Higher Human Biology
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2 - Physiology and Health Questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
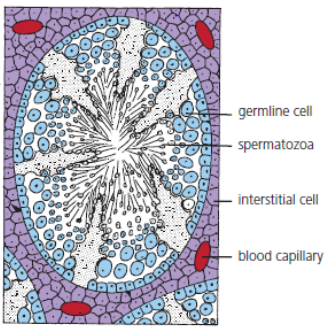
Name the site of sperm production in the testes? (1)
Seminiferous tubules.
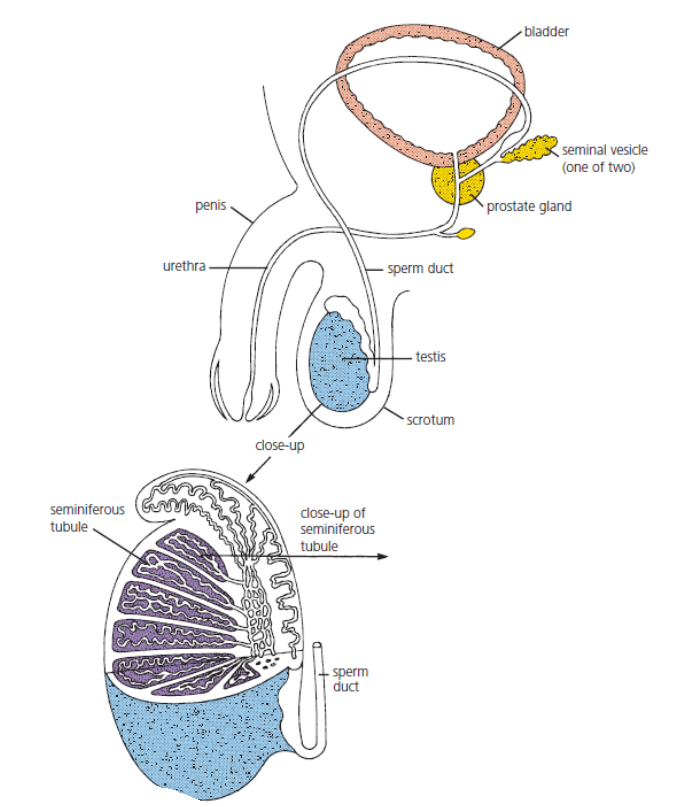
Name the hormone produced in the testes? (1)
Testosterone.
Name the cells that produce testosterone hormone? (1)
Interstitial cells.
Name the male organs that produce liquids? (2)
The prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
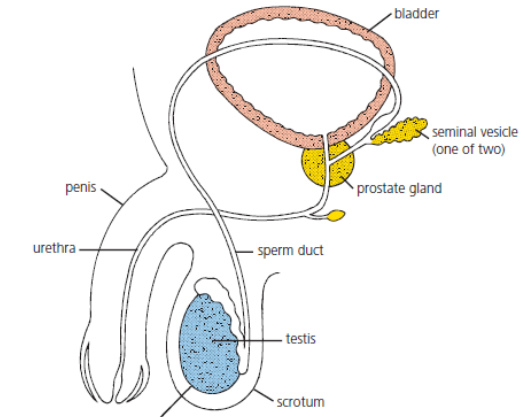
Explain the importance of the male liquids to the sperm? (1)
Maintains the mobility and viability of the sperm.
Describe the function of the follicle that surrounds the ovum? (2)
Protects the developing ovum and secretes the hormone oestrogen.
Describe what happens to the follicle after ovulation? (2)
The follicle develops into a corpus luteum which secretes the hormone progesterone.
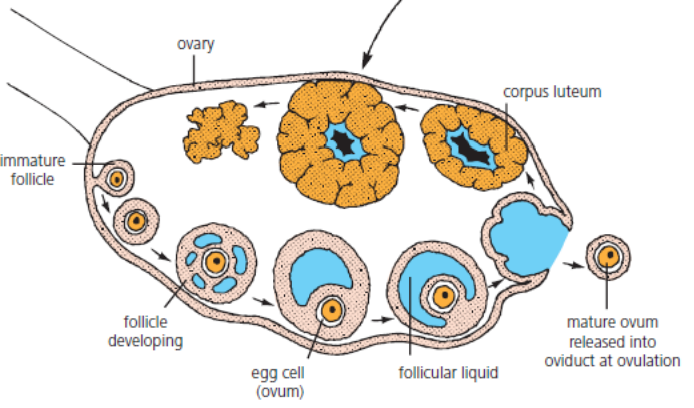
State where fertilisation occurs? (1)
Oviduct
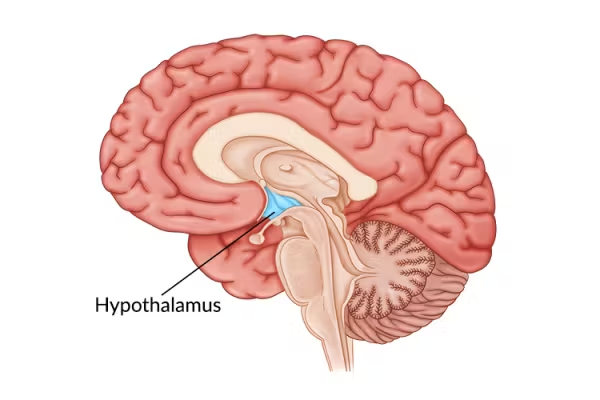
Name the part of the brain that secretes a releaser hormone which targets the pituitary gland? (1)
Hypothalamus
Name the two hormones released by the pituitary gland in males? (4)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH)
What does FSH do in males? (1)
Promotes sperm production.
What does ICSH do in males? (1)
Stimulates the production of testosterone.
Describe two functions of the hormone testosterone? (2)
Stimulates sperm production in the seminiferous tubules.
Activates the prostate gland and seminal vesicles to produce fluid secretions.
Explain how testosterone levels are maintained through negative feedback control? (3)
As the concentration of testosterone builds up in the bloodstream, it reaches a level where it inhibits the secretion of FSH and ICSH by the pituitary gland.
Which leads to a decrease in testosterone concentration.
As testosterone concentration decreases, the pituitary gland resumes production of FSH and ICSH and testosterone concentration increases once more.
This is negative feedback control.
State how longs the menstrual cycle typically lasts? (1)
The menstrual cycle takes approximately 28 days with the first day of menstruation regarded as day one.
Identify the point of the menstrual cycle at which menstruation begins? (1)
Days 4-14 (out of the 28 days in the menstrual cycle).
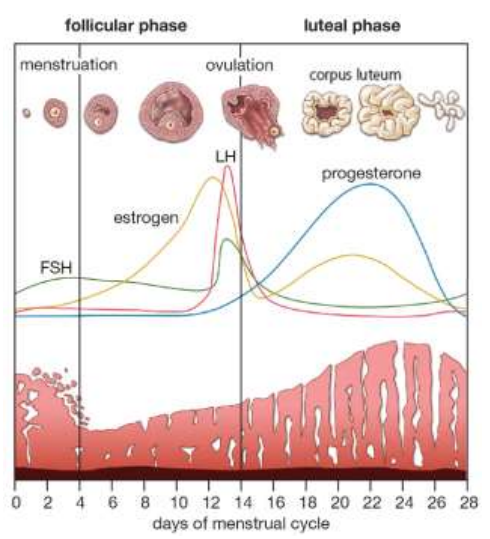
State the definition of ovulation? (1)
Ovulation is the release of an egg (ovum) from a follicle in the ovary.
Identify the point of the menstrual cycle at which ovulation typically occurs? (1)
Around day 14 (out of the 28 days in the menstrual cycle).
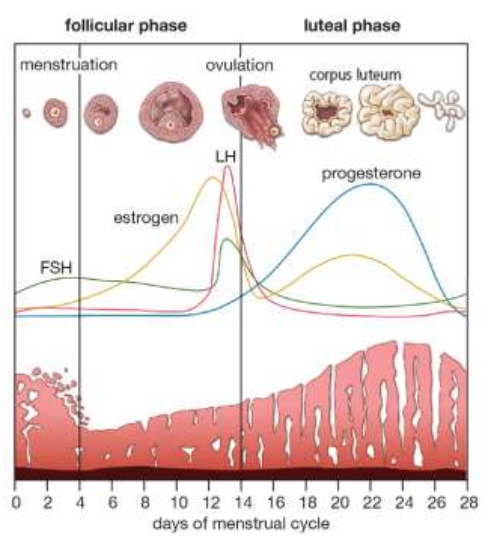
Name the first phase of the menstrual cycle? (1)
Follicular phase.
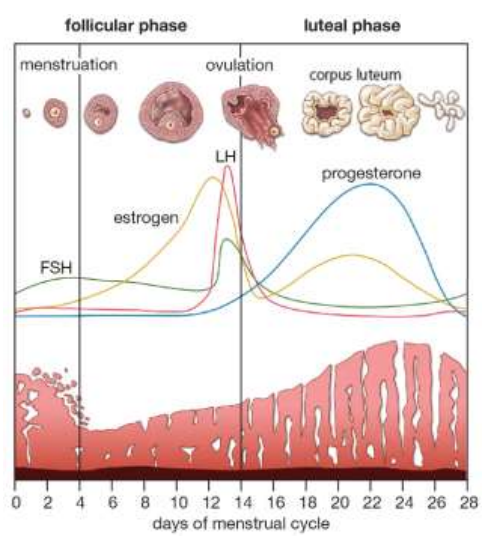
Name the second phase of the menstrual cycle? (1)
Luteal phase.
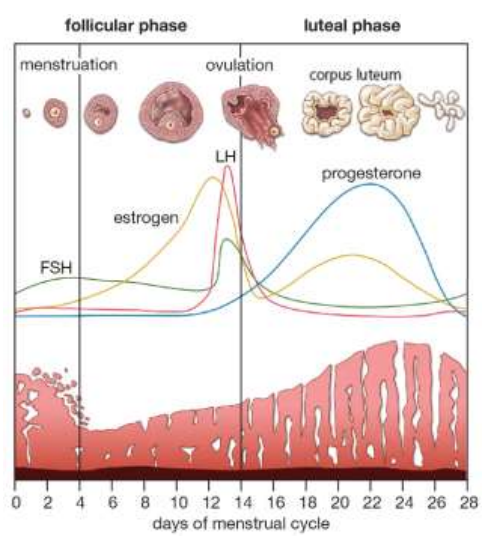
Name the two hormones released by the pituitary gland in females? (2)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Describe two functions of FSH? (2)
Stimulates the development of a follicle.
Stimulates the production of oestrogen by the follicle in the follicular phase.
Describe three functions of oestrogen? (3)
Stimulates proliferation (cell division) of the lining of the uterus known as the endometrium.
Affects the consistency of cervical mucus making it more easily penetrated by sperm.
Peak levels of oestrogen stimulate a surge in the secretion of LH.
Describe two functions of LH? (2)
Triggers ovulation.
In the luteal phase LH stimulates the follicle to develop into a corpus luteum which secretes progesterone.
Describe the function of progesterone? (1)
Promotes further development and vascularisation (growing blood vessels) of the endometrium.
Explain how negative feedback prevents further follicles from developing? (2)
The combined high levels of the ovarian hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) during the luteal phase trigger an inhibitory effect on the pituitary gland.
Concentrations of FSH and LH drop as a result preventing further follicles from developing at this time.
This is negative feedback.
Describe what happens when LH levels drop? (3)
Leads to degeneration of the corpus luteum.
Drop in progesterone levels.
Menstruation takes place.
Describe what happens to the corpus luteum if fertilisation occurs? (2)
Does not degenerate.
Progesterone levels remain high.
Explain what is meant by cyclical fertility in females? (1)
Women are only fertile for a few days during each menstrual cycle (cyclical fertility).
Explain what is meant by continuous fertility in males? (1)
Men show continuous fertility as they continuously produce sperm in their testes.
Describe two changes to the female body after ovulation? (2)
The female’s body temperature rises by 0·5°C.
Cervical mucus becomes thin and watery to allow easier access for sperm.
Describe how ovulation may be stimulated to treat infertility? (2)
By different drugs that either prevent the negative feedback effect of oestrogen on FSH secretion or mimic the action of FSH and LH.
Explain what can happen if the treatment is so effective it leads to ‘super ovulation’? (2)
Release of multiple eggs during a cycle.
May result in multiple births or allow ova to be collected for in vitro fertilisation (IVF) programmes
Explain why artificial insemination may be used to treat infertility? (2)
If male has a low sperm count.
If the male is sterile and a donor is being used to provide semen
Describe the process of artificial insemination? (2)
The insertion of semen into the female tract by means other than sexual intercourse.
Several samples of semen are collected over a period of time, and then released into the female at the time when she is most likely to be fertile.
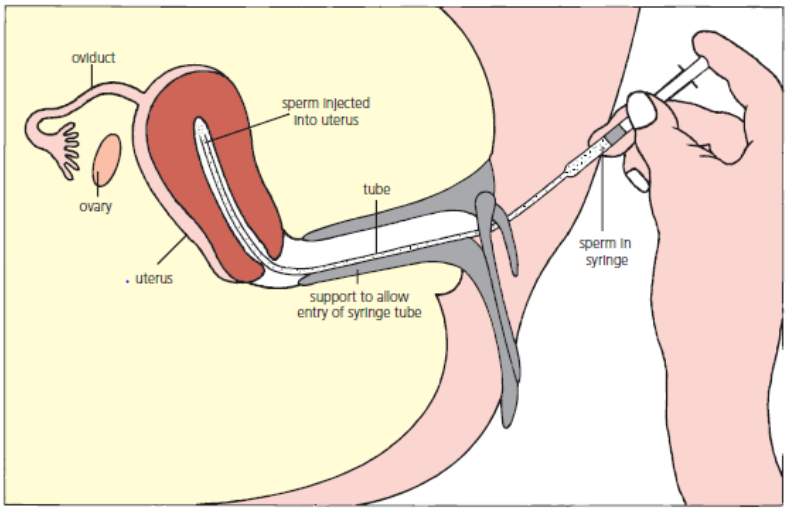
Explain why intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used to treat infertility? (2)
If mature sperm are defective.
Sperm are very low in number.
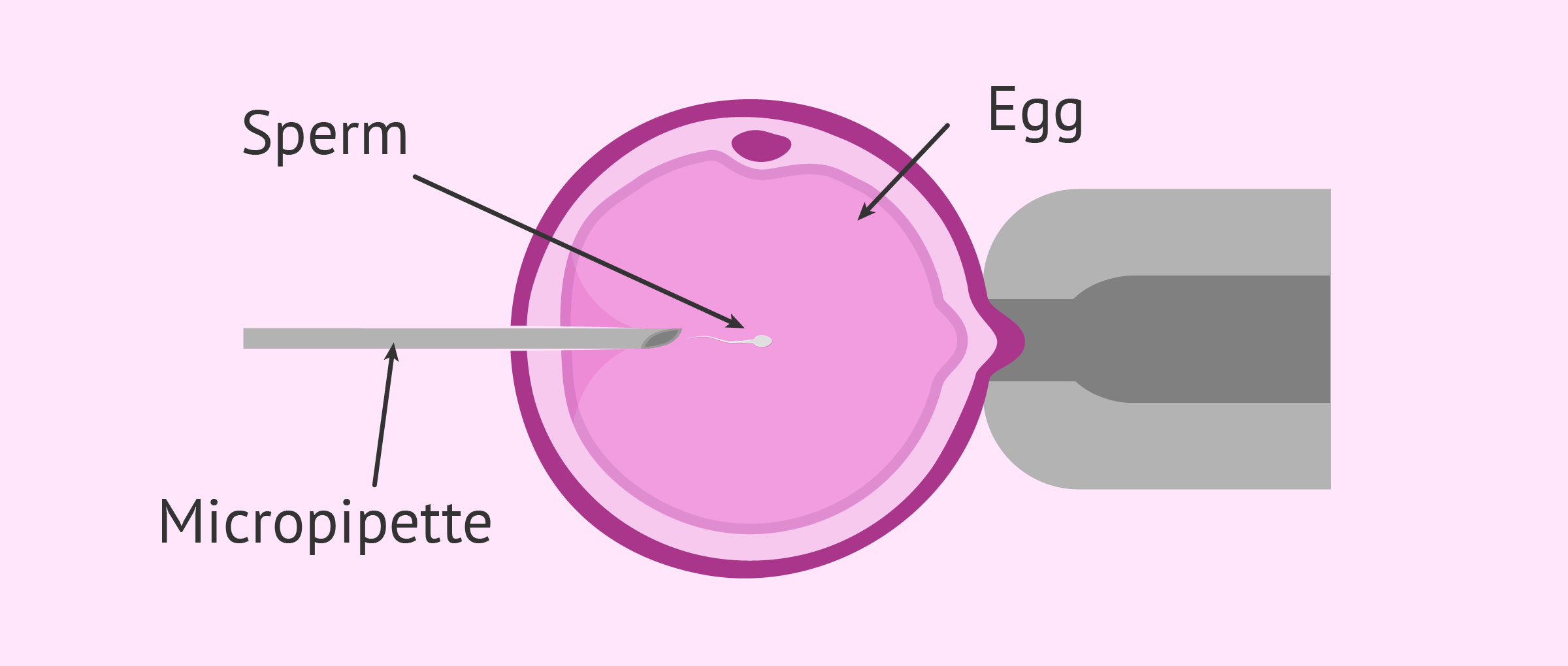
Describe the process of intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)? (1)
The head of a sperm is drawn into a needle and injected directly into the egg to achieve fertilisation.
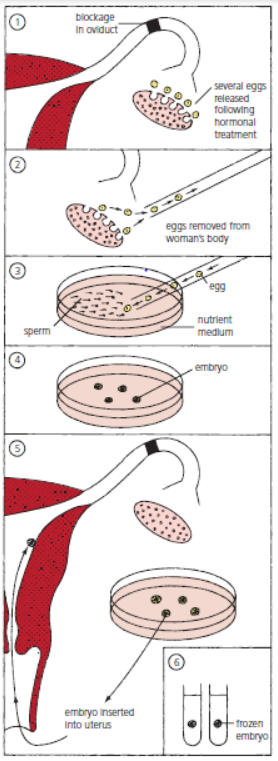
Describe the process of in vitro fertilisation (IVF)? (5)
Hormones are used to stimulate the release of multiple eggs.
Eggs are surgically removed from the ovaries.
The eggs are then mixed with sperm in a culture dish.
fertilised eggs are incubated until they have formed at least eight cells.
The embryos are then transferred to the uterus for implantation.
Explain why pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is carried out during IVF? (1)
To identify single gene disorders and chromosomal abnormalities before the embryo is implanted into the uterus.
Name and the method of physical contraception that prevents sperm reaching the ovum? (1)
Barriers - Something that prevents the sperm from reaching the ovum such as condoms, diaphragm or cervical caps.
Name and the method of physical contraception that prevents implantation of an embryo into the endometrium? (1)
Intra-Uterine Devices (IUD) - A structure fitted into the uterus that prevents implantation of an embryo into the endometrium.
Name and the method of physical contraception that involves cutting and tying of sperm ducts or oviducts? (2)
Sterilisation Procedures -
In males, vasectomy involves the cutting and tying of the sperm ducts.
In females, tubal ligation involves the cutting and tying of the oviducts.
How does the oral contraceptive pill prevent pregnancy? (2)
It contains a combination of synthetic oestrogen and progesterone that mimics negative feedback preventing the release of FSH and LH from the pituitary gland.
How does the progesterone only (mini) pill prevent pregnancy? (1)
It causes thickening of the cervical mucus, preventing sperm access to the uterus.
How does the emergency contraceptive pill prevent pregnancy? (1)
Prevents or delays ovulation.
State when the emergency contraceptive pill can be taken to be effective? (1)
They can be taken up to 72 hours or 120 hours after sex, depending on which type of pill is used.
Name two methods of antenatal screening? (2)
Antenatal (prenatal) screening identifies the risk of the fetus having a particular disorder.
Ultrasound Imaging.
Blood and Urine Tests.
State when a dating scan takes place? (1)
Around 8 to 14 weeks.
State what a dating scan is used for? (1)
To determine the stage of pregnancy and due date.
State when an anomaly scan takes place? (1)
Around 18 to 20 weeks.
State what an anomaly scan is used for? (1)
to detect serious physical abnormalities in the fetus.
Explain why the concentration of marker chemicals are measured? (1)
To monitor the concentrations of marker chemicals. If an atypical (abnormal) marker chemical concentration is detected, diagnostic testing may be carried out to determine if the fetus has a medical condition.
Explain why it is important to measure marker chemicals at the correct times during pregnancy? (1)
Marker chemicals vary normally during pregnancy, therefore measuring a marker chemical at the wrong time could lead to a false positive result.
Name two types of diagnostic tests which may be carried out during pregnancy? (2)
Amniocentesis.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS).
Describe the process of Amniocentesis? (1)
Involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid containing fetal cells.
Describe the process of Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)? (1)
Involves taking a sample of placental cells from the mothers reproductive tract.
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of diagnostic tests for pregnancy? (2)
Amniocentesis is carried out later in the pregnancy, but has a lower risk of miscarriage.
CVS can be carried out earlier in the pregnancy, but has a higher risk of miscarriage.
Explain what karyotypes show and why they are useful? (3)
Cells taken from amniocentesis or CVS samples are cultured and used to produce a karyotype.
A karyotype shows an individual’s chromosomes arranged as homologous pairs.
Can be used to diagnose a range of conditions.
State the cause of PKU? (1)
PKU is caused by a substitution mutation which means the enzyme which converts phenylalanine to tyrosine is non-functional.
Explain the treatment for individuals with PKU? (1)
Individuals with high levels of phenylalanine are placed on a (Low protein) restricted diet.
State the term used to describe the X and Y chromosomes? (1)
Sex chromosomes.
State the term used to describe all the chromosomes apart from the X and Y chromosomes? (1)
Autosomes.
State the term used to describe a genotype containing two of the same alleles? (1)
Homozygous.
State the term used to describe a genotype containing two different alleles? (1)
Heterozygous.
State the term used to describe a person that has an allele for a genetic condition, but not the condition itself? (1)
A carrier.
State the term used to describe the use of family trees to assess the probability that parents may pass a genetic disorder to their offspring? (1)
Pedigree analysis chart.
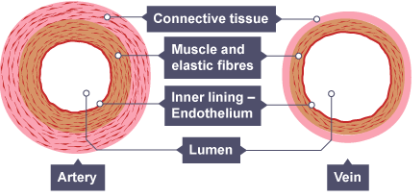
Which term is used for the channel in the blood vessel that carries blood? (1)
Lumen
Describe the process of vasodilation and the impact it has on controlling blood flow? (2)
Vasodilation is the process where blood vessels widen due to the relaxation of smooth muscle in the vessel walls.
Lowers blood pressure in turn increasing blood flow.
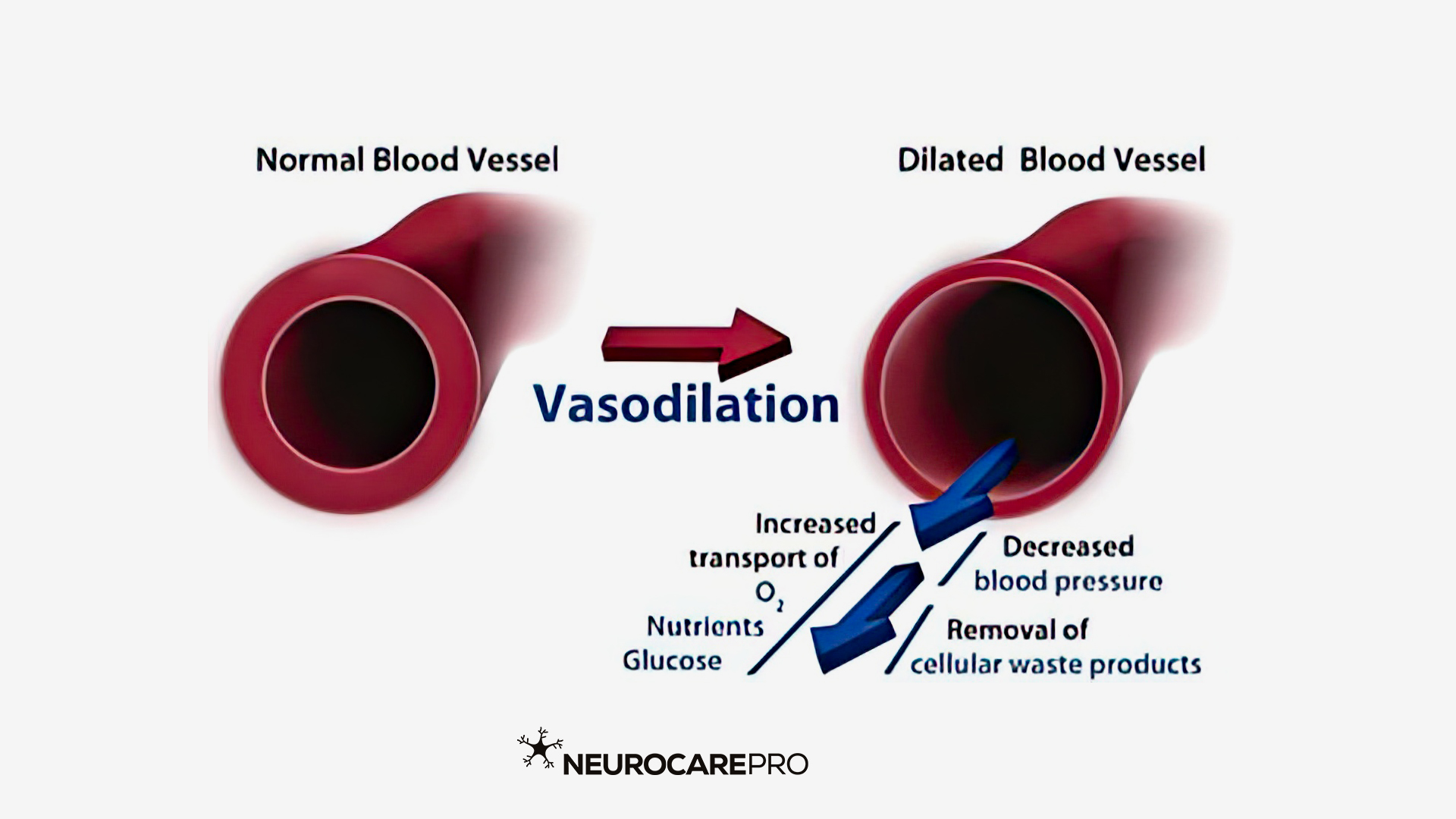
Describe the process of vasoconstriction and the impact it has on controlling blood flow? (2)
Vasoconstriction is the process where blood vessels narrow due to the contraction of smooth muscle in the vessel walls.
Increases blood pressure in turn decreasing blood flow.
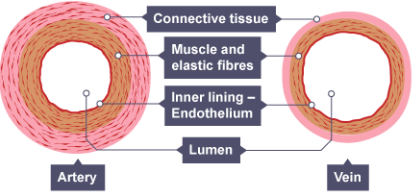
Describe the structure difference between an artery and vein? (2)
Veins have an outer layer of connective tissue containing elastic fibres but a much thinner muscular wall than arteries.
Veins contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
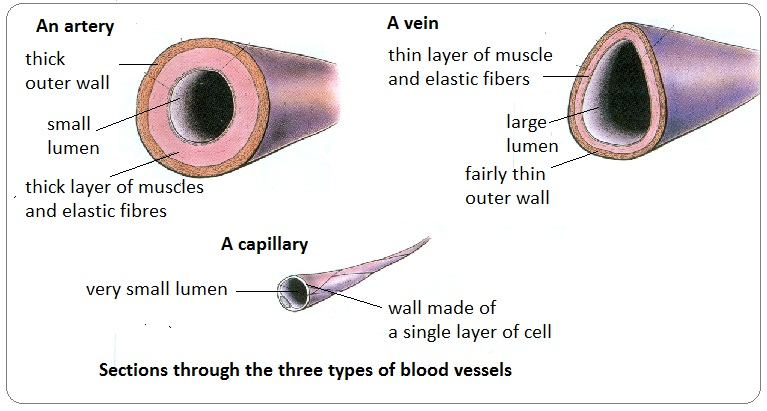
Name the cells which make up the lining of the blood vessels? (1)
The endothelium cells.
Describe the process of pressure filtration? (2)
As blood travels at high pressure in the arteries towards the capillaries.
Pressure filtration occurs which causes blood plasma to pass through the capillary walls into the tissue fluid surrounding the cells.
Name the molecules too large to be filtered through the capillary walls? (1)
Plasma proteins.
Explain what happens to excess tissue fluid following the process of pressure filtration? (1)
Excess tissue fluid that remains after pressure filtration is drained into the lymphatic system, where it is processed and returned to the circulatory system, ensuring proper fluid balance in the body.
Name the structure which separates the right and left ventricle?(1)
Interventricular septum.
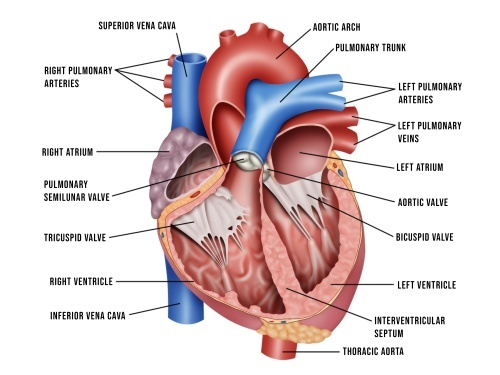
Name the valve which prevents blood flowing back into the right atrium? (1)
Tricuspid valve.
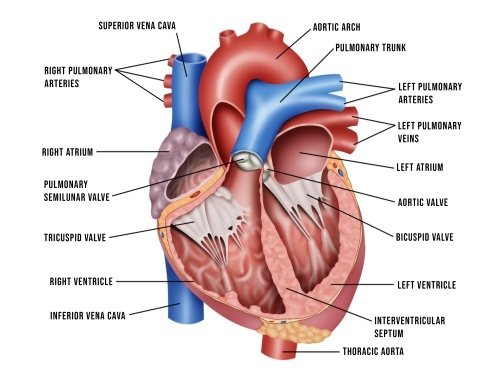
Name the valve which prevents blood flowing back into the left atrium? (1)
Bicuspid valve.
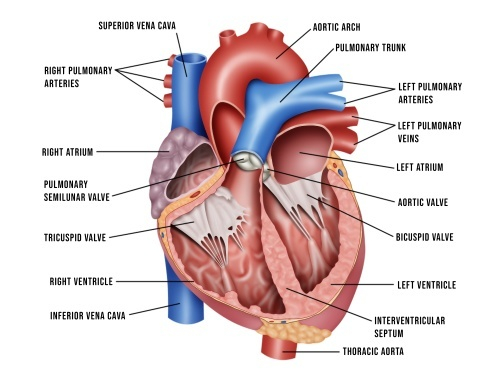
Explain the function of the semilunar valves? (2)
Pulmonary semilunar valve: Located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. It prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle after it is pumped into the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Aortic semilunar valve: Located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle after it is pumped into the aorta, which carries oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Both semilunar valves ensure that blood flows in the correct direction during the heart's contraction and relaxation phases, maintaining efficient circulation.
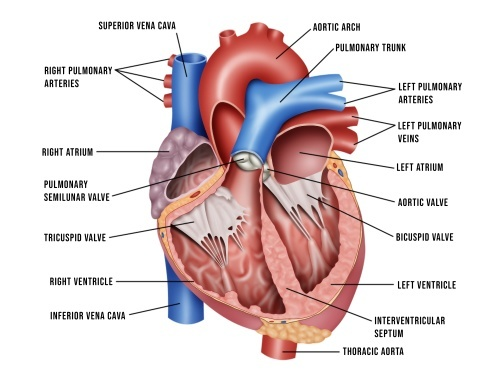
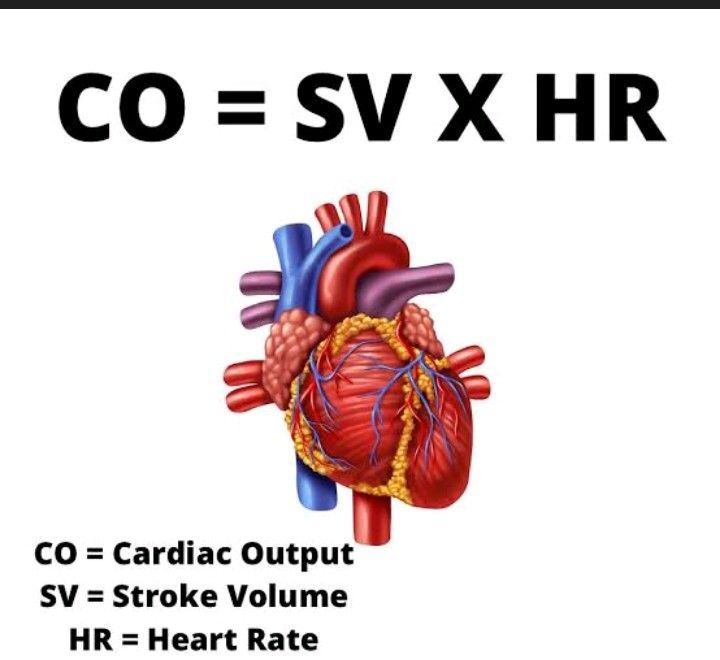
The formula used to calculate cardiac output (the volume of blood pumped through each ventricle each minute)? (1)
Cardiac Output (CO) = Stroke Volume (SV) × Heart Rate (HR)
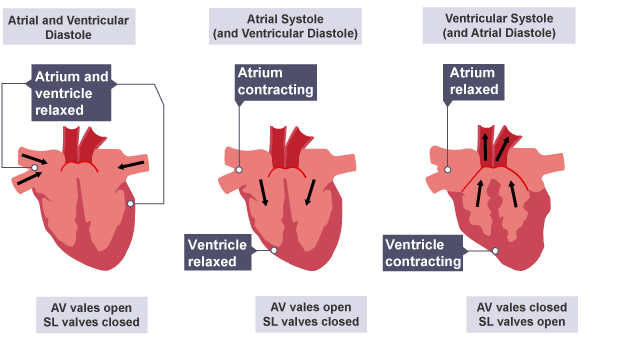
Describe the three stages of the cardiac cycle? (3)
The cardiac cycle has 3 stages:
1. Atrial and Ventricular diastole (chambers are relaxed and filling with blood)
2. Atrial systole (atria contract and remaining blood is pushed into ventricles)
3. Ventricular systole (ventricles contract and push blood out through aorta and pulmonary artery)
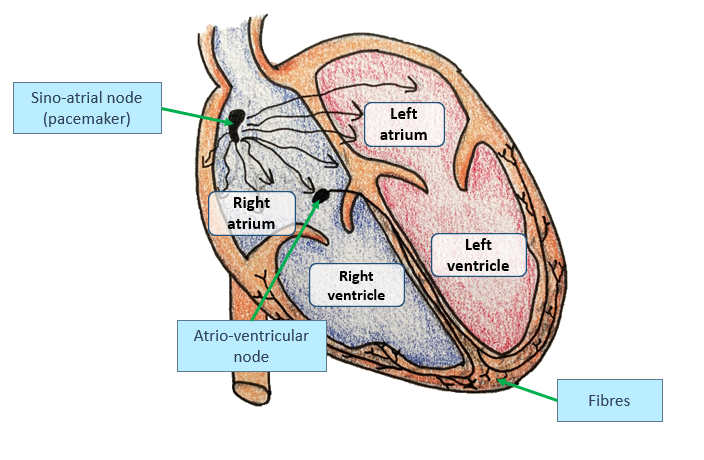
Where is the SAN or pacemaker located in the heart? (1)
The SAN is found in the wall of the right atrium.
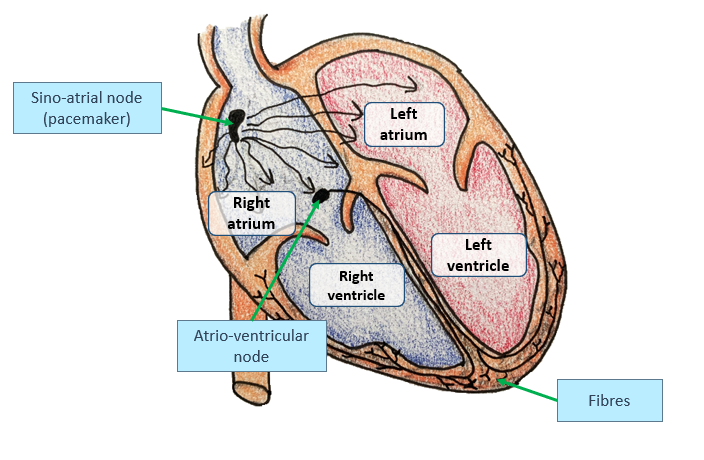
What’s the function of the SAN or pacemaker in the heart? (1)
Responsible for initiating the electrical impulses that regulate the heart's rhythm, setting the pace for the heart rate
Describe the role of the AVN in the cardiac conduction system? (2)
Once the impulse from the SAN reaches the AVN causes a brief delay before the impulse is passed to conducting fibres which travel down the central wall of the heart.
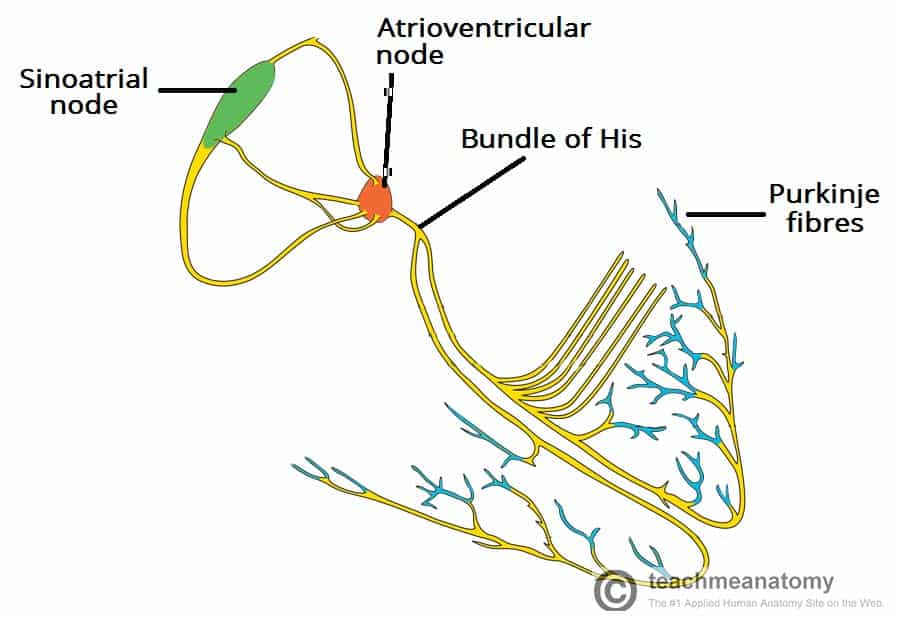
Which nerve pathway releases noradrenaline which increases heart rate? (1)
The sympathetic nerve pathway.
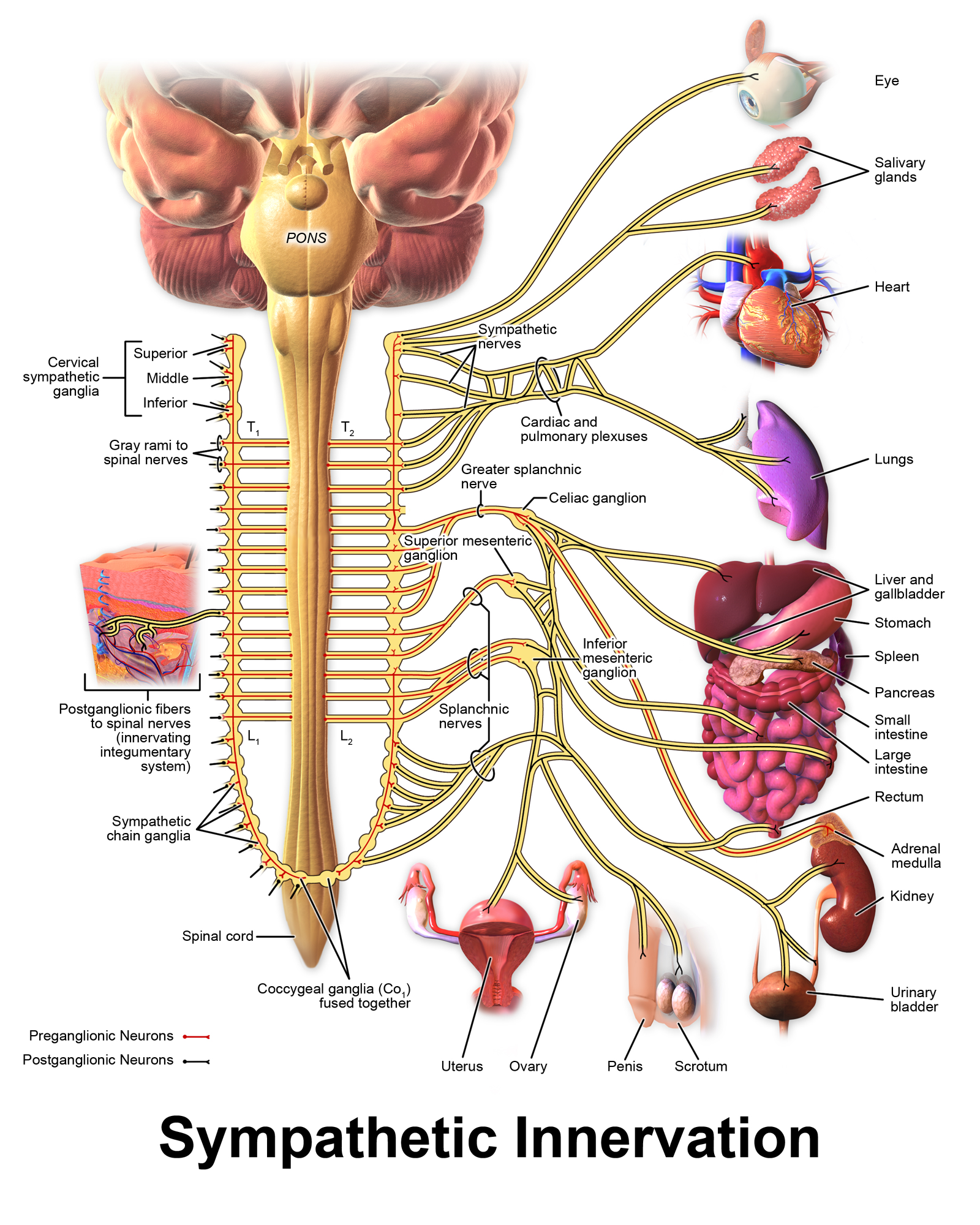
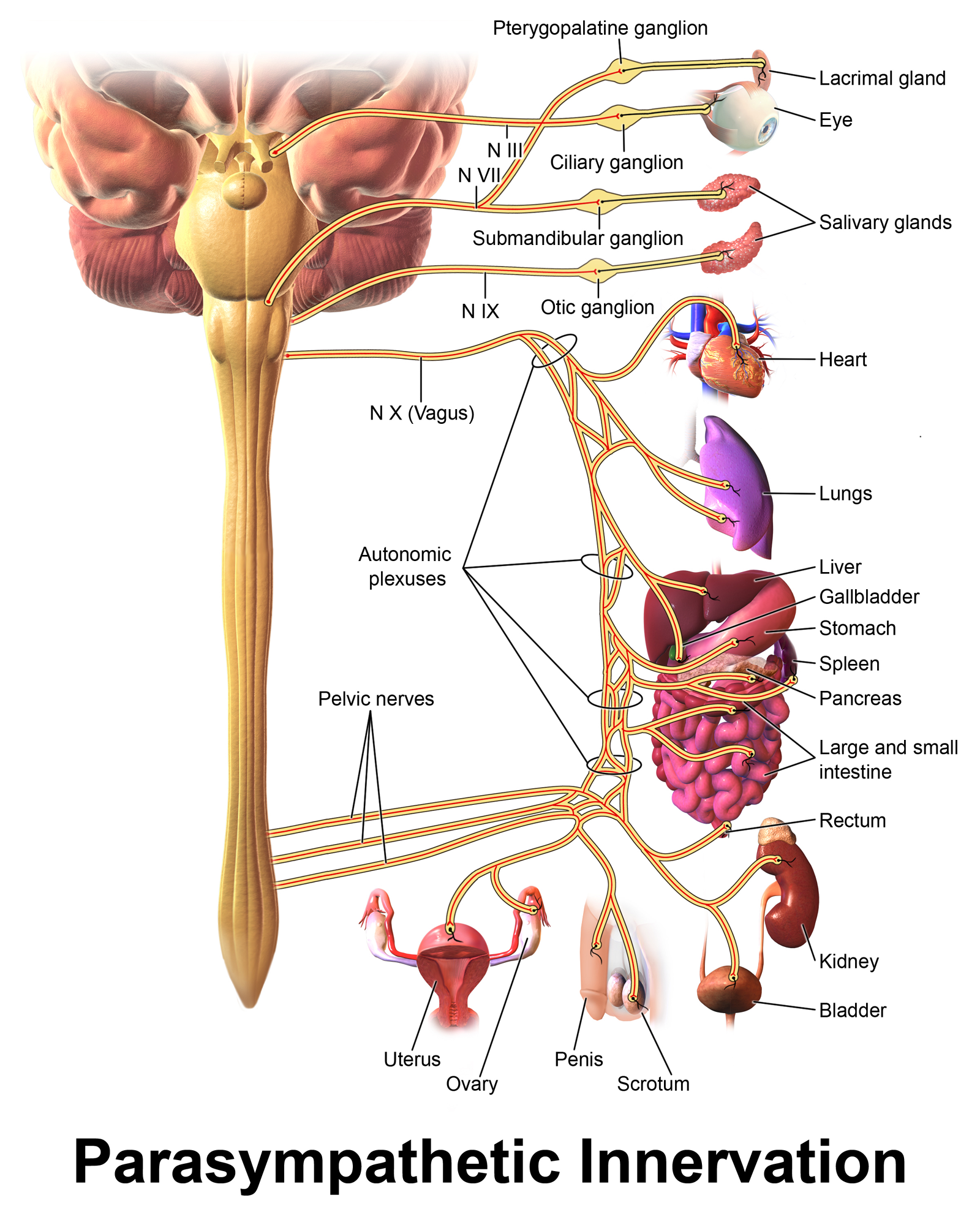
Which nerve pathway releases acetylcholine which decreases heart rate? (1)
The parasympathetic pathway.
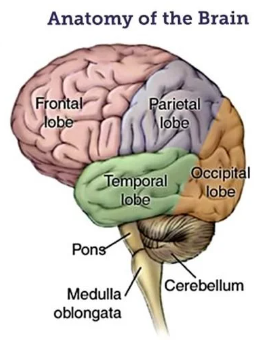
Name the structure in the brain which controls heart rate? (1)
Medulla.
Name the structure in the heart that sets the heart rate? (1)
Sinoatrial Node (SAN).
What is the average blood pressure for an adult? (1)
A typical blood pressure reading for a young adult is 120/80 mmHg.
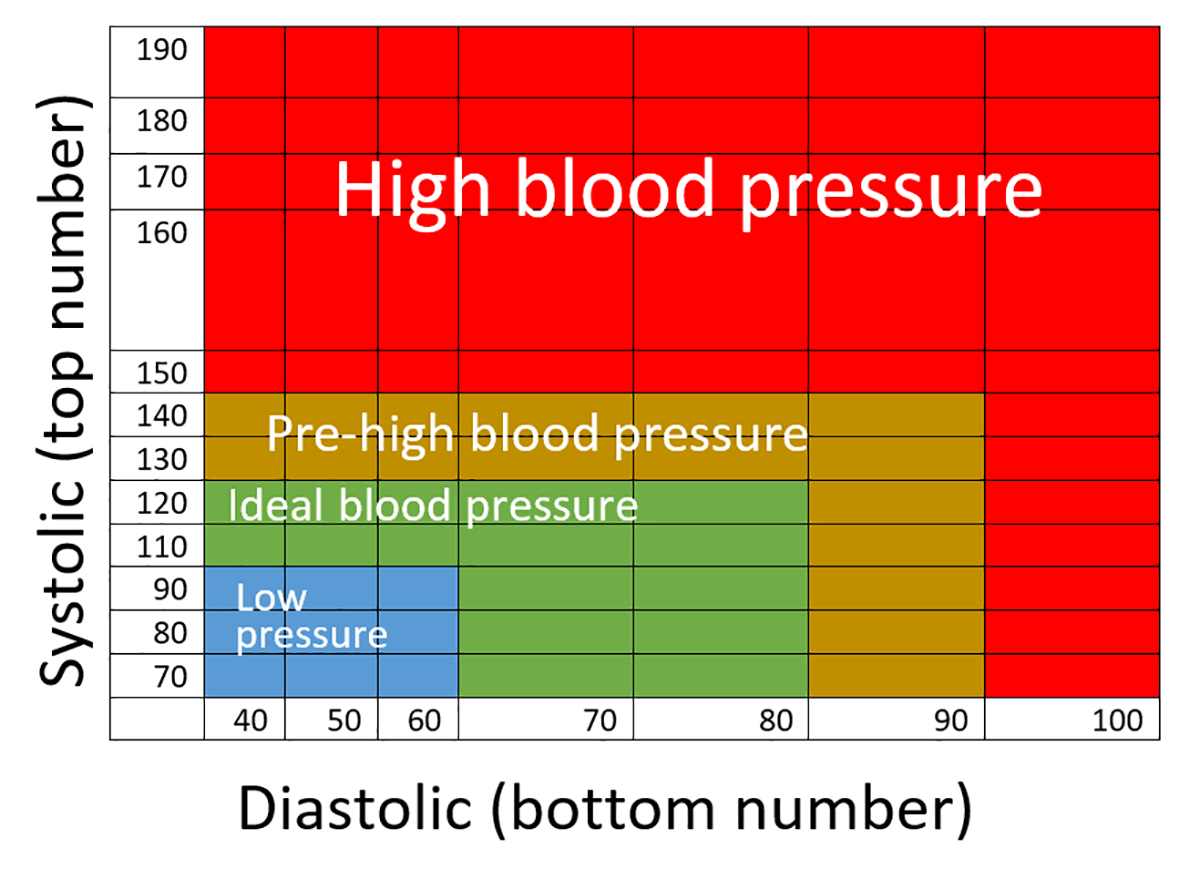
Which term is used for high blood pressure? (1)
Hypertension
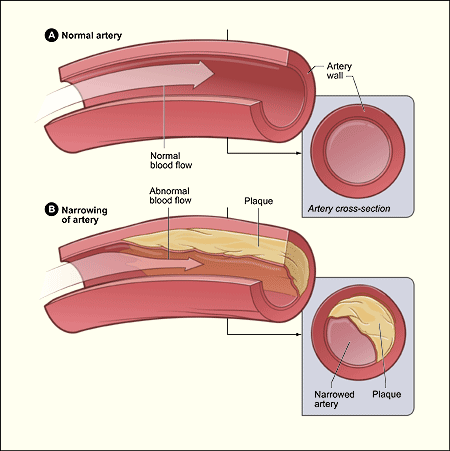
Name the process which builds up fatty material under the endothelium? (1)
Atherosclerosis
Describe what happens to the elasticity and lumen diameter of an artery during atherosclerosis? (2)
The build-up forms an atheroma (degeneration of the walls of the arteries) under the endothelium (cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels).
As the atheroma grows the artery thickens and loses its elasticity.
The diameter of the lumen becomes reduced.
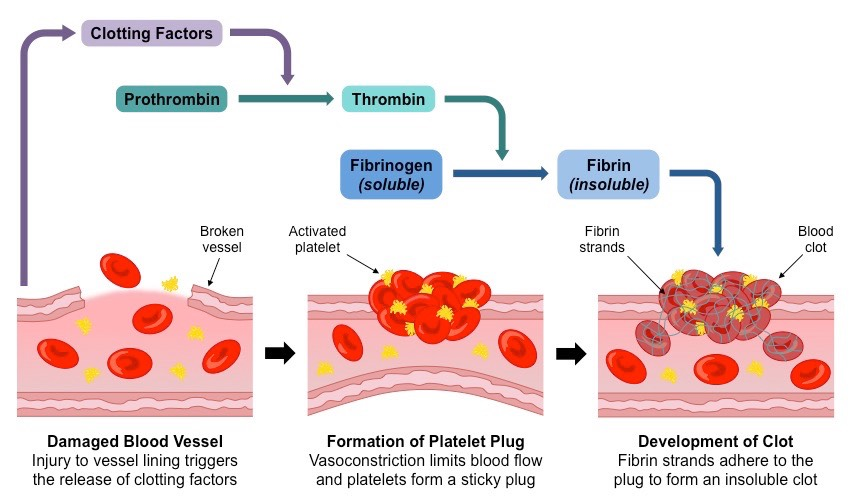
Describe the events which lead to the formation of a blood clot? (5)
1. damage to the endothelium releases clotting factors.
2. clotting factors convert the enzyme prothrombin to thrombin.
3. thrombin causes the plasma protein fibrinogen to form threads of fibrin.
4. fibrin threads mesh clotting the blood and sealing the wound.
5. scar tissue forms on this scaffold creating a clot.
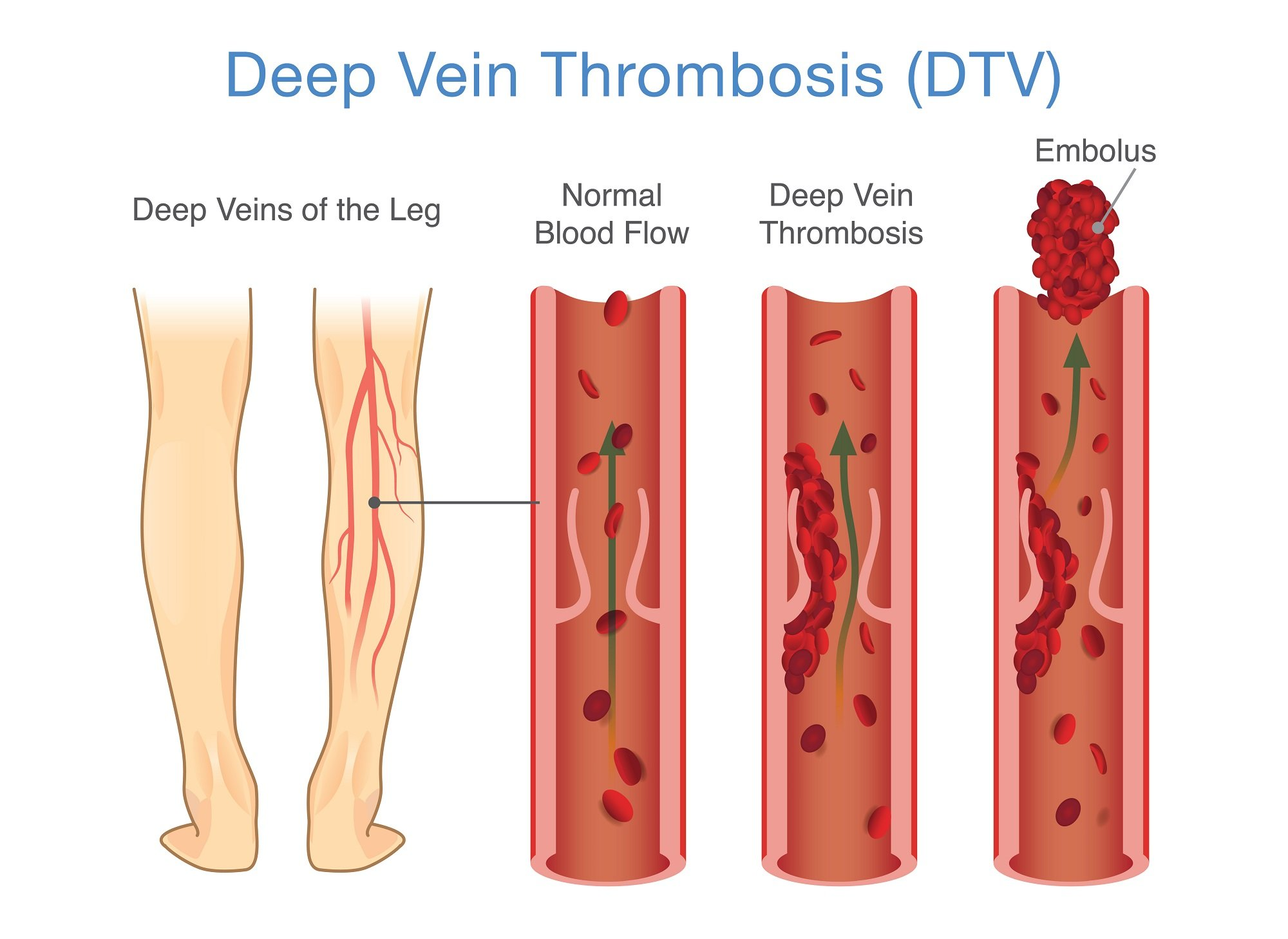
Which term is given to the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel? (1)
Thrombosis.
Name the condition caused by a blood clot commonly in the leg? (1)
Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Describe a role of cholesterol? (1)
Used to synthesise sex hormones (such as testosterone, oestrogen and progesterone).
Name the two types of cholesterol carrying proteins? (2)
HDL
LDL
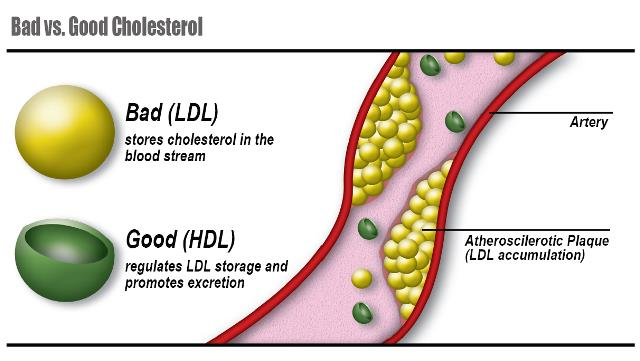
Where is most of cholesterol produced and how much? (2)
25% of all cholesterol produced comes from the liver.
Name the drugs used to reduce blood cholesterol levels by inhibiting synthesis of cholesterol in the liver? (1)
Statins.
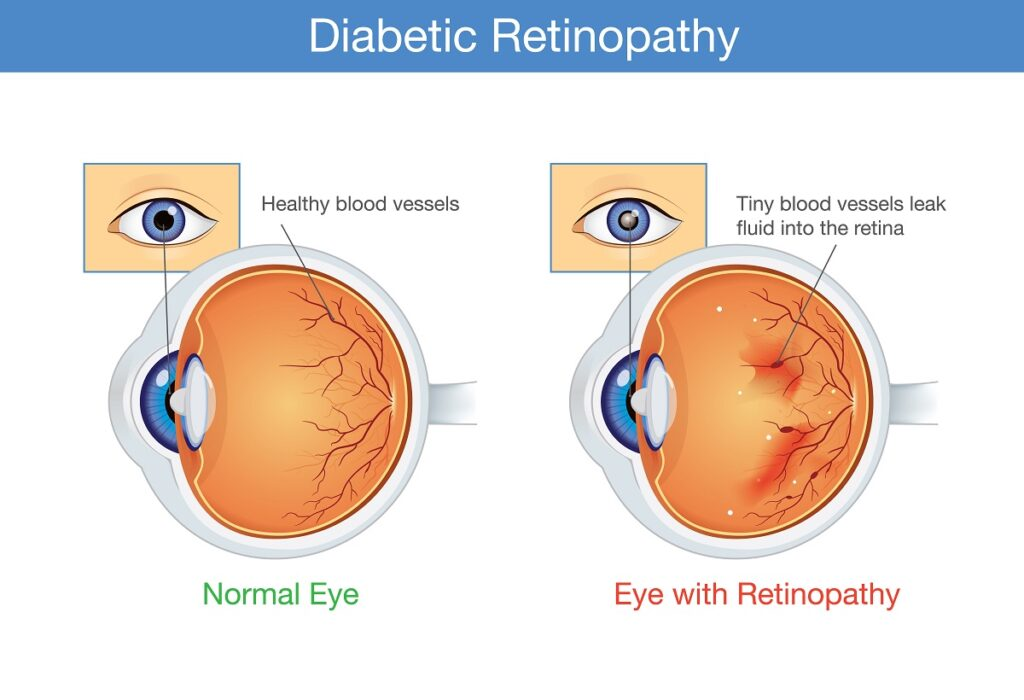
Explain how chronic elevated levels of glucose can affect the retina of the eye? (2)
Chronic elevated levels of glucose can damage the small blood vessels in the retina, leading to leakage of fluid and blood, causing swelling and bleeding.
This can result in diabetic retinopathy, where the damaged vessels may also lead to the formation of abnormal new blood vessels, further impairing vision and potentially causing blindness.
Explain how chronic elevated levels of glucose can cause cardiovascular diseases? (2)
Chronic elevated levels of glucose can lead to damage of the blood vessels by promoting the formation of plaques (atherosclerosis), which narrow and harden the arteries.
This increases the risk of heart attack and stroke by restricting blood flow and raising blood pressure.