Peripheral Vascular System
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Anatomy & Physiology of the Peripheral Vascular & Lymphatic System
Peripheral Vascular System
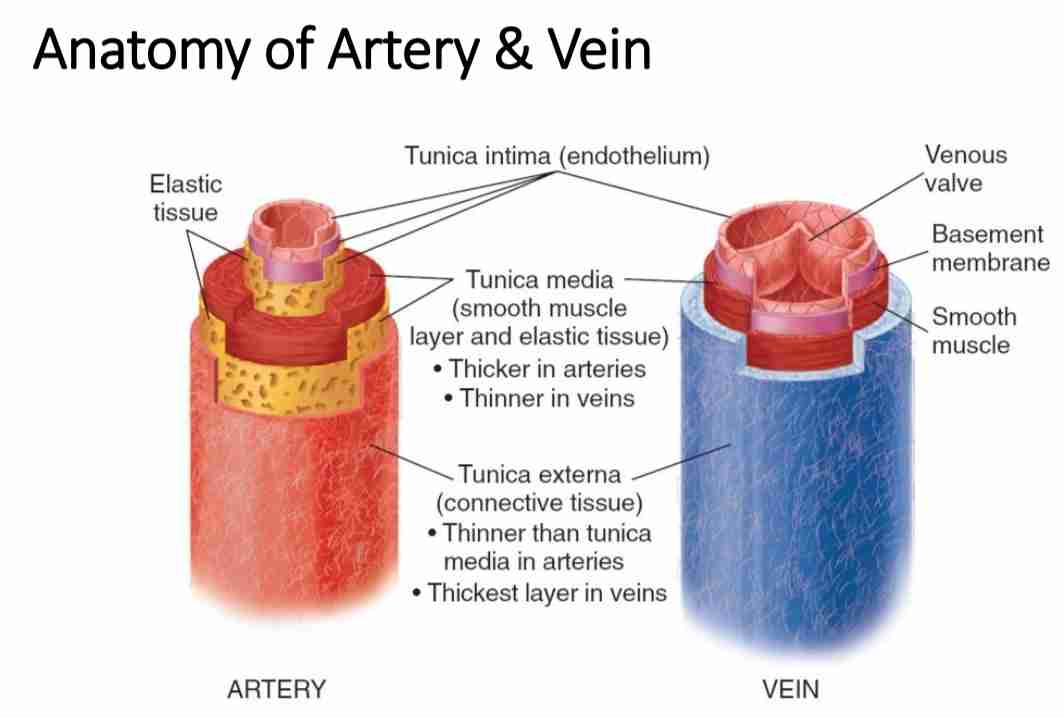
The peripheral vascular system consists of arteries, veins, and capillaries responsible for blood circulation outside the heart and lungs.
Arteries: Carry oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues.
Examples: Carotid, Brachial, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, Dorsalis Pedis, Posterior Tibial arteries.
Veins: Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Examples: Jugular, Subclavian, Femoral, Great & Small Saphenous veins.
Capillaries: Microscopic vessels for gas and nutrient exchange
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system helps in fluid balance, immune defense, and waste removal.
Lymph Nodes: Filter fluid and trap pathogens.
Locations: Cervical, Axillary, Epitrochlear, Inguinal, Popliteal nodes.
Lymphatic Vessels: Drain excess fluid from tissues into venous circulation.
Physical Examination Techniques
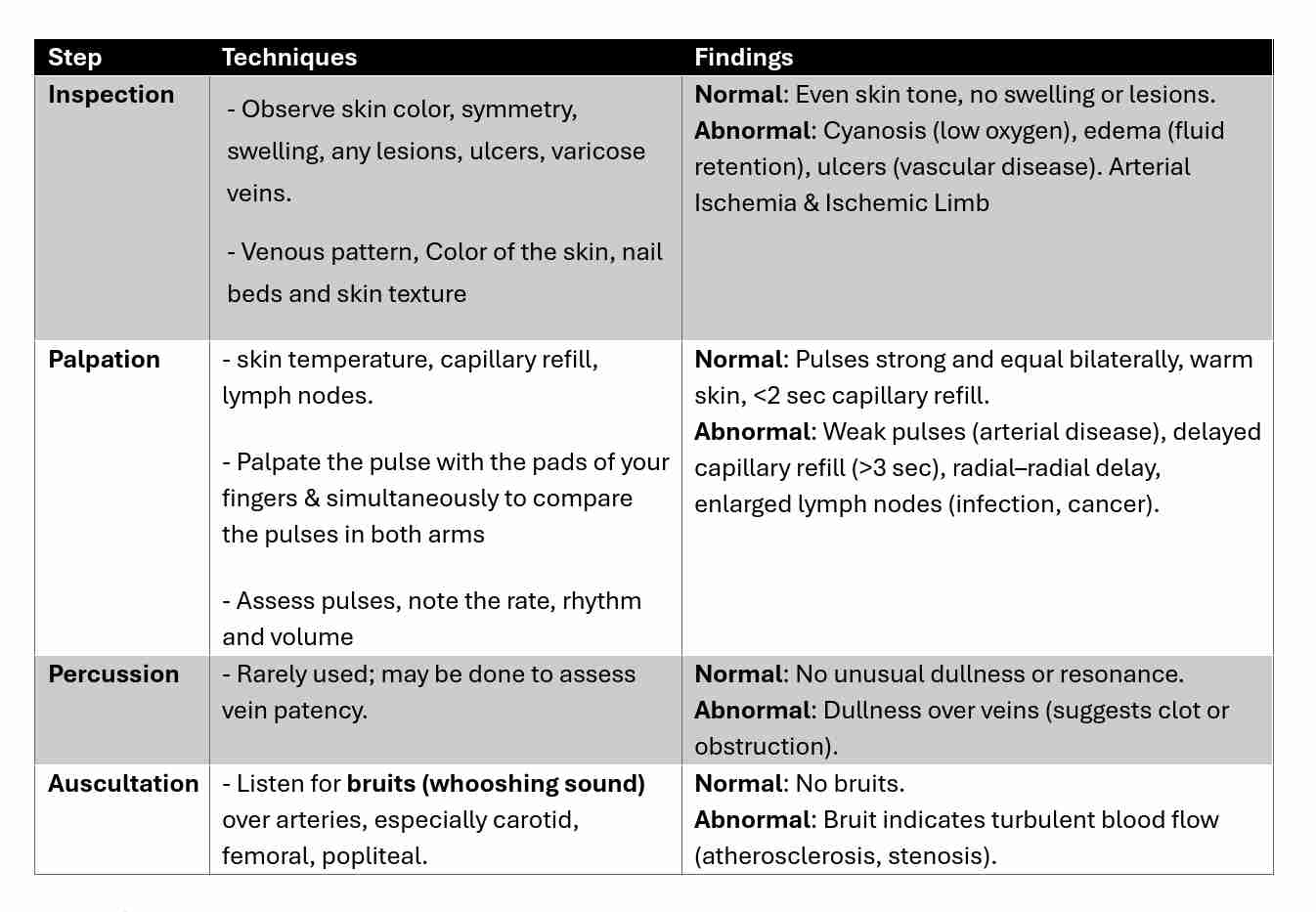
Key Pulse Points
Upper Limb: Radial, Brachial, Carotid.
Lower Limb: Femoral, Popliteal, Dorsalis Pedis, Posterior Tibialis.
Differentiating Normal & Abnormal Findings
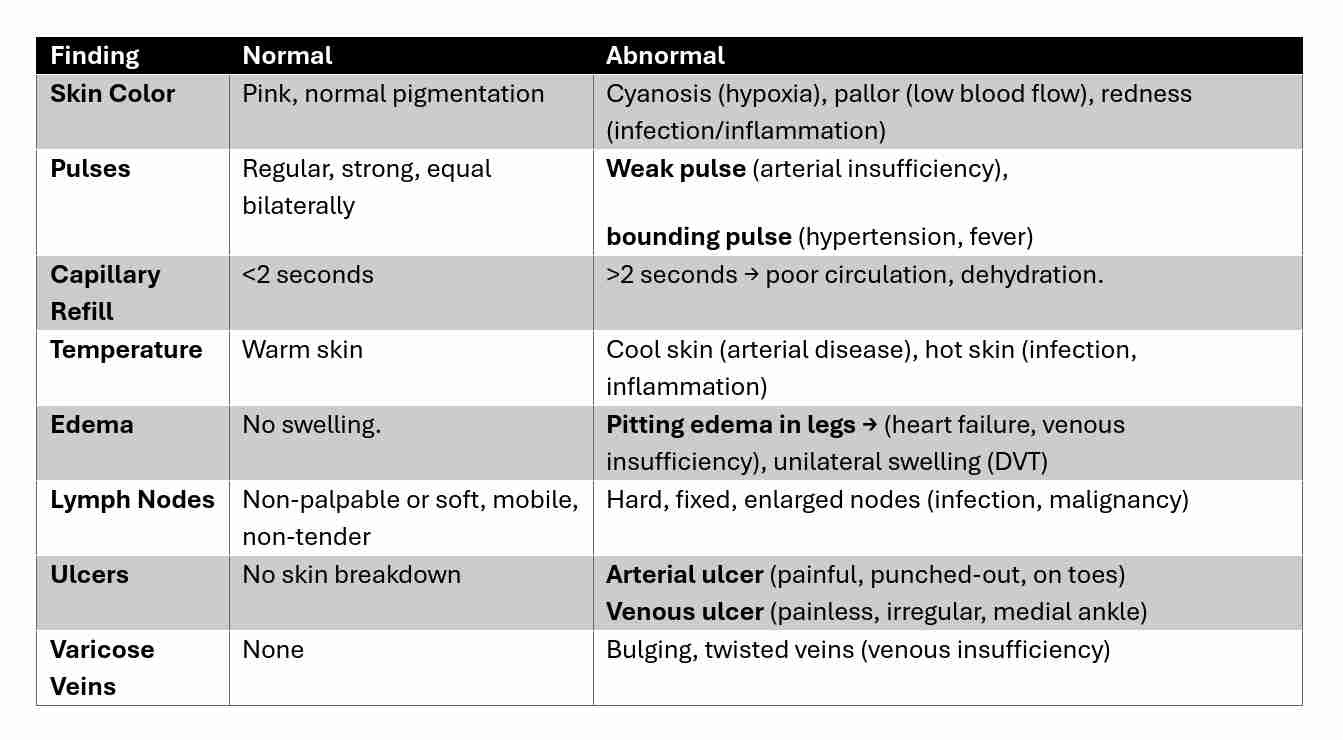
Analyzing Findings from Interviews, General Survey &
Interview Findings:
Chief complaints: Leg pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, non-healing wounds.
History of: Smoking, diabetes, hypertension, previous DVT, varicose veins.
General Survey:
Ensure the patient is adequately exposed with draping in between the legs
Remember to compare sides
Vitals: bilateral and orthostatic blood pressures
Physical Exam
Specific locations
Upper extremities (from the finger tips to the shoulder)
Lower extremities (from the groin and buttocks to the toes)
Inspect for:
Masses, scars, lesions,
Symmetry: muscle bulk (atrophy/hypertrophy)
Size: swelling, thickening
Continue…
Arterial insufficiency
Cyanosis: central (frenulum and buccal mucosa) and peripheral (nails)
Skin: cool, pale extremities, increased pigmentation, swelling, heaviness and aching in legs (usually medial lower third of legs)
Ulcers: ischemic ulceration due to trauma of the toes and heel, develops rapidly, painful, and has discretely visible edges
Venous stasis
Skin: warm, thickening and erythema over the ankle and lower leg (dependent areas), thickened (woody) fibrosis/lipodermatosclerosis
Ulcers: stasis ulceration of ankle or above medial malleolus, develops slowly, painless, diffuses with no distinct borders
Veins: engorgement, varicosities
Cont….
Palpation and Auscultation
Arterial
Skin temperature: feel with back of hand warm vs. cool
Capillary refill: compress nailbeds and determine the duration for return of
Circulation: normal adult = 2-3s
Pulses
Rate: tachycardia >100 bpm, bradycardia <60 bpm
Rhythm: regular, regularly irregular (consistent pattern), irregularly irregular
Amplitude