughter cells are formed.
5. Homologous chromosomes are separated.
1. Sister chromatids are separated.
2. The chromosome number per cell is conserved.
3. The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end.
4. Four daughter cells are formed.
5. Homologous chromosomes are separated.
5. homologous chromosomes are separated
8
New cards
What was the most significant conclusion that Gregor Mendel drew from his experiments with pea plants?
1. Recessive genes occur more frequently in the F1 generation than do dominant ones.
2. An organism that is homozygous for many recessive traits is at a disadvantage.
3. There is considerable genetic variation in garden peas.
4. Genes are composed of DNA.
5. Traits are inherited in discrete units, and are not the results of "blending."
1. Recessive genes occur more frequently in the F1 generation than do dominant ones.
2. An organism that is homozygous for many recessive traits is at a disadvantage.
3. There is considerable genetic variation in garden peas.
4. Genes are composed of DNA.
5. Traits are inherited in discrete units, and are not the results of "blending."
5. traits are inherited in discrete units', and are not the results of “blending”
9
New cards
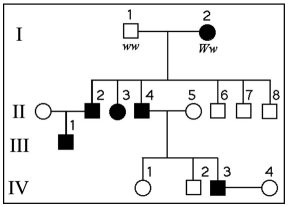
The following question refers to the pedigree chart in the figure below for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, *W*. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle. \n
What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
1. 100%
2. 50%
3. 75%
4. 0%
5. 25%
What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
1. 100%
2. 50%
3. 75%
4. 0%
5. 25%
2. 50%
10
New cards
In the cross *AaBbCc* × *AaBbCc*, what is the probability of producing the genotype *AABBCC*?
1. 1/4
2. 1/8
3. 1/16
4. 1/32
5. 1/64
1. 1/4
2. 1/8
3. 1/16
4. 1/32
5. 1/64
5. 1/64
11
New cards
Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio for a particular trait. What does this suggest?
1. that the trait shows incomplete dominance
2. that the parents were true-breeding for contrasting traits
3. that each offspring has the same alleles for each of two traits
4. that the parents were both heterozygous for a single trait
5. that a blending of traits has occurred
1. that the trait shows incomplete dominance
2. that the parents were true-breeding for contrasting traits
3. that each offspring has the same alleles for each of two traits
4. that the parents were both heterozygous for a single trait
5. that a blending of traits has occurred
4. that the parents were both heterozygous for a single trait
12
New cards
A sexually reproducing animal has two unlinked genes, one for head shape (*H*) and one for tail length (*T*). Its genotype is *HhTt*. Which of the following genotypes is possible in a gamete from this organism?
1. *tt*
2. *HT*
3. *T*
4. *HhTt*
5. *Hh*
1. *tt*
2. *HT*
3. *T*
4. *HhTt*
5. *Hh*
2. HT
13
New cards
What do we mean when we use the terms *monohybrid cross* and *dihybrid cross*?
1. A monohybrid cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces two progeny.
2. A monohybrid cross can result in a 9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio whereas a dihybrid cross can give a 3:1 phenotype ratio.
3. A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
4. A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
5. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
1. A monohybrid cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces two progeny.
2. A monohybrid cross can result in a 9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio whereas a dihybrid cross can give a 3:1 phenotype ratio.
3. A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
4. A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
5. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
5. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one
14
New cards
Why did the F1 offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
1. The traits blended together during fertilization.
2. One phenotype was completely dominant over another.
3. Different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
4. No genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
5. Each allele affected phenotypic expression.
1. The traits blended together during fertilization.
2. One phenotype was completely dominant over another.
3. Different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
4. No genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
5. Each allele affected phenotypic expression.
2. One phenotype was completely dominant over another
15
New cards
Which of the following might result in a human zygote with 45 chromosomes?
1. an error in the alignment of chromosomes on the metaphase plate
2. fertilization of a 23-chromosome human egg by a 22-chromosome sperm of a closely related species
3. an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase
4. failure of the egg nucleus to be fertilized by the sperm
5. lack of chiasmata in prophase I
1. an error in the alignment of chromosomes on the metaphase plate
2. fertilization of a 23-chromosome human egg by a 22-chromosome sperm of a closely related species
3. an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase
4. failure of the egg nucleus to be fertilized by the sperm
5. lack of chiasmata in prophase I
3. an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase
16
New cards
When homologous chromosomes cross over, what occurs?
1. Two chromatids get tangled, resulting in one re-sequencing its DNA.
2. Maternal alleles are "corrected" to be like paternal alleles and vice versa.
3. Two sister chromatids exchange identical pieces of DNA.
4. Each of the four DNA strands of a tetrad is broken and the pieces are mixed.
5. Specific proteins break the two strands and re-join them with their homologues.
1. Two chromatids get tangled, resulting in one re-sequencing its DNA.
2. Maternal alleles are "corrected" to be like paternal alleles and vice versa.
3. Two sister chromatids exchange identical pieces of DNA.
4. Each of the four DNA strands of a tetrad is broken and the pieces are mixed.
5. Specific proteins break the two strands and re-join them with their homologues.
5. specific proteins break the two strands and re-join them with their homologues
17
New cards
A certain gene found in a diploid species is known to have 18 alleles (variants). Any given organism of that species can/must have which of the following?
1. a haploid number of 9 chromosomes
2. up to 18 genes for that trait
3. up to, but not more than, 18 different traits
4. 2 alleles for that gene
5. up to 18 chromosomes with that gene
1. a haploid number of 9 chromosomes
2. up to 18 genes for that trait
3. up to, but not more than, 18 different traits
4. 2 alleles for that gene
5. up to 18 chromosomes with that gene
4. two alleles for that gene
18
New cards
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called
1. Mendelian genetics.
2. evolution.
3. inheritance.
4. natural selection.
5. dominance.
1. Mendelian genetics.
2. evolution.
3. inheritance.
4. natural selection.
5. dominance.
3. inheritance
19
New cards
Chromatids are separated from each other.
1. The statement is true for mitosis only.
2. The statement is true for meiosis I only.
3. The statement is true for meiosis II only.
4. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
5. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
1. The statement is true for mitosis only.
2. The statement is true for meiosis I only.
3. The statement is true for meiosis II only.
4. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
5. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
5. the statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II
20
New cards
When both traits are exhibited in the phenotype, it is said that the alleles display
1. gene silencing.
2. co-dominance.
3. incomplete dominance.
4. recessive traits.
5. complete dominance.
1. gene silencing.
2. co-dominance.
3. incomplete dominance.
4. recessive traits.
5. complete dominance.
2. co-dominance
21
New cards
The fact that all seven of the pea plant traits studied by Mendel obeyed the principle of independent assortment most probably indicates which of the following?
1. None of the traits obeyed the law of segregation.
2. The diploid number of chromosomes in the pea plants was 7.
3. The formation of gametes in plants occurs by mitosis only.
4. All of the genes controlling the traits were located on the same chromosome.
5. All of the genes controlling the traits behaved as if they were on different chromosomes.
1. None of the traits obeyed the law of segregation.
2. The diploid number of chromosomes in the pea plants was 7.
3. The formation of gametes in plants occurs by mitosis only.
4. All of the genes controlling the traits were located on the same chromosome.
5. All of the genes controlling the traits behaved as if they were on different chromosomes.
5. All of the genes controlling the traits behaved as if they were on different chromosomes
22
New cards
The individual with genotype *AaBbCCDdEE* can make many kinds of gametes. Which of the following is the major reason?
1. segregation of maternal and paternal alleles
2. recurrent mutations forming new alleles
3. the tendency for dominant alleles to segregate together
4. different possible alignments of chromosomes
5. crossing over during prophase I
1. segregation of maternal and paternal alleles
2. recurrent mutations forming new alleles
3. the tendency for dominant alleles to segregate together
4. different possible alignments of chromosomes
5. crossing over during prophase I
4. different possible alignments of chromosomes
23
New cards
If a cell has completed the first meiotic division and is just beginning meiosis II, which of the following is an appropriate description of its contents?
1. It is identical in content to another cell from the same meiosis.
2. It has one-fourth the DNA and one-half the chromosomes as the originating cell.
3. It has the same number of chromosomes but each of them has different alleles than another cell from the same meiosis.
4. It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis.
5. It has half the chromosomes but twice the DNA of the originating cell.
1. It is identical in content to another cell from the same meiosis.
2. It has one-fourth the DNA and one-half the chromosomes as the originating cell.
3. It has the same number of chromosomes but each of them has different alleles than another cell from the same meiosis.
4. It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis.
5. It has half the chromosomes but twice the DNA of the originating cell.
4. it has hald the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis
24
New cards
How does the sexual life cycle increase the genetic variation in a species?
1. by allowing crossing over
2. by conserving chromosomal gene order
3. by allowing fertilization
4. by decreasing mutation frequency
5. by increasing gene stability
1. by allowing crossing over
2. by conserving chromosomal gene order
3. by allowing fertilization
4. by decreasing mutation frequency
5. by increasing gene stability
1. by allowing crossing over
25
New cards
How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that have replicated their DNA and are just about to begin meiosis?
1. They have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
2. They have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
3. They have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
4. They have twice the amount of cytoplasm and half the amount of DNA.
5. They have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
1. They have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
2. They have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
3. They have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
4. They have twice the amount of cytoplasm and half the amount of DNA.
5. They have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
5. they have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA
26
New cards
A given organism has 46 chromosomes in its karyotype. We can therefore conclude which of the following?
1. It must be an animal.
2. It must be a primate.
3. It must be sexually reproducing.
4. It must be human.
5. Its gametes must have 23 chromosomes.
1. It must be an animal.
2. It must be a primate.
3. It must be sexually reproducing.
4. It must be human.
5. Its gametes must have 23 chromosomes.
5. its gametes must have 23 chromosomes
27
New cards
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
2. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
3. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
4. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
5. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
2. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
3. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
4. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
5. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
1. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids
28
New cards
A tetrad includes which of the following sets of DNA strands?
1. eight sets of sister chromatids
2. two sets of sister chromatids that have synapsed
3. four sets of sister chromatids
4. two single-stranded chromosomes that have synapsed
5. four sets of unique chromosomes
1. eight sets of sister chromatids
2. two sets of sister chromatids that have synapsed
3. four sets of sister chromatids
4. two single-stranded chromosomes that have synapsed
5. four sets of unique chromosomes
2. two sets of sister chromatids that have synapsed
29
New cards
Use the following information to answer the question below. \n \n A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the alleles *R* and *r*, respectively. A third gene for the MN blood group has codominant alleles *M* and *N*. \n \n \n If both children are of blood type M, which of the following is possible?
1. Neither parent can have the *N* allele.
2. Both children are heterozygous for this gene.
3. Each parent must be type M.
4. Each parent is either M or MN.
5. The MN blood group is recessive to the ABO blood group.
1. Neither parent can have the *N* allele.
2. Both children are heterozygous for this gene.
3. Each parent must be type M.
4. Each parent is either M or MN.
5. The MN blood group is recessive to the ABO blood group.
4. each parent is either M or MN
30
New cards
Which of the following differentiates between independent assortment and segregation?
1. The law of independent assortment is accounted for by observations of prophase I.
2. The law of segregation is accounted for by anaphase of mitosis.
3. The law of segregation requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
4. The law of independent assortment requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
5. The law of segregation requires having two or more generations to describe.
1. The law of independent assortment is accounted for by observations of prophase I.
2. The law of segregation is accounted for by anaphase of mitosis.
3. The law of segregation requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
4. The law of independent assortment requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
5. The law of segregation requires having two or more generations to describe.
4. the law of independent assortment requires describing two or more genes relative to one another
31
New cards
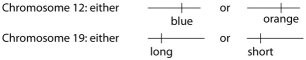
Use the following information to answer the question below. \n \n A certain (hypothetical) organism is diploid, has either blue or orange wings as the consequence of one of its genes on chromosome 12, and has either long or short antennae as the result of a second gene on chromosome 19, as shown in this figure.
A certain female's number 12 chromosomes both have the blue gene and number 19 chromosomes both have the long gene. As cells in her ovaries undergo meiosis, her resulting eggs (ova) may have which of the following?
1. either two number 19 chromosomes with long genes or two with short genes
2. either two number 12 chromosomes with blue genes or two with orange genes
3. either one blue or one orange gene in addition to either one long or one short gene
4. one chromosome 12 with one blue gene and one chromosome 19 with one long gene
A certain female's number 12 chromosomes both have the blue gene and number 19 chromosomes both have the long gene. As cells in her ovaries undergo meiosis, her resulting eggs (ova) may have which of the following?
1. either two number 19 chromosomes with long genes or two with short genes
2. either two number 12 chromosomes with blue genes or two with orange genes
3. either one blue or one orange gene in addition to either one long or one short gene
4. one chromosome 12 with one blue gene and one chromosome 19 with one long gene
4. one chromosome 12 with one blue gene and one chromosome 19 with one long gene
32
New cards
Use the following information to answer the question below. \n \n Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a black female with a brown male, results can be either all black puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow puppies. \n \n \n These results indicate which of the following?
1. Black is dominant to brown and to yellow.
2. Epistasis is involved.
3. Brown is dominant to black.
4. Yellow is dominant to black.
5. There is incomplete dominance.
1. Black is dominant to brown and to yellow.
2. Epistasis is involved.
3. Brown is dominant to black.
4. Yellow is dominant to black.
5. There is incomplete dominance.
2. epistasis is involved
33
New cards
Use the following information to answer the question below. \n \n Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with long being the dominant characteristic. \n \n \n If true-breeding red long radishes are crossed with true-breeding white oval radishes, the F1 will be expected to be which of the following?
1. purple and oval
2. red and long
3. purple and long
4. red and oval
5. white and long
1. purple and oval
2. red and long
3. purple and long
4. red and oval
5. white and long
3. purple and long