Comprehensive Neuroscience: Vision, Audition, Proprioception, Nociception, Olfaction, and Taste
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
What is the only input our brains receive from the real world?
A series of action potentials passed along the neurons of our various sensory pathways.
What do sensory receptors do?
They transduce (convert) sensory energy into neural activity.
What type of energy do visual receptors respond to?
Light energy, which is converted into chemical energy.
What is the difference between sensation and perception?
Sensation is the registration of physical stimuli, while perception is the interpretation of those sensations by the brain.
What is the structure of the eye that focuses light?
The lens.
What is the function of the retina?
It is where light energy initiates neural activity and contains photoreceptor cells.
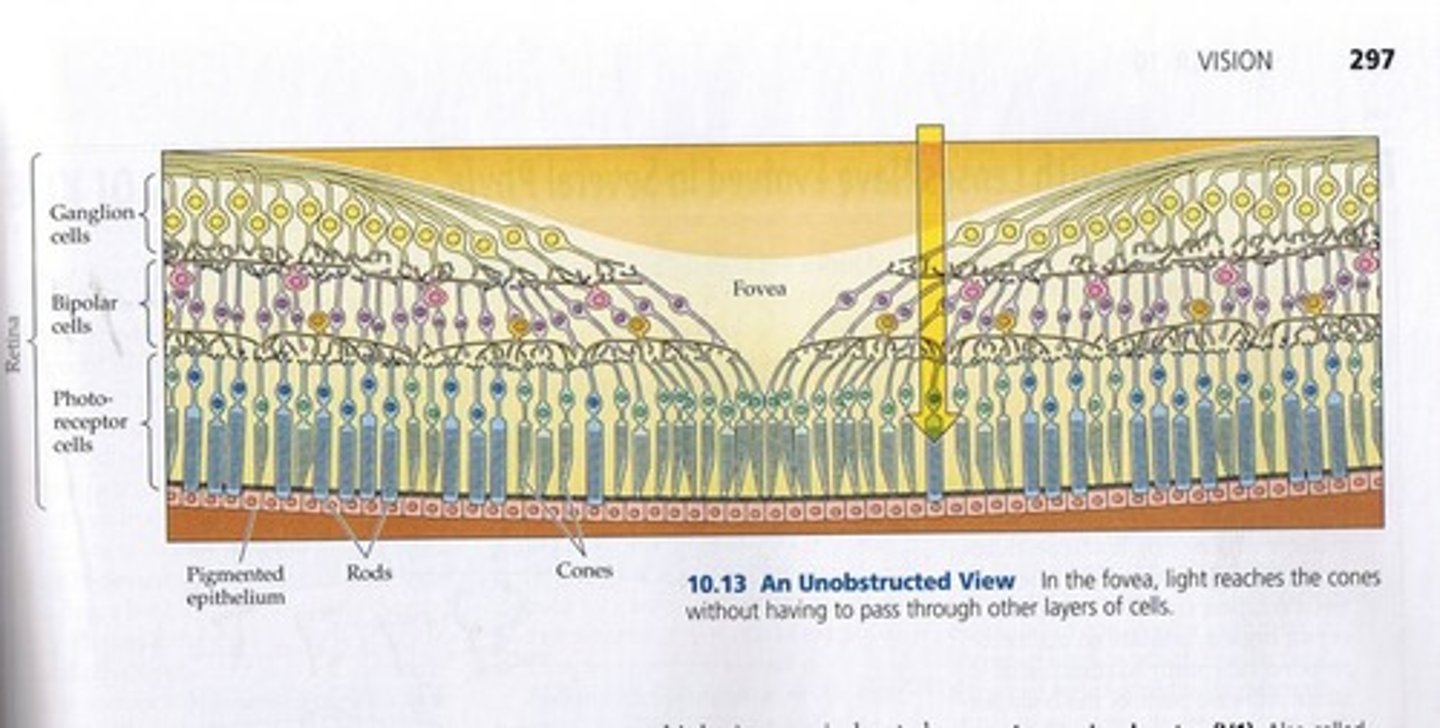
What is the fovea specialized for?
High acuity vision.
What types of cells do retinal ganglion cells receive information from?
Photoreceptors via bipolar cells and amacrine cells.
What is the role of retinal ganglion cells?
They transmit visual information from the retina to various brain regions.
What are the two types of photoreceptors in the retina?
Rods and cones.
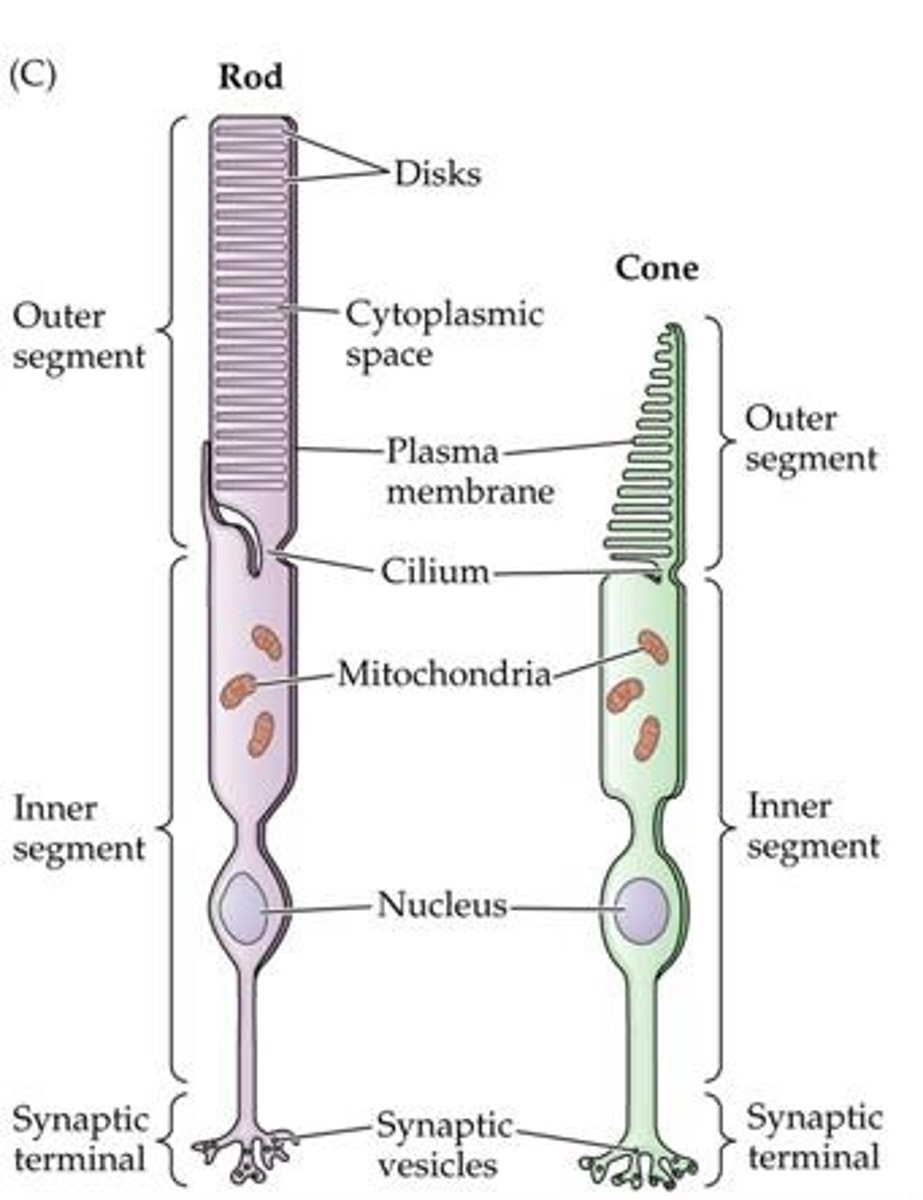
What is the primary function of rods?
They are sensitive to low levels of light and are used mainly for night vision.

What is the primary function of cones?
They are responsive to bright light and are specialized for color and high visual acuity.
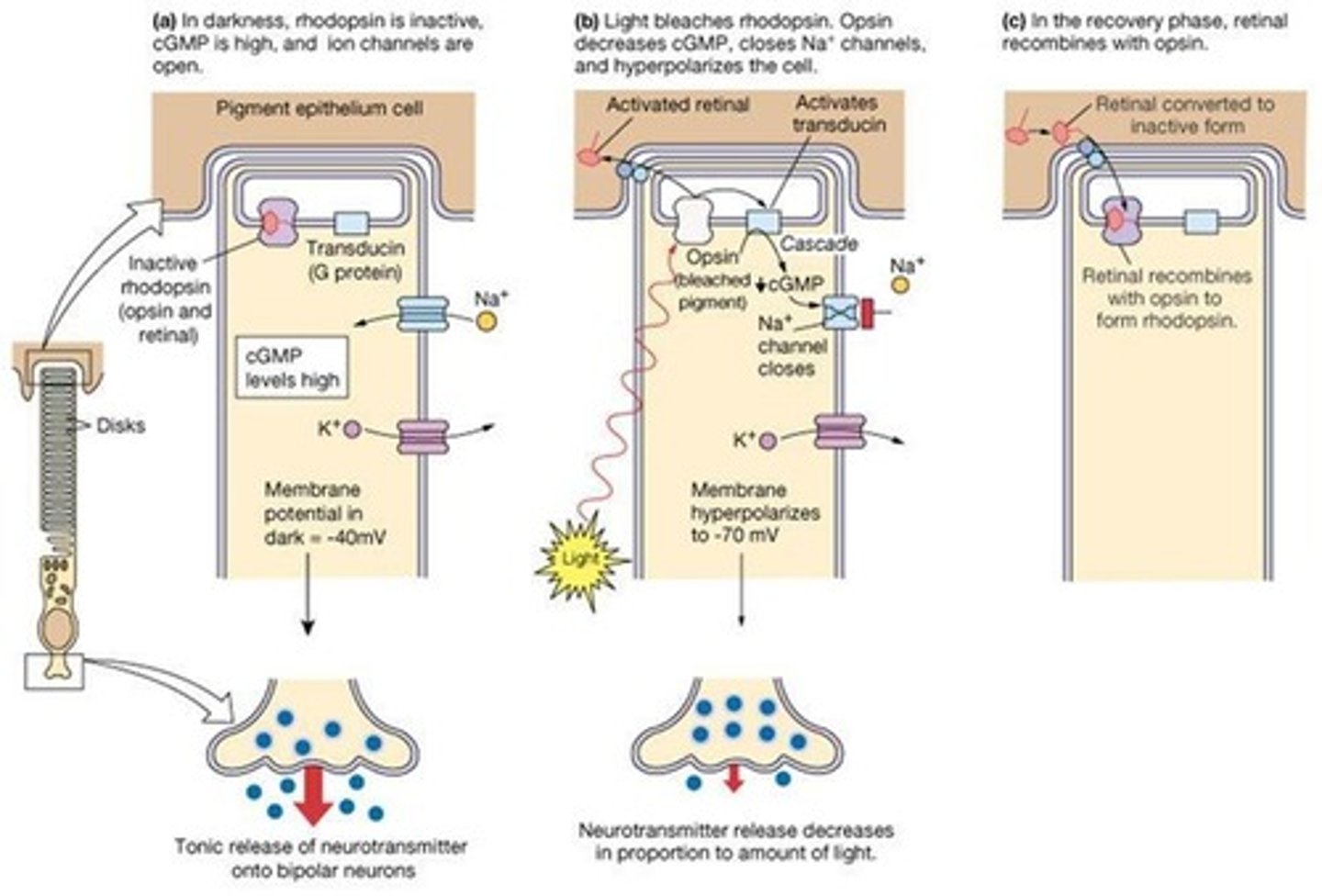
What happens to rhodopsin when it absorbs a photon of light?
It undergoes a change in 3D shape and initiates phototransduction.
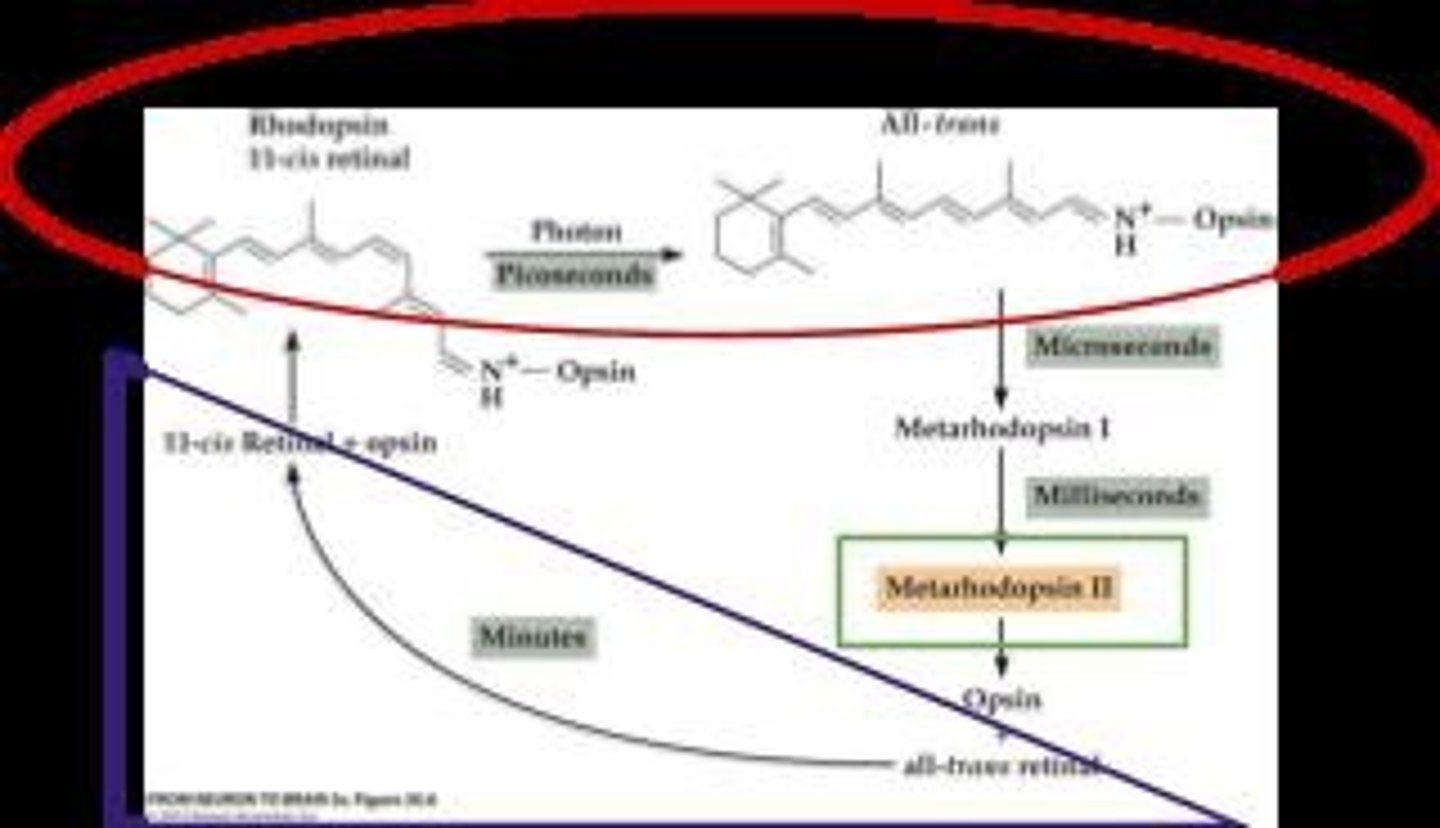
What is metarhodopsin II's role in phototransduction?
It activates second messenger systems after photoactivation.
What is the significance of all-trans retinal?
It is a precursor for the synthesis of 11-cis retinal and cannot be synthesized by humans.
How do photoreceptors of vertebrates respond to light?
With a hyperpolarization graded response.
What initiates the phototransduction cascade?
Photoactivated rhodopsin (metarhodopsin II) binds and activates the G-protein transducin.
What are the two main visual pathways in the brain?
The geniculostriate system and the tectopulvinar system.
What is the dorsal visual stream responsible for?
Guiding actions toward objects (the 'how' pathway).
What is the ventral visual stream responsible for?
Identifying what an object is (the 'what' pathway).
What is the role of the retinohypothalamic tract?
It regulates circadian rhythms and the pupillary reflex.
What is the relationship between sensory experience and sensory reality?
Perceptual experiences are subjective constructions of reality, not objective reproductions.
What happens to Na+ and Ca++ channels in photoreceptors in the dark?
They remain open, causing depolarization.
What is the effect of light on photoreceptor channels?
Light causes the channels to close, leading to hyperpolarization.
What is the function of the synaptic terminal in photoreceptors?
It is involved in neurotransmission.
What is the role of opsin in phototransduction?
Opsin is a G-protein-linked receptor that plays a crucial role in the phototransduction process.
What is the primary function of the cornea?
It serves as the clear outer covering of the eye.
What is the significance of vitamin A in vision?
Vitamin A deficiencies can lead to night blindness, as it is necessary for the synthesis of retinal.
What is sound?
A pressure wave composed of different frequencies important for speech, music, and other natural sounds.
What are the properties of sound?
Sound involves compression of air molecules, with pitch corresponding to frequency and amplitude corresponding to loudness or intensity.
What is a pure tone?
A sound wave that is a sine wave, which is rarely found in nature.
How are sound waves converted in the cochlea?
Sound waves are converted to fluid waves, causing vibration of the basilar membrane.

What is the role of hair cells in the cochlea?
Hair cells transduce sound waves into neural impulses through movement and stimulation.
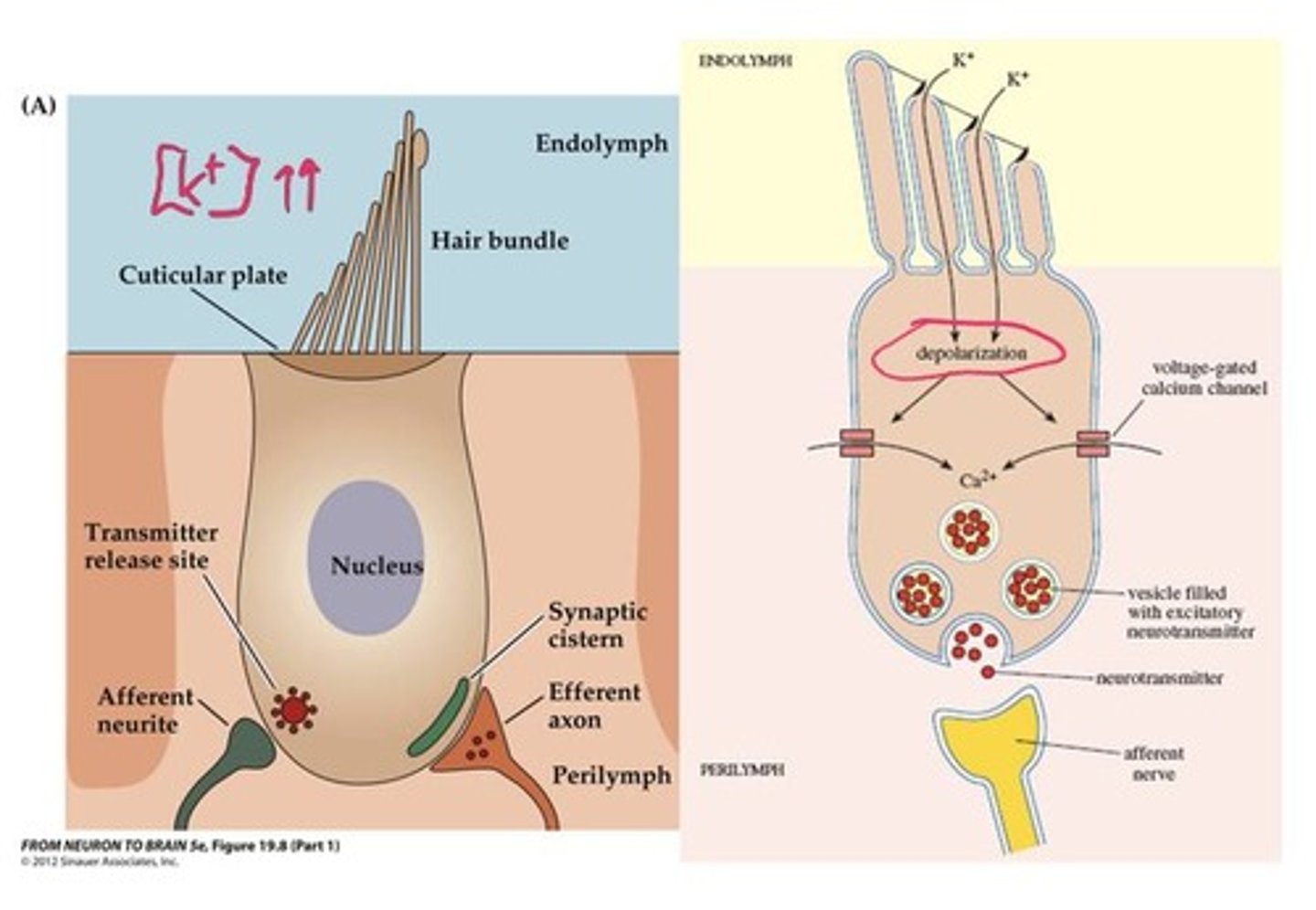
What happens when hair cells are stimulated?
Movement of the basilar membrane stimulates hair cells, causing changes in membrane potential and neurotransmitter release.
What is the function of the inner hair cells?
Inner hair cells are sensory receptors with afferent nerve fibers, responsible for transmitting auditory information.
What is the role of outer hair cells?
Outer hair cells receive efferent output from the brain and modulate basilar membrane movements.
What is the medial superior olive (MSO)?
A brain structure that optimizes binaural differences for sound localization.
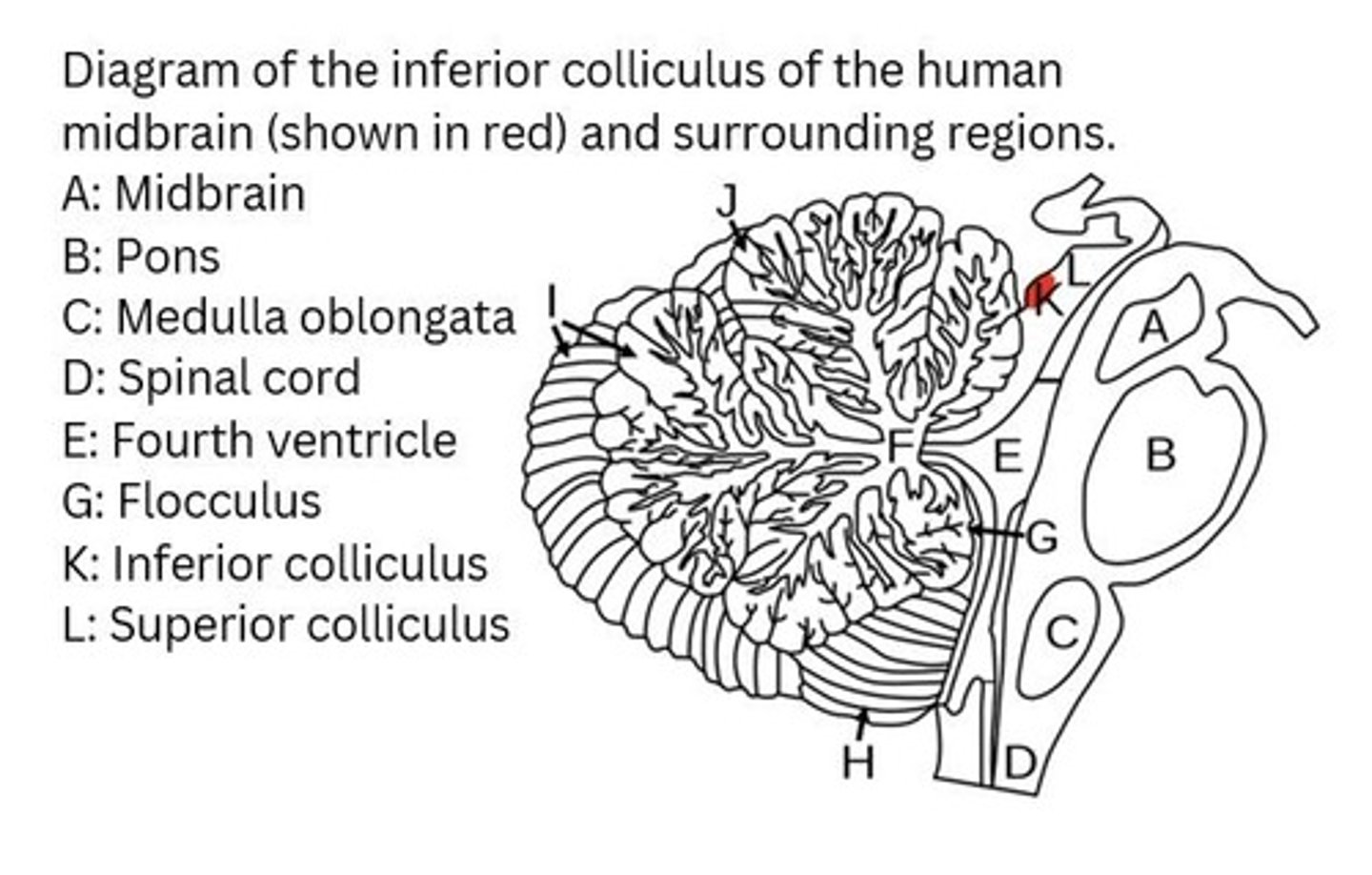
What is the inferior colliculus involved in?
Integration and routing of multi-modal sensory perception, including the startle response and vestibulo-ocular reflex.
What is the primary auditory cortex (A1)?
The area in the cerebral cortex that processes auditory information, located in Heschl's gyrus.
What is proprioception?
The perception of location and movement of the body, sensitive to stretch of muscles and tendons.
What are the three types of somatosensory receptors?
Nociception (pain), hapsis (fine touch), and proprioception (body position and movement).
What is the difference between slowly and rapidly adapting afferents?
Slowly adapting afferents fire continuously while the stimulus is present; rapidly adapting afferents fire at the start and sometimes at the end of a stimulus.
What do Merkel cells express?
Piezo2 ion channels that open in response to mechanical stimuli.
What are muscle spindles?
Proprioceptors that detect changes in muscle stretch and length, consisting of intrafusal muscle fibers.
What are Golgi tendon organs (GTOs)?
Low threshold mechanoreceptors found in tendons that provide information about muscle tension.
What is the function of the presynaptic active zone in hair cells?
It couples Ca++ influx to the release of synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters.
How does hair cell depolarization occur?
Deflection of hair cell bundles opens K+ channels, leading to depolarization and neurotransmitter release.
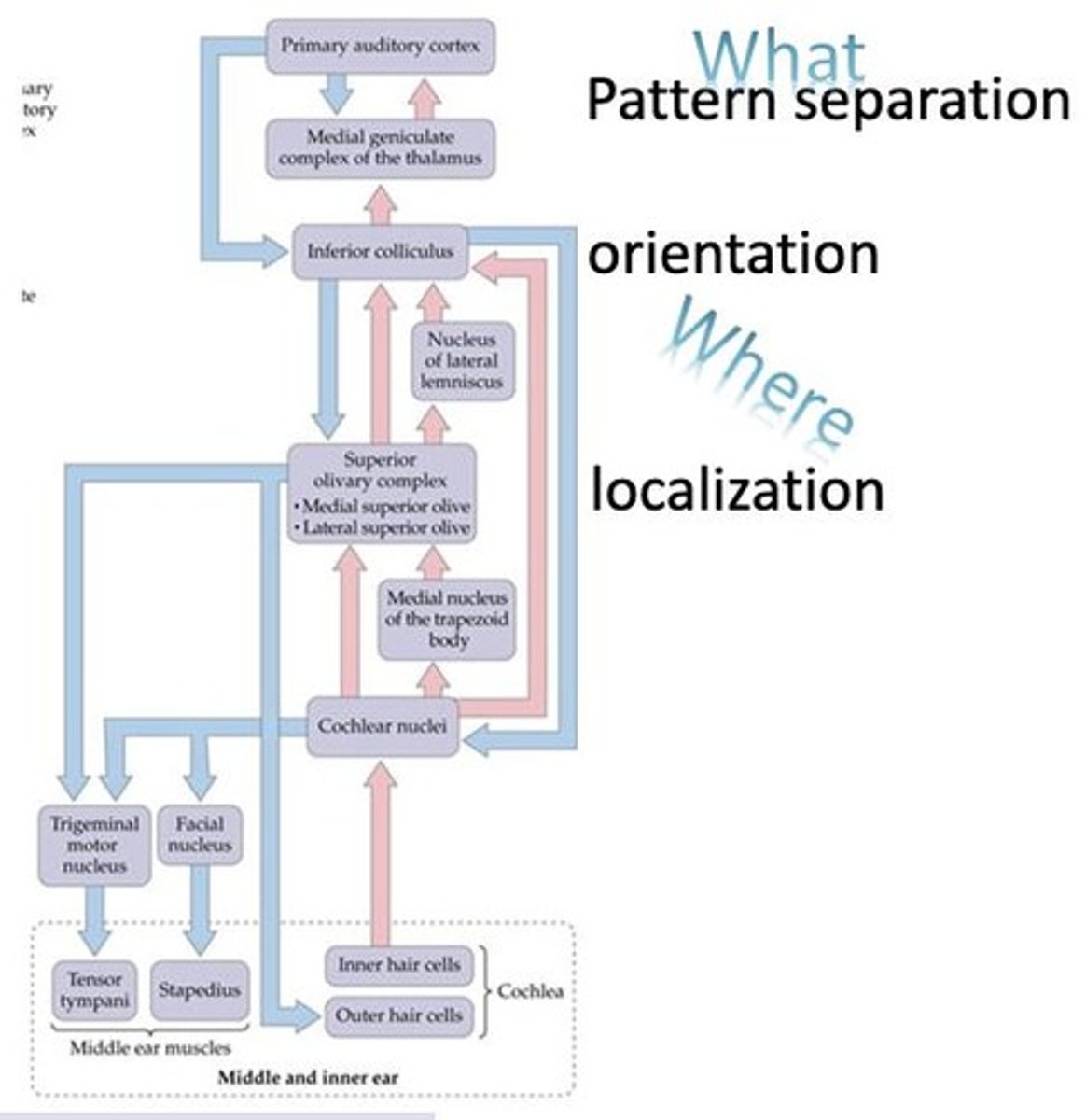
What is the role of the thalamus in auditory processing?
The medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) projects auditory information to the primary auditory cortex (A1).
What is the significance of the auditory cortex's asymmetrical structures?
They are involved in processing different frequencies of sound.
What is the relationship between sound frequency and the basilar membrane?
High frequencies cause maximum displacement near the base, while low frequencies displace near the apex.
What is the importance of mechanical forces on the skin?
They are conveyed to the CNS via somatosensory afferent neurons, informing about the size, shape, and movement of stimuli.
What is the difference between high and low threshold receptors?
High threshold receptors (nociceptors) respond to pain, while low threshold receptors are sensitive to non-painful stimuli.
What is the function of the olivary complex?
It helps with sound localization by processing sensory information from both hemispheres.
What is pattern separation in auditory processing?
The process of distinguishing different sound patterns, facilitated by the medial geniculate nucleus and auditory cortex.
What are the sensory endings of a mechanosensory neuron responsible for?
Detecting changes in muscle tension and sending this information to the CNS via group 1b afferents.
What are the three types of mechanoreceptors embedded in joints?
Type I (slowly adapting, outer layers of the joint capsule), Type II (rapidly adapting), Type III (slowly adapting, in ligaments and terminal regions of tendon).
What is the composition of a mammalian muscle spindle?
It is composed of small intrafusal fibers embedded in the bulk of the muscle.
Which neurons innervate the muscle spindle?
Large muscle fibers are supplied by alpha-motoneurons, and intrafusal fibers are supplied by gamma efferent fibers.
What are Group Ia afferents responsible for?
They are large diameter, fast conducting fibers that form primary nerve endings sensitive to the rate of change of stretch.
What do Group II afferents detect?
They are smaller, conduct more slowly, and form secondary nerve endings sensitive to the level of static tension.
How do mechanoreceptors open their channels?
Channels can be opened by forces conveyed through lipid tension or through structural proteins linked to ion channels.
What is the pathway for haptic-proprioceptive axons to the brain?
They ascend the spinal cord ipsilaterally but cross at the level of the brainstem.
Where do nociceptive nerve fibers synapse?
They synapse with neurons whose axons cross to the contralateral side of the spinal cord before ascending to the brain.
What do proprioceptive afferents for the lower body synapse on?
They synapse on neurons in the dorsal and ventral horn of the spinal cord.
What is the role of the primary somatosensory cortex?
It receives projections from the thalamus and begins the process of constructing perceptions from somatosensory information.
What areas of the brain correspond to the primary somatosensory cortex?
Brodmann's areas 3-1-2.
What does the secondary somatosensory cortex do?
It refines the construction of perceptions and projects to the frontal cortex.
What is the homunculus in the primary somatosensory cortex?
It reveals that the sensitivity of a body part is proportional to the amount of somatosensory cortex receiving input from that body part.
What is the function of the vanilloid receptor?
It is a member of the TRP family found on the endings of Aδ and C fibers, involved in nociceptive signal transduction.
What do TRP channels mediate?
They mediate responses to endogenous and exogenous chemical, mechanical, and thermal stimuli.
What is peripheral sensitization?
It is when activated nociceptors stimulate the influx of non-neuronal cells and substances that contribute to inflammation.
What is hyperalgesia?
It is the perception that pain is worse than it would normally be considered.
What are the two types of nociceptive-transmitting afferent fibers?
Aδ lightly myelinated axons and C unmyelinated axons.
What is the role of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in pain sensitivity?
It can initiate and maintain hyperalgesia.
How do NSAIDs help in pain management?
They inhibit cyclooxygenase, reducing prostaglandin synthesis, which decreases inflammation and pain.
What is allodynia?
It is a nociceptive response produced by a non-noxious stimulus.
What is the effect of inflammation on TRP channels?
Changes in TRP channels can switch neurons to an altered state, leading to peripheral sensitization.
What is the significance of the medial lemniscus in somatosensory pathways?
It carries proprioceptive and tactile information to the thalamus after crossing the midline.
What is the function of the dorsal column nuclei?
They send their axons across the midline and ascend through the medial lemniscus to the ventral posterior nucleus.
What are nociceptors?
Nociceptors are sensory receptors that detect potentially damaging stimuli and signal pain.
What are the two categories of pain?
1. Sharp first pain carried by Aδ fibers. 2. Dull second pain carried by C fibers.
What types of Aδ fibers exist?
Type I: Mechanical; high heat thresholds. Type II: Thermal; low heat threshold.
What is the function of C fibers?
C fibers carry delayed, broadly acting, dull second pain and respond to all types of nociceptive stimuli.
What is the anterolateral system (AL)?
A central pain pathway that transmits pain, temperature, and crude touch information to the somatosensory cortex.
What does the dorsal-column medial lemniscal system (DCML) carry?
It carries mechanical stimuli such as touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception.
What is the pain matrix?
An extensive network of forebrain regions that enables the experience of the full range of pain.
What neurotransmitters are involved in pain modulation?
Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
What is Melzack and Wall's Gate Control Theory of Pain?
It suggests that activation of low-threshold mechanoreceptors can mitigate ascending nociceptive signals.
What is the olfactory system responsible for?
Processing airborne molecules that influence behaviors such as seeking food and social interactions.
How do odorants interact with the olfactory system?
Odorants bind to olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) in the olfactory epithelium.
What is the role of the olfactory bulb?
It processes signals from ORNs and sends information to the brain via the olfactory tract.
What are glomeruli in the olfactory bulb?
Spherical accumulations of neuropil where axons of receptor neurons contact mitral cells.
What is the vomeronasal system?
A system used to detect pheromones and kairomones, prominent in carnivores and rodents.
What is the function of Bowman's glands?
They secrete mucus that acts as an initial defense against harmful microorganisms.
What is the process of olfactory transduction?
Chemical signals are converted into electrical signals by ORNs, which are then relayed to the CNS.
What is the role of GPCRs in olfactory transduction?
GPCRs activate G-proteins that lead to a cascade resulting in neuronal depolarization.
How many types of odorant receptor genes are found in humans?
Humans have 500-750 odorant receptor genes, with 100-200 producing functional products.
What accounts for the diversity of odorant recognition?
Variation in the amino acid sequences of the transmembrane domains of olfactory receptors.
What is the significance of the olfactory epithelium?
It contains ORNs that detect odorants and initiate the olfactory transduction process.
What is the main output of the olfactory bulb?
Mitral cells, which project to various brain regions including the pyriform cortex.