Eye Anatomy & Physiology - Chapter 16
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
good luck brotatochip

Eyeball
u know where the eye is

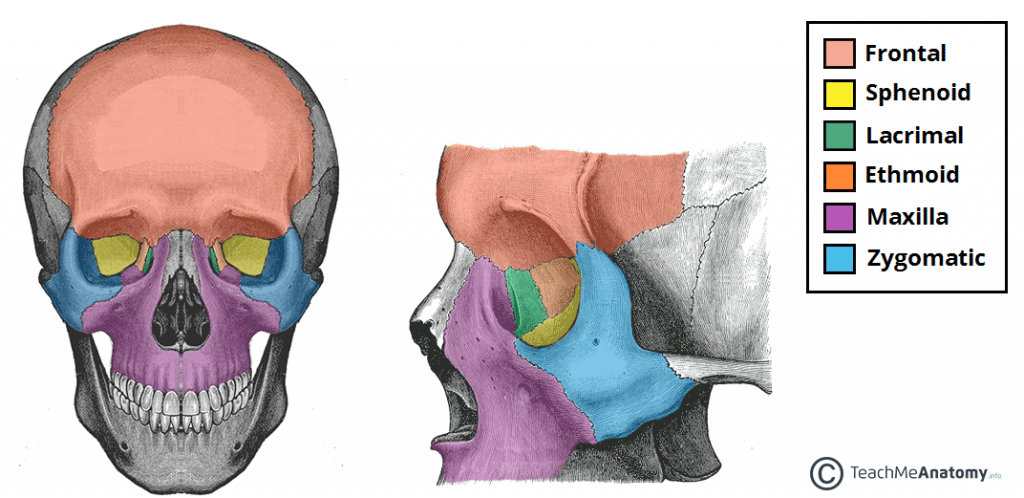
Bones of the Orbital Cavity:
Frontal
Maxilla
Zygomatic
Sphenoid
Lacrimal
Ethmoid
Palatine
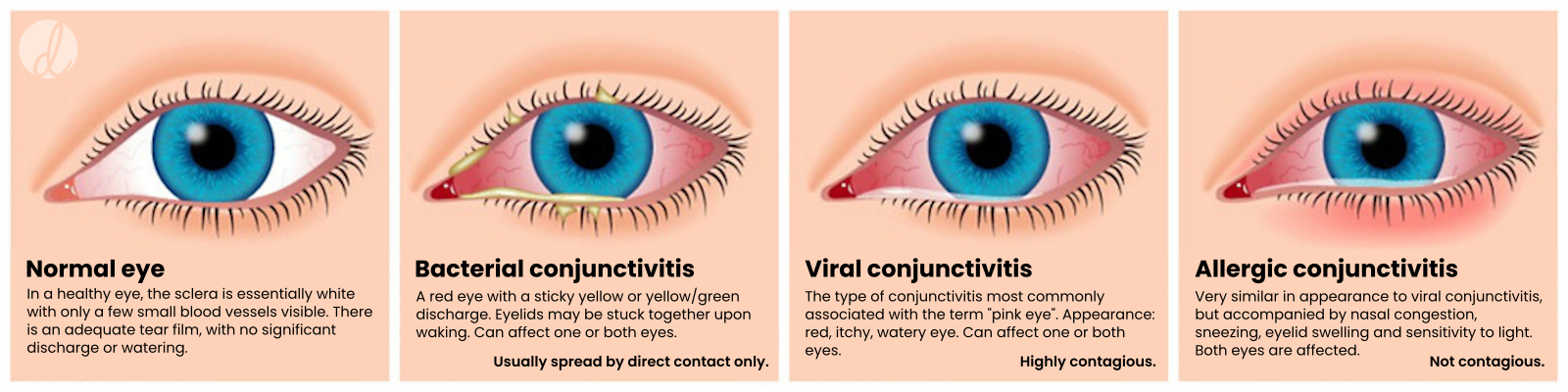
Palpebral
Superior and inferior palpebral are your eyelids
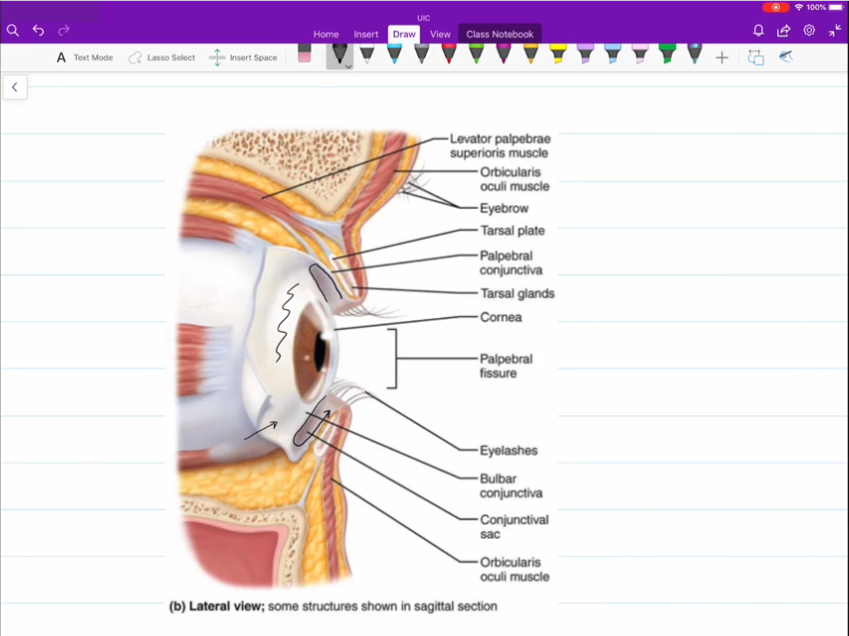
Bulbar Conjunctiva
Covering that sits atop the surface of your eye.
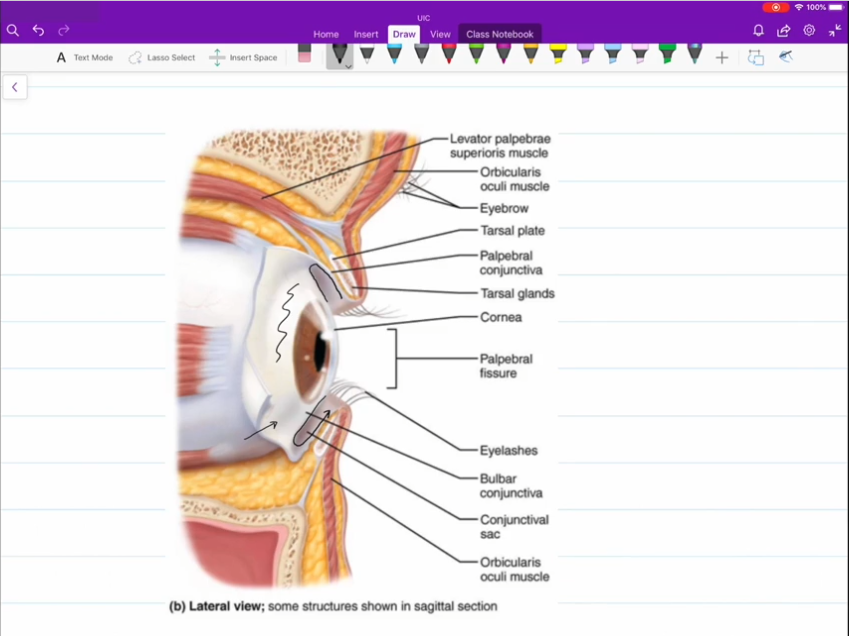
Palpebral Conjuctiva
Covering that rests on the inner surface of the superior and inferior palpebral.
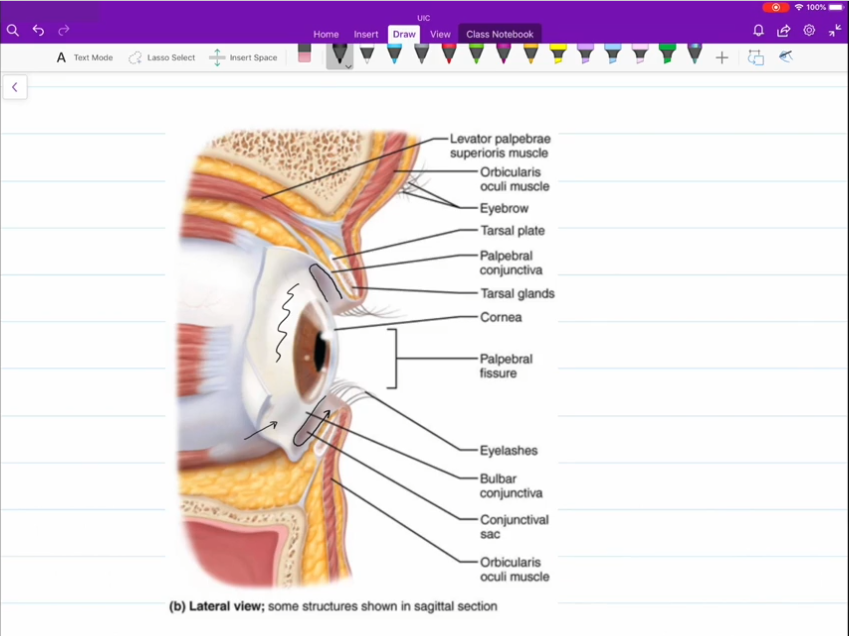
Medial and Lateral Commissure
Corner of the eyes
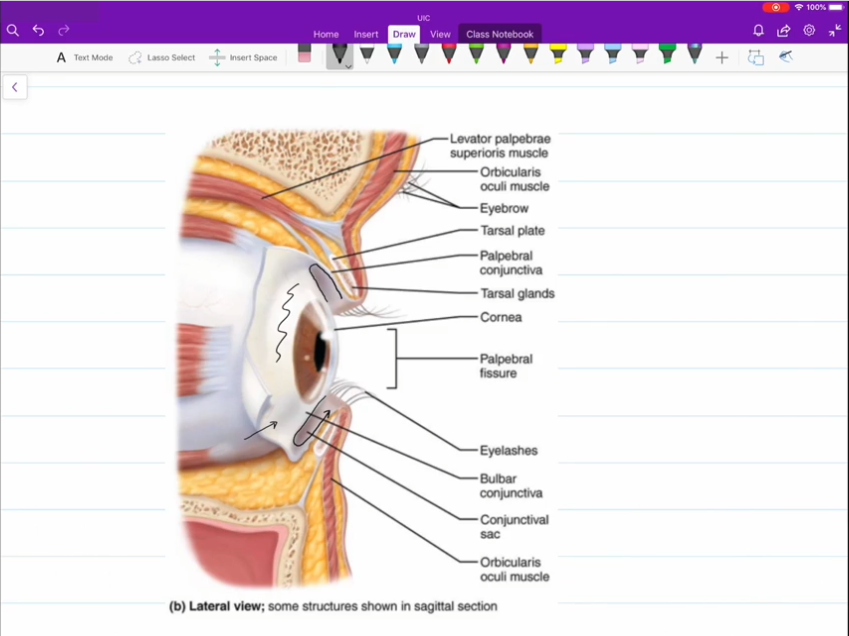
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the Conjunctiva
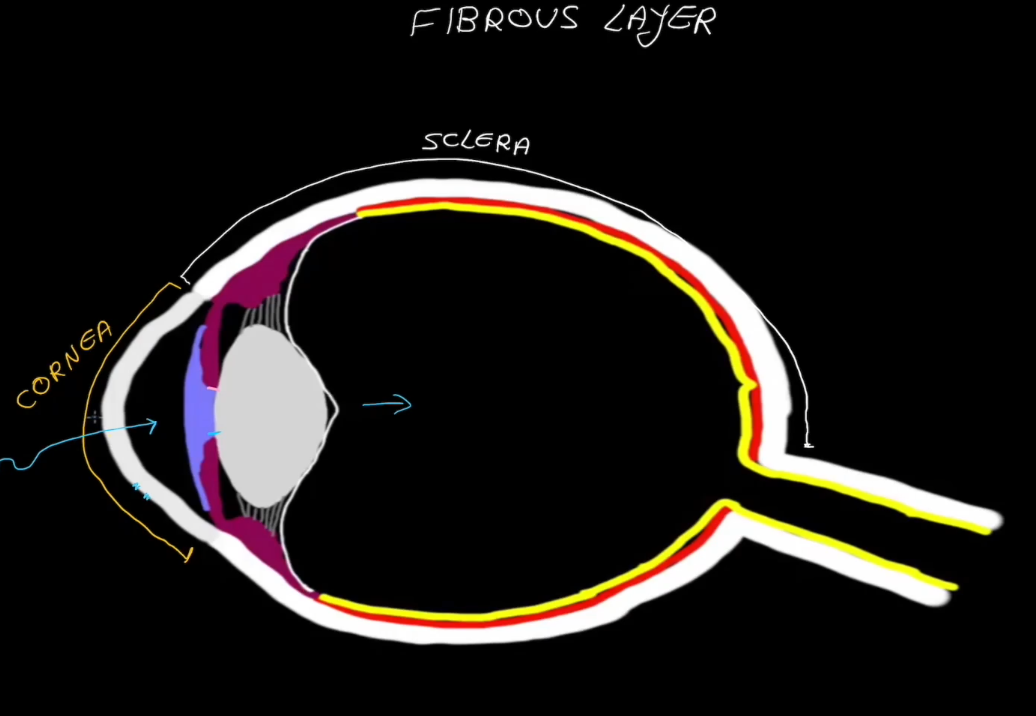
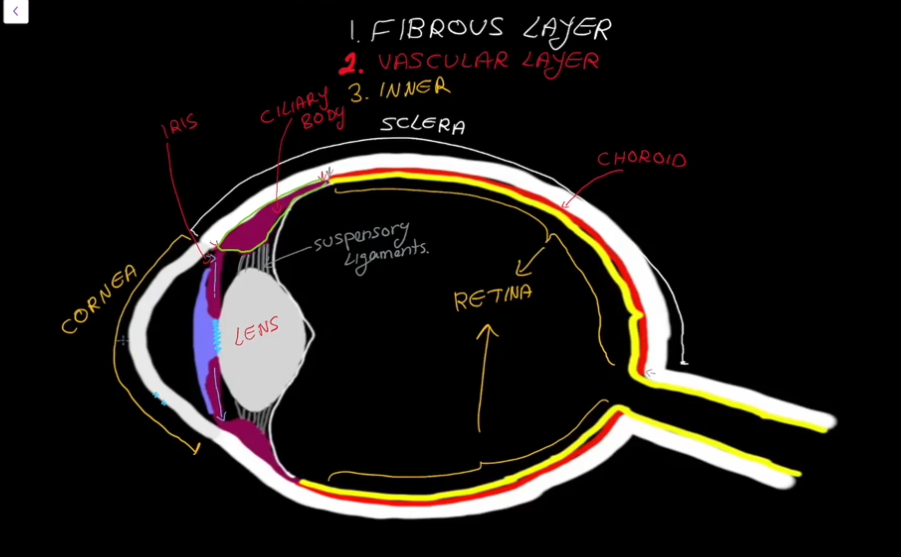
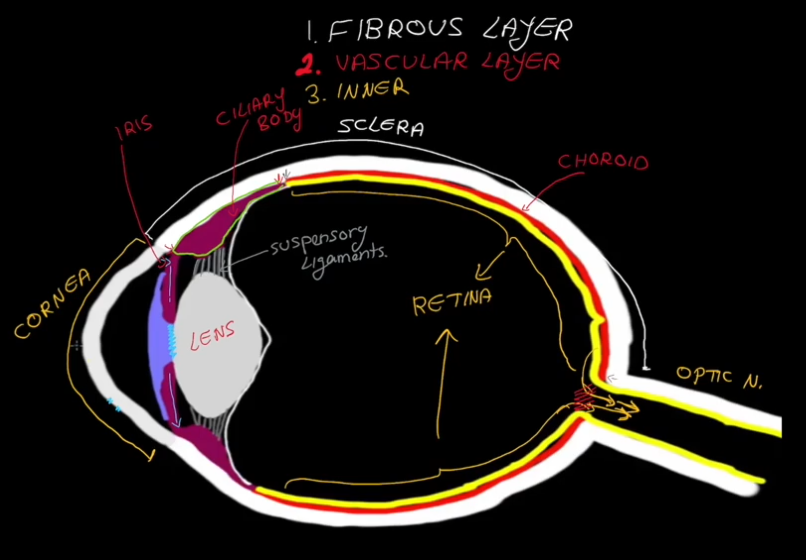
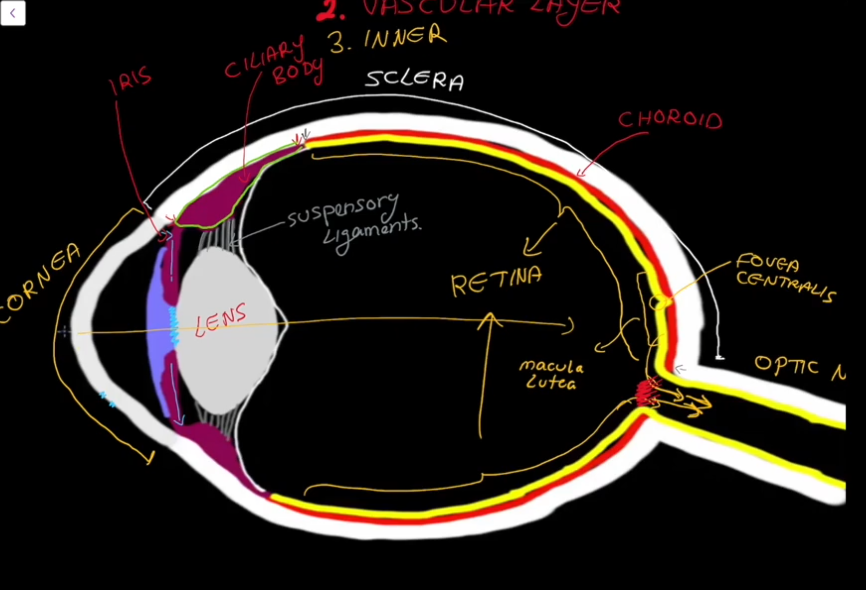
Layers of the Eyeball:
Fibrous
Vascular
Inner
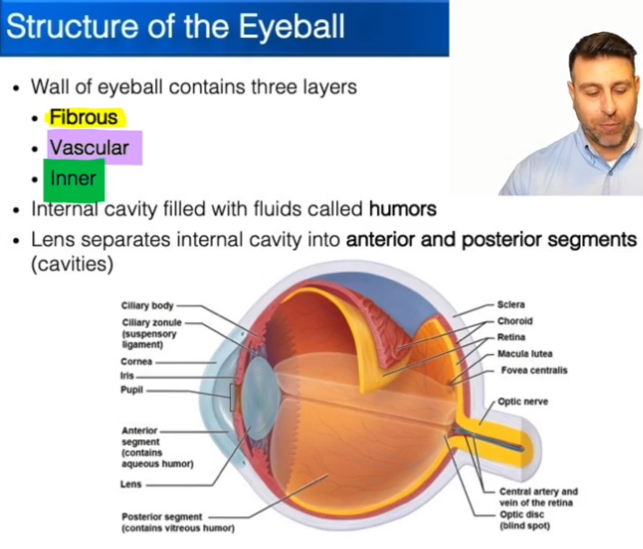
What is a Humor?
Sacs of liquid in the eye that help to keep the shape
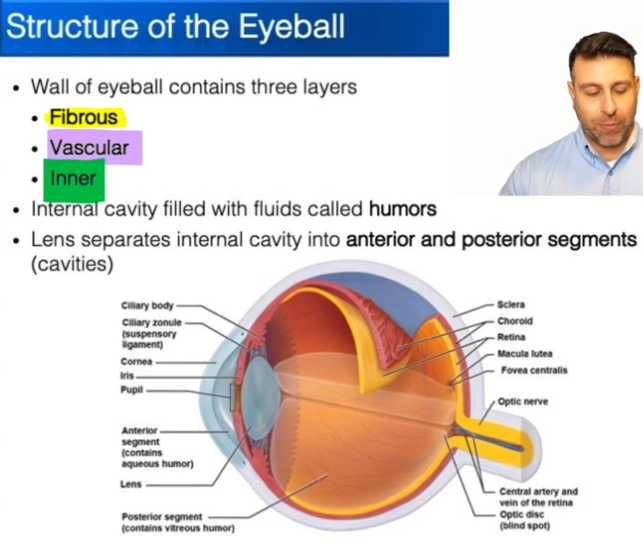
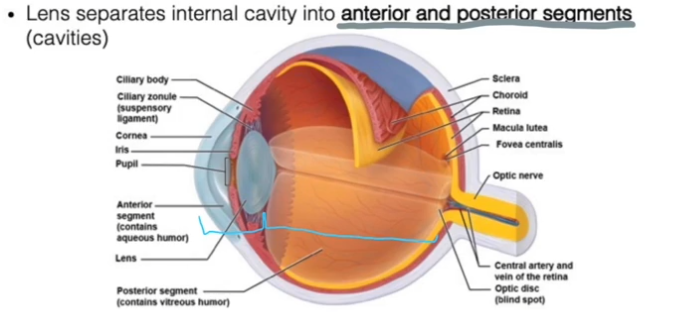
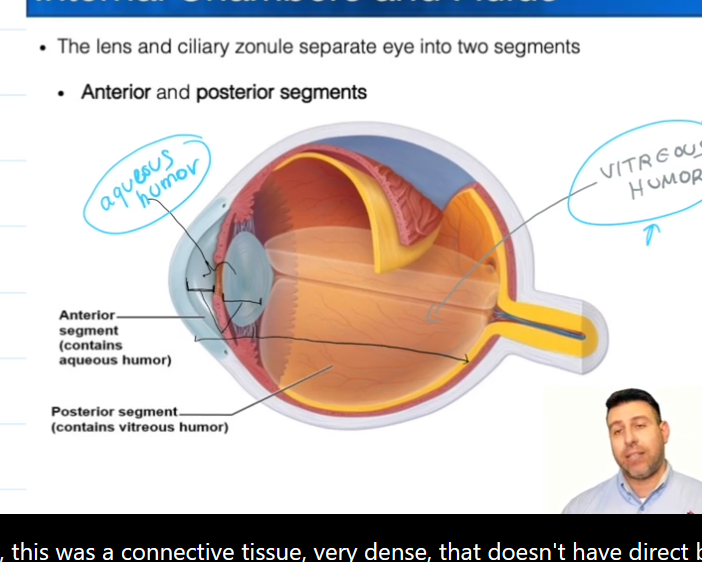
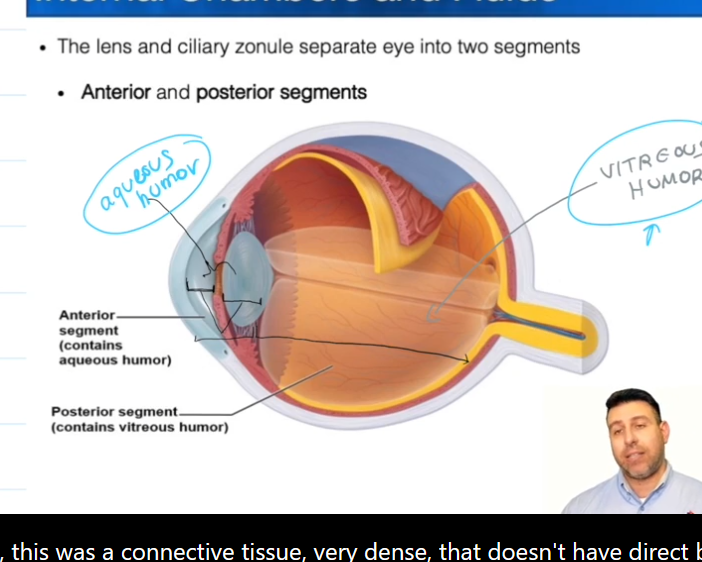
Segments of the eye:
Anterior segment is everything in-front of the lens.
Posterior segment is everything behind the lens
Fibrous Layer Structure:
Outermost layer, has no blood supply
Contains the Sclera
Contains the Cornea
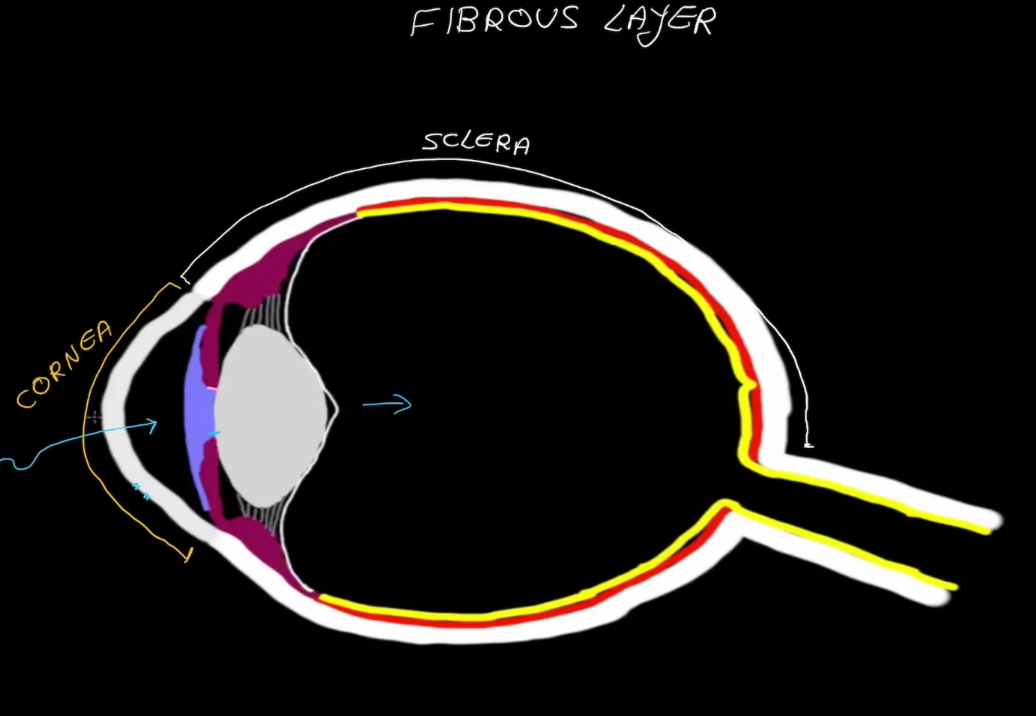
Sclera
White in color.
Dense connective tissue
Shapes the eye and is the point of muscle attatchment.
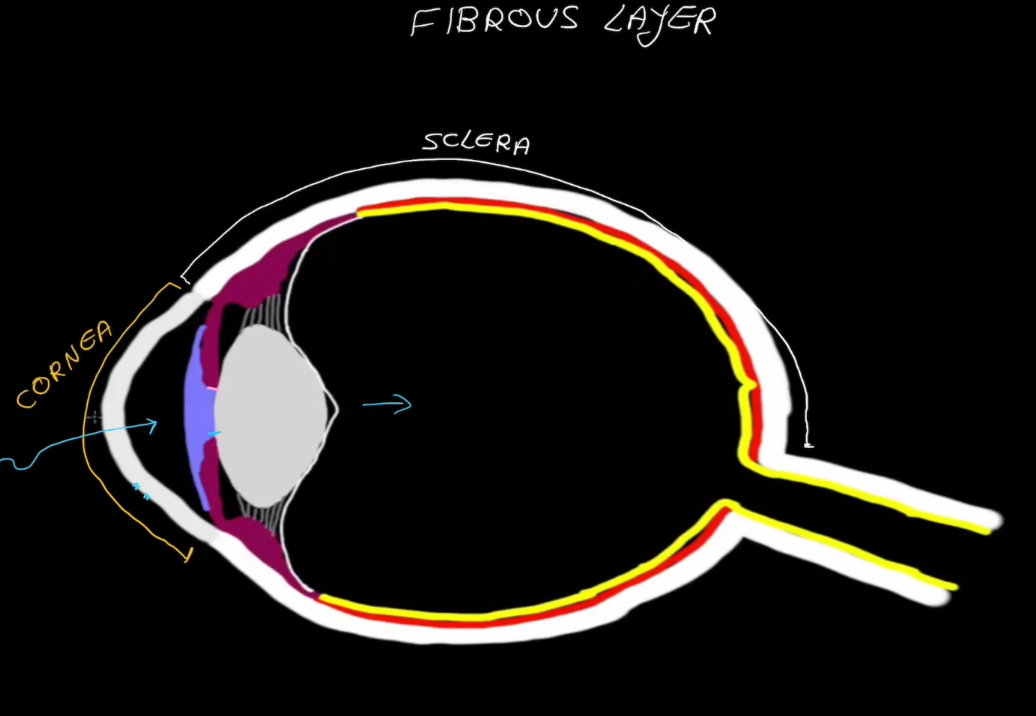
Cornea
Transparent
Dense connective tissue
Vascular Layer
Contains the choroid
Contains the cillary
Contains the pupil
Contains the Iris
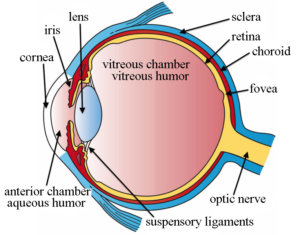
Choroid Region
Supplies blood to the eyes.
Contains brown pigment to prevent light from scattering around the eyes.
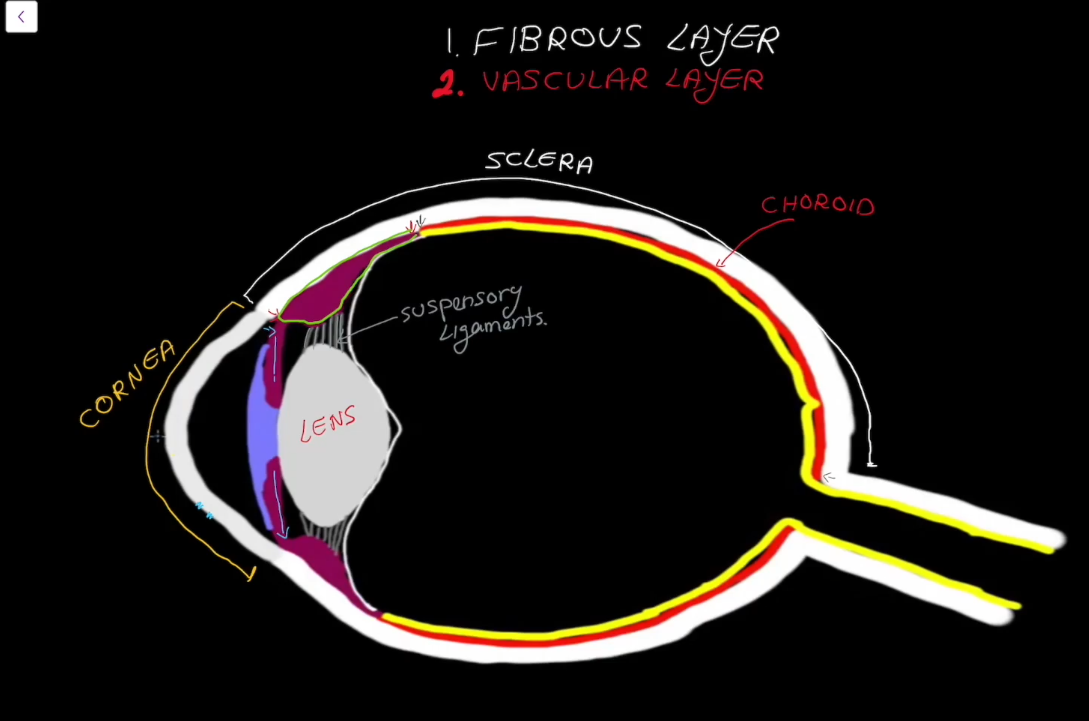
Cillary Region
Surrounds the lens of the eye.
Has suspending ligaments that connect to the lens of the eye.
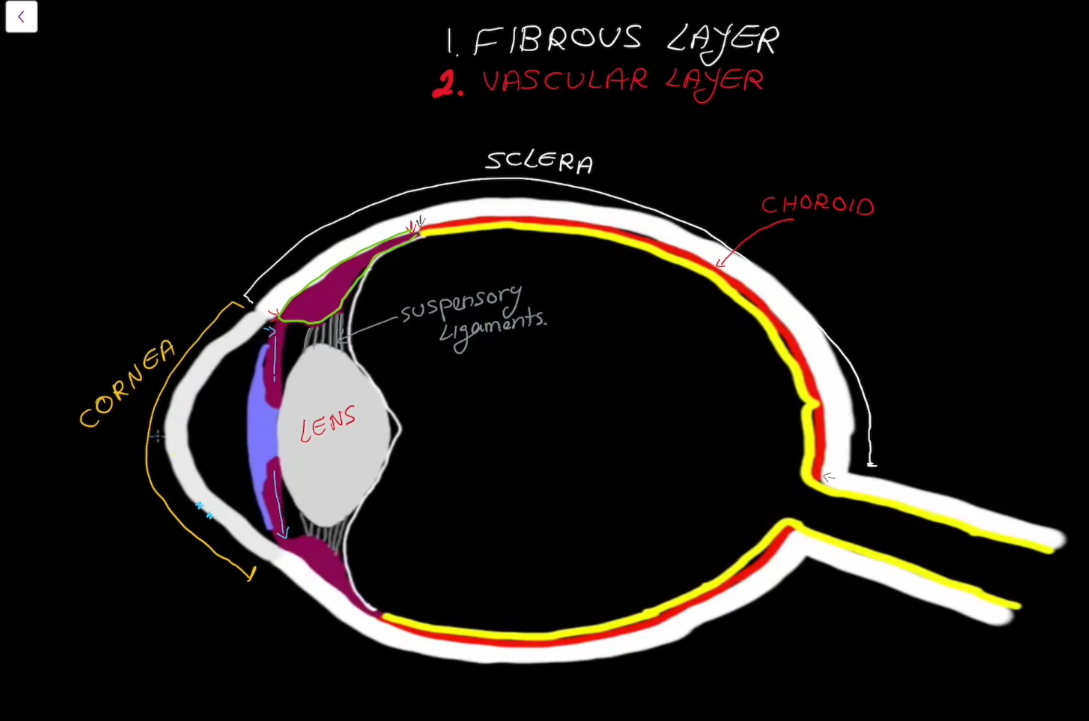
Pupil Gap
Gap for da pupil
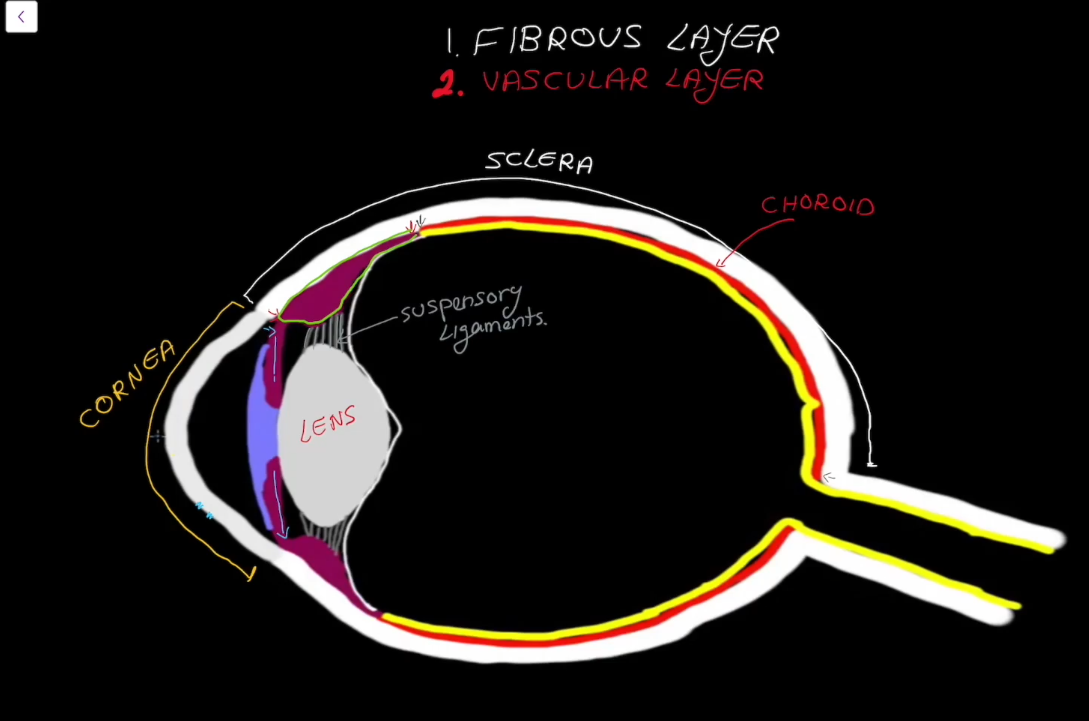
Iris
Colored part of the eye, contains the pupil.
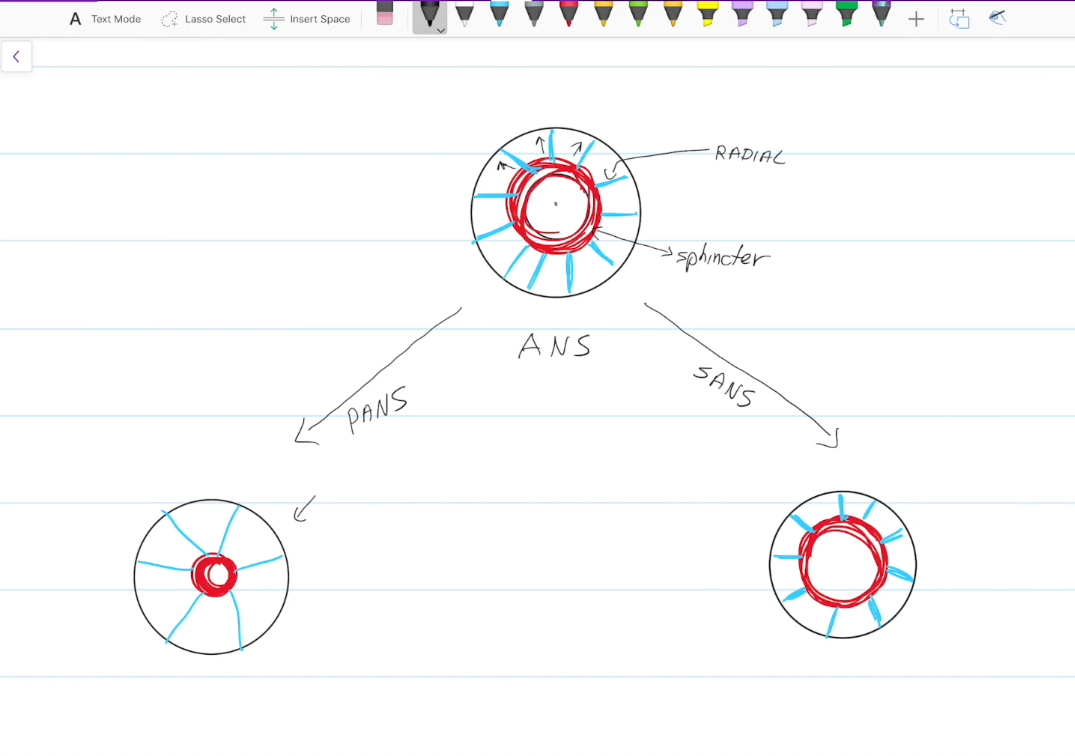
Has circular (sphincter) muscles
Has straight (radial) muscles
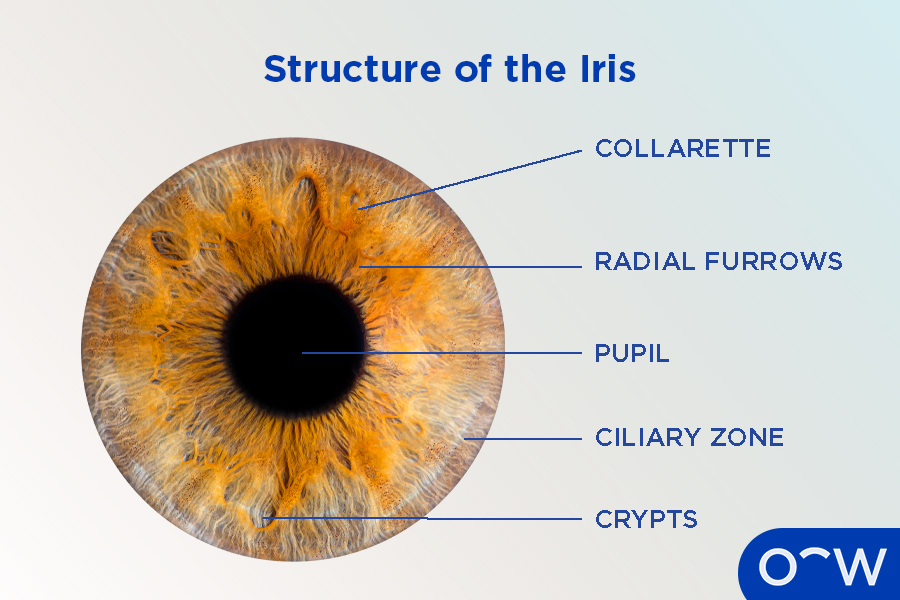
Sphincter Muscles
Controled by the parasympathetic nervous system.
Contraction constricts the pupils
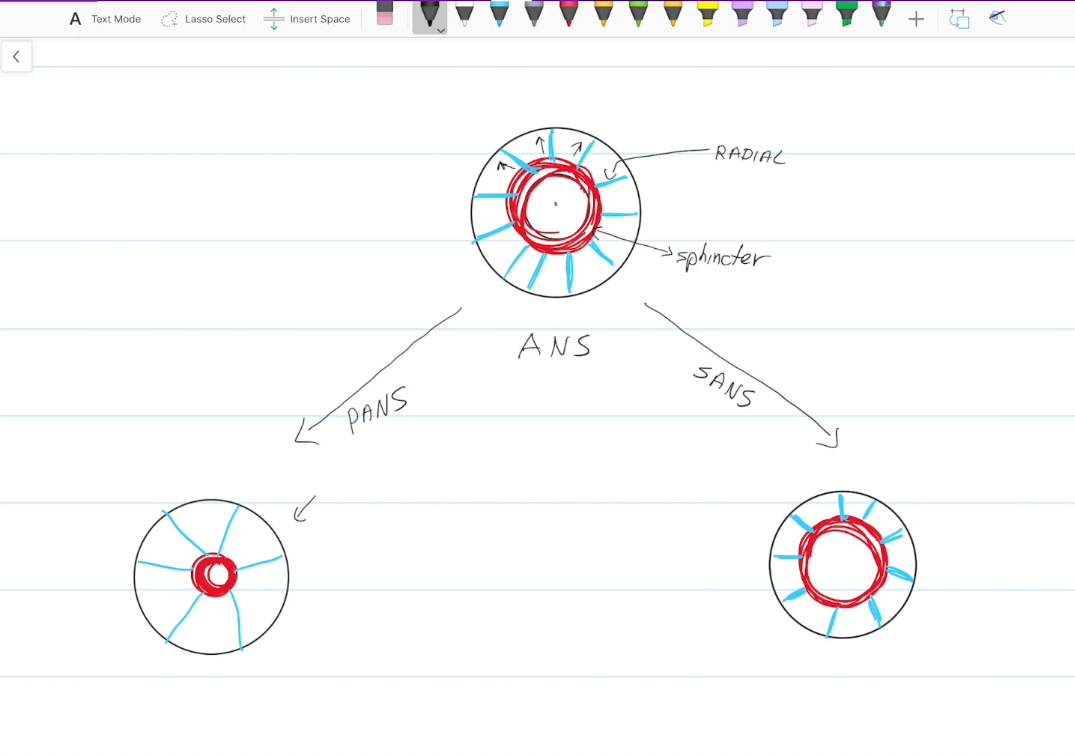
Radial Muscles
Controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
Contraction dilates the pupils
Inner (Retina) Layer
Contains an outer layer (pigament and stores vitamin A)
Contains an innter layer
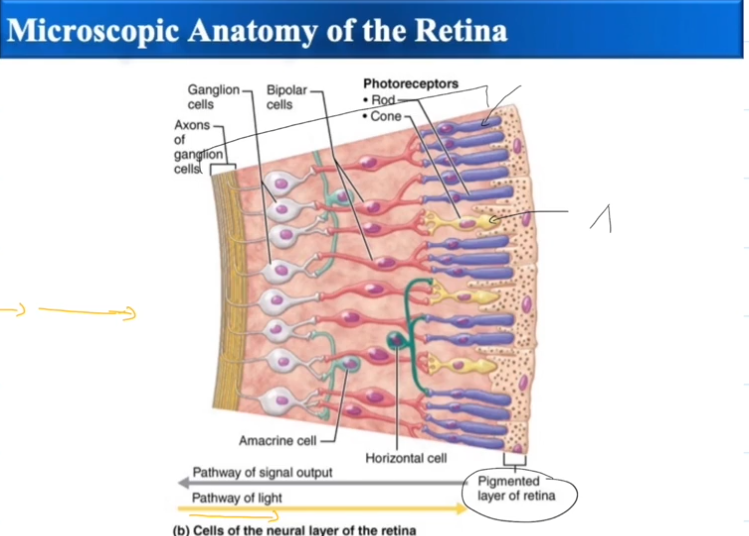
Inner (neural) layer of the Retina
Made up of photoreceptors, rods and cones.
Has a blindspot where the axons of the photoreceptors meet and form the optic nerve.
Contains the Marcula Lutea, which the contains the Fovea Centrialis
Rods
Rods absorb dim light and specialize in peripheral vision
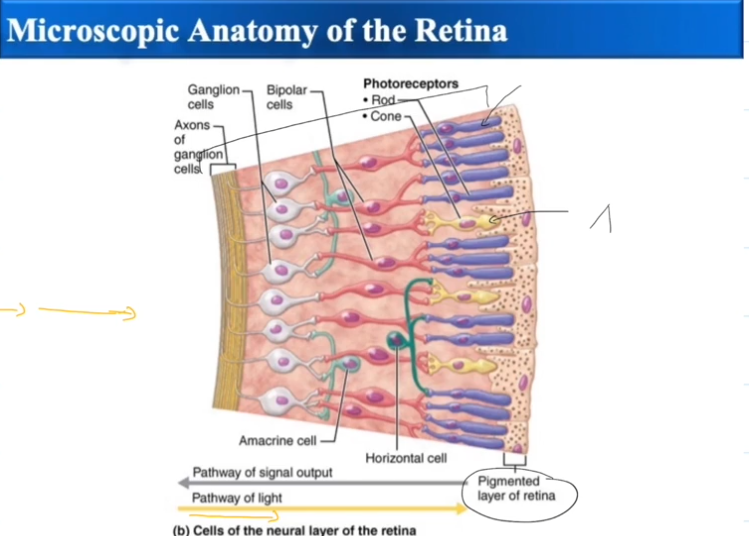
Cones
Cones absorb bright light and specialize in color vision
Macula Lutea
Area in the back of the eyes that contains a lot of Cones
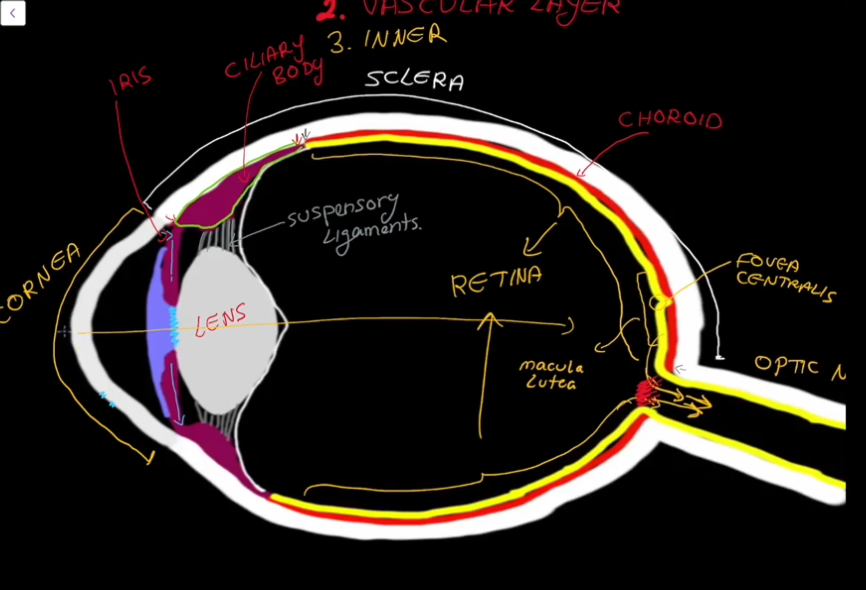
Fovea Centrialis
Area in the macula lutea that only contains cones
Posterior Segment
Contains vitreous humor, which is formed during the embryonic stage of life.
Supports the posterior surface of the lense
Keeps the neural layer pushed up against the pigmented layer
Maintains the shape of the eyeball
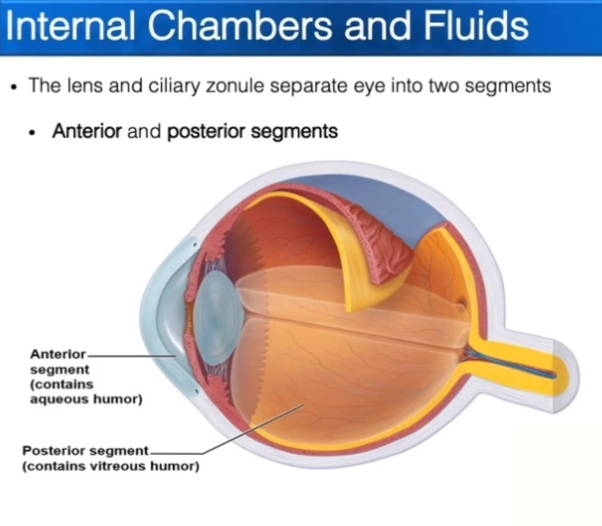
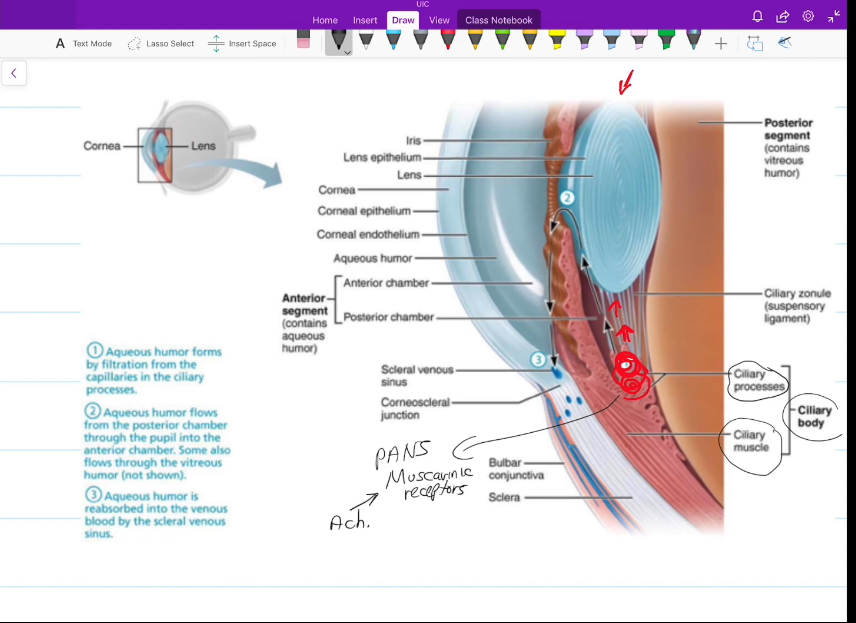
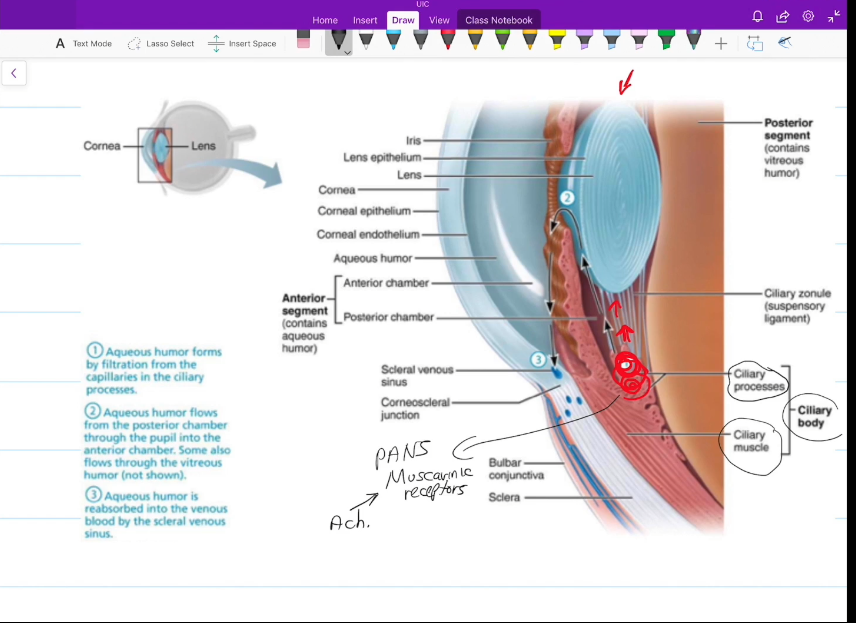
Anterior Segment
Contains the Posterior and Anterior Chambers
Contains Aqueous Humor, which is constantly being made and
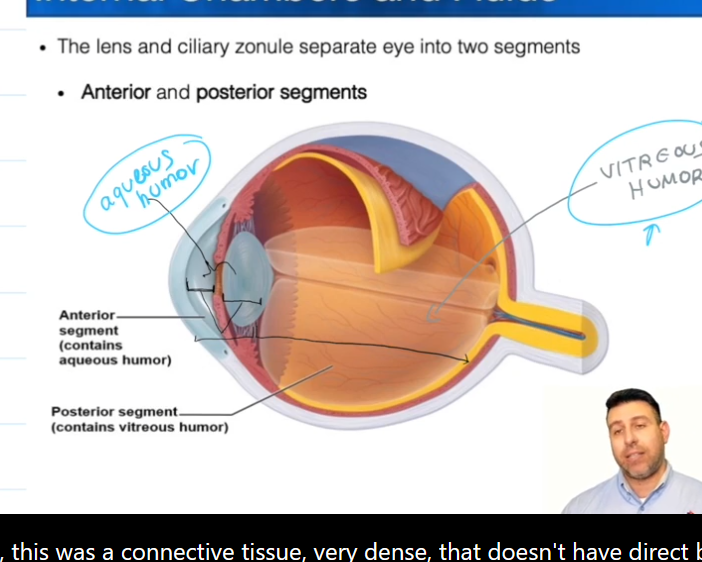
Aqueous Humor
Nourishes the fibrous layer of the eye
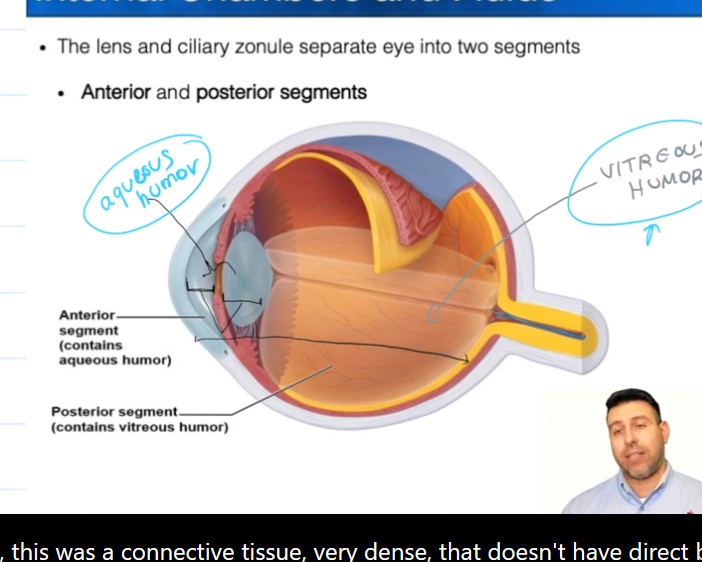
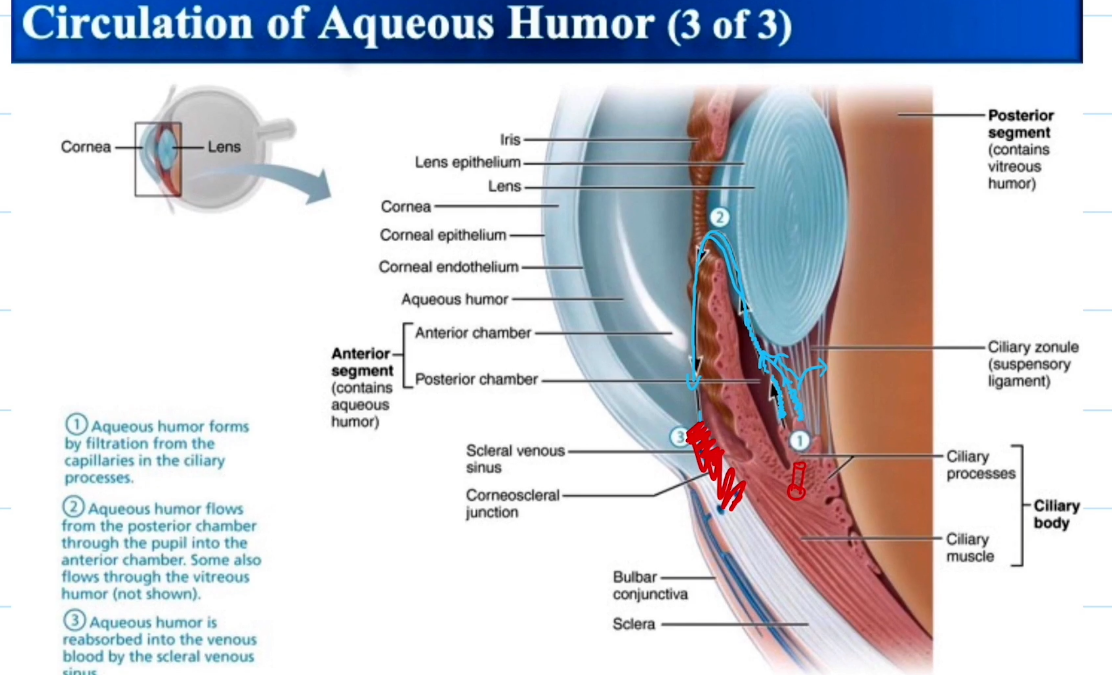
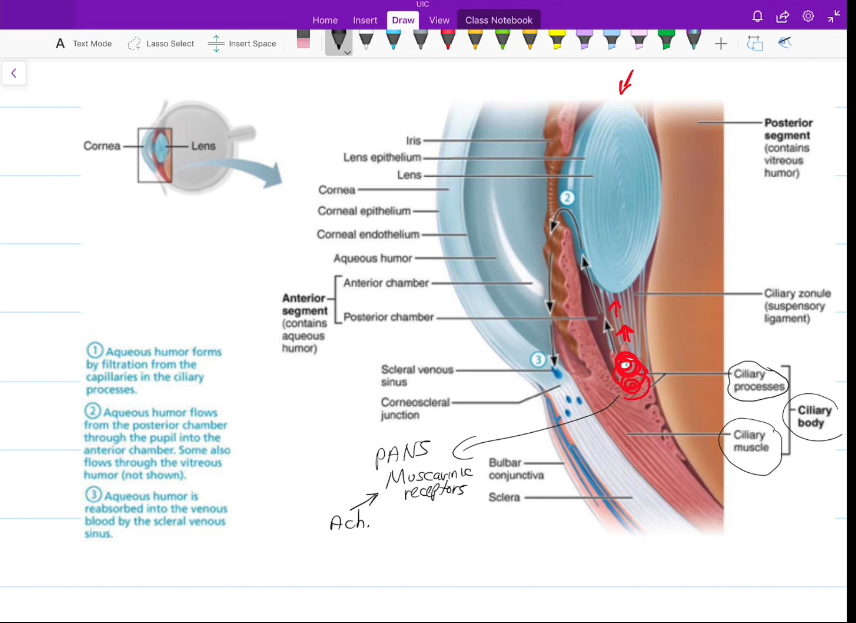
Posterior Chamber
Iris to “here”
Anterior Chamber
iris to cornea
Aqueous Humor Pathway
Aqueous Humor forms from the filtered blood from the capillaries in the ciliary process
aqueous humor flows to other parts of the eye
Aqueous humor is reabosbred into vienous blood via the canal of schlemm
Lens, General Functionality:
Focus light onto the retina so we can see
Lens for seeing close
Ciliary body muscles contract and push the ligaments connected to the lens to make it bulge
Lens for seeing far
Ciliary body muscles relax and pull the ligaments connected to the lens to make it flat
What happens to the Lens when u age
basically those ligaments go bad and u cant see close no more

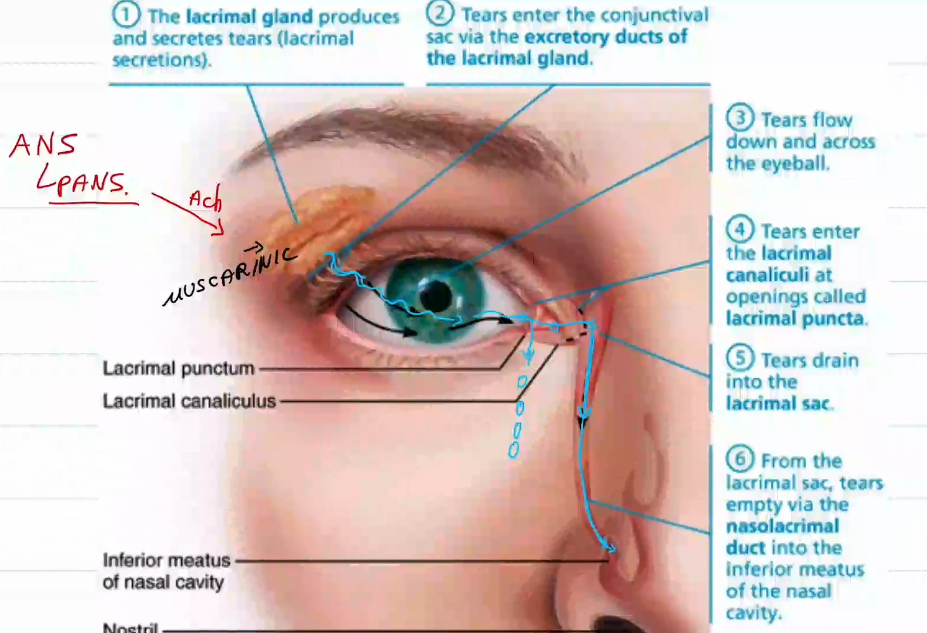
Lacrimal Gland Location:
Lateral side of the eye
Lacrimal Gland Function:
Produce tears.
Tears go to lacrimal sac and drain into the nose.
If too many tears then they roll down da face
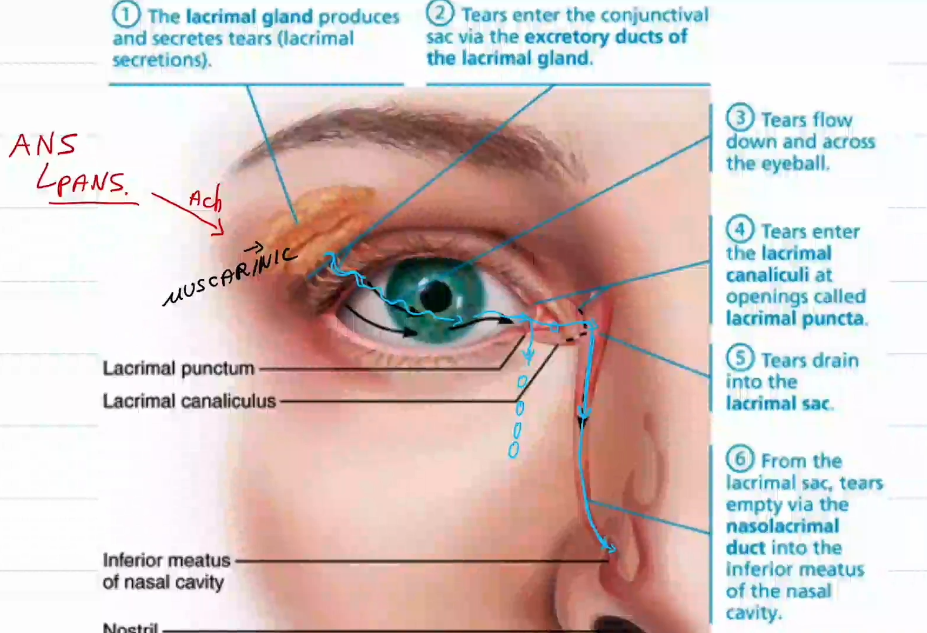
What controls the lacrimal gland
The ANS
more specifically, the parasympathetic division
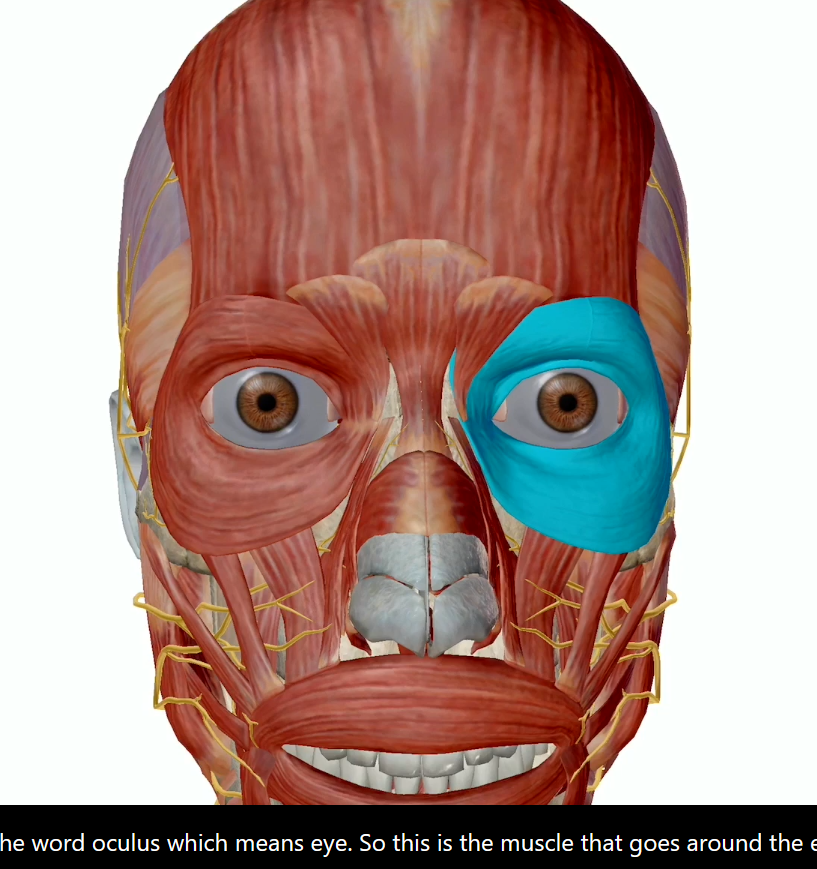
Muscles of the Eyelid:
blow yo shi smoooooove off twin
Orbicularis Oculi
Levator Palpebrae
Extrinsic Eye Muscles (Recuts and Oblique)

Orbicularis Oculi
Innervated by cranial nerve numero seven (Facial nerve)
Closes the eyelids
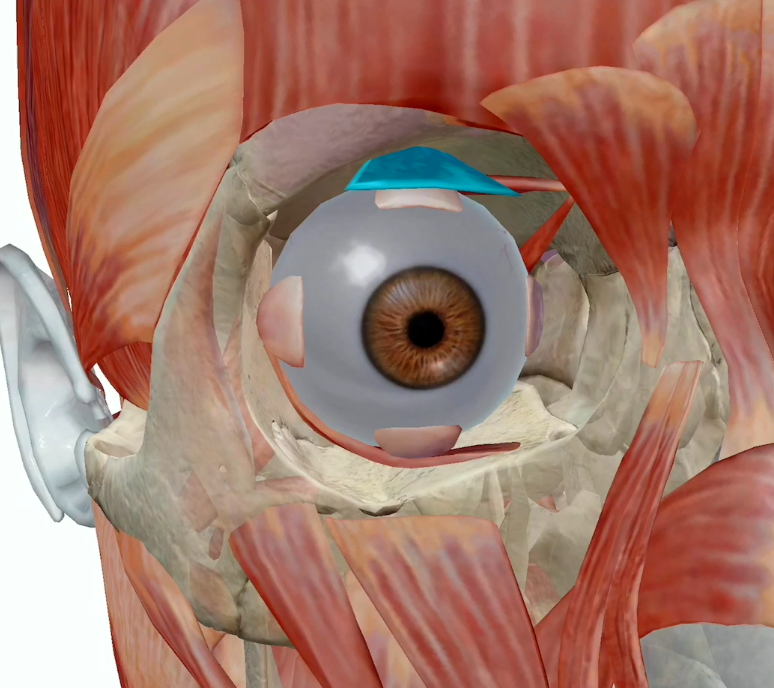
Levator Palpebrae
Occular Motor Nerve cranial nerve number 3
Elevate and retract the eyelid
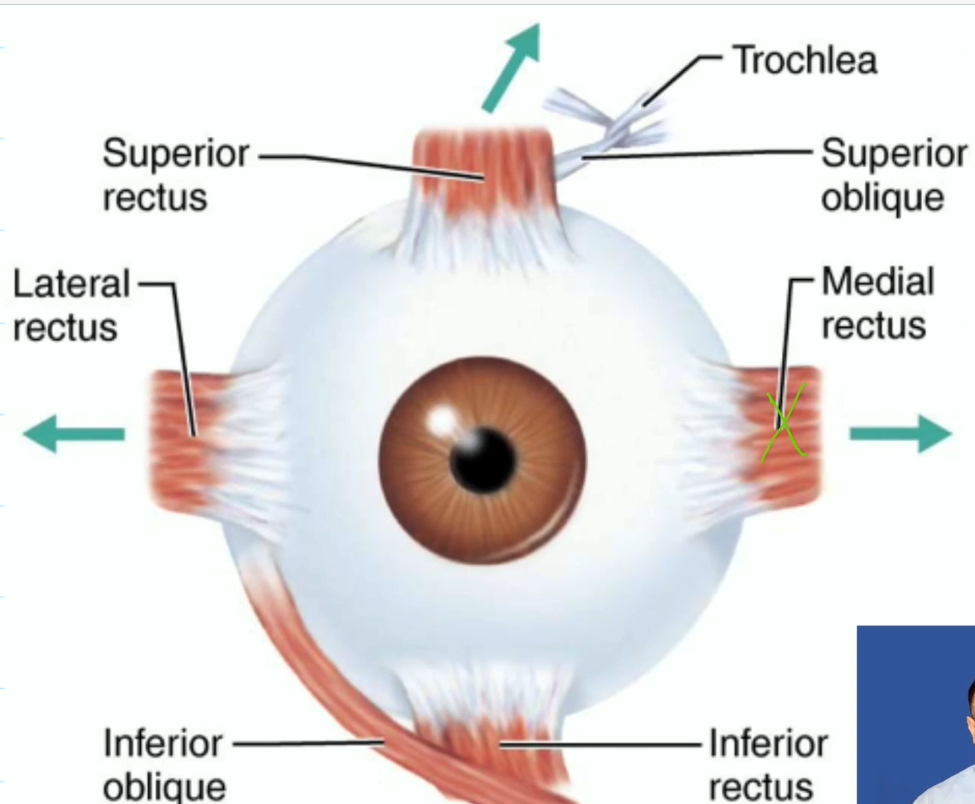
Extrinsic Eye Muscles (6)
Six straplike muscles
Originate from the bony orbit and insert on eyeball
four rectus muscles, superior, inferior, lateral, medial
two oblique muscles, superior and inferior oblique
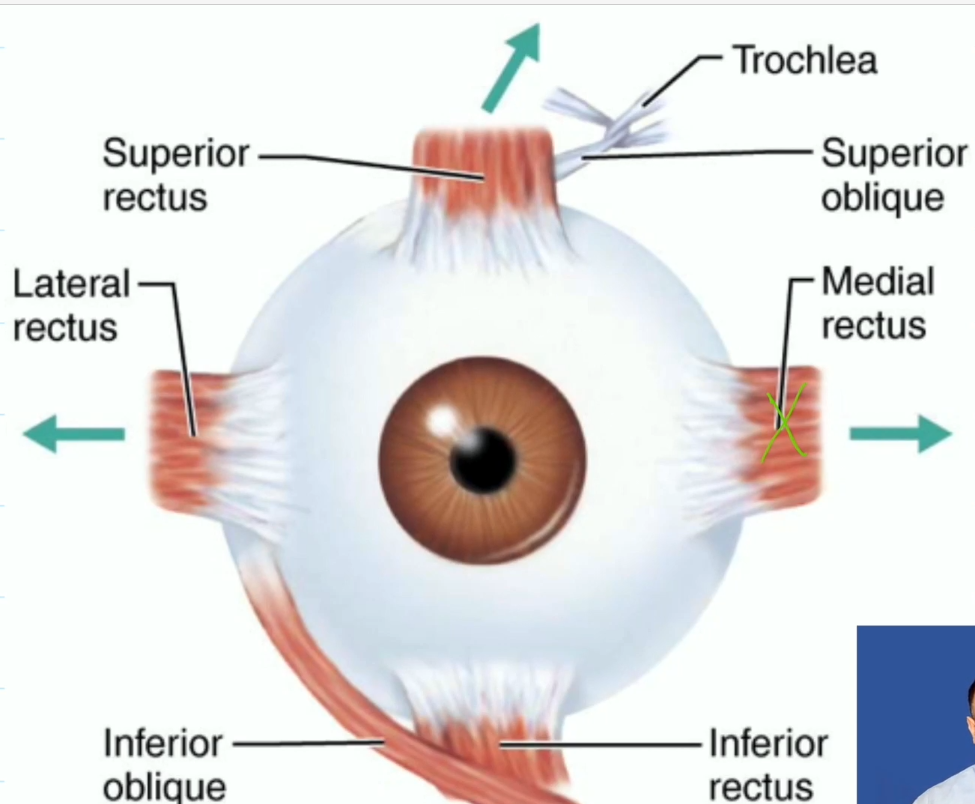
Rectus Muscles
Superior Rectus, move eye up, oculomotor (third nerve)
Inferior Rectus, move eye down, oculomotor (third nerve)
Lateral Rectus, move eye laterally, abducens (sixth nerve)
Medial Rectus, move eye medially, oculomotor (third nerve)
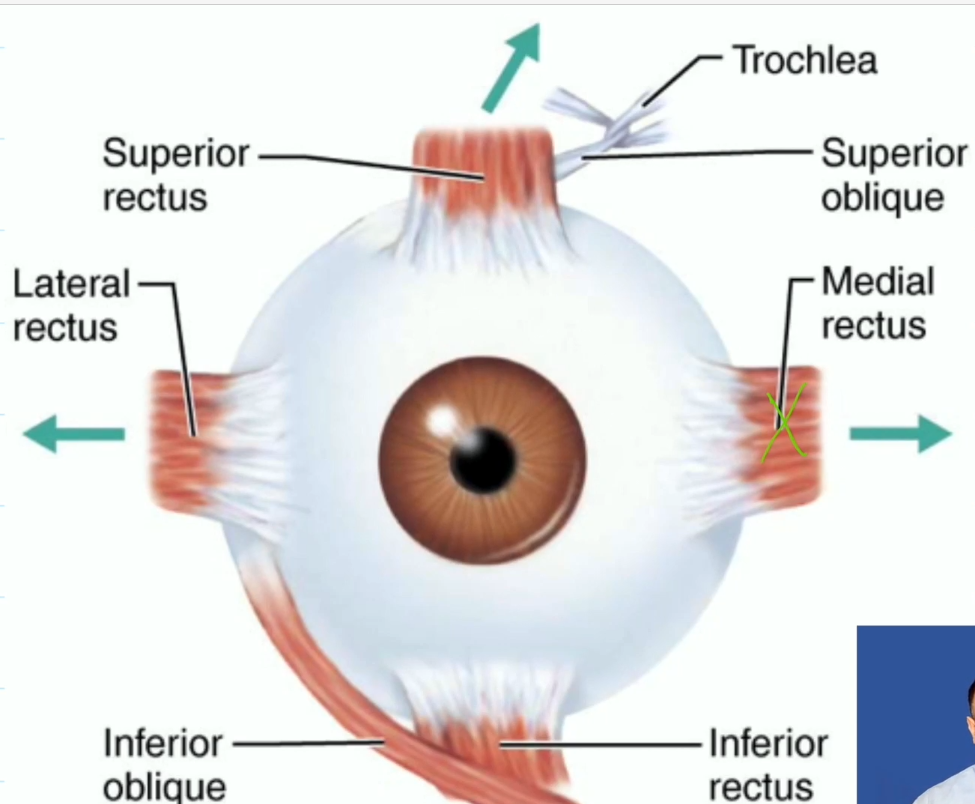
Oblique Muscles
Superior Oblique, depress the eye, trochlear (fourth nerve)
Inferior Oblique, elevate the eye, oculomotor (third nerve)
Refraction:
Light enters into our eye via the cornea, however the light has to be refracted into the eye ball or else it just wont get inside. The issue with this is that if the light comes at an angle, the image will be received as upside down, so then the nervous system has to turn the image around again.
Macroscale Vision Pathway
When light hits the Rods, the Rods deactivate.
Neurotransmitters that normally inhibit the bipolar cells are no longer released.
Bipolar cells activate ganglion cells and sight occurs.
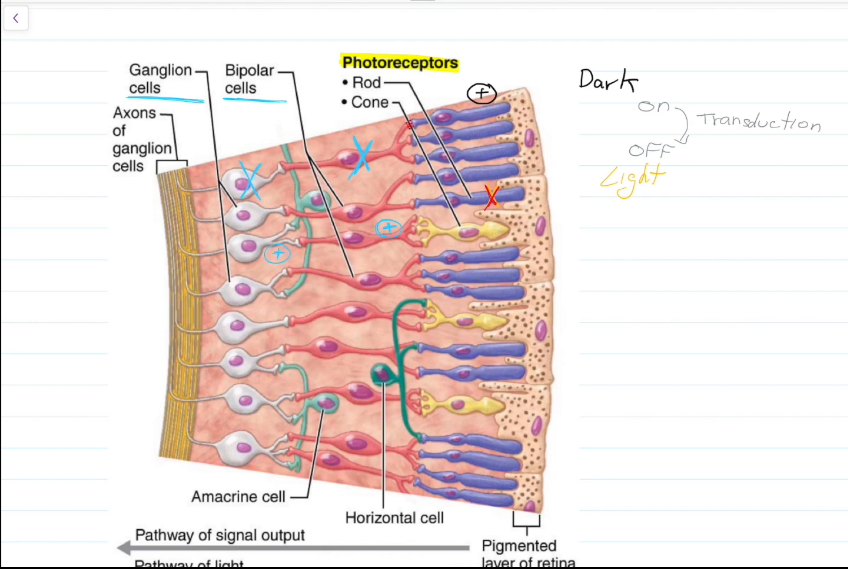
Important Molecule on the rod Disks that causes this whole thing to happen?
Rhodopsin, and its protein Retinal (which is made of vitamin A)
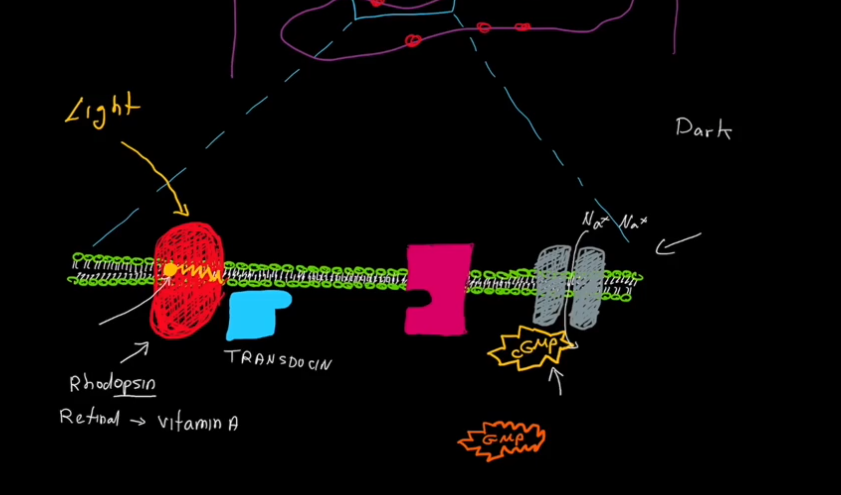
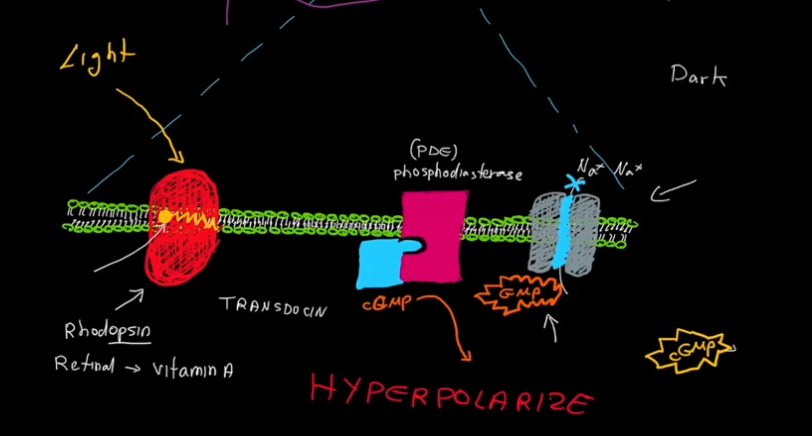
Microscale Vision Pathway
Cyclic GMP (cGMP) keeps Na+ channels open.
Light hits the rod.
The molecule retinal, within Rhodopsin, loses its bend and becomes straight.
Transducin detatches from Rhodopsin, and attatches to phosphodiasterase (PDE)
PDE turns cGMP into GMP.
cGMP is removed from Na+ channels.
Na+ Channels close.
K+ continues to leave the cell, and the cell becomes hyperpolarized and can no longer fire action potentials.
Bipolar cells are no longer inhibited, and vision occurs.
Pathway pic continued
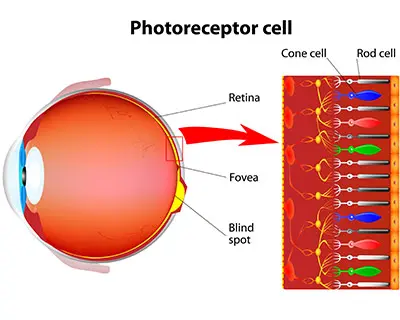
How many rods and cones do we have?
120 million rods, 6 million cones (60% red, 30% green, 10% blue)
Rods Functional Characteristics:
Very sensitive to light.
Best suited for night and peripheral vision
Contains a single pigment.
Perceived input in grey tones only
Pathways converge, causing fuzzy, indistinct images.
Cones Functional Characteristics:
Needs bright light for activation.
Reacts more quickly
Have one of three pigments for colored view.
Non-converging pathways results in detailed, high-resolution vision
Color Blindness: Resulting from lack of one or more cone pigments.
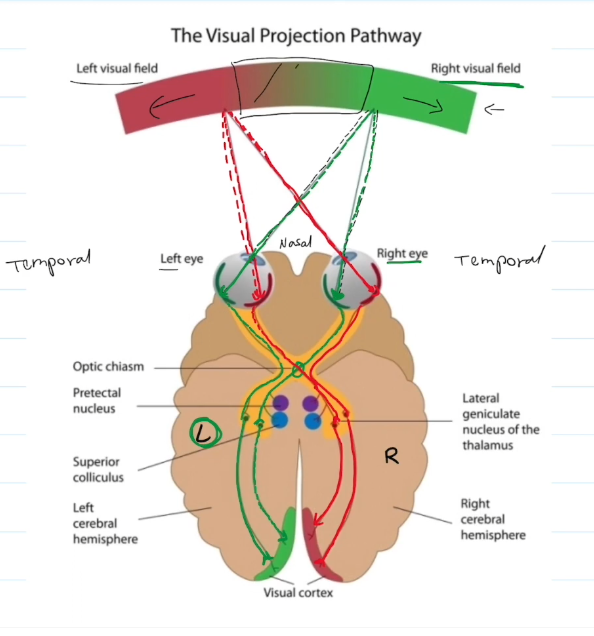
The Visual Projection Pathway
Each eye has two visual fields: One on the temporal side, the other on the nasal side.
The temporal side remains on the side of the brain, and the nasal side switches over.
Temporal side handles peripheral vision from the opposing visual field. Nasal side handles direct vision from the correlated visual field.
An issue with the optic chasm results in loss of direct vision. An issue with the temporal side results in loss of peripheral vision.
Pupillary Light Reflex
Basically, if there is too much light, the pupil will constrict to protect the photo-receptors