Rocky Intertidal Ecosystems
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Rocky Intertidal Ecosystems
also driven by tides. make up ¾ of coastlines, may be rocky cliffs, boulder fields, rock pools, platforms etc. Biologically rich, a home or nursery for many fish and crustaceans. Feeding grounds for fish, sea turtles, and shore birds. Organisms must tolerate daily changes.
characterized by tides, winds, sunlight, temperature.
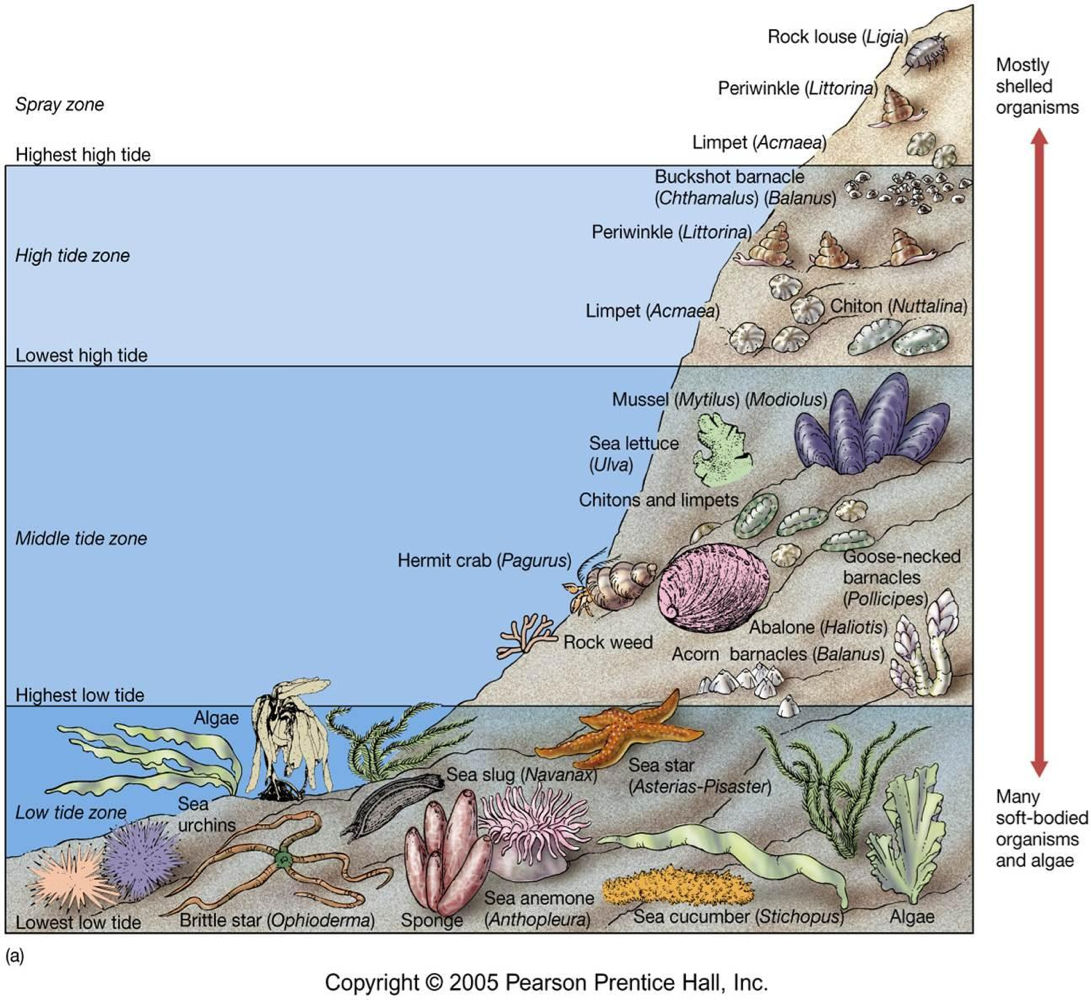
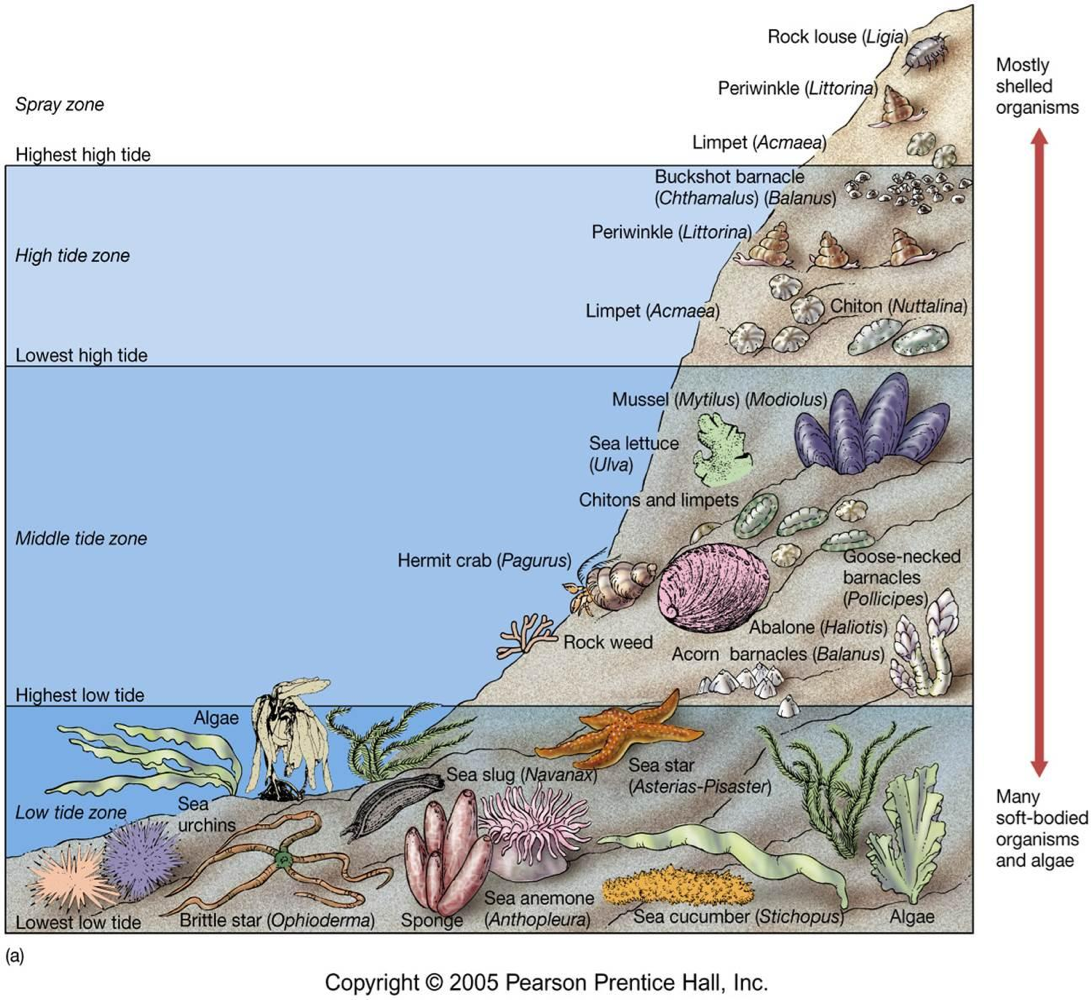
Supratidal zone
aka splash zone, the upper region around high tide mark. mostly exposed to air so desiccation, temperature changes, respiration and food availability are all stressors. Least diverse because predation is high from lack of shelter + lack of food.
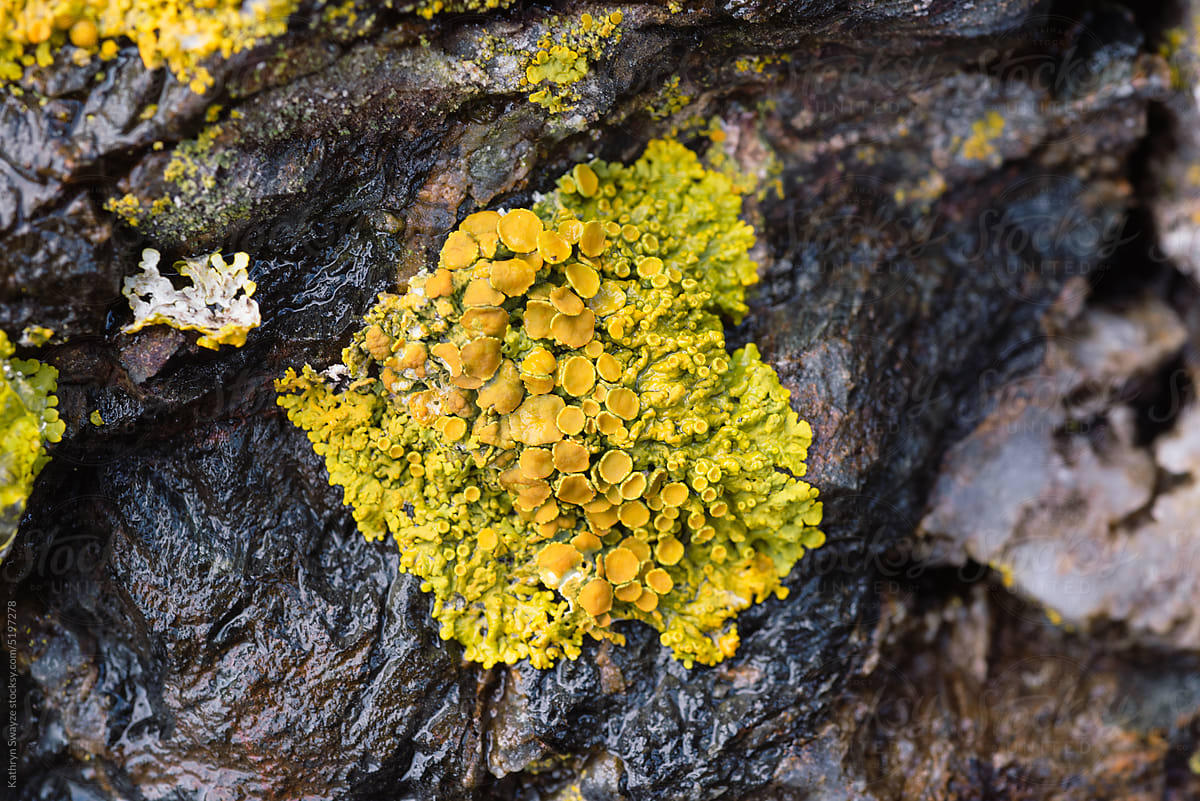
Lichen
Supratidal organism that is a combination between fungi, which traps moisture, and algae, which photosynthesizes

Cyanobacteria Mats
Supratidal organism, thick green mats that are protected by drying due to jelly coating. Can fix nitrogen from air

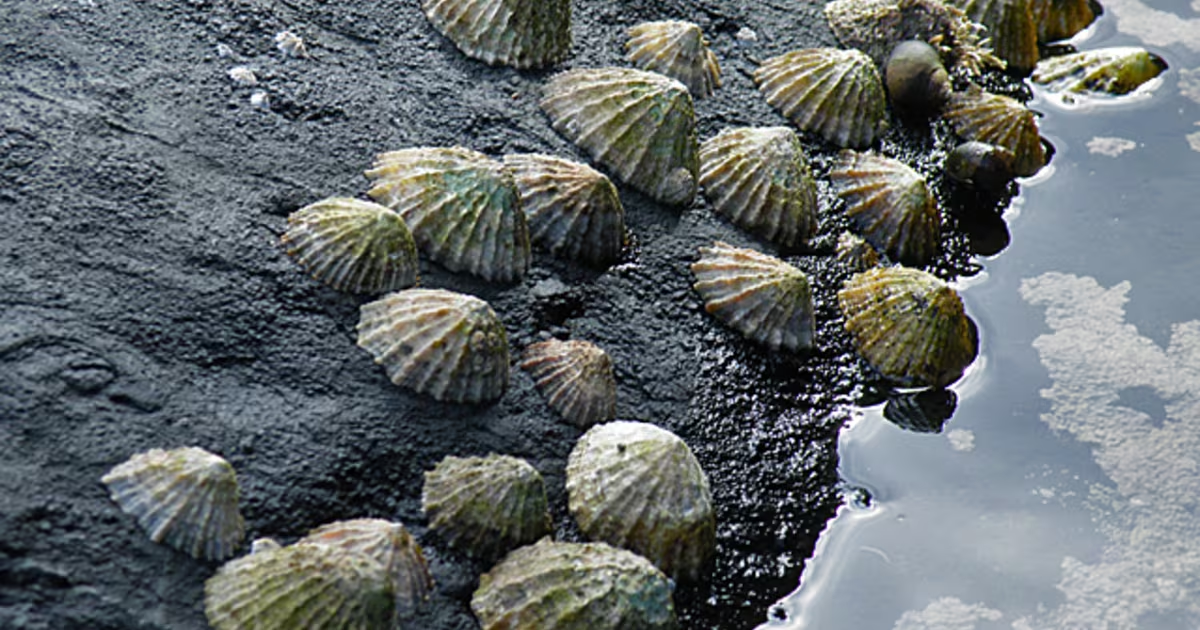
Limpets
Supratidal grazer

Periwinkles
graze algae off of rocks, may breathe air and live out of water for months so tolerant to extreme temperatures

Sea lice
or sea roaches, a supratidal organism that can breathe air, live above waters edge and move into splash zone at low tide
Upper Shore
the high tide zone, mainly exposed to air except at high tide
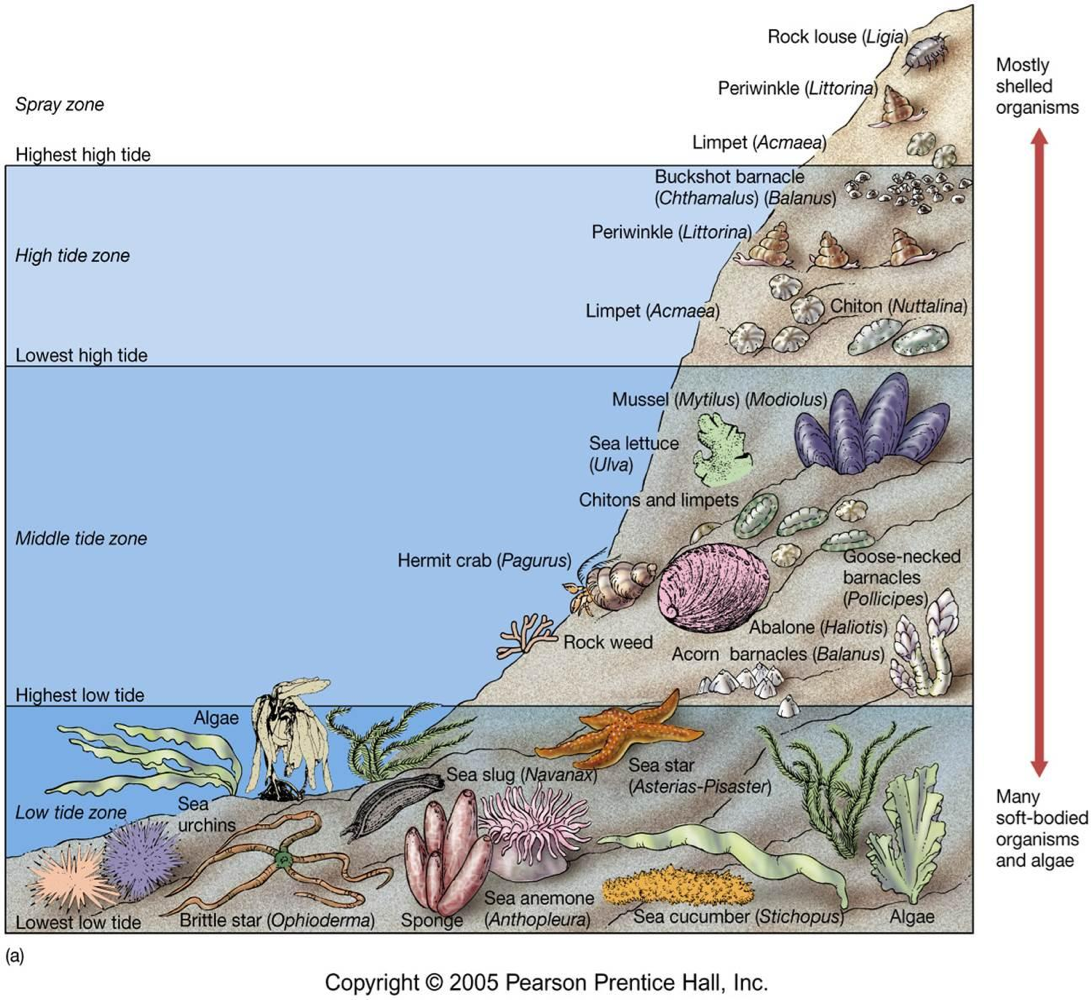
Middle Shore
aka midlittoral zone, has equal exposure to air and water
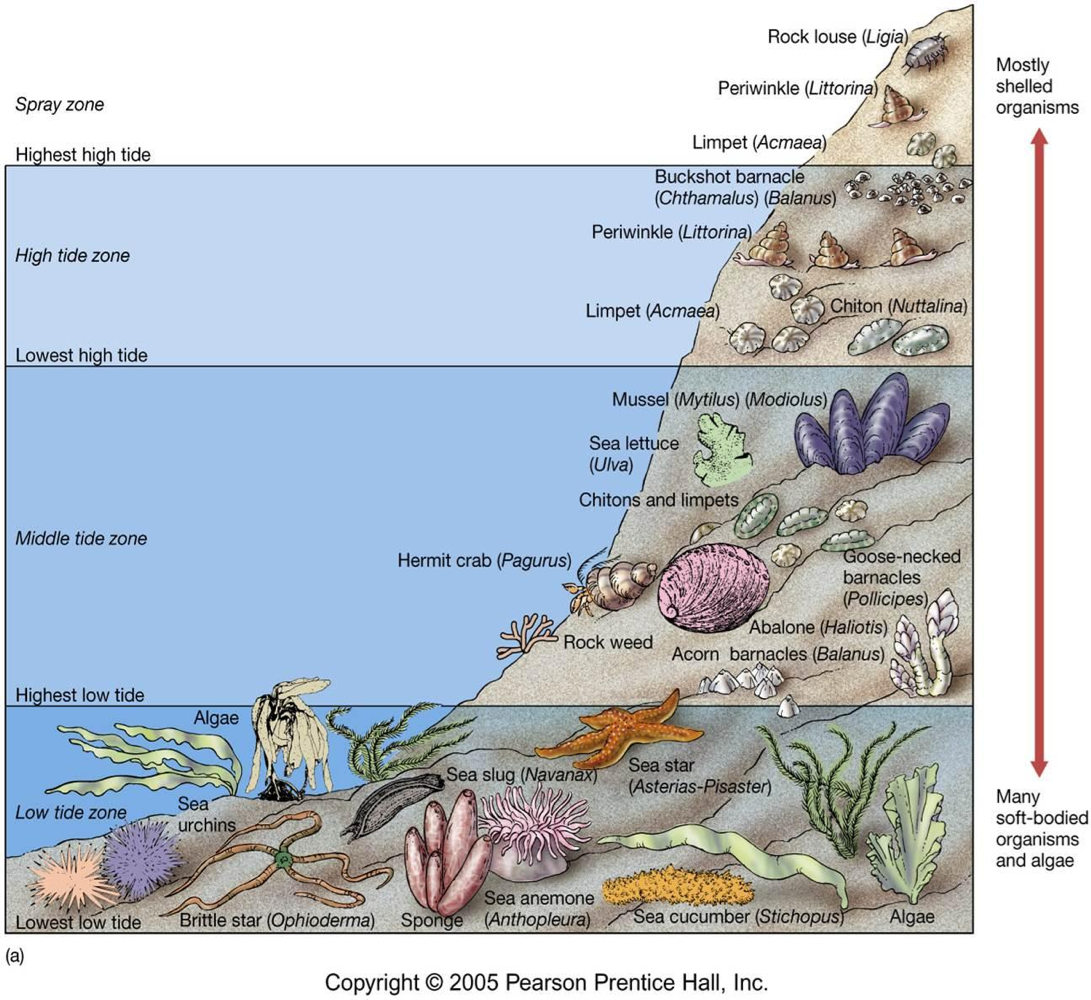
Lower Shore
aka lowerlittoral zone, is always exposed to water except at very low tides. organisms here are not adapted to long periods of dryness or extreme temps
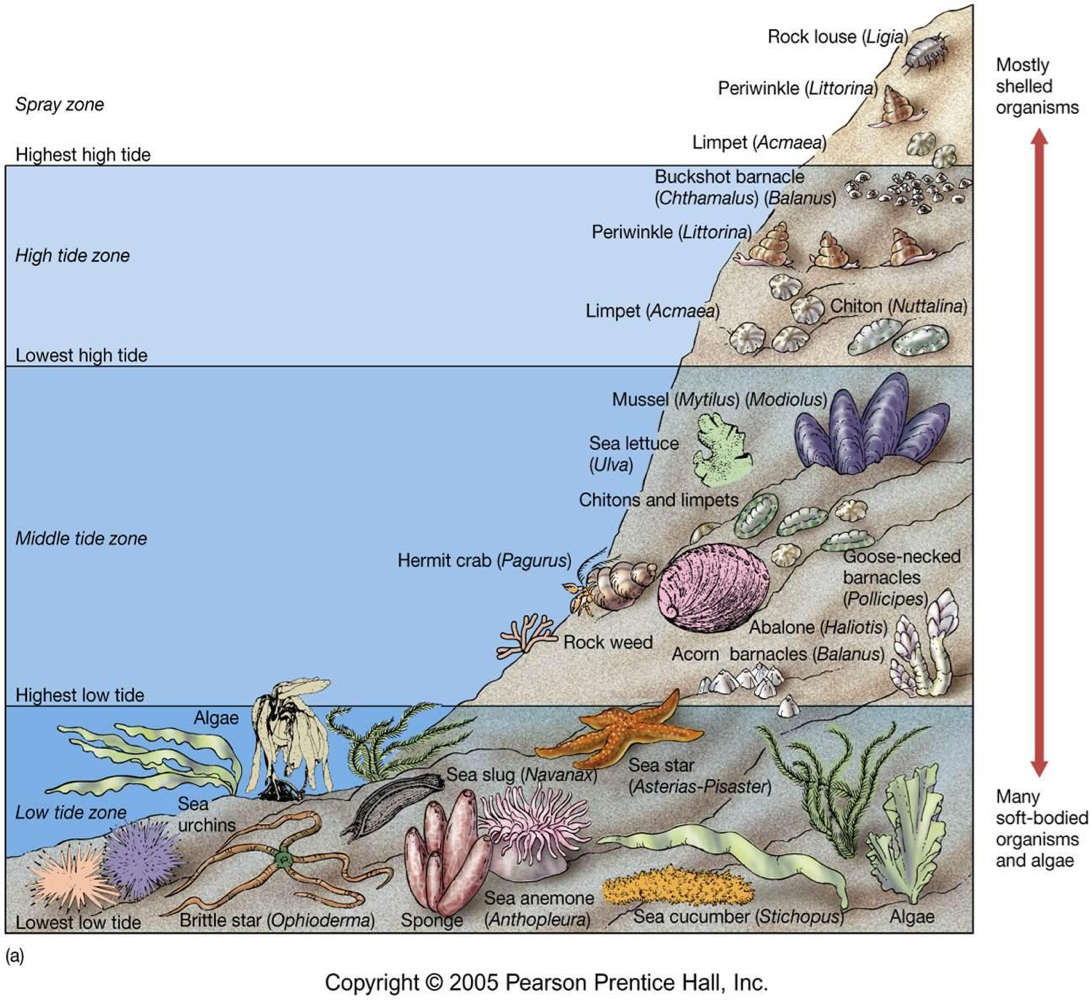
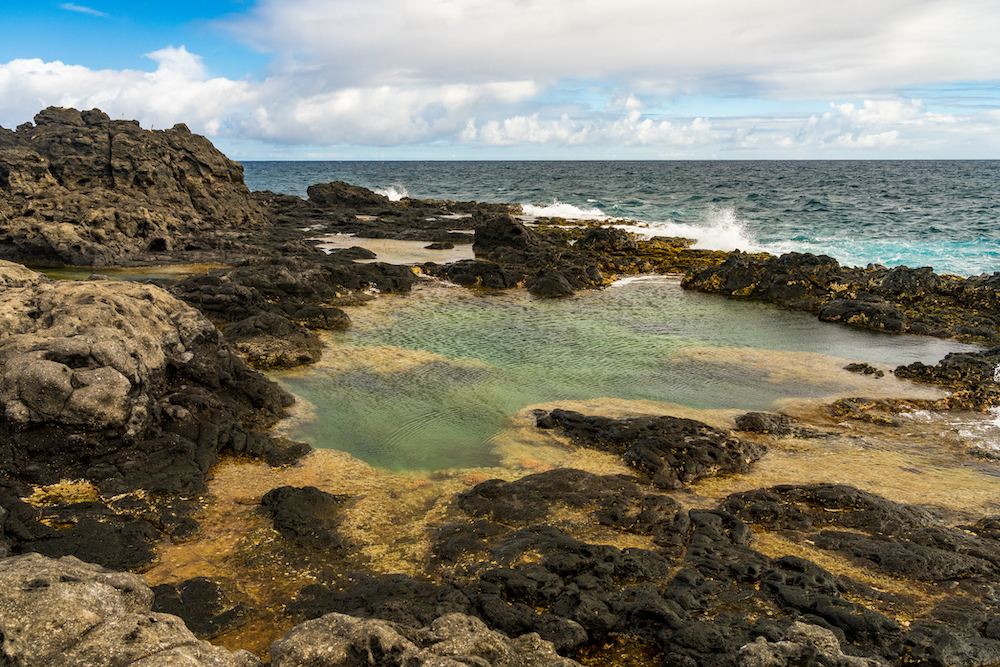
Tide Pools
pools of water left behind when the tides go out that generally appear in the Intertidal Zone
The smallest tide pools are typical found at high intertidal, while the biggest tide pools are found at the lower intertidal zone.

Subtidal Zone
below the intertidal zone, always exposed to water. more stable than intertidal zone because no fluctuations in temperature, water pressure, sunlight, and species don’t dry out as often as higher zones
Zonation Drivers
Predation (more at subtidal or lower shore because water column predators)
Competition for space (mussels smother competitors because move with byssal threads)
Larval and adult preferences - planktonic larvae are gregariousness, so settle near high density of species. larval of sessile species locate best tidal height
Abiotic Stressors
Respiration if they breathe with water because tide goes out
Temperature changes, including freezing
Desiccation if no water or high wind
UV Radiation (too much they dry out or can’t capture light, too little can’t grow or reproduce if photosynthetic) so use melanin or shells
Salinity because when tide pools evaporate, salinity increases and most species are osmoconformers so can’t control their salt content
Waves
Respiration adaptations
mantle cavity like lung in Limpets
Periwinkle gils can gas exchange
Barnacle species store air bubbles in gills
Sessile animals reduce metabolic rate, and mobile animals just move with tide
Temperature adaptations
since they are mostly ectotherms:
They have evaporative cooling and circulation of body fluids
Homeoviscous adaptation (membrane fluidity)
Heat shock proteins
Light coloration
Increase surface area (ribbed shells)
Cryoprotectants (cold)
Increase in osmolytes (such as glycerol and sucrose) (cold)
Desiccation Adaptations
Desiccation resistant egg cases
Reduction of exposed surface area across with water loss takes place
A temporary reduction in metabolic and developmental rates
Storage of water in body/mantle cavities
Mobility
Salinity Adaptations
Produce osmolytes that keep intracellular fluid at the same concentration as the marine env. to avoid the negative effects of salinity changes.
Wave Adaptations
Permanent attachment though it cannot be used by all organisms - especially those that must move to feed themselves. Bivalves byssal threads or a foot to attach to rocks or other organisms or will lay on their side and cement their lower valve to the substrate bellow (Oysters & Scallops)
Burrow into sediment (harder to do on rocky shores), or seek shelter in crevices.